Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleCreative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported Licence
Extracellular vesicles derived from ovarian cancer cell lines discriminated by biochemical and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy approaches†
Lefkothea
Pantazi
 ab,
Valérie
Untereiner
ab,
Valérie
Untereiner
 c,
Paolo
Rosales
c,
Paolo
Rosales
 ad,
Romain
Rivet
ad,
Romain
Rivet
 a,
Sandra
Audonnet
a,
Sandra
Audonnet
 e,
Isabelle
Proult
e,
Isabelle
Proult
 a,
Laurent
Ramont
a,
Laurent
Ramont
 af,
Ganesh D.
Sockalingum
af,
Ganesh D.
Sockalingum
 *g and
Stéphane
Brézillon
*g and
Stéphane
Brézillon
 *a
*a
aUniversité de Reims Champagne-Ardenne, UMR CNRS 7369, MEDyC, Reims, France. E-mail: stephane.brezillon@univ-reims.fr; Tel: +33-326-913734
bUniversity of Patras, Biochemistry, Biochemical Analysis & Matrix Pathobiology Research Group, Laboratory of Biochemistry, Department of Chemistry, Patras, Greece
cUniversité de Reims Champagne-Ardenne, URCATech, PICT, Reims, France
dUNNOBA/CIT NOBA (UNNOBA-UNSADA-CONICET), Laboratorio de Microambiente Tumoral, CIBA, Junín, Argentina
eUniversité de Reims Champagne-Ardenne, URCATech, URCACyt, Reims, France
fCHU de Reims, Service Biochimie-Pharmacologie-Toxicologie, Reims, France
gUniversité de Reims Champagne-Ardenne, UR7506, BioSpecT, Reims, France. E-mail: ganesh.sockalingum@univ-reims.fr; Tel: +33 3 26 91 35 53
First published on 28th February 2025
Abstract
Ovarian cancer is the most lethal cancer among gynaecological malignancies. Due to the lack of early symptoms and screening tools, patients are diagnosed in advanced stages. Cancer invasion and metastasis through the extracellular matrix (ECM) are enhanced by tumour cell Extracellular Vesicles (EV). The aim of this study was to characterise the EVs derived from two ovarian cancer cell lines (ES2 and SKOV3) using biochemical and vibrational spectroscopic approaches. EVs were prepared by ultracentrifugation and characterised by Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis. Their surface proteins were assessed by MACSPlex EV kit for human exosomes. The presence of MMP14 and integrin subunits was evaluated in EVs and cell protein extracts by Western immunoblotting. Both EVs and cells were measured by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) and data were analysed by hierarchical cluster analysis (HCA). Spectral differences were observed in the lipids and polysaccharides regions both between the SKOV3 and ES2 cells and their corresponding EVs, which allowed a good delineation by HCA. The differences in the biochemical data were confirmed by similar and specific features exhibited in their respective infrared spectral signatures. ES2 EVs exhibited an enrichment in MMP14 in agreement with the aggressiveness of this ovarian cancer metastatic cell line.
Introduction
Ovarian cancer (OC) is the most lethal cancer among gynaecological malignancies. It ranks as the fifth and sixth most frequent cause of female cancer-related mortality in Europe and worldwide, respectively.1 Due to the lack of early symptoms and screening tools, patients are diagnosed at advanced stages. OC is typically staged using the International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics (FIGO) system, which consists of four stages, I to IV.2,3 The diagnosis of OC often occurs at an advanced stage due to its generally nonspecific symptoms, posing challenges for curative treatment. In fact, more than 70% of OC cases are not identified until reaching stage III or IV, further complicating effective intervention.3,4OC is divided into non-epithelial and epithelial types, but only 10% have a non-epithelial origin.2 Epithelial OC is categorised into various subtypes determined by histology and representing the visual characteristics of tumor cells.
Late detection and rapid progression of OC are the main reasons for poor survival rate. For the early diagnosis of OC, several biomarkers have been identified, with CA125 and HE4 (Human Epididymis Protein 4) being the most common. In the early 1980s the CA125 mouse monoclonal antibody (OC125) was specifically isolated from cancerous ovarian tissue compared to healthy ovarian tissue. However, today HE4 is considered as a more reliable biomarker for detecting OC. It is a glycoprotein belonging to the whey acidic 4-disulfide central protein family. HE4 was first identified in human epididymal epithelial cells as a small, acidic single-signal peptide encoded by the WFDC2 gene, with high expression in OC tissues, but low or no expression in normal ovarian tissues.5 The specificity and sensitivity of HE4 for detecting OC was 96% and 67%, respectively. Determination of both HE4 and CA125 has a significantly higher accuracy than determination of CA125 or HE4 levels alone for the diagnosis of malignant OC, with a specificity of 95% and a sensitivity of 76%.5 Thus, matricellular receptors and macromolecules of the ECM represent potential biomarkers. Cancer invasion and metastasis through the ECM are enhanced by tumor cell Extracellular Vesicles (EVs) contributing to the remodeling of the ECM. EVs are lipid layered vesicles that enclose and deliver macromolecules from cell to cell and enzymes able to degrade the ECM.6 They can be of different sizes, vary in contents and surface markers and are produced and released from cells under normal and pathological conditions.7 EVs from plasma of OC patients, patients with benign disease and healthy controls were evaluated in several studies which showed that higher levels of exosomal proteins were found in the plasma of the OC compared to patients with benign tumors and healthy controls. Proteomic comparisons of cancer EVs demonstrate differences in vesicle cargo even among various ovarian adenocarcinoma models in vitro; hence, it is possible that EV cargo differs among various OC subtypes.8
Moreover, EVs secreted from OC cells have been implicated in tumor metastasis. Activated MMPs, including MMP2, MMP9 and uPA have also been found in OC-derived EVs, suggesting that EVs secretion from OC cells may result in increased ECM degradation, promoting tumor cell invasion and metastasis.8 The presence of integrins in EVs, especially α6 and β1, is related to the progression of epithelial OC. It has been demonstrated that tumor-derived EVs contain specific integrin subunits, namely α6β1, α6β4, αvβ5 and αvβ3, which determine and predispose the formation of pre-metastatic niches in different organs and guide organ-specific metastasis.8
OC is an aggressive and complex malignancy involving the interaction between cancer cells and their microenvironment, including the extracellular matrix (ECM). Dysregulation of the ECM, involving imbalance in its synthesis, deposition, post-translational modifications and degradation, is implicated in all OC stages from precursor lesion to metastasis to distant organs.9–12
During OC, the expression of the majority of ECM macromolecules is altered. Collagen becomes progressively remodeled into short thick fibrils, randomly orientated into tracks at angles tending toward perpendicular rather than parallel to the epithelial boundary.9 Decorin is downregulated, while versican and fibronectin are upregulated. Overexpression of proteolytic enzymes, such as MMPs and cathepsins, leads to basal membrane and stroma degradation, promoting tumor invasion and metastasis. Higher expression of specific integrin subunits has been demonstrated to facilitate tumor migration and metastasis, as well as enhance cell proliferation, by activating the anti-apoptotic pathway PI3K/Akt and pathways involving FAK and Src kinases.13 Recently, Laurent-Issartel and collaborators showed that ascites and their fibrinogen/fibrin composition affect the integrity of the mesothelium and promote the integrin-dependent implantation of OC spheroids in the mesothelium.14
In addition to biochemical approaches, spectroscopic analyses of disease-related EVs have been quite recently considered as promising tools to detect biomarkers in cancer15 and in Alzheimer's disease.16 A more recent study of plasma-derived EVs from Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy patients showed distinct infrared spectral signatures associated to protein and lipid changes.17 EVs can be characterised by Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy based on molecular content and in particular on Amide and C–H stretching vibrations.18 Complementary to FTIR spectroscopy, Raman spectroscopy has also been employed to analyse EVs derived from mesenchymal stromal cells,19 breast cancer cells20 and bile from gall bladder cancer.21 Application of FTIR technologies to the characterisation of EVs has been recently reported in a review by Di Santo et al.22
FTIR is a vibrational spectroscopic technique largely used for analysing the wavelengths of light absorbed by materials after interaction with a mid-infrared polychromatic radiation source (2.5–25 μm or 4000–400 cm−1). In particular, the ratio of the transmitted/incident light is calculated and depending on the nature of the chemical bonds and their environment, specific peaks appear in the spectrum. First, an interferogram is measured that is then converted into a spectrum by Fourier transformation. The analysis can be performed in the absorption, reflection or transflection mode. FTIR spectroscopy is used for structural and compositional analysis due to its ability to give a “molecular fingerprint” of the sample.23,24
At the tissue level, FTIR imaging, combined with multivariate data analysis, was successfully used to evidence ECM disorganisation in melanoma and more specifically collagen fiber orientation.25 It has shown the ability to discriminate inflammatory from non-inflammatory breast cancer tissues26 and metastatic from non-metastatic lymph nodes in melanoma patients.27
In addition, melanoma primary tumors treated with or without lumican-derived peptide were discriminated through infrared spectral imaging.28 In a previous study, dermis of wild-type versus lumican-deficient mice were characterised by infrared spectral imaging.29 It has further been employed to characterise ovarian cancer cells and tissues.30,31
In the present preliminary study, the aim was to characterise the extracellular vesicles and the two ovarian cancer cell lines from which they derive, ES2 and SKOV3, using both biochemical and FTIR spectroscopic approaches. EVs from ES2 cells displayed a higher level of MMP14 in agreement with the higher aggressiveness of this ovarian cancer metastatic cell line. Spectroscopic data revealed a good discrimination between highly invasive and less invasive cells, but more pronounced in EVs. This could be associated to a higher carbohydrate/protein ratio in EVs compared to cells. This study provides promising data for the development of early and less invasive ovarian cancer diagnosis based on spectroscopic analysis of EVs.
Experimental
Cell culture
Cell culture of ES2 (highly metastatic, ATCC number: CRL-1978) and SKOV3 (poorly metastatic, ATCC number: HTB-77) human ovarian cancer cell lines was performed. ES2 is a fibroblast-like cell line that was isolated from the ovary of a patient with clear cell carcinoma. This tumor was described as a poorly differentiated ovarian clear cell carcinoma. SKOV3 is a cell line with epithelial morphology that was isolated from the ovary of a 64-year-old, white, female with ovarian adenocarcinoma. SKOV3 cells are more resistant than ES2.The ovarian cancer cells were cultured in high-glucose (4.5 g L−1) Dulbecco's Modified Eagle's Medium (DMEM) (Gibco) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) (Sigma-Aldrich), 1% penicillin (final concentration, 50 U mL−1; Gibco) and 1% streptomycin (final concentration, 50 U mL−1; Gibco). Cells were cultured at 37 °C under 5% CO2 humid atmosphere. The ovarian cancer cell lines were cultured up to 80% of confluency. All the cell lines were confirmed to be mycoplasma free, based on routine PCR detection method.
Antibodies and reagents
The following primary antibodies were used: Rabbit anti-CD81, dilution of 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1000 (WB, Cell signaling, #56039); rabbit anti-actin, dilution of 1
1000 (WB, Cell signaling, #56039); rabbit anti-actin, dilution of 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10
10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 (WB, Cell signaling, #4970s); rabbit anti-β1ITG, dilution of 1
000 (WB, Cell signaling, #4970s); rabbit anti-β1ITG, dilution of 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1000 (WB, Cell signaling, #34971); rabbit anti-β3ITG, dilution of 1
1000 (WB, Cell signaling, #34971); rabbit anti-β3ITG, dilution of 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1000 (WB, Santa Cruz, sc-46655); rabbit anti-MMP14, dilution of 1
1000 (WB, Santa Cruz, sc-46655); rabbit anti-MMP14, dilution of 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1000 (WB, Abcam, ab51074); rabbit anti-α2ITG, dilution of 1
1000 (WB, Abcam, ab51074); rabbit anti-α2ITG, dilution of 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1000 (WB, Merk-Millipore, AB1936); rabbit anti-α5ITG, dilution of 1
1000 (WB, Merk-Millipore, AB1936); rabbit anti-α5ITG, dilution of 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1000 (WB, Cell signaling, #4705s); rabbit anti-αvITG, dilution of 1
1000 (WB, Cell signaling, #4705s); rabbit anti-αvITG, dilution of 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1000 (WB, Cell signaling, #4711s). The following secondary antibody was used: HRP-conjugated goat anti-rabbit IgG (H + L), dilution of 1
1000 (WB, Cell signaling, #4711s). The following secondary antibody was used: HRP-conjugated goat anti-rabbit IgG (H + L), dilution of 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10
10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 (WB, GE Healthcare, NA934V).
000 (WB, GE Healthcare, NA934V).
Ovarian cancer-derived EVs production and isolation
ES2 and SKOV3 human ovarian cancer cells were cultured in 150 cm2 flasks in complete medium. When 80–90% confluence is reached, cells were washed twice with DPBS and incubated 48 h in FBS free media at 37 °C under 5% CO2 humid atmosphere. Conditioned media (CM) were collected and EVs were enriched via a three steps protocol. First, CM were filtrated through 0.22 μm pore size filter. Then, CM were ultracentrifuged (Beckman Coulter) at 100![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000g for 2 h at 4 °C to pellet the EVs using a Beckman Coulter Type 50.2 Ti Rotor. The EV pellets were resuspended with PBS and ultracentrifuged at 100
000g for 2 h at 4 °C to pellet the EVs using a Beckman Coulter Type 50.2 Ti Rotor. The EV pellets were resuspended with PBS and ultracentrifuged at 100![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000g for 1 h 30 at 4 °C using a Beckman Coulter TLA110 rotor. Finally, EVs pellets were resuspended in 100 μL of distilled water. These steps as well as the protocols described below are summarised in the workflow in Fig. 1.
000g for 1 h 30 at 4 °C using a Beckman Coulter TLA110 rotor. Finally, EVs pellets were resuspended in 100 μL of distilled water. These steps as well as the protocols described below are summarised in the workflow in Fig. 1.
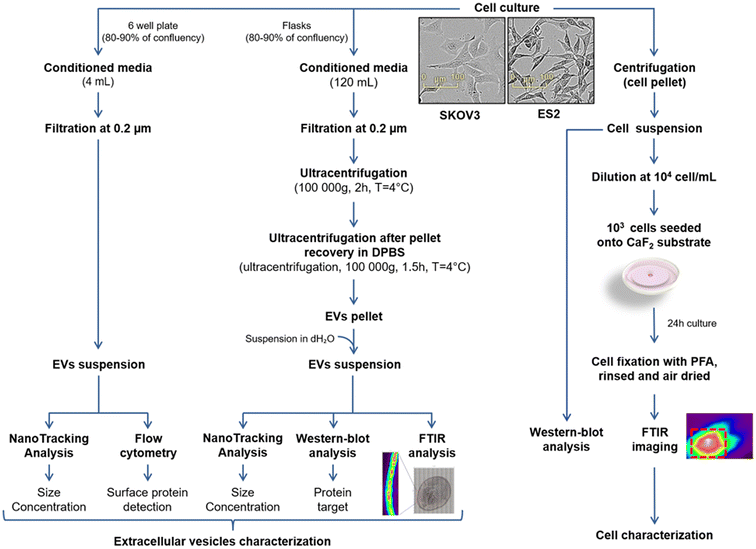 | ||
| Fig. 1 Workflow showing the preparation of EVs (left) and cell suspensions (right) of SKOV3 and ES2 cell lines for biochemical and spectroscopic analyses. | ||
We have submitted all relevant data of our experiments to the EV-TRACK knowledge base (EV-TRACK ID: EV240181).32 For MACSPlex analysis, ES2 and SKOV3 cells were cultured in 6 well plates in complete medium. When 80–90% confluence is reached, cells were washed twice with DPBS and incubated 48 h in FBS free media at 37 °C under 5% CO2 humid atmosphere. CM were collected and filtrated through 0.22 μm pore size filter.
Nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA)
EVs suspensions were analysed for size and concentration using nanoparticle tracking analysis. Samples were diluted in PBS and analysis was performed on a NanoSight NS300 (Malvern analytical) system (acquisition settings: Laser Type Blue488; Camera level 15). Three videos of 60 s were taken under controlled fluid flow with a pump speed to 30 (arbitrary units). Videos were analysed using the batch analysis tool of NanoSight NTA software version 3.4 build 3.4.4 (video analysis settings: Detect Threshold: 3). The average area under the histogram from the three videos was used for particle concentration measurement.Western-blot analysis
Cells were lysed in RIPA lysis and extraction buffer (Sigma-Aldrich) supplemented with protease and phosphatase (Thermo Fisher Scientific) inhibitors. Proteins were quantified using the DC Protein Assay (Bio-Rad). Subsequently, 25 μg of cell lysate proteins or EV proteins were heat denaturated at 98 °C for 5 min in Laemmli buffer and separated by SDS-PAGE. Proteins were then transferred onto polyvinylidene difluoride membranes (GE Healthcare Life Sciences). Membranes were blocked in a 5% Non-Fat Dry Milk (NFDM) in TBS-T for 2 h at room temperature (RT). The primary antibodies were incubated overnight at 4 °C in 1% NFDM in TBS-T. After extensive washes in TBS-T, the incubation with horseradish peroxidase-conjugated secondary anti-IgG antibodies was performed at RT for 90 min in 1% NFDM in TBS-T. Immunoreactive bands were revealed using ECL chemiluminescence detection kit (Amersham Biosciences, GE Healthcare Life Sciences). Acquisition and processing were obtained using the ChemiDoc MP imaging device and ImageLab (Bio-Rad Laboratories).Flow cytometry
Detection of surface proteins on EVs was performed using the MACSPlex Exosome kit human (Miltenyi Biotec) following the manufacturer's protocol for overnight capture in tubes. This kit enables the detection of 37 markers (CD1c, CD2, CD3, CD4, CD8, CD9, CD11c, CD14, CD19, CD20, CD24, CD25, CD29, CD31, CD40, CD41b, CD42a, CD44, CD45, CD49e, CD56, CD62p, CD63, CD69, CD81, CD86, CD105, CD133.1, CD142, CD146, CD209, CD326, HLA-ABC, HLA-DR DP DQ, MCSP, ROR1 and SSEA-4) simultaneously and include two isotype controls (mIgG1 and REA control). Briefly, ES2 and SKOV3 CM samples were filtered with a 0.22 μm filter. Hundred and twenty μL of each CM or medium only as blank control were incubated with 15 μL capture beads (containing the antibody-coated bead subsets) overnight at RT under gentle agitation. After washing, 15 μL of detection antibody mixture (CD9, CD63 and CD81 conjugated to APC) were added to the beads, samples were then incubated for 1 h at RT under gentle agitation. The samples were washed two times before being analysed on a BD LSRFortessa cytometer running BD FACSDiva™ software (BD Biosciences).The 39 individual bead populations were selected to allow determination of the APC signal intensity on the respective bead population and the median fluorescence intensity (MFI) for each captured bead was measured. MFI of each bead obtained from the control sample (PBS only) was subtracted from the signal intensities of the respective beads incubated with the sample. The mean of the MFI of the MACSPlex Exosome Capture Beads CD9, CD63 and CD81 was used as the normalisation factor for each sample.
Cell preparation for FTIR analysis
For the spectroscopic analysis of ES2 and SKOV3 cell lines, calcium fluoride (CaF2) slides were utilised. The substrates were placed into a 6-well-plate and 5000 cells were seeded on them. The cells were cultured with DMEM 10% FBS and incubated overnight. Subsequently, the substrates were rinsed with DPBS and fixed for 20 min in 4% paraformaldehyde. Following this, the substrate was rinsed again with DPBS and, then with distilled water – to prevent crystal formation on the sample due to DPBS. They were finally dried at room temperature.EVs preparation for FTIR analysis
The EV samples were recovered in distilled water after the second ultracentrifugation to prevent crystals due to DPBS. The EVs protein concentration was quantified using the Lowry method and then the appropriate volume of EV samples was pipetted onto the substrate in order to ensure a final protein amount of at least 1 μg. Specifically, 3 μL of SKOV3-derived EVs and 2 μL of ES2-derived EVs were deposited onto CaF2 substrates. The samples were dried at RT for approximately 10 min.Infrared microimaging of EVs and cells
Both EV and cell preparations were imaged using an FTIR imaging microscope, coupled with a Frontier spectrometer (PerkinElmer, Villebon-sur-Yvette, France) at a pixel size of 6.25 × 6.25 μm2 and spectral resolution of 4 cm−1. Each pixel spectrum was an average of 128 scans for samples and 240 scans for background, measured in the transmission mode over 4000–800 cm−1 spectral range. The background spectrum from the CaF2 window, recorded before an image acquisition, was automatically subtracted from the data. The instrument and the sample compartment were continuously purged with dry air throughout the process to minimise atmospheric interferences from water vapor and carbon dioxide.The two EV samples obtained from the two cell lines were deposited on CaF2 slides and measured as dried drops. Spectral images acquired from the drop's periphery exhibited higher absorbances, due to the “coffee ring” effect.
Regarding the cell lines, thirteen SKOV3 and six ES2 cell images were collected and processed. These were obtained from three biological replicates.
FTIR data preprocessing and processing
The range of the recorded spectra was 4000–800 cm−1. Due to non-informative data, the spectral range was reduced to 3700–900 cm−1. The raw images were subjected to atmospheric correction algorithm (Spectrum-Image, version 1.6, PerkinElmer) to compensate for water vapor and CO2 contributions present in the sample environment. The process was repeated for all spectral images obtained. All the spectra were preprocessed as follows: baseline correction, vector normalisation and offset correction (OPUS software version 3.1, Bruker Optics®, Ettlingen, Germany). Following this, the average spectrum for each cell and EV drop was computed from the preprocessed spectra.In order to compare the two cell lines and their derived-EVs, Hierarchical Cluster Analysis (HCA) was performed on the mean spectra in the 1800–900 cm−1 region. HCA is an unsupervised method based on the calculation of Euclidean distances between the spectra and between the groups according to their similarities. The endpoint is a set of clusters, where each cluster is distinct from the others and the objects within each cluster are broadly similar to each other. The spectral distances are represented by a heterogeneity scale. The clustering method was previously described.33,34 Further analysis was performed by calculating intensity ratios of carbohydrate/protein (I1082/I1655).
Statistical analysis
Data were expressed as the mean ± SD. Student's t test was used for in vitro experiments. For all tests, statistical significance was assumed when p < 0.05 (*), p < 0.01 (**), and p < 0.001 (***).Results
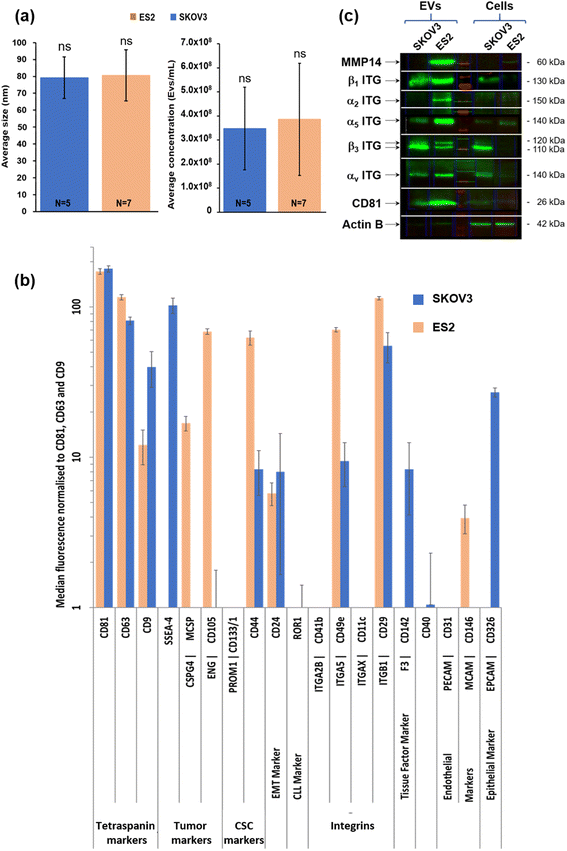
Characterisation of SKOV3- and ES2-derived EVs
In the first step, small EV size distribution and concentration were analysed by NTA. The SKOV3 EV mean size was 79.2 ± 12.5 nm (N = 7 independent EVs production) and the ES2 EV mean size was 80.6 ± 15.2 nm (N = 5 independent EVs production) (Fig. 2a, left). Thus, no difference in the mean size of the EVs of the two different cell lines was observed.The mean SKOV3 EV concentration was 3.5 × 108 ± 1.7 × 108 EVs per mL of supernatant (N = 7 independent EVs production). The mean ES2 EV concentration was 3.9 × 108 ± 2.3 × 108 EVs per mL of supernatant (N = 5 independent EVs production) (Fig. 2a, right). Thus, no difference in the mean concentration of the EVs of the two different cell lines was observed.
In second step, surface protein abundance on small EVs was determined by Flow cytometry. The conditioned media were collected and EV surface proteins (37 beads coupled to specific antibodies raised against different markers including CD9, CD63 and CD81, MACSPlex, Miltenyi) were characterised by flow cytometry (Fig. 2b).
In addition to CD9, CD63, CD81, ES2 EVs exhibited high levels of CSPG4, CD105, CD44, CD49e (α5 ITG), CD29 (β1 ITG), and CD146. The distribution profile of SKOV3 EVs was partly similar except for SSEA-4, CD142 and CD326 which were highly present in SKOV3 EVs in comparison with ES2 EVs.
Thirdly, EVs and cell protein extracts from SKOV3 and ES2 cells were identified by western blot EVs and cell protein extracts from SKOV3 and ES2 cells were analysed by western blot to evaluate the expression in cells and the distribution in EVs of MMP14 and β1, α2, α5, β3 and αV integrin subunits (Fig. 2c). MMP14 (60 kDa) was detected in ES2 but not in SKOV3 cells and EVs. It was very high in ES2 EVs in comparison with ES2 cells after normalisation to actin expression. The integrin β1 subunit (130 kDa) was expressed in both cells at similar levels, but the presence was higher in EVs, especially in ES2 EVs. The integrin α2 subunit (150 kDa) was not detected in both cells nor in SKOV3 EVs, but was strongly present in ES2 EVs. The integrin α5 subunit (140 kDa) was present in both cell lines but mostly in ES2 cells and EVs.
The integrin β3 subunit (110–120 kDa) was expressed in SKOV3 cells and abundant in SKOV3 EVs. It was not detected in ES2 cells but two forms were found in ES2 EVs. The integrin αv subunit (140 kDa) was barely expressed in ES2 cells, but it was strongly detected in ES2 EVs. It was also detected in both SKOV3 cells and EVs at similar levels. CD81 (EV biomarker) was detected in EVs of both cell lines.
Characterisation of SKOV3- and ES2-derived EVs and cells by FTIR spectroscopy
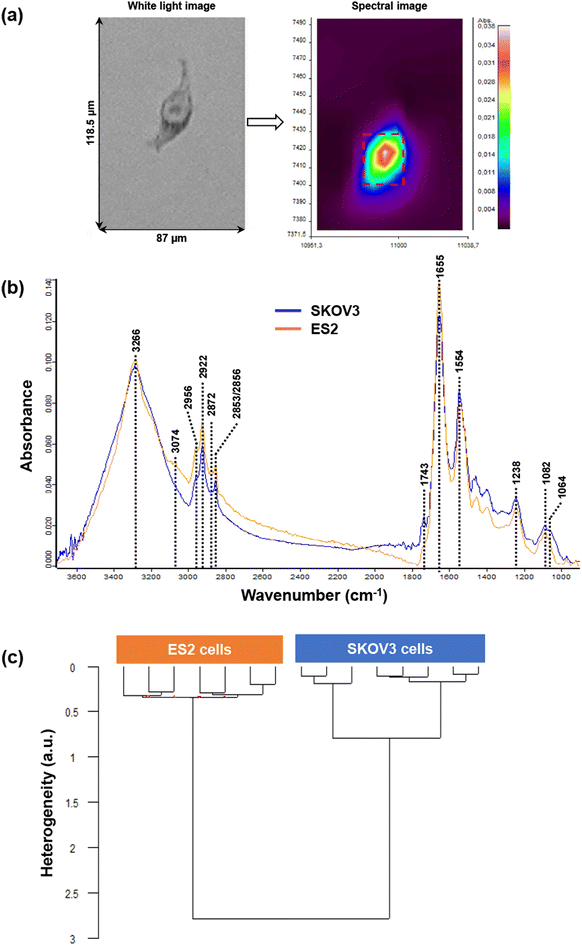
Both EVs and cells were measured by FTIR spectroscopy and data were analysed by an unsupervised chemometrics approach based on HCA (Fig. 3 and 4).In a first step, SKOV3- and ES2-derived EVs were characterised by FTIR spectroscopy. Fig. 3a shows an example of a white light image of an EV dried drop and the peripheral region (left) where the IR image was acquired. The insert illustrates the raw spectral image with different absorbance intensities (right). After preprocessing, FTIR mean spectra of EVs derived from SKOV3 (blue line) and ES2 (orange line) cell lines are shown in Fig. 3b. By comparing the two mean spectra, differences can be observed in the specific regions as described hereafter. The mean and standard deviation of the FTIR spectra of the two cell lines derived EVs are shown in Fig. S1.†
The peak at 3296 cm−1 assigned to N–H bond vibration of proteins was quite different; the peak for SKOV3-derived EVs was wider (could be due to presence of water) and its intensity was slightly higher than the one of ES2-derived EVs. For ES2 EVs, the band was sharper and two shoulders were also present. As for the protein Amide bands (Amide I at 1665 cm−1 and Amide II at 1547 cm−1), the shape of the peaks was the same; however, the peak intensity of SKOV3-derived EVs was much lower than that of ES2-derived EVs.
Regarding the lipid profile, there were two common peaks for the two types of EVs; one at 2853 cm−1 (symmetric vibration of CH2 groups) and one at 2923 cm−1 (CH2 asymmetric stretch). One peak in ES2-derived EVs and one shoulder for SKOV3 at 2956 cm−1 (CH3 asymmetric stretching) were also present. In the region 1800–1700 cm−1 no peaks were detected. However, one shoulder at 1744 cm−1 was observed in both types of EVs, corresponding to the carbonyl (C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O) stretching of phospholipids. The main protein peaks assigned to Amide I at 1655 cm−1 (mainly C
O) stretching of phospholipids. The main protein peaks assigned to Amide I at 1655 cm−1 (mainly C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O vibration) and Amide II at 1544 cm−1 (mainly assigned to C–N stretch) have a similar profile in both EVs. The peak at 1293 cm−1, assigned to Amide III, was present in both types of EVs, with the intensity of ES2-derived EVs being much stronger than the one of SKOV3-derived EVs. Significant differences were observed in the carbohydrate absorption region (1200–900 cm−1) of the spectra. In particular, the peak at 1031 cm−1 was detected only in SKOV3-derived EVs and corresponds to vibrational modes of -CH2OH groups. Moreover, the peak at 1152 cm−1, that could be due to C–O vibration of carbohydrates, was observed only in SKOV3-derived EVs. However, it can be noted that the carbohydrate/protein ratio was higher in SKOV3 than in ES2 derived-EVs. The HCA analysis was conducted on both cell and EVs samples to evaluate the concordance of the data obtained. Fig. 3c displays the HCA results of ES2- and SKOV3-derived EVs mean spectra. The dendrogram shows that two main clusters emerged, indicating a clear distinction and, thus significant differences between the two types of EVs. Moreover, the heterogeneity within each cluster was very low, almost zero (0.055 for SKOV3-derived EVs and 0.022 for ES2-derived EVs), suggesting high intra-sample similarity. These values were negligible compared to the inter-group variability (4.2 between ES2 and SKOV3).
O vibration) and Amide II at 1544 cm−1 (mainly assigned to C–N stretch) have a similar profile in both EVs. The peak at 1293 cm−1, assigned to Amide III, was present in both types of EVs, with the intensity of ES2-derived EVs being much stronger than the one of SKOV3-derived EVs. Significant differences were observed in the carbohydrate absorption region (1200–900 cm−1) of the spectra. In particular, the peak at 1031 cm−1 was detected only in SKOV3-derived EVs and corresponds to vibrational modes of -CH2OH groups. Moreover, the peak at 1152 cm−1, that could be due to C–O vibration of carbohydrates, was observed only in SKOV3-derived EVs. However, it can be noted that the carbohydrate/protein ratio was higher in SKOV3 than in ES2 derived-EVs. The HCA analysis was conducted on both cell and EVs samples to evaluate the concordance of the data obtained. Fig. 3c displays the HCA results of ES2- and SKOV3-derived EVs mean spectra. The dendrogram shows that two main clusters emerged, indicating a clear distinction and, thus significant differences between the two types of EVs. Moreover, the heterogeneity within each cluster was very low, almost zero (0.055 for SKOV3-derived EVs and 0.022 for ES2-derived EVs), suggesting high intra-sample similarity. These values were negligible compared to the inter-group variability (4.2 between ES2 and SKOV3).
In the second step, SKOV3 and ES2 cells were characterised by FTIR spectroscopy. Regarding the cell lines, thirteen SKOV3 and six ES2 cell spectra were collected and processed. Fig. 4a shows an example of a white light image (left) of a single ES2 cell and its corresponding infrared image (right) (Fig. 4a) where its nucleus and cytoplasm can be visualised in the raw image. Mean spectra from SKOV3 and ES2 cell images are displayed in Fig. 4b. The mean and standard deviation of the FTIR spectra of the two cell lines are shown in Fig. S2.†
Regarding the protein profile of the two cell lines, the wide peak at approximately 3266 cm−1 due to the N–H vibration of proteins had the same intensity for both cell lines. Amide I peak appeared at 1655 cm−1, with the intensity of ES2 peak being higher than that of the SKOV3 peak. Amide II peaks at 1554 cm−1 (assigned to N–H bend and C–N stretch) were very similar to each other.
In the range 3100–3800 cm−1, the peak at 3074 cm−1 appeared only in ES2 cells and corresponds to ![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH (sp2) vibrations in alkenes and aromatic rings. The peaks at 2956 cm−1 (CH3 asymmetric stretch), at 2922 cm−1 (CH2 asymmetric stretch) and 2852/2856 cm−1 (symmetric vibration of CH2 groups) were present in both cell lines, with the peaks in SKOV3 being lower in intensity. A very weak peak at 2872 cm−1 (assigned to CH3 symmetric vibration) was present only in ES2 cells and is due to CH2 symmetric stretch of lipids and proteins. In the lipid area from 1800–1700 cm−1, only one very weak peak appeared in SKOV3 cells but not in ES2 at 1743 cm−1 due to ester (C
CH (sp2) vibrations in alkenes and aromatic rings. The peaks at 2956 cm−1 (CH3 asymmetric stretch), at 2922 cm−1 (CH2 asymmetric stretch) and 2852/2856 cm−1 (symmetric vibration of CH2 groups) were present in both cell lines, with the peaks in SKOV3 being lower in intensity. A very weak peak at 2872 cm−1 (assigned to CH3 symmetric vibration) was present only in ES2 cells and is due to CH2 symmetric stretch of lipids and proteins. In the lipid area from 1800–1700 cm−1, only one very weak peak appeared in SKOV3 cells but not in ES2 at 1743 cm−1 due to ester (C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O) stretching of phospholipids. At this wavenumber a shoulder was present in the ES2 cell line.
O) stretching of phospholipids. At this wavenumber a shoulder was present in the ES2 cell line.
Differences in the intensity of the peaks were also detected in the carbohydrate absorption region of the spectra, indicating differences in the polysaccharide amount and composition between the two cell lines. One characteristic peak at this region was the one at 1238 cm−1 due to asymmetric phosphodiester vibration of nucleic acids, the intensity of which was lower in ES2 cells compared to SKOV3 cells.
Fig. 4c presents the HCA results of FTIR spectra from ES2 and SKOV3 cells. The dendrogram shows that spectra could be differentiated into two distinct clusters, one corresponding to ES2 cells and the other to SKOV3 cells, indicating that the two groups differed significantly from each other. The intra-group variabilities were very similar to each other, as indicated by the low heterogeneity values (0.35 for ES2 cells and 0.8 for SKOV3 cells) but remained much smaller than the inter-group variability (2.75 between ES2 and SKOV3).
Discussion
In this study, two ovarian cancer cell lines with different phenotypes were compared by biochemical approaches and FTIR spectroscopy. First, the size characterisation of ES2- and SKOV3-derived EVs was performed by NTA. These measurements showed EV sizes in the same range around 80 nm. Regarding their concentration, NTA data showed that the concentration of ES2-derived EVs was slightly higher compared to that of SKOV3-derived EVs.Then, the expression profile in cell extracts demonstrated the presence of membrane protein involved in cancer development. The results from the detection and quantification of the surface epitopes of EVs demonstrated the presence of tetraspanins markers CD9, CD63 and CD81 indicating the enrichment of exosomes in EVs fractions. Differences observed between the EVs were both qualitative and quantitative. Qualitatively, ES2 EVs exhibited specifically CSPG4, CD105 and CD146 while SKOV3 EVs were characterised specifically by the presence of SSEA-4, CD142 and CD326. CSPG4, CD105 and CD146 were described to be associated to aggressive ovarian cancers.35–40 The detection of these markers in higher amount on the surface of ES2-derived EVs was expected, due to the higher aggressiveness of ES2 cell line, compared to the SKOV3 one. On the other hand, SSEA-4 was found in larger amounts on the SKOV3-derived EVs. SSEA-4 is highly expressed in several tumors and may be considered as a marker of chemoresistance.41 SSEA-4, CD142 and CD326 are reported to be potential targets in antitumor therapy of ovarian cancer.42–44
Quantitatively, the presence of the other biomarkers was similar in both EVs. Interestingly, CD44, CD49e (α5 integrin subunit), CD29 (β1 integrin subunit) and CD105 as a receptor of TGF-β, are well-known for their contribution to tumor aggressiveness and development were present on the EVs suggesting their role in tumor spread.14,39
The strong presence of MMP14 on ES2-derived EVs was confirmed by Western blot. These results suggest the role of EVs in promoting metastasis by the degradation of ECM of the peritoneum or distant organs. In addition, EVs from both cell lines were shown to present CD44. Interestingly, it has been previously described that subgroup of patients with double expression of MMP14 and CD44 had a poor prognosis.45 The colocalisation of CD44 and MMP14 in invadopodia of breast cancer cells has been already described where CD44 is reported to be a central mediator for invadopodia activity and ECM degradation.46 The CD44s splice isoform is a central mediator for invadopodia activity. In an ovarian cancer cohort of 44 patients with metastases in lymph nodes, spleen, and/or liver, the presence of MMP14, MMP2, CD44, and Chondroitin Sulfate-E (CSE) was demonstrated in both the primary tumor and the metastases by immunohistochemistry and was related to clinical characteristics.47 Numerous studies concluded that MMP14 plays a role in ovarian tumors progression.48 The presence of MMP14 was demonstrated on the surface of cultured OC cells derived from primary ovarian tumors, metastatic tissues and ascites.48 MMP14 mRNA expression from human tumor cells was associated with increased tumor size and tumor spread.49 As demonstrated in a 3D collagen model, hypoxia induces MMP14 dependent proliferation and invasion.50 MMP14, along with MMP9 and MMP3, has been demonstrated to promote Epithelial Mesenchymal Transition (EMT), resulting in the detachment of cancer cells from the primary tumor and their diffusion into the peritoneal cavity.51 Interestingly, ascites and their fibrinogen/fibrin composition were shown to affect the integrity of the mesothelium and promote the integrin-dependent implantation of OC spheroids in the mesothelium.14
In the present report, all the investigated integrin subunits were detected confirming their presence in ovarian cancer cells and/or EVs. Notably, the expression of integrin subunits on the cell extracts varies from barely to highly detectable. Most of the integrin subunits were detected in both types of EVs except for integrin α2 which was absent from SKOV3-derived EVs. The results indicate the enrichment of molecules in EVs that positively modulate tumor progression. The results of Western blots concerning the presence of β1 and α5 integrin subunits on EVs surface are compatible to the results obtained via flow cytometry analysis. Both techniques detected the presence of these subunits on EVs; notably, their presence is stronger in ES2-derived EVs compared to the SKOV3 ones as suggested by the intensity of the bands on Western blot membranes and the fluorescence values in flow cytometry analysis. Integrin α5, αv, α2, as well as integrin β1 and β3 subunits are the most studied integrin members in OC, which can form α5β1, αvβ1, α2β1 and αvβ3 heterodimeric receptors. Most studies support their function as oncogenic genes promoting adhesion, migration and proliferation in OC.52 Integrin α5β1 is expressed in 40% of the epithelial OC cases and is involved in dissemination of the tumor. Patients with high expression of α5β1 have worse survival. Implantation of ovarian tumor spheroids involve fibrinogen/fibrin and αv and α5β1 integrins.14 Integrin α2β1 is involved in spheroid adhesion of OC cells to peritoneal cells through binding to laminin.8
The above approaches on OC cells and their derived-EVs were complemented by a biophysical approach based on FTIR spectroscopy that gives a global picture of their macromolecular contents.
Apart from differences in spectral profiles, the ratio of functional groups absorption intensities can be used to compare the spectral data. Carbohydrates contain many different types of O–H and C–O bonds and the region 1200–900 cm−1 is often used as its fingerprint region, the intensity and position being specific for every carbohydrate. By calculating the carbohydrate/protein ratio (I1082/I1655), it can be noticed that this was about four times higher in SKOV3 (1.01) derived-EVs than those of ES2 (0.245). The fact that the carbohydrate/protein ratio is much smaller in cells than in EVs could be explained by a higher protein content in cells due to the existence of the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus in the cytoplasm. These organelles are the sites of the synthesis and maturation, respectively. These organelles are not present in the EVs, the role of which is to act as cargos. Furthermore, this high increase in carbohydrate/protein ratio in SKOV3 EVs could be associated to the high abundance of glycosaminoglycans as reported by Vallen and collaborators.53 This study demonstrated that CSE is associated with metastatic legions and that it provides tumors with adhesive properties. In addition, chondroitin sulfate disaccharide described as serum markers for primary serous epithelial ovarian cancer.54–56 Moreover, proteoglycan like CSPG4 was described as protein biomarker associated with poor survival in ovarian cancer patients by promoting spheroid formation.35,36 Similarly, the cell surface heparan sulfate proteoglycan Syndecan-3 was shown to promote ovarian cancer pathogenesis and the formation of spheroids of SKOV3 cells.57,58
Due to these strong differences in macromolecular contents, a clear-cut separation could be obtained between SKOV3 and ES2 EVs using HCA with a low intra-group heterogeneity, demonstrating a high homogeneity in the EV preparations. In contrast to EVs results, SKOV3 and ES2 cells exhibit smaller differences in their spectral profiles. The carbohydrate/protein ratio in SKOV3 cells (0.16) and ES2 cells (0.13) is much smaller than in EVs. By comparing the two cell lines, the ratio comes out to about 1 compared to 4 for their corresponding EVs. A bigger intra-group heterogeneity was observed for cell measurements (slightly higher for SKOV3) compared to their corresponding EVs. This heterogeneity could arise from individual single cell measurement. In contrast, the EVs being similar in size and concentration, displayed more homogeneous spectral profiles. In spite of this intra-group heterogeneity, the two cell lines could be delineated based on their phenotypic differences. A specific spectral signature of serum and plasma-derived extracellular vesicles for cancer screening has been already published.59,60 Modifications of the glycosylation of EVs may alter their biodistribution61 and their capacity to bind peptides.62
Conclusions
In summary, this pilot study combining Fourier-transform Infrared spectroscopy and biochemical analyses compares for the first time two ovarian cancer cell lines, ES2 and SKOV3, and their derived extracellular vesicles, differing by their levels of aggressiveness. Indeed, ES2 EVs exhibited an enrichment in MMP14 in agreement with the aggressiveness of this ovarian cancer metastatic cell line. Application of multivariate data analysis based on Hierarchical Cluster Analysis (HCA) to both cell and EV spectra showed that cell-derived EVs demonstrated a better discrimination between highly invasive and less invasive situations. Spectral differences were mainly observed in the lipids and polysaccharides absorption regions, both between the SKOV3 and ES2 cells and their corresponding EVs. These results suggest that rapid, non-invasive, and reagent-free FTIR spectroscopy represents a promising approach that can be potentially applied for the EV-based diagnosis of ovarian cancer patients alongside existing and globally accepted diagnostic approaches.Author contributions
LP., methodology, investigation, and formal analysis; VU., methodology, data curation and analysis, writing and editing, formal analysis; PR., methodology and investigation; RR., methodology, formal analysis, editing; SA., investigations and editing; IP., editing; LR., conceptualisation, project administration, editing, and funding acquisition; GDS., conceptualisation, supervision, data analysis, writing original draft, writing review, and editing; SB., conceptualisation, project administration, supervision, data analysis, writing original draft, writing review, funding acquisition, and editing.Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest and all authors have read the journal's authorship statement.Acknowledgements
The funding from the Ligue Contre le Cancer (CCIR-GE) is gratefully acknowledged. L. Pantazi was an Erasmus+ Master student and P. Rosales was funded by the Horizon Europe Hepinib Programme. This project has received funding from the European Union's Horizon Europe programme Staff Exchanges under the Marie Sklodowska-Curie grant agreement No. 101086322. The authors thank the URCATech, PICT-IBiSA and URCACyt platforms of the University of Reims Champagne-Ardenne for instrument facilities.References
- T. I. A. for R. on Cancer (IARC), Global Cancer Observatory, https://gco.iarc.fr/, (accessed October 3, 2024).
- P. Gaona-Luviano, L. A. Medina-Gaona and K. Magaña-Pérez, Chin. Clin. Oncol., 2020, 9, 47–47 CrossRef PubMed.
- R. R. Da Cunha Colombo Bonadio, R. N. Fogace, V. C. Miranda and M. D. P. E. Diz, Clinics, 2018, 73, e450s CrossRef PubMed.
- C. N. Landen, M. J. Birrer and A. K. Sood, J. Clin. Oncol., 2008, 26, 995–1005 CrossRef PubMed.
- H. Wang, P. Liu, H. Xu and H. Dai, Am. J. Transl. Res., 2021, 13, 14141–14148 CAS.
- R. D. Sanderson, S. K. Bandari and I. Vlodavsky, Matrix Biol., 2019, 75–76, 160–169 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. A. Kumar, S. K. Baba, H. Q. Sadida, S. A. Marzooqi, J. Jerobin, F. H. Altemani, N. Algehainy, M. A. Alanazi, A.-B. Abou-Samra, R. Kumar, A. S. Al-Shabeeb Akil, M. A. Macha, R. Mir and A. A. Bhat, Signal Transduction Targeted Ther., 2024, 9, 27 CrossRef PubMed.
- M. Hergueta-Redondo and H. Peinado, EJC Suppl., 2020, 15, 38–48 CrossRef PubMed.
- A. Cho, V. M. Howell and E. K. Colvin, Front. Oncol., 2015, 5, 245 Search PubMed.
- W. Tian, N. Lei, J. Zhou, M. Chen, R. Guo, B. Qin, Y. Li and L. Chang, Cell Death Dis., 2022, 13, 64 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. Samuel, L. A. Mulcahy, F. Furlong, H. O. McCarthy, S. A. Brooks, M. Fabbri, R. C. Pink and D. R. F. Carter, Philos. Trans. R. Soc., B, 2018, 373, 20170065 CrossRef PubMed.
- M. Asare-Werehene, L. Communal, E. Carmona, Y. Han, Y. S. Song, D. Burger, A.-M. Mes-Masson and B. K. Tsang, Cancer Res., 2020, 80, 3959–3971 CrossRef PubMed.
- Y. Brown, S. Hua and P. S. Tanwar, Matrix Biol., 2023, 118, 16–46 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Laurent-Issartel, A. Landras, R. Agniel, F. Giffard, C. Blanc-Fournier, E. Da Silva Cruz, C. Habes, J. Leroy-Dudal, F. Carreiras and S. Kellouche, Exp. Cell Res., 2024, 441, 114155 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X.-L. Yap, B. Wood, T.-A. Ong, J. Lim, B.-H. Goh and W.-L. Lee, Membranes, 2021, 11, 591 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. Soares Martins, S. Magalhães, I. M. Rosa, J. Vogelgsang, J. Wiltfang, I. Delgadillo, J. Catita, O. A. B. da Cruz E Silva, A. Nunes and A. G. Henriques, J. Alzheimer's Dis., 2020, 74, 391–405 Search PubMed.
- A. Rajavel, N. Essakipillai, R. Anbazhagan, J. Ramakrishnan, V. Venkataraman and R. Natesan Sella, Spectrochim. Acta, Part A, 2025, 326, 125236 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Mihály, R. Deák, I. C. Szigyártó, A. Bóta, T. Beke-Somfai and Z. Varga, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, Biomembr., 2017, 1859, 459–466 CrossRef PubMed.
- N. M. Ćulum, T. T. Cooper, G. I. Bell, D. A. Hess and F. Lagugné-Labarthet, Anal. Bioanal. Chem., 2021, 413, 5013–5024 CrossRef PubMed.
- J. Penders, A. Nagelkerke, E. M. Cunnane, S. V. Pedersen, I. J. Pence, R. C. Coombes and M. M. Stevens, ACS Nano, 2021, 15, 18192–18205 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. T. Bui, E. Jang, J. H. Shin, T. H. Kim, H. Kim, D. Choi, T. D. Vu and H. Chung, Analyst, 2023, 148, 4156–4165 RSC.
- R. Di Santo, B. Niccolini, S. Romanò, M. Vaccaro, F. Di Giacinto, M. De Spirito and G. Ciasca, Spectrochim. Acta, Part A, 2024, 305, 123346 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. J. Baker, J. Trevisan, P. Bassan, R. Bhargava, H. J. Butler, K. M. Dorling, P. R. Fielden, S. W. Fogarty, N. J. Fullwood, K. A. Heys, C. Hughes, P. Lasch, P. L. Martin-Hirsch, B. Obinaju, G. D. Sockalingum, J. Sulé-Suso, R. J. Strong, M. J. Walsh, B. R. Wood, P. Gardner and F. L. Martin, Nat. Protoc., 2014, 9, 1771–1791 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- E. Wiercigroch, E. Szafraniec, K. Czamara, M. Z. Pacia, K. Majzner, K. Kochan, A. Kaczor, M. Baranska and K. Malek, Spectrochim. Acta, Part A, 2017, 185, 317–335 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Jeanne, V. Untereiner, C. Perreau, I. Proult, C. Gobinet, C. Boulagnon-Rombi, C. Terryn, L. Martiny, S. Brézillon and S. Dedieu, Sci. Rep., 2017, 7, 7700 CrossRef PubMed.
- H. T. Mohamed, V. Untereiner, I. Proult, S. A. Ibrahim, M. Götte, M. El-Shinawi, M. M. Mohamed, G. D. Sockalingum and S. Brézillon, Analyst, 2018, 143, 6103–6112 RSC.
- N. Wald, N. Bordry, P. G. Foukas, D. E. Speiser and E. Goormaghtigh, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, Mol. Basis Dis., 2016, 1862, 202–212 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Brézillon, V. Untereiner, H. T. Mohamed, E. Ahallal, I. Proult, P. Nizet, C. Boulagnon-Rombi and G. D. Sockalingum, Front. Cell Dev. Biol., 2020, 8, 377 CrossRef PubMed.
- L. Nannan, V. Untereiner, I. Proult, C. Boulagnon-Rombi, C. Colin-Pierre, G. D. Sockalingum and S. Brézillon, Front. Cell Dev. Biol., 2020, 8, 320 CrossRef PubMed.
- L. Li, X. Bi, H. Sun, S. Liu, M. Yu, Y. Zhang, S. Weng, L. Yang, Y. Bao, J. Wu, Y. Xu and K. Shen, J. Ovarian Res., 2018, 11, 64 CrossRef PubMed.
- P. Nizet, V. Untereiner, G. D. Sockalingum, I. Proult, C. Terryn, A. Jeanne, L. Nannan, C. Boulagnon-Rombi, C. Sellier, R. Rivet, L. Ramont and S. Brézillon, Cancers, 2021, 13, 5950 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- EV-TRACK Consortium, J. Van Deun, P. Mestdagh, P. Agostinis, Ö. Akay, S. Anand, J. Anckaert, Z. A. Martinez, T. Baetens, E. Beghein, L. Bertier, G. Berx, J. Boere, S. Boukouris, M. Bremer, D. Buschmann, J. B. Byrd, C. Casert, L. Cheng, A. Cmoch, D. Daveloose, E. De Smedt, S. Demirsoy, V. Depoorter, B. Dhondt, T. A. P. Driedonks, A. Dudek, A. Elsharawy, I. Floris, A. D. Foers, K. Gärtner, A. D. Garg, E. Geeurickx, J. Gettemans, F. Ghazavi, B. Giebel, T. G. Kormelink, G. Hancock, H. Helsmoortel, A. F. Hill, V. Hyenne, H. Kalra, D. Kim, J. Kowal, S. Kraemer, P. Leidinger, C. Leonelli, Y. Liang, L. Lippens, S. Liu, A. Lo Cicero, S. Martin, S. Mathivanan, P. Mathiyalagan, T. Matusek, G. Milani, M. Monguió-Tortajada, L. M. Mus, D. C. Muth, A. Németh, E. N. M. Nolte-'t Hoen, L. O'Driscoll, R. Palmulli, M. W. Pfaffl, B. Primdal-Bengtson, E. Romano, Q. Rousseau, S. Sahoo, N. Sampaio, M. Samuel, B. Scicluna, B. Soen, A. Steels, J. V. Swinnen, M. Takatalo, S. Thaminy, C. Théry, J. Tulkens, I. Van Audenhove, S. van der Grein, A. Van Goethem, M. J. van Herwijnen, G. Van Niel, N. Van Roy, A. R. Van Vliet, N. Vandamme, S. Vanhauwaert, G. Vergauwen, F. Verweij, A. Wallaert, M. Wauben, K. W. Witwer, M. I. Zonneveld, O. De Wever, J. Vandesompele and A. Hendrix, Nat. Methods, 2017, 14, 228–232 CrossRef PubMed.
- D. Helm, H. Labischinski, G. Schallehn and D. Naumann, Microbiology, 1991, 137, 69–79 CAS.
- J. H. Ward Jr., J. Am. Stat. Assoc., 1963, 58, 236–244 CrossRef.
- J. Yang, Q. Liao, M. Price, B. Moriarity, N. Wolf, M. Felices, J. S. Miller, M. A. Geller, L. Bendzick, R. Hopps, T. K. Starr, C. H. O'Connor, S. Tarullo, A. C. Nelson, E. Turley, J. Wang and J. B. McCarthy, Transl. Oncol., 2022, 16, 101318 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. Uno, Y. Koya, M. Yoshihara, S. Iyoshi, K. Kitami, M. Sugiyama, E. Miyamoto, K. Mogi, H. Fujimoto, Y. Yamakita, X. Wang, A. Nawa and H. Kajiyama, Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2024, 25, 1626 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Bai, W. Zhu, L. Coffman, A. Vlad, L. E. Schwartz, E. Elishaev, R. Drapkin and R. J. Buckanovich, Cancers, 2019, 11, 1710 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Zhang, X. Sang, R. Zhang, J. Chi and W. Bai, Am. J. Transl. Res., 2021, 13, 12461–12479 CAS.
- J. Zhang, B. Yuan, H. Zhang and H. Li, Oncol. Lett., 2019, 17, 5351–5360 CAS.
- A. Kumar, U. Khurana, R. Chowdhary, A. Halder and N. Kapoor, Turk. J. Obstet. Gynecol., 2024, 21, 43–50 CrossRef PubMed.
- I. Vannini, T. Rossi, M. Melloni, M. Valgiusti, M. Urbini, A. Passardi, G. Bartolini, C. Gallio, I. Azzali, S. Bandini, V. Ancarani, L. Montanaro, G. L. Frassineti, F. Fabbri and I. G. Rapposelli, Mol. Ther. – Methods Clin. Dev., 2023, 29, 473–482 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. J. Monzo, K. Kalander, M. M. Hyytiäinen, E. Elbasani, J. Wall, L. Moyano-Galceran, J. Tanjore Ramanathan, J. Jukonen, P. Laakkonen, A. Ristimäki, J. W. Carlson, K. Lehti, S. Salehi, P. Puolakkainen, C. Haglund, H. Seppänen, S. Leppä and P. M. Ojala, Mol. Cancer Ther., 2023, 22, 1319–1331 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. M. J. Price, Y. Hisada, J. Hazeldine, V. Bae-Jump, T. Luther, N. Mackman and P. Harrison, Res. Pract. Thromb. Haemostasis, 2023, 7, 100177 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Z. Tavsan and H. Ayar Kayalı, Cell Adhes. Migr., 2020, 14, 57–68 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. C. Vos, E. Hollemans, N. Ezendam, H. Feijen, D. Boll, B. Pijlman, H. van der Putten, P. Klinkhamer, T. H. van Kuppevelt, A. A. M. van der Wurff and L. F. A. G. Massuger, J. Ovarian Res., 2016, 9, 53 CrossRef PubMed.
- P. Zhao, Y. Xu, Y. Wei, Q. Qiu, T.-L. Chew, Y. Kang and C. Cheng, J. Cell Sci., 2016, 129, 1355–1365 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. C. Vos, E. Hollemans, S. C. H. A. van der Steen, T. H. van Kuppevelt, A. A. M. van der Wurff and L. F. A. G. Massuger, Int. J. Gynecol. Pathol., 2020, 39, 184–192 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. C. Vos, A. A. M. Van Der Wurff, T. H. Van Kuppevelt and L. F. A. G. Massuger, J. Ovarian Res., 2021, 14, 101 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. F. Drew, T. J. Blick, M. A. Lafleur, E. L. M. Tim, M. J. Robbie, G. E. Rice, M. A. Quinn and E. W. Thompson, Gynecol. Oncol., 2004, 95, 437–448 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. Sun, P. Lin, Z. Qin, Y. Liu, L.-L. Deng and C. Lu, Exp. Biol. Med., 2015, 240, 1434–1445 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. Carey, E. Low, E. Harper and M. S. Stack, Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2021, 22, 3403 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Wu, S. Zhang, J. Liu, Y. Huang, W. Deng, G. Shu and G. Yin, Front. Genet., 2020, 11, 705 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. J. E. Vallen, S. Schmidt, A. Oosterhof, J. Bulten, L. F. A. G. Massuger and T. H. Van Kuppevelt, PLoS One, 2014, 9, e111806 CrossRef PubMed.
- K. Biskup, C. Stellmach, E. I. Braicu, J. Sehouli and V. Blanchard, Diagnostics, 2021, 11, 1143 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. J. E. Vallen, L. F. A. G. Massuger, G. B. ten Dam, J. Bulten and T. H. Van Kuppevelt, Gynecol. Oncol., 2012, 127, 202–209 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- G. B. ten Dam, E. M. A. van de Westerlo, A. Purushothaman, R. V. Stan, J. Bulten, F. C. G. J. Sweep, L. F. Massuger, K. Sugahara and T. H. van Kuppevelt, Am. J. Pathol., 2007, 171, 1324–1333 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. Hillemeyer, N. A. Espinoza-Sanchez, B. Greve, N. Hassan, A. Chelariu-Raicu, L. Kiesel and M. Götte, Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2022, 23, 5793 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Oto, Q.-K. Le, S. D. Schäfer, L. Kiesel, J. Marí-Alexandre, J. Gilabert-Estellés, P. Medina and M. Götte, Cancers, 2023, 15, 3125 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Krafft, K. Wilhelm, A. Eremin, S. Nestel, N. von Bubnoff, W. Schultze-Seemann, J. Popp and I. Nazarenko, Nanomedicine, 2017, 13, 835–841 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. Veliz, T. T. Cooper, I. Grenier-Pleau, S. A. Abraham, J. Gomes, S. H. Pasternak, B. Dauber, L. M. Postovit, G. A. Lajoie and F. Lagugné-Labarthet, ACS Sens., 2024, 9, 272–282 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- F. Royo, U. Cossío, A. Ruiz de Angulo, J. Llop and J. M. Falcon-Perez, Nanoscale, 2019, 11, 1531–1537 RSC.
- A. Gori, A. Romanato, G. Bergamaschi, A. Strada, P. Gagni, R. Frigerio, D. Brambilla, R. Vago, S. Galbiati, S. Picciolini, M. Bedoni, G. G. Daaboul, M. Chiari and M. Cretich, J. Extracell. Vesicles, 2020, 9, 1751428 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
Footnote |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available. See DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/d5an00024f |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2025 |