Tetra-coordinated organoboron complexes with triaminoguanidine-salicylidene based ligands: aggregation induced enhanced emission and mechanoresponsive features†‡
Balamurugan
Tharmalingam§
 ab,
Rajendran
Kishore Kumar§
ab,
Rajendran
Kishore Kumar§
 a,
Ottoor
Anitha
a,
Ottoor
Anitha
 a,
Werner
Kaminsky
c,
Jan Grzegorz
Malecki
a,
Werner
Kaminsky
c,
Jan Grzegorz
Malecki
 d and
Balasubramanian
Murugesapandian
d and
Balasubramanian
Murugesapandian
 *a
*a
aDepartment of Chemistry, Bharathiar University, Coimbatore, 641046, Tamil Nadu, India. E-mail: mpandian@gmail.com; bmurugesapandian@buc.edu.in; Fax: +91-422-2422387; Tel: +91-422-2428312
bState Key Laboratory of Fine Chemicals, Frontier Science Center for Smart Materials, School of Chemical Engineering, Dalian University of Technology, Dalian 116024, P. R. China
cDepartment of Chemistry, University of Washington, Seattle, WA 98195, USA
dInstitute of Chemistry, University of Silesia, Szkolna 9, 40-006 Katowice, Poland
First published on 25th January 2025
Abstract
Organoboron complexes have garnered significant attention due to their remarkable optical properties and diverse applications. However, synthesizing stable fused five-, six- and seven-membered organoboron complexes possess significant challenges. In this study, we successfully developed novel mono-nuclear (6–8 & 10) and di-nuclear (9) organoboron complexes supported by triaminoguanidine-salicylidene based C3-symmetric Schiff base ligands via one-step condensation reaction with excess phenylboronic acid. Single-crystal X-ray diffraction analysis revealed that in the mononuclear complexes (6–8 & 10), boron atoms adopt tetrahedral geometry with fused five-membered N–B–N and six-membered O–B–N chelate ring whereas in the dinuclear complex (9), two boron atoms exist in distinct coordination environment, forming four fused boron-incorporated rings, including six-membered N–B–N, six-membered O–B–N, seven-membered N–B–O and five-membered N–B–N chelate rings. Our findings provide a unique family of mononuclear organoboron complexes and dinuclear organoboron complex with ESIPT unit. Aggregation induced enhanced emission features of the compounds were established in THF–water mixture and supported by DLS and SEM analyses. Interestingly, compound 6, 9 and 10 shows interesting mechanoresponsive features upon grinding.
Introduction
Compact organic solid-state fluorescent molecules, exhibiting photoluminescence, have garnered considerable interest due to their potential applications in the fields of biomedical science and material science.1–4 Persistent efforts to develop new fluorescent dyes for diverse applications have resulted in the creation of novel fluorescent molecules and the refinement of existing ones.5 Notably, aggregated-state fluorescent molecules have gained considerable attention.6,7 Conventional fluorophores often exhibit fluorescence in solution state experiences aggregation-caused quenching (ACQ), limiting their practical applications. To address this issue, Tang et al. pioneered the concept of aggregation-induced emission (AIE) or aggregation induced enhanced emission (AIEE) by developing a molecule that shows fluorescence in the solid or aggregated state.8,9 Organic fluorophores exhibiting excited-state intramolecular proton transfer (ESIPT) have garnered significant attention due to their potential applications in laser dyes, optical sensors, and optoelectronic devices.10,11 These molecules typically display distinct spectral characteristics, including spectral sensitivity to the surrounding medium and dual emission bands corresponding to enol and keto forms, accompanied by large Stokes shift. A crucial requirement for ESIPT behavior is the formation of hydrogen bonding between a hydroxyl or amine group (proton donor) and the nitrogen of an imine group or oxygen of a carbonyl group (proton acceptor) within the molecule.12,13 Fluorescent materials with AIEE features and ESIPT have found various applications in different field.14,15 The rise of organoboron as a key element in creating novel fluorophores with stable tetrahedral structures have significant implications for various applications in the field like sensors, organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs), self-assembly, and catalysis.16–18 Within the realm of organic fluorophores, organoboranes stand out as promising candidates owing to their exceptional responsiveness to various stimuli, including mechanical stress (mechanochromism/mechanoluminescence)19,20 and aggregation-induced emission (AIE).21–23 Among the developed organoboron dyes, the BODIPY (4,4-difluoro-4-bora-3a,4a-diaza-s-indacene) dye, characterized by its rigid structure with BF2− units, has gained popularity due to its versatile structure alteration, promising and adjustable spectroscopic properties.24,25 Serving as a vibrant fluorophore, the BODIPY dye quickly became a versatile platform for further modifications. Subsequent modifications of the BODIPY dye have resulted in the creation of π-extended molecules with shifted absorption and fluorescence towards the red spectrum.26 However, these BODIPY dyes often suffer from poor solubility and a lack of emission in the solid or aggregated state, primarily due to their planar structure and the π–π stacking arrangement of the ring systems.27 Hence, modified organoboron dyes (Chart 1) such as boronic-acid derived salicylidenehydrazone28–31 (BASHY) and its modified derivatives, boronic acid derived salicylidenehydrazinopyridine (BOSPY)32 and its modified derivatives, boronic-acid-derived pyrrolide salicyl-hydrazone (BPSHY)33 and Schiff-base coupled phenyl boronic acid derivatives34,35 featuring substituted aromatic groups attached to the boron atom, which provide steric shielding and prevent potential π–π stacking arrangements and other coordination provided by different salicyl-hydrazone framework36–39 exhibits various interesting optical features and few of them showed bright solid-state emission.40Another class of boron-based dyes, BOPHY (bis(difluoroboron)1,2-bis((1H-pyrrol-2-yl)methylene)hydrazine) and modified BOPHY supported by pyrrole-hydrazine conjugate showed interesting optical behaviour.41,42 Salicylaldimine-based another family of boron complexes have emerged as promising candidates for mechanochromic applications due to their exceptional responsiveness to mechanical stress.43,44 Recently, tetra-coordinate boron-based organic fluorescent compounds with aggregation-induced emission (AIE) properties have been extensively developed and utilized for numerous applications.8,45,46 Organoboron derivative supported by salicyl-hydrazone framework bearing ESIPT unit has not received much attention. In this context, we have chosen triaminoguanidinium-salicylidene as scaffold to develop organoboron derivative. Triaminoguanidine is a versatile building block for constructing star-shaped C3-symmetric ligands or probes with ESIPT unit.47–49 Our group and others have developed diverse multi-functional luminescent materials, hydrogen bonded supramolecular network, magnetic materials and sensors based on C3-symmetric triaminoguanidinium chloride, incorporating various salicylidene moieties.50–56 These compounds exhibit intriguing AIE,51 ICT-coupled excited-state intramolecular proton transfer (ESIPT),56 and mechanochromic properties.56 The triaminoguanidinium-salicylidene derivative features three binding sites, each consisting of phenolic hydroxyl, imine nitrogen, and NH groups from triaminoguanidine units and it can accommodate three metal ions using three NNO donors.53,54 They can be synthesized via facile condensation reactions on a multi-gram scale. Inspired by this potential, here we would like to integrate organoboron into the triaminoguanidinium-salicylidene framework, leveraging its ability to accommodate three boron atoms via three ONN donor sets (Chart 1) may results interesting optical features. In this context, organoboron compounds with aggregation induced emission features are well known, whereas organoboron compound featured with ESIPT unit are rare (Table S1‡).
Utilizing a simple one-step condensation strategy, we developed a new series of AIEE-active organoboron-derived C3-symmetric triaminoguanidine-salicylidene Schiff bases (6–10) from the respective parent Schiff bases (1–5). Four mono-nuclear (6–8 & 10) and one di-nuclear (9) organoboron compounds were synthesized, supported by this framework through NNO-B chelate rings. The design incorporates two key features like tetracoordinated organoboron with axial aromatic groups, mitigating potential aggregations57 and tunable functionalities on the C3-symmetric triaminoguanidinium-based Schiff base ligand. Compounds 6 to 10, represents a unique example for family of compounds where it contain an organoboron moiety with an ESIPT unit. All five synthesized compounds (6–10) display distinct aggregation-induced enhanced emission (AIEE) properties in THF–H2O mixtures. Notably, compounds 6, 9 and 10 showed mechano responsive behavior when subjected to grinding as an external stimulus.
Experimental section
Material and instruments
4-Diethylaminosalicylaldehyde, 2-hydroxy-1-naphthaldehyde, ortho-vanillin, and phenylboronic acid were purchased from Sigma Aldrich. Salicylaldehyde was purchased from Loba chemie. 3,5-Di-tert-butyl-2-hydroxybenzaldehyde was purchased from TCI India. All the other reagents and solvents were analytical reagent grade and used without any further purification for the current analysis. Star-shaped triaminoguanidine Schiff base compounds 1–5 were synthesized as previously reported method.50–52,56,58 Absorption spectral measurements were performed with a JASCO V-630 UV-vis spectrophotometer using solvents as reference. Quartz cuvettes of path length 1.0 cm were used to record the absorption spectra. All emission spectral measurements were performed with JASCO FP-6600/JASCO FP-8300 spectrofluorometer equipped with a 1.0 cm quartz cuvette. Fluorescence lifetime were measured with an IBH time-correlated single photon counting (TCSPC) system. The size and morphologies of the aggregates and its parent compounds were identified on a FEI Quanta-250.Single crystal XRD analysis
Single crystal X-ray structural analysis for all the compounds (6, 8–10) were collected at −173 °C and compound 7 was measured at 25 °C on a Bruker APEX II single crystal X-ray diffractometer using Mo-radiation as source. The data was integrated and scaled using SAINT, SADABS within the APEX2 software package by Bruker. Solution by direct methods (SHELXS25 or SIR97![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 59,60) produced a complete heavy atom phasing model consistent with the proposed structure. The structure was completed by difference Fourier synthesis with SHELXL.61,62 Scattering factors are from Waasmair and Kirfel. Hydrogen atoms were placed in geometrically idealized positions and constrained to ride on their parent atoms with C⋯H distances of 0.95–1.00 Å. Isotropic thermal parameters Ueq were fixed such that they were 1.2Ueq of their parent atom Ueq for CH's and 1.5 Ueq of their parent atom Ueq in case of methyl groups. All non-hydrogen atoms were refined anisotropically by full-matrix least-squares. The contribution of disordered water or other solvent molecules to the diffraction pattern was removed with SQUEEZE program. Data collection and refinement parameters are summarized in Table S6.‡ The crystallographic data for the compounds 6–10 are available in CCDC with deposition numbers 1996722 (compound 6), 2370980 (compound 7) 1996724 (compound 8), 1996723 (compound 9), 1996725 (compound 10).‡
59,60) produced a complete heavy atom phasing model consistent with the proposed structure. The structure was completed by difference Fourier synthesis with SHELXL.61,62 Scattering factors are from Waasmair and Kirfel. Hydrogen atoms were placed in geometrically idealized positions and constrained to ride on their parent atoms with C⋯H distances of 0.95–1.00 Å. Isotropic thermal parameters Ueq were fixed such that they were 1.2Ueq of their parent atom Ueq for CH's and 1.5 Ueq of their parent atom Ueq in case of methyl groups. All non-hydrogen atoms were refined anisotropically by full-matrix least-squares. The contribution of disordered water or other solvent molecules to the diffraction pattern was removed with SQUEEZE program. Data collection and refinement parameters are summarized in Table S6.‡ The crystallographic data for the compounds 6–10 are available in CCDC with deposition numbers 1996722 (compound 6), 2370980 (compound 7) 1996724 (compound 8), 1996723 (compound 9), 1996725 (compound 10).‡
General method for the synthesis of the boron complexes (6–10)
The general procedure for the preparation of these boron compounds is as follows. The preparation of the boron compounds were adopted by simple condensation reaction of corresponding ligands with phenylboronic acid. The solution of phenylboronic acid in dry acetonitrile was slowly added to the ligand in dry acetonitrile and the mixture was stirred at 80 °C for 2 days in nitrogen atmosphere. After the completion of reaction, the reaction mixture was slowly cooled to room temperature, allowed to evaporate slowly, in 6–10 days crystals were obtained. The crystallized compounds were washed several times in cold ethanol.Characterization data of boron compounds
Compound 6: Yield (80%): 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) (Fig. S1‡) δ:11.24 (s, 1H), 11.01 (s, 1H), 9.89 (s, 1H), 8.82 (s, 1H), 8.56 (s, 1H), 8.52 (s, 1H), 7.99 (dd, J = 1.6 Hz, J = 1.6 Hz, 1H), 7.84–7.82 (m, 4H), 7.62 (dd, J = 1.6 Hz, 1H), 7.52 (t, J = 8 Hz, 1H), 7.47 (t, J = 8 Hz, 1H), 7.43 (t, J = 8 Hz, 1H), 7.39 (d, J = 4 Hz, 2H), 7.31 (d, J = 4 Hz, 2H), 7.26–7.20 (m, 1H), 7.16–7.11 (m, 1H), 7.00–6.97(m, 1H), 6.89–6.84 (m, 1H) ppm; 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6) (Fig. S2‡) δ: 160.29, 157.25, 156.07, 155.07, 147.69, 142.02, 139.08, 134.39, 134.13, 131.92, 131.33, 130.88, 130.18, 130.09, 129.10, 127.43, 126.77, 120.68, 120.38, 119.51, 119.34, 119.18, 119.00, 118.72, 116.50, 116.07 ppm; 11B NMR (128 MHz, DMSO-d6) (Fig. S3‡) δ: 3.47 ppm. HRMS [M + 1] (Fig. S4‡) calculated for C28H24BN6O3 503.1925; found: 503.2002.Compound 7: Yield (80%): 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) (Fig. S5‡) δ: 10.97 (s, 1H), 10.03 (s, 1H), 9.35 (s, 1H), 8.27 (s, 1H), 8.20 (s, 1H), 7.93 (s, 1H), 7.37–734 (dd, J = 2.0 Hz, 2H), 7.10–7.09 (m, 3H), 7.00 (t, J = 5.20 Hz, 1H), 6.93 (dd, J = 1.6 Hz, 1H), 6.84–6.80 (m, 4H), 6.78–6.75 (m,3H), 3.98 (s, 3H), 3.92 (s, 3H), 3.79 (s, 3H) ppm; 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6) (Fig. S6‡) δ:160.33, 149.36, 148.08, 147.94, 147.5, 146.94, 145.66, 145.01, 141.86, 138.94, 134.11, 131.71, 127.41, 121.00, 120.39, 120.13, 119.70, 119.33, 119.18, 118.83, 113.78, 112.67, 56.46, 56.01, 55.97 ppm; 11B NMR (128 MHz, CDCl3) (Fig. S7‡) δ: 4.17 ppm, HRMS [M + 1] (Fig. S8‡) calculated for C31H30BN6O6 593.2242; found: 593.2317.
Compound 8: Yield (80%): 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) (Fig. S9‡) δ: 11.80 (s, 1H), 11.68 (s, 1H), 9.90 (s, 1H), 8.70 (s, 1H), 8.58 (s, 1H), 8.53(s, 1H), 7.52 (s, 1H), 7.19 (d, J = 8 Hz, 2H), 7.09 (d, J = 4.0 Hz, 2H), 6.90 (d, J = 4 Hz, 1H), 2.06 (s, 2H), 1.57 (s, 9H), 1.41 (s, 19H), 1.28 (d, J = 8 Hz, 19H), 1.23 (s, 9H) ppm; 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6) (Fig. S10‡) δ: 158.65, 154.45, 152.90, 151.65, 151.28, 150.25, 141.69, 141.06, 140.62, 136.39, 136.10, 135.65, 134.11, 131.11, 131.66, 127.89, 127.73, 127.40, 126.02, 125.55, 118.29, 117.29, 117.18, 35.04, 34.71, 34.04, 33.96, 33.75, 31.35, 31.21, 31.14, 29.65, 29.39 ppm; 11B NMR (128 MHz, CDCl3) (Fig. S11‡) δ: 4.08 ppm, HRMS (Fig. S12‡) [M + 1] calculated for C52H71BN6O3 839.5789; found: 839.5776.
Compound 9: Yield (80%): 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) (Fig. S13‡) (δ, ppm); 11.21 (s, 1H), 10.61 (s, 1H), 9.65 (s, 1H), 8.48 (s, 1H), 8.44 (s, 1H), 8.33 (s, 1H), 8.22 (s, 1H), 8.15 (s, 1H), 8.03 (s, 1H), 7.95 (s, 1H), 7.79 (d, J = 4 Hz, 1H), 7.77 (d, J = 4 Hz, 1H), 7.76 (s, 1H), 6.71 (t, 2H), 6.55 (t, 2H), 6.42 (s, 1H), 6.28 (d, J = 4 Hz, 1H), 6.35 (d, J = 4 Hz, 2H), 6.03 (d, J = 4 Hz, 1H), 5.98 (s, 1H), 2.88 (s, 3H), 2.73 (s, 3H), 1.16 (s, 6H), 1.10 (t, 18H):13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6) (Fig. S14‡) (δ, ppm) 162.39, 159.35, 158.91, 157.64, 152.46, 149.84, 149.52, 134.11, 132.03, 131.91, 131.28, 130.06, 127.58, 127.40, 127.18, 107.86, 106.82, 103.64, 97.65, 44.05, 43.84, 35.83, 30.82, 12.06 ppm; 11B NMR (128 MHz, CDCl3) (Fig. S15‡) δ: 28.61, 4.67 ppm; HRMS (Fig. S16‡) [M + 1] calculated for C46H53B2N9O3·CH3CN 843.4867; found: 843.4796.
Compound 10: Yield (80%): 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) (Fig. S17‡) δ: 12.46 (s, 1H), 11.54 (s, 1H), 10.66 (s, 1H), 9.60 (s, 1H), 9.17 (s, 1H), 9.05 (s, 1H), 8.31 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H), 8.23 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H), 8.14 (dd, J = 3.2 Hz, J = 2.8 Hz, 2H), 7.95–7.89 (m, 4H), 7.86 (t, J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 7.63–7.54 (m, 4H), 7.41–7.38 (m, 4H), 7.27 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 1H), 7.20 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 1H), 7.12 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 2H), 7.04 (t, J = 4.0 Hz, 1H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6) (Fig. S18‡) δ: 162.37, 159.49, 157.77, 155.90, 154.88, 146.94, 145.03, 136.95, 135.68, 132.62, 132.17, 132.03, 131.06, 131.58, 130.84, 128.73, 128.13, 128.04, 127.93, 127.88, 127.79, 127.74, 127.60, 124.48, 123.62, 123.50, 122.14, 120.98, 120.28, 118.99, 118.35, 112.26, 110.06, 108.76 ppm; 11B NMR (128 MHz, DMSO-d6) (Fig. S19‡) δ: 4.45 ppm; HRMS [M + CH3OH] (Fig. S20‡) calculated for C40H29BN6O3·CH3OH 684.2656; found: 684.2032.
Results and discussion
Design and synthesis of boron complexes
Recently organoboron compounds received significant attention due to their considerable application in different fields like optical property, solar cells, medicinal chemistry and so on. Organoboron compounds can be easily prepared by the simple condensation reaction between Schiff base ligands and phenylboronic acid. As it can be easily prepared, it is possible to synthesis on the gram scale. Due to the availability of three binding sites in the triaminoguanidinium-salicylidene derivative, it can accommodate three boron atoms via NNO donors. Further, to evaluate the substituent dependent emission feature of boron complexes, here we have synthesized five different triaminoguanidinium based Schiff base ligands 1 (salicylidene derivative), 2 (o-vanillin derivative, –OCH3 group substitution at o-position), 3 (3,5-di-tert-butyl salicylidene derivative), 4 (4-(N,N-diethylamino)salicylidene derivative) and 5 (2-naphthol derivative) (Scheme 1) and their respective organoboron complexes were synthesized in good yields by simple condensation reaction. Formations of all the five boron complexes were confirmed by spectral characterizations such as 1H-NMR, 13C-NMR, 11B-NMR and mass analysis (Fig S1–S20‡). The expected tetra coordinated boron was confirmed by 11B-NMR, which shows signal around 3.37 to 4.67 ppm compounds 6–8 and 10 [3.47 ppm (6), 4.17 ppm (7), 4.08 ppm (8) and 4.45 ppm (10)] whereas compound 9 shows two signal at 28.61 and 4.67 ppm which indicate the presence of two distinct boron atom in compound 9 and it has different structure features than the other compounds 6–8 and 10. The solution-state stability of the complexes were confirmed by mass spectrometry, as evidenced by the presence of the molecular ion peak. Further, the structures of the complexes were authentically confirmed by single crystal X-ray measurements.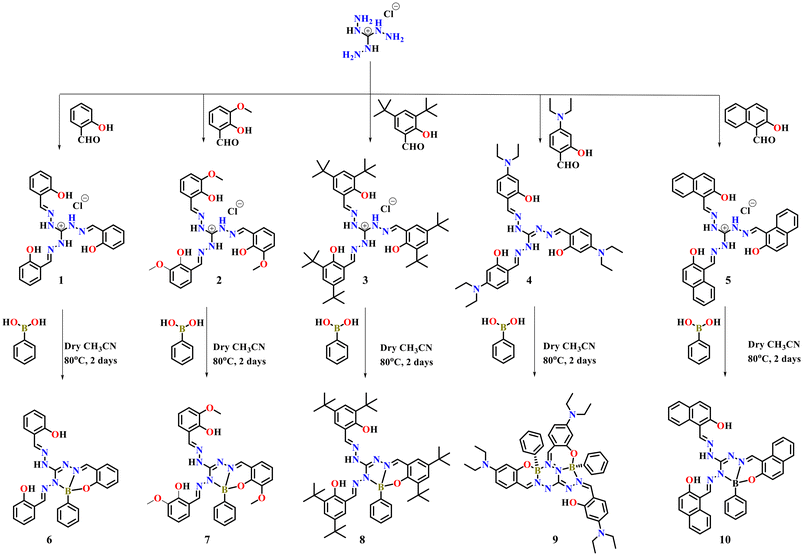 | ||
| Scheme 1 Synthesis of organoboron complexes 6–10 from triaminoguanidine-salicylidene Schiff bases (1–5). | ||
Solid state structure of boron complexes 6–10
Single crystal structure analysis is a significant method to confirm the molecular structure of the compounds as well as important to understand the molecular packing which is significant to correlate the photophysical properties of compounds in solid state. Suitable crystals of boron compounds 6–9 were obtained by the slow evaporation from their CH3CN solution and crystals of 10 was obtained through slow diffusion of MeOH solvent into DMF solution of 10. The crystallized boron compounds 6 and 8–10 belong to triclinic cell system with the P![[1 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0031_0304.gif) space group, whereas boron compound 7 belongs to the monoclinic cell system with P2(1)/c space group. The crystal structures of compounds 6–10 reveal the following compositions in their asymmetric units, two boron molecules and two water molecules in compound 6, one boron molecule, two acetonitrile molecules, and one water molecule in compound 7, one boron molecule and 1.5 acetonitrile solvent molecules in compound 8, two dinuclear boron molecules in compound 9 and one boron molecule and one DMF solvent molecule in compound 10.
space group, whereas boron compound 7 belongs to the monoclinic cell system with P2(1)/c space group. The crystal structures of compounds 6–10 reveal the following compositions in their asymmetric units, two boron molecules and two water molecules in compound 6, one boron molecule, two acetonitrile molecules, and one water molecule in compound 7, one boron molecule and 1.5 acetonitrile solvent molecules in compound 8, two dinuclear boron molecules in compound 9 and one boron molecule and one DMF solvent molecule in compound 10.
The molecular structure of boron compounds 6 to 10 is shown in Fig. 1A–E and it shows that the structure consists of a three-ring fused framework in compounds 6–8 and 10, whereas a six-ring fused skeleton was observed in compound 9. In compounds 6–8 and 10, boron is present in the tetracoordinate environment and surrounded by a phenyl carbon atom, imino nitrogen atom, deprotonated phenoxy oxygen atom (O−) and deprotonated hydrazino nitrogen atom (N−). Hence the coordination of ligand occurs via N, O, N to the boron atom in a dianionic fashion which provides fused six-membered O–C–C–C–N–B and five-membered N–N–C–N–B heterocycles with salicylidene ring results three-ring fused framework. In compound 10, inclusion of naphthyl rings results four-ring fused framework. Here, in all the compounds, boron atom is coordinated with salicylidene moiety via phenoxy oxygen and imino nitrogen from the one wing and deprotonated hydrazino nitrogen from the other wing.
Interestingly, the asymmetric unit of compound 9 comprises two molecules and each molecule contains two boron atoms present in different coordination environments and both of them adopt tetrahedral geometry [Fig. 1D and F]. Among the two boron atoms, one of the boron atom (B4) fuse the six-membered N15–B4–N13 chelate ring and six membered O6–B–N15 chelate ring and another boron atom (B3) fuse the seven membered N12–B–O5 chelate ring and five membered N12–B3–N11 chelate ring and over all its forms four fused boron incorporated rings provides a unique example. The coordination of the boron atom with ligand results in the formation of one five, two six and one seven-membered fused heterocycles. In all the compounds, boron atoms are present in the outside plane of hydrazone moiety. The bond distances of B–Cphenyl, B–O phenoxy, B–Nimine and B–Nhydrazino are analogous to the reported bond distances and characteristics of the four coordinated boron compounds.34,35 The important bond distances for all the compounds are provided in the Table 1. The average bond distance between the boron atom to the oxygen atom, B–Ophenoxy, is 1.450(4)–1.469(4) Å and the bond distance between the boron atom to imino nitrogen are in the range of 1.578(3)–1.564(3) Å, the bond distance between the boron atom to hydrazine nitrogen atom is in the range of 1.542(5)–1.558(4) Å and boron atom and its phenyl carbon bond distance in the range of 1.597(3)–1.607(2) Å. The observed bond distances are well agreed with the reported four coordinated boron molecules which indicate the strong interaction between the boron atom and coordinated nitrogen atoms.
| Compound | Bond distance (Å) | Compound | Bond distance (Å) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6 | B1–N3 | 1.566(4) | 9 | B1–N1 | 1.520(3) |
| B1–N2 | 1.583(4) | B1–N6 | 1.571(5) | ||
| B1–O1 | 1.450(4) | B1–O1 | 1.462(4) | ||
| B1–C23 | 1.597(3) | B1–C35 | 1.592(1) | ||
| B2–N8 | 1.578(3) | B2–N2 | 1.573(3) | ||
| B2–N9 | 1.558(4) | B2–N6 | 1.566 (2) | ||
| B2–O4 | 1.453(3) | B2–O2 | 1.444(3) | ||
| B1–C50 | 1.60(4) | B2–C41 | 1.599(2) | ||
| 7 | B1–N1 | 1.574(2) | B3–N11 | 1.578(4) | |
| B1–N3 | 1.561(2) | B3–N12 | 1.521(3) | ||
| B1–O1 | 1.459(3) | B3–O5 | 1.469(4) | ||
| B1–C26 | 1.611(3) | B3–C81 | 1.596(4) | ||
| 8 | B1–N3 | 1.542(5) | B4–N13 | 1.578(4) | |
| B1–N2 | 1.567(3) | B4–N15 | 1.568(3) | ||
| B4–O1 | 1.454(3) | B4–O6 | 1.451(2) | ||
| B1–C47 | 1.605(5) | B4–C87 | 1.592(4) | ||
| 10 | B1–N2 | 1.564(3) | |||
| B1–N3 | 1.561(1) | ||||
| B1–O1 | 1.463(1) | ||||
| B1–C35 | 1.607(2) | ||||
Notably, in all the boron compounds, only one (6–8 and 10) or two deprotonated phenolic OH (9) participated in the coordination with the boron atoms and the uncoordinated phenolic OH were involved in the strong intra-molecular hydrogen bonds with the imine nitrogen from the same wing except in compound 7. In compound 7, one of the OH is involved in hydrogen bonding with an imine nitrogen atom and other OH is not involved in hydrogen bonding interaction. Hence the existence of strong hydrogen bond interaction between the phenolic hydroxyl group and nitrogen atom (O–H⋯N) in the entire series of boron compounds is as indicated in the molecular structure which is shown in Fig. 1A–E, which stimulates the occurrence of proton transfer in the exited state. The whole boron compound becomes somewhat partly rigid compare to the parent ligands.
All the compounds involved in weak interactions with neighboring molecule and solvent molecules which results interesting supramolecular network. In compound 6, the intramolecular hydrogen bond was observed between the H atom of OH and N atom of imine moiety [bond distance and bond angles: O2–OH2⋯N4 1.895(2) Å and O2–OH2–N4 145.5(2)°, O3–OH3⋯N6 1.845(3) Å and O3–OH3–N6 146.3(2)°, O5–OH5⋯N10 1.904(2) Å and O5–OH5–N10 145.9(2)°, O6–OH6⋯N12 1.834(2) Å and O6–OH6–N12 146.4(2)°]. Water molecules are involved in hydrogen bonding via OH⋯N [O8–PH2⋯N7 2.029(3) Å and O8–PH2–N7 159.0(3)°], N–H⋯O [N5–N5H⋯O7 1.951(3) Å and N5–N5H–O7 166.0(3)°] interaction results in water molecule bridged dimers. The neighboring molecules were connected by different weak interactions which led to the formation of the 2D supramolecular network (Fig. S21‡). In compound 7, one of the phenolic hydroxyl groups is not involved in the intramolecular hydrogen bonding with imine nitrogen atom instead it is involved in hydrogen bonding with a solvent water molecule [O5–H5⋯O7 2.066(3) Å and O5–H5⋯O7 154.3(3)°]. In addition, two acetonitrile nitrogen atoms were involved in hydrogen bonding interaction with hydrazine H–N [N7⋯H5A–N5 2.200(1) Å and N7–H5A–N5 162.4(2)°] and water molecule hydrogen [N8⋯H7BO7 2.147(3) Å and N8–H7B–O7 166.7(1)°]. Further, it forms a two-dimensional network through various weak interactions (Fig. S22‡). The intramolecular hydrogen bonding interaction present in compound 8 is similar to the compound 6. Further, via various weak interactions, compound 8 also forms two-dimensional polymeric network structures (Fig. S23‡). In compound 9, two molecules are connected by C–H⋯O [C44–H44⋯O4 2.693(2) Å and C44–H44–O4 157.8(1)°] which results in a dimeric structure (Fig. S24‡). In this dimer, all the phenyl groups are present inside the dimeric unit. These dimeric units are connected to neighboring molecules via various weak interactions like C–H-π interaction [C11–H11B⋯π 2.814 Å] and end up with interesting supramolecular two-dimensional networks (Fig. S25‡). Intramolecular hydrogen bonding interaction present in the molecule 10 is similar to other molecules 6 and 8. The compound 10 is connected to neighboring molecules via multiple weak interactions like C–H-π interactions and results in the formation of supramolecular two-dimensional networks (Fig. S26‡).
Photophysical behaviors of boron compounds
Incorporation of the donor–acceptor unit, besides proton transfer moieties in the molecules, will provide the photophysical properties that are more dominated by ICT or ESIPT or ICT coupled ESIPT phenomena. Further, the existence of dual emission in different solvents is a characteristic of ESIPT behavior present in the molecules. Photophysical properties of organoboron compounds 6–10 were investigated in various solvents with different polarity at room temperature by using UV-visible absorption and emission measurements at a concentration of 5 × 10−5 M. UV-visible absorption spectral results of all the boron complexes in various solvents were displayed in Fig. S27‡ and exhibited two absorption bands and the shorter wavelength band was assigned to π–π* (around 340 nm) electronic transition and the longer wavelength band was assigned to n–π* (around 440 nm) electronic transition. The results indicate that the position of the absorption band was not altered much when changing the polarity of the solvent and it suggests the solvent-independent absorption feature of the compounds. Further, alteration in the electronic and steric features in the periphery of the ligands results in a minor change in the position of absorption bands.Like UV-visible absorption spectral measurements, emission measurements for all the boron complexes 6–10 were carried out in various solvents with different polarities with excitation at 420 nm and the results are provided in Fig. 2. All the organoboron compounds contain strong hydrogen bonding between OH and imino nitrogen, hence we envisioned for excited state intramolecular proton transfer reaction in the excited state and it results in the appearance of dual emission in emission measurements. Compound 6, a simple salicylaldehyde derivative, shows a broad emission peak of around 500 nm with shoulder around 485 nm. Upon increasing the polarity, the intensity of the emission peak was decreased it might be due to intramolecular charge transfer phenomenon. Whereas for compound 7, organoboron derived o-vanillin derivative exhibits broad emission in highly polar DMF and DMSO and strong emission at 500 nm with shoulder around 540 nm in toluene. Compound 8 showed an emission peak around 502 nm to 536 nm with a shoulder peak around 480 nm, here changes in polarity induced a shift in the longer wavelength emission peak. The emission spectra of compound 9 in different solvents with varying polarity showed interesting features. In toluene and CHCl3, strong emission was observed at 510 nm with a shoulder around 540 nm, whereas in THF, DMF and DMSO solvents, a predominant peak appeared around 550 to 560 nm with a shoulder around 490 nm. Naphthyl appended boron compound 10 shows dual emission in all the solvents, the shorter wavelength emission peak centered on 505 nm and the longer wavelength emission peak appeared around 540 to 550 nm. In all the compounds, the shorter wavelength peak is attributed to the enol emission and the longer wavelength peak is attributed to keto emission. In all the compounds, the polarity of the solvents significantly influences the optical properties and notably affecting the position and intensity of the emission peaks. As illustrated in Fig. 2, compound (6–10) exhibits a pronounced solvatochromic shift upon UV irradiation. This positive solvatochromism was confirmed by the decrease in the emission intensity and red shifted with increasing solvent polarity which suggests that the compounds excited state is stabilized by interactions with polar solvents. Thus, changes in solvent polarity can influence electron density distribution within the molecule and facilitate intramolecular charge transfer (ICT) processes. Thus, the compounds (6–10) exhibit different intensities in different solvents due to ICT process.63 To understand the molecular behavior of organoboron complexes, we conducted a theoretical analysis using density functional theory (DFT). As shown in Tables S2 & S3,‡ the calculated bond lengths of organoboron complexes 6–10 align well with the values determined from X-ray crystallography. Theoretical calculation results are shown in Fig. S28 and S29‡ which illustrate the molecular orbitals and their corresponding energies for the organoboron complexes 6–10. The electron density is predominantly concentrated on the triaminoguanidine-salicylidene ligands in all the organoboron complexes. Additionally, the UV-vis spectra for complexes 6–10 were calculated using the same theoretical approach. The predicted absorption bands, ranging from 370 to 420 nm, are in good agreement with the experimental data. These absorption bands are attributed to the S0–S1 transitions, driven by π–π* electronic transitions across the molecule.
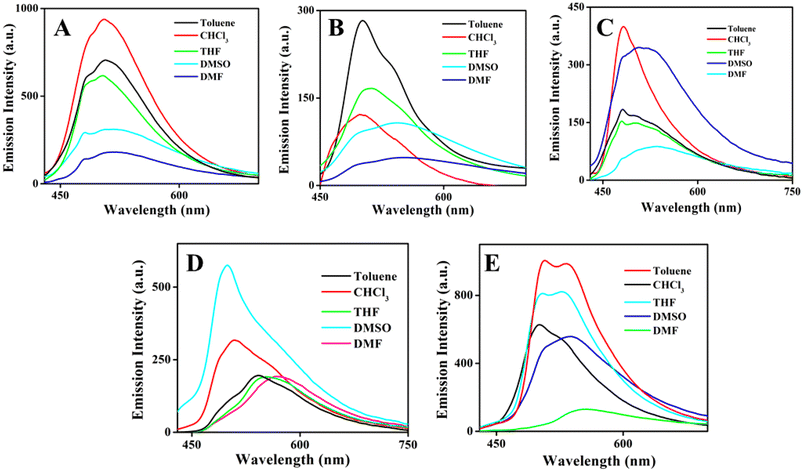 | ||
| Fig. 2 Emission spectra of boron compounds 6–10 (A–E) in various solvents with different polarities at room temperature. | ||
To further validate the ESIPT features, lifetime measurements were performed for all compounds across various solvents. Notably, a bi-exponential decay was observed, comprising two distinct lifetime components. One component exhibited a longer lifetime of around 50 picoseconds (ps), while the other component was too short to be detected with our current instrumentation due to limitations in time resolution.64,65 The unresolved shorter life time component indicated that the ESIPT process is indeed occurring, resulting in the population of the proton-transferred keto form. The above results support the presence of excited state intramolecular proton transfer reaction in the excited state of compound 6–10.
Normally, the enol form was stabilized in a non-polar solvent like toluene and the keto form was stabilized in a polar solvent and the same feature was seen in compound 9. Furthermore, the presence of electron donating groups such as –OMe and NEt2, steric hindrance (–t-butyl) groups, π-extended system groups together influence the emission feature of the organoboron compounds.
The quantum yield values for 6–10 in different solvents were calculated and the corresponding values were tabulated (Table S4‡) with emission and UV-visible absorption maximum. The boron complexes 9 showed a maximum quantum yield value in comparison with other boron complexes.
Aggregation-induced enhanced emission behavior of boron compounds
Nowadays, the development of AIEE-active organic materials has been a fascinating area due to their potential applications in modern fields of biotechnology and optoelectronics.66–68 Most of the ESIPT-active compounds display aggregation-induced enhanced emission (AIEE).21 In general, compounds encompassing freely rotatable and easily isomerisable groups deactivate their excited energy via non-radiative phenomenon easily. Thus, restricting molecular motions through molecular aggregation suppresses non-radiative relaxation pathways, leading to enhanced emission behavior. Due to the presence of easily rotatable N–N bond, freely isomerisable CH![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N group and photo-tautomerisable group CH
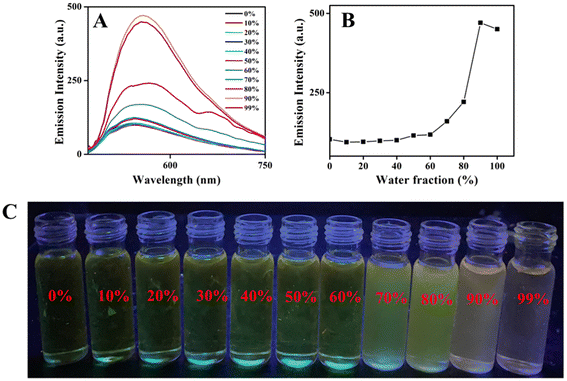
N group and photo-tautomerisable group CH![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N⋯HO (ESIPT-active unit) in all the compounds 6–10, the consequence of molecular aggregation on photophysical properties was explored. To understand the photophysical properties of boron complexes 6–10 in the aggregated state, emission measurements were carried out in THF–H2O mixture with varying water fractions. Stock solutions of boron complexes 6–10 were prepared in pure THF with a concentration of 1 × 10−3 M. Addition of increasing amounts of water fractions fw was deliberated for the UV-visible absorption and emission spectral analysis. The emission spectral results for the boron complexes 6–8 are given in Fig. S30–S32,‡ and emission spectral data for the compounds 9 and 10 are given in Fig. 3 and 4. Compounds 6–10 exhibited weak emission in pure THF. Upon increasing the water fraction in the THF–H2O mixture, the emission intensity was not altered much up to 60%, where emission intensity reached a maximum and then intensity was found to decrease when water content attained 99%. The results indicate that highly emissive species were formed in the range of 70% to 90% water content in the THF–H2O mixture. Depending on the nature of the compound, the enhancement in emission intensity varied from 3-fold to 11-fold (3-fold for 6 and 7, 5-fold for 8, and 11-fold for 9 and 10). A high fold enhancement was achieved only in compounds 9 and 10, which were visible to the naked eye under a UV lamp (Fig. 3C & 4C). Significant changes in the fluorescence wavelength (red shift of 10 nm) were noted for complexes 9 and 10 upon aggregation.
N⋯HO (ESIPT-active unit) in all the compounds 6–10, the consequence of molecular aggregation on photophysical properties was explored. To understand the photophysical properties of boron complexes 6–10 in the aggregated state, emission measurements were carried out in THF–H2O mixture with varying water fractions. Stock solutions of boron complexes 6–10 were prepared in pure THF with a concentration of 1 × 10−3 M. Addition of increasing amounts of water fractions fw was deliberated for the UV-visible absorption and emission spectral analysis. The emission spectral results for the boron complexes 6–8 are given in Fig. S30–S32,‡ and emission spectral data for the compounds 9 and 10 are given in Fig. 3 and 4. Compounds 6–10 exhibited weak emission in pure THF. Upon increasing the water fraction in the THF–H2O mixture, the emission intensity was not altered much up to 60%, where emission intensity reached a maximum and then intensity was found to decrease when water content attained 99%. The results indicate that highly emissive species were formed in the range of 70% to 90% water content in the THF–H2O mixture. Depending on the nature of the compound, the enhancement in emission intensity varied from 3-fold to 11-fold (3-fold for 6 and 7, 5-fold for 8, and 11-fold for 9 and 10). A high fold enhancement was achieved only in compounds 9 and 10, which were visible to the naked eye under a UV lamp (Fig. 3C & 4C). Significant changes in the fluorescence wavelength (red shift of 10 nm) were noted for complexes 9 and 10 upon aggregation.
Further evidence for the aggregate formation was obtained from UV-visible absorption measurements. When the water fraction was low (0–50%), the UV-visible absorption spectra of the boron complexes remained the same as in pure THF solvent. When water fraction was increased beyond 50% (i.e. from 60%) noticeable changes were observed in the UV-visible spectra for the entire boron complexes. The bathochromic shift in the absorption spectra, accompanied by a significant decrease in the UV-visible peak (Mie light scattering), confirms the formation of nano-aggregates (Fig. S33‡). This bathochromic shift in the UV-visible spectra is a characteristic feature of J-aggregate formation, indicating the AIEE characteristics of all boron complexes in the THF–H2O mixture.
To confirm the aggregate formation, DLS measurement was performed for the complexes 6–10 (Fig. S34‡). The complexes 6–10 in pure THF solvent did not show any particle size, when the water content is increased the particle size was also found to be increased. The percentage of water and particle size from DLS data for the boron complexes 6–10 was summarized in Table S5.‡
In addition, field emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM) analysis for the compounds in the aggregated state was measured at their respective water fraction and the results were displayed in Fig. 5. The morphology of compounds 6–10 indicates the formation of aggregates. Entire boron complexes show weak emission in highly soluble solvents like THF. This is due to the presence of easily rotatable N–N bond, easily isomerizable CH![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N unit and ESIPT unit CH
N unit and ESIPT unit CH![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N⋯HO unit in the organoboron compounds 6–10. These molecules deactivate their energy from their excited state to the ground state via a non-radiative pathway and end up with weak emission. When poor solvent like water was added to the THF solution, it resulted in the emissive aggregated state, which is due to the restriction of molecular motion in the aggregated state where the motion of molecules got arrested and the molecules are deactivated to their ground state from excited state via a radiative pathway. These observations deliberately describe that AIEE features of all boron complexes might be due to the restricted intramolecular motion. Further evidence for the occurrence of restricted intramolecular motion was obtained from the emission measurements of the compounds in THF–glycerol (10
N⋯HO unit in the organoboron compounds 6–10. These molecules deactivate their energy from their excited state to the ground state via a non-radiative pathway and end up with weak emission. When poor solvent like water was added to the THF solution, it resulted in the emissive aggregated state, which is due to the restriction of molecular motion in the aggregated state where the motion of molecules got arrested and the molecules are deactivated to their ground state from excited state via a radiative pathway. These observations deliberately describe that AIEE features of all boron complexes might be due to the restricted intramolecular motion. Further evidence for the occurrence of restricted intramolecular motion was obtained from the emission measurements of the compounds in THF–glycerol (10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 90), which shows high emission intensity, compared to emission features in THF–H2O (10
90), which shows high emission intensity, compared to emission features in THF–H2O (10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 90) mixture (Fig. S35‡). Furthermore, all the molecules exhibited various weak interactions in their solid state, which play a crucial role in restricting intramolecular motion. This restriction leads to enhanced emission in the aggregated or solid state.
90) mixture (Fig. S35‡). Furthermore, all the molecules exhibited various weak interactions in their solid state, which play a crucial role in restricting intramolecular motion. This restriction leads to enhanced emission in the aggregated or solid state.
Mechanoresponses of boron complexes
Organic compounds that modify their emission properties when exposed to external stimuli have drawn considerable attention for their potential applications. In general, AIE and ESIPT-active molecules show a stimuli-responsive behavior.Our previous work established that the ICT-coupled ESIPT-active star-shaped AIE emissive compound56 is a valuable approach for constructing mechanoresponsive materials. Hence, the mechanoresponsive emissive behavior of five boron complexes was investigated by solid-state emission measurements. The solid-state emission was performed for boron complexes 6–10 before and after grinding, but the compounds 7 & 8 did not demonstrate the mechanoresponsive features. As depicted in Fig. 6, crystals of compounds 6, 9, and 10 initially emit weak green, orange, and yellow fluorescence, respectively, under UV light. Upon mechanical grinding with a pestle, their emission intensifies and shifts: compound 6 showed transitions from weak green to bright green, compound 9 shift its emission from yellow to intense yellowish-orange, and compound 10 move from weak yellow to vibrant yellow colour emission under UV light. This observation highlights the mechanoresponsive behavior of boron complexes 6, 9, and 10. To confirm the visible emission color changes, solid-state emission spectra were recorded. The emission peaks for compounds 6, 9, and 10 under grinding conditions are shown in Fig. 6 and Fig. S37‡, while the solid-state emission spectra for compounds 7 and 8 are provided in Fig. S36.‡ The solid-state emission spectra of the boron complex (6) in the crystal exhibit dual emission peaks around 490 nm and 525 nm. Mechanical grinding of the crystal resulted in an approximately 3-fold increase in emission at shorter wavelength, along with decline in the emission peak at 525 nm. For boron complex 9, the solid-state emission spectrum displayed a peak at 610 nm, which, upon grinding, exhibited a 5-fold enhancement in emission intensity and a blue shift of around 20 nm. Then the solid-state emission spectral studies were also performed for the complex (10). The crystal displayed a weak emission at 575 nm initially. After grinding the crystal, 100-fold enhanced emission with blue shift in emission wavelength by almost 30 nm was observed.
Additionally, SEM analysis was also exhibited to confirm the morphological changes from the crystal state to the ground state after grinding of compounds 9 and 10 (Fig. S38‡).
Conclusion
In summary, a series of new, cost-effective fluorescent boronic acid derived triaminoguanidine-salicylidene complexes were synthesized through a simple one-pot condensation reaction employing C3 symmetric Schiff base with phenylboronic acid. The molecular structure of compounds 6–10 was verified using single-crystal X-ray analysis. Single-crystal X-ray diffraction analysis revealed that in the mononuclear complexes (6–8 & 10), boron atoms adopt tetrahedral geometry with fused five-membered N–B–N and six-membered O–B–N chelate ring. Notably, the crystal structure of boron compound 9 reveals the presence of two boron atoms in distinct coordination environment, forming four fused boron-incorporated heterocyclic rings, including six-membered O–B–N, six-membered N–B–N, seven-membered N–B–O and five-membered N–B–N chelate rings in the solid state. All these compounds displayed ESIPT behavior and AIEE properties. AIEE feature of the organoboron derivative in a THF–H2O mixture due to the prevention of intramolecular rotation and C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N isomerization as well as rigidification of ligand by organoboron coordination. More precisely, compound 9 and 10 exhibit a red-shifted AIEE effect in binary solvents of THF and water, attributed to the formation of J-aggregation. Remarkably, compounds 6, 9 and 10 also demonstrate mechanoresponsive behavior when subjected to grinding as an external stimulus. This designed approach demonstrates that how easily tune the fluorescent feature of organoboron derivative by varying the periphery of C3 symmetric Schiff base.
N isomerization as well as rigidification of ligand by organoboron coordination. More precisely, compound 9 and 10 exhibit a red-shifted AIEE effect in binary solvents of THF and water, attributed to the formation of J-aggregation. Remarkably, compounds 6, 9 and 10 also demonstrate mechanoresponsive behavior when subjected to grinding as an external stimulus. This designed approach demonstrates that how easily tune the fluorescent feature of organoboron derivative by varying the periphery of C3 symmetric Schiff base.
Author contributions
Balamurugan Tharmalingam: formal analysis, software, data curation, validation, writing – original draft. Rajendran Kishore Kumar: formal analysis, data curation, validation, writing – original draft. Ottoor Anitha: data curation, visualization, validation. Werner Kaminsky: validation, formal analysis. Jan Grzegorz Malecki: validation, formal analysis. Balasubramanian Murugesapandian: supervision, visualization, writing – original draft, writing & editing, project administration, funding acquisition.Data availability
Data will be made available on request.Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.Acknowledgements
B. M. thanks UGC, New Delhi, India for UGC FRP faculty award [F.4-5(94-FRP)/2014(BSR)], SERB, New Delhi, India (CRG/2023/004394) for the financial assistance. Authors acknowledge the NMR facility, CIC, Bharathiar University supported by DST PURSE Phase-II program. B. T. gratefully acknowledge Prof. Jianzhang Zhao, State Key Laboratory of Fine Chemicals, Frontier Science Center for Smart Materials, School of Chemical Engineering, Dalian University of Technology, Dalian 116024 (P. R. China) for theoretical calculations. The authors also acknowledge Prof. D. Nataraj, Department of Physics, Bharathiar University and his scholar Varsha. K for lifetime measurements.References
- H. B. Cheng, X. Cao, S. Zhang, K. Zhang, Y. Cheng, J. Wang, J. Zhao, L. Zhou, X. J. Liang and J. Yoon, Adv. Mater., 2023, 35, 2207546 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. J. Kim and T. Yasuda, Adv. Opt. Mater., 2022, 10, 2201714 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Li, H. Kim, F. Xu, J. Han, Q. Yao, J. Wang, K. Pu, X. Peng and J. Yoon, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2022, 51, 1795–1835 RSC.
- J. P. Antonio, R. Russo, C. P. Carvalho, P. M. Cal and P. M. Gois, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2019, 48, 3513–3536 RSC.
- E. Y.-X. Chen and T. J. Marks, Chem. Rev., 2000, 100, 1391–1434 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Z. Zhao, H. Zhang, J. W. Lam and B. Z. Tang, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2020, 59, 9888–9907 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Hong, J. W. Lam and B. Z. Tang, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2011, 40, 5361–5388 RSC.
- J. Mei, N. L. Leung, R. T. Kwok, J. W. Lam and B. Z. Tang, Chem. Rev., 2015, 115, 11718–11940 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. C. Giel and Y. Hong, Aggregate, 2023, 4, e336 CrossRef CAS.
- S.-Z. Yi, B.-N. Li, P.-Y. Fu, M. Pan and C.-Y. Su, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2023, 15, 3172–3181 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Zhang, Y. Bai, J. Deng, P. Zhuang and H. Wang, Aggregate, 2024, 5, e517 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Kothavale, Y. Erande and N. Sekar, ChemistrySelect, 2017, 2, 5013–5024 CrossRef CAS.
- U. Duraisamy, P. Jerome, N. Vijay and T. H. Oh, J. Lumin., 2023, 120350 Search PubMed.
- G. Niu, X. Zheng, Z. Zhao, H. Zhang, J. Wang, X. He, Y. Chen, X. Shi, C. Ma and R. T. Kwok, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2019, 141, 15111–15120 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- B. Shen, L. Liu, Y. Huang, J. Wu, H. Feng, Y. Liu, H. Huang and X. Zhang, Aggregate, 2024, 5, e421 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Ji, S. Griesbeck and T. B. Marder, Chem. Sci., 2017, 8, 846–863 RSC.
- W. E. Piers, S. C. Bourke and K. D. Conroy, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2005, 44, 5016–5036 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X.-J. Jiang, M. Li, H.-L. Lu, L.-H. Xu, H. Xu, S.-Q. Zang, M.-S. Tang, H.-W. Hou and T. C. Mak, Inorg. Chem., 2014, 53, 12665–12667 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Saotome, K. Suenaga, K. Tanaka and Y. Chujo, Mater. Chem. Front., 2020, 4, 1781–1788 RSC.
- R. Yoshii, K. Suenaga, K. Tanaka and Y. Chujo, Chem. – Eur. J., 2015, 21, 7231–7237 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- F. Qi, J. Lin, X. Wang, P. Cui, H. Yan, S. Gong, C. Ma, Z. Liu and W. Huang, Dalton Trans., 2016, 45, 7278–7284 RSC.
- J. S. Hansen, T. Hoeg-Jensen and J. B. Christensen, Tetrahedron, 2017, 73, 3010–3013 CrossRef CAS.
- Z. Zhang, Z. Wu, J. Sun, P. Xue and R. Lu, RSC Adv., 2016, 6, 43755–43766 RSC.
- P. M. Gurubasavaraj, V. P. Sajjan, B. M. Muñoz-Flores, V. M. J. Pérez and N. S. Hosmane, Molecules, 2022, 27, 1877 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Gemen, J. Ahrens, L. J. Shimon and R. Klajn, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2020, 142, 17721–17729 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. Ozdemir, S. Atilgan, I. Kutuk, L. T. Yildirim, A. Tulek, M. Bayindir and E. U. Akkaya, Org. Lett., 2009, 11, 2105–2107 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H.-T. Feng, J.-B. Xiong, Y.-S. Zheng, B. Pan, C. Zhang, L. Wang and Y. Xie, Chem. Mater., 2015, 27, 7812–7819 CrossRef CAS.
- M. M. Alcaide, F. M. Santos, V. n. F. Pais, J. I. s. Carvalho, D. Collado, E. Perez-Inestrosa, J. s. F. Arteaga, F. Bosca, P. M. Gois and U. Pischel, J. Org. Chem., 2017, 82, 7151–7158 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- F. M. Santos, J. N. Rosa, N. R. Candeias, C. P. Carvalho, A. I. Matos, A. E. Ventura, H. F. Florindo, L. C. Silva, U. Pischel and P. M. Gois, Chem. – Eur. J., 2016, 22, 1631–1637 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. J. Silva, Y. Zhang, R. Vinck, F. M. Santos, J. P. Antonio, L. Gourdon-Grunewaldt, C. Zaouter, A. Castonguay, S. A. Patten and K. Cariou, Bioconjugate Chem., 2023, 34, 2337–2344 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- F. M. Santos, Z. Domínguez, J. P. Fernandes, C. P. Carvalho, D. Collado, E. Perez-Inestrosa, M. V. Pinto, A. Fernandes, J. F. Arteaga and U. Pischel, Chem. – Eur. J., 2020, 26, 14064–14069 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Wang, X. Guo, W. Bu, Z. Kang, C. Yu, Q. Wu, L. Jiao and E. Hao, Dyes Pigm., 2023, 210, 111013 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Yu, G. Di, Q. Li, X. Guo, L. Wang, Q. Gong, Y. Wei, Q. Zhao, L. Jiao and E. Hao, Inorg. Chem., 2024, 63, 21397–21409 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Ibarra-Rodriguez, B. M. Munoz-Flores, A. Gomez-Trevino, R. Chan-Navarro, J. C. Berrones-Reyes, A. Chavez-Reyes, H. R. Dias, M. S. Vazquez and V. M. Jimenez-Perez, Appl. Organomet. Chem., 2019, 33, e4718 CrossRef.
- M. Ibarra-Rodriguez, B. M. Munoz-Flores, H. R. Dias, M. Sanchez, A. Gomez-Treviño, R. Santillan, N. Farfan and V. M. Jimenez-Perez, J. Org. Chem., 2017, 82, 2375–2385 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Jia and J. Wen, Tetrahedron Lett., 2021, 71, 153006 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Yuan, Y. Yuan, X. Tian, H. Wang, Y. Liu and R. Feng, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2019, 123, 29838–29855 CrossRef CAS.
- V. G. Jimenez, F. M. Santos, S. Castro-Fernandez, J. M. Cuerva, P. M. Gois, U. Pischel and A. G. Campana, J. Org. Chem., 2018, 83, 14057–14062 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. P. Nandi, P. Sudhakar, N. K. Kalluvettukuzhy and P. Thilagar, Chem. – Eur. J., 2020, 26, 16306–16317 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Yu, G. Di, Q. Li, X. Guo, L. Wang, Q. Gong, Y. Wei, Q. Zhao, L. Jiao and E. Hao, Inorg. Chem., 2024, 63(45), 21397–21409 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- I.-S. Tamgho, A. Hasheminasab, J. T. Engle, V. N. Nemykin and C. J. Ziegler, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2014, 136, 5623–5626 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Wang, X. Fang, X. Guo, Q. Wu, Q. Gong, C. Yu, E. Hao and L. Jiao, Org. Lett., 2021, 23, 4796–4801 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Aoyama, S. Ito and K. Tanaka, Macromolecules, 2024, 57, 6559–6567 CrossRef CAS.
- D. Caceres-Castillo, G. Miron-Lopez, M. C. Garcia-Lopez, R. Chan-Navarro, R. F. Quijano-Quinones, F. M. Briceno-Vargas, R. Cauich-Kumul, H. Morales-Rojas and A. D. Herrera-Espana, J. Mol. Struct., 2023, 1271, 134048 CrossRef CAS.
- A. C. Murali, P. Nayak and K. Venkatasubbaiah, Dalton Trans., 2022, 51, 5751–5771 RSC.
- R. V. R. N. Chinta, S. Sulava, B. P. R. Aradhyula, H. Jandhyam, D. P. Alone and K. Venkatasubbaiah, New J. Chem., 2023, 47, 14508–14514 RSC.
- P. Pallavi, V. Kumar, M. W. Hussain and A. Patra, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2018, 10, 44696–44705 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- V. Kumar, B. Sk, S. Kundu and A. Patra, J. Mater. Chem. C, 2018, 6, 12086–12094 RSC.
- S. Mukherjee, A. V. Desai, A. I. Inamdar, B. Manna and S. K. Ghosh, Cryst. Growth Des., 2015, 15, 3493–3497 CrossRef CAS.
- B. Tharmalingam, M. Mathivanan, O. Anitha, W. Kaminsky and B. Murugesapandian, J. Solid State Chem., 2022, 305, 122637 CrossRef CAS.
- B. Tharmalingam, M. Mathivanan, O. Anitha and B. Murugesapandian, J. Photochem. Photobiol., 2021, 406, 112983 CrossRef CAS.
- B. Tharmalingam, M. Mathivanan and B. Murugesapandian, Spectrochim. Acta, Part A, 2020, 242, 118749 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- E. T. Spielberg, A. Gilb, D. Plaul, D. Geibig, D. Hornig, D. Schuch, A. Buchholz, A. Ardavan and W. Plass, Inorg. Chem., 2015, 54, 3432–3438 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- B. Kintzel, M. Bohme, D. Plaul, H. Gorls, N. Yeche, F. Seewald, H.-H. Klauss, A. A. Zvyagin, E. Kampert and T. Herrmannsdorfer, Inorg. Chem., 2023, 62, 3420–3430 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Zhou, Z.-X. Li, S.-Q. Zang, Y.-Y. Zhu, H.-Y. Zhang, H.-W. Hou and T. C. Mak, Org. Lett., 2012, 14, 1214–1217 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- B. Tharmalingam, M. Mathivanan, G. Dhamodiran, K. S. Mani, M. Paranjothy and B. Murugesapandian, ACS Omega, 2019, 4, 12459–12469 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. C. Murali, P. Pratakshya, P. Patel, P. Nayak, S. Peruncheralathan and K. Venkatasubbaiah, New J. Chem., 2023, 47, 17835–17842 RSC.
- B. Tharmalingam, M. Mathivanan, K. S. Mani, W. Kaminsky, A. Raghunath, M. Jothi, E. Perumal and B. Murugesapandian, Anal. Chim. Acta, 2020, 1103, 192–201 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Altomare, M. Burla, M. Camalli, G. Cascarano, C. Giacovazzo, A. Guagliardi, A. Moliterni, G. Polidori and R. Spagna, J. Appl. Crystallogr., 1999, 32, 115–119 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Altomare, G. Cascarano, C. Giacovazzo and A. Guagliardi, J. Appl. Crystallogr., 1993, 26, 343–350 CrossRef.
- G. Sheldrick, SHELXL-93, 1993 Search PubMed.
- G. M. Sheldrick, Acta Crystallogr., Sect. C: Struct. Chem., 2015, 71, 3–8 Search PubMed.
- K. Anandhan, M. Ceron, V. Perumal, P. Ceballos, P. Gordillo-Guerra, E. Perez-Gutierrez, A. E. Castillo, S. Thamotharan and M. J. Percino, RSC Adv., 2019, 9, 12085–12096 RSC.
- V. Thiagarajan and P. Ramamurthy, Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn., 2007, 80, 1307–1315 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Ziołek, J. Kubicki, A. Maciejewski, R. Naskrecki and A. Grabowska, J. Chem. Phys., 2006, 124, 124518 CrossRef PubMed.
- S. K. Mellerup and S. Wang, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2019, 48, 3537–3549 RSC.
- H.-W. Zheng, Y. Kang, M. Wu, Q.-F. Liang, J.-Q. Zheng, X.-J. Zheng and L.-P. Jin, Dalton Trans., 2021, 50, 3916–3922 RSC.
- R. Yoshii, A. Hirose, K. Tanaka and Y. Chujo, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2014, 136, 18131–18139 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
Footnotes |
| † We would like to dedicate this work to Prof. Vadapalli Chandrasekhar on the occasion of his 65th birthday and for his contribution in Main Group Chemistry. |
| ‡ Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available. CCDC 1996722, 2370980, 1996724, 1996723 and 1996725. For ESI and crystallographic data in CIF or other electronic format see DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/d4dt03217a |
| § Equal contribution. |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2025 |