Effects of loosely bound electrons and electron–phonon interaction on the thermoelectric properties of electrenes†
Yi-Ming
Zhao
 a,
Zishen
Wang
a,
Zishen
Wang
 b,
Jun
Zhou
b,
Jun
Zhou
 c,
Chun
Zhang
c,
Chun
Zhang
 de,
Sunmi
Shin
de,
Sunmi
Shin
 *a and
Lei
Shen
*a and
Lei
Shen
 *a
*a
aDepartment of Mechanical Engineering, National University of Singapore, Singapore, 9 Engineering Drive 1, 117575, Singapore. E-mail: mpeshin@nus.edu.sg; shenlei@nus.edu.sg
bDepartment of NanoEngineering, University of California San Diego, 9500 Gilman Dr, La Jolla, CA 92093-0448, San Diego, 0448, USA
cInstitute of Materials Research and Engineering (IMRE), Agency for Science, Technology and Research (A*STAR), 2 Fusionopolis Way, Innovis, #08-03, 138634, Singapore
dDepartment of Physics, Faculty of Science, National University of Singapore, Singapore, 2 Science Drive 3, Blk S12, Level 2, 117551, Singapore
eDepartment of Chemistry, National University of Singapore, Singapore, Block S8 Level 3, 3 Science Drive 3, 117543, Singapore
First published on 6th August 2024
Abstract
The low carrier mobility in conventional two-dimensional materials limits their thermoelectric (TE) applications due to high “density of scatterings”. Electrene, a new type of two-dimensional material has spatially interstitial electrons. These loosely bound electrons with a longer carrier–lattice distance undergo a weaker lattice perturbation, resulting in a higher mobility. Here, we systematically study the effect of loosely bound electrons, electron–phonon interaction, and spin orbital interaction on the TE properties of an electrene, HfI2, via first-principles calculations. We found that the p-type Seebeck coefficient is relatively large compared with those of other 2D materials with small effective mass. The larger hole relaxation time of HfI2 results in high p-type electrical conductivity and power factor compared with n-type ones. It is found that the spin-orbital interaction splits the spin-degenerate bands near the Fermi level inducing a decrease of the bandgap and an increase of electrical conductivity. The electron–phonon interaction also affects the phonon transport which decreases the lattice thermal conductivity by 16% under the n-type doping. Overall, our high-fidelity calculations show that the maximum ZT value of HfI2 reaches 1.12 at a temperature of 1200 K under p-type doping. Our work provides a physical picture of the effects of loosely bound electrons and their interaction with phonons and orbitals on thermoelectric properties, providing suggestions for further design of high-performance 2D thermoelectric materials.
1 Introduction
Thermoelectric materials are promising for the conversion between heat and electricity in a clean and quiet way leveraging the transport by inside electrons and phonons in solids with no mechanical part like pistons and turbines.1,2 The thermoelectric energy conversion efficiency is usually evaluated using the figure of merit, ZT (= S2σT/(κl + κe)), where S is the Seebeck coefficient, σ is the electrical conductivity, T is the temperature, κe is the electron thermal conductivity and κl is the lattice thermal conductivity.3,4 Ideal thermoelectric materials are usually narrow bandgap semiconductors with higher σ and low κ at the same time.5,6 Two-dimensional (2D) thermoelectric materials are particularly suitable for wearable devices due to their flexible monolayer structure, which will supply electric power for other carried equipment.7,8 However, the σ of 2D materials is usually lower compared with those of bulk structures because of the lower carrier mobility (μ) induced by a higher “density of scatterings”.9 The electron density of states (DOS) is higher for 2D materials (D(E) = constant) compared with the 3D case (D(E) ∝ E1/2).10,11 More phonons in a low energy range also increase the “density of scatterings”. Besides, the lattice thermal conductivity of 2D materials without interlayer interaction is usually higher than that of bulk materials.12,13 Thus, 2D semiconductors with high mobility and low thermal conductivity are favorable for thermoelectric applications.The high carrier mobility and high Seebeck coefficient, unfortunately, seldom simultaneously coexist in a common individual material as a high S generally requires a large band effective mass or a small band curvature, but a high mobility requires a small band effective mass.14 Recently, Zhang et al. found that several 2D structures including HfI2 and ZrI2 with a narrow bandgap exhibit a carrier mobility greater than 4000 cm2 V−1 s−1 (the mobility of bulk Silicon is around 1400 cm2 V−1 s−1).15 For HfI2 and ZrI2 with a MoS2-like structure (2H phase), there are excess electrons by checking the oxidation states (Hf and Zr: +4, I: −1) and these electrons are neither close to metal nor to halogen atoms but are distributed at the geometric center of hexagons.16 Such a new type of 2D material with loosely bound electrons is also named electrene.17,18 The interstitial electrons in the HfI2-type structures undergo a weak lattice perturbation, resulting in a significantly high hole mobility. In addition, these interstitial electrons behave like quantum dots, of which the electron DOS should exhibit a sharp peak.19 The Seebeck coefficient is relatively high because of the large energy derivative of the DOS according to the formula of the Seebeck coefficient from the Boltzmann transport equation (BTE).20
The higher lattice thermal conductivity of 2D materials is another shortcoming for achieving high thermoelectric energy conversion efficiency. The reported κl of another 2D electrene, ZrI2, with only three-phonon (3ph) interactions is around 20.3 W m−1 K−1 at room temperature.21 The large atomic weight of Hf in the HfI2 structure will ensure a much lower lattice thermal conductivity compared with that of ZrI2. Besides, the interstitial electrons also affect the phonon transport. The electron–phonon scattering decreases κl in structures like silicene and phosphorene.22 Furthermore, Kim et al. reported that the cage structure 12CaO·7Al2O3, a zero-dimensional (0D) electride with anionic electrons in the cage center, exhibits the characteristic of phonon glass and electron crystal (PGEC).23 The concept of PGEC is a well-known strategy for the design of high-performance thermoelectric materials due to the coexistence of high σ and low κl.24 2D HfI2 with localized interstitial electrons is also a 0D electride according to the definition.25 Overall, the 2D electrene, HfI2, may have high S, σ and low κl, favorable for the TE applications in flexible nanodevices. Currently, the electrene HfI2 has not been synthesized experimentally. But the electride structures like Ca2N and Y2C are synthesized and remain stable under the atmosphere of inert gases.26,27 The 2D structures like black phosphorene are also synthesized and kept stably under the protection of inert BN in experiments.28 Theoretical investigations on the thermoelectric properties will motivate experimental researchers to prepare electrene samples and examine their performance.
Here, we studied the thermoelectric properties of a 2D HfI2 structure with fully considering the effects of loosely bound electrons, spin-orbital interaction (SOI), and electron–phonon interaction (EPI). Our calculated results show that the p-type Seebeck coefficient is relatively high compared with those of some other high mobility 2D materials due to a high DOS peak at the valence band. The spin splitting induced by the SOI slightly decreases the bandgap and increases the carrier relaxation time. The maximum hole relaxation time reaches 0.7 ps, significantly higher than that of electrons due to the weaker lattice perturbation on charge states of the valence band maximum (VBM). The p-type σ is also higher than the n-type value consistent with the higher hole relaxation time. The phonon relaxation time contributed by the electron–phonon scattering under electron doping is even smaller than that of the three-phonon scattering in a low phonon frequency range. As a result, κl decreases from 7.80 to 6.58 W m−1 K−1 at an electron doping concentration of 1014 cm−2. Our investigation helps to gain a better understanding about the effect of interstitial electrons on the thermoelectric properties of this 2D electrene system.
2 Computational methodology
We implemented the calculations based on density functional theory (DFT) to obtain the relaxed geometric structure and the electron band structure using the Quantum Espresso (QE) package.29 The Perdew–Burke–Ernzerhof (PBE) functional is adopted to approximate the exchange–correlation of electrons.30 The behavior of core electrons is approximated using norm-conserving pseudopotentials.31 The spin-orbital interaction needs to be considered for the structures with heavy elements to obtain a more accurate electronic band structure.32,33 We utilized the Heyd–Scuseria–Ernzerhof (HSE06) hybrid functional,34 together with the SOI to calculate the electron band structure. The calculations of electron localization function and partial charge density are carried out using the Vienna ab initio simulation package (VASP).35 The phonon properties are calculated based on the density functional perturbation theory (DFPT)36 implemented using the ph.x code in the QE package.To accurately evaluate the thermoelectric properties of the electrene structure, we need to calculate the carrier relaxation time from EPI. The electron and phonon transports are coupled due to the EPI, and the relaxation times of electrons (τe) and phonons (τphλ) obtained from the EPI provide an effective way to decouple the electron and phonon transport behavior.37,38 The τe results from the EPI are significantly different from the constant one calculated based on deformation potential theory because τe is not a constant value but varies with the chemical potential.39 The investigation of the EPI for the 2D HfI2 structures will contribute to providing more accurate τe and τphλ results, thereby revealing the effect of anionic electrons on the thermoelectric transport behavior. The EPI is investigated utilizing the electron–phonon Wannier (EPW) method based on the calculated electron and phonon properties.40 The Fröhlich interaction is included to obtain a more accurate electron–phonon interaction and carrier relaxation time.41 Then, the electrical conductivity, Seebeck coefficient, and electron thermal conductivity are calculated by solving the electron BTE with the BoltzTraP2 code42 using the electron relaxation time obtained from EPW. The phonon BTE is solved to obtain the lattice thermal conductivity utilizing the ShengBTE code.43 The detailed parameters like cut-off energy and the k-point mesh are listed in the ESI.† In addition, the lattice thermal conductivity under the effect of EPI is evaluated by the following equation using the phonon group velocity (v), τphλ and frequencies (ω):
 | (1) |
 | (2) |
τ 3ph λ and τel–phλ are obtained from the output of ShengBTE and EPW, respectively.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Electron and phonon properties
We firstly evaluated the structural stability by checking the phonon band structure and lattice vibration in the ab initio molecular dynamics (AIMD) simulation process. There are no imaginary phonon frequencies inside the phonon band structure as shown in Fig. 1a, indicating that the atoms in 2D HfI2 are in the lowest positions of the potential energy surface. The highest phonon frequency is only 185 cm−1 (5.55 THz) because of the large atomic weight of the Hf and I elements. There is a small frequency gap between the acoustic and optical phonons, which will not strongly block the three-phonon interaction between these phonon modes. So, the four-phonon interaction will not influence the phonon transport significantly. Both the low maximum phonon frequency and small frequency gap should lead to a low κl. 2D HfI2 is still stable at a temperature of 1200 K as the energy curve does not diverge after 8000 fs in AIMD simulations and the structure does not collapse as shown in Fig. 1b–d. Hence, the 2D HfI2 structure should exist stably if synthesized successfully in the laboratory. The high temperature stability enables HfI2 to work in a high temperature environment.The electronic band structures are the basis for further investigation of the electron transport properties. We calculate the electron and phonon properties based on the optimized monolayer structure with a lattice parameter of 3.77 Å. The bandgap reaches 0.77 eV when calculating with the PBE functional as shown in Fig. 2a. The DOS peak of the valence band around −1 eV is quite sharp as shown in Fig. 2b, which enhances the imbalance of DOS below and above the Fermi level under p-type doping. Then, the p-type Seebeck coefficient will be relatively large compared with those of other structures with small effective mass and small energy derivative of DOS near the band edges. The DOS near the CBM also changes rapidly with energy (large slope), indicating a high n-type Seebeck coefficient. The SOI leads to the splitting of spin degenerate bands near the VBM and the conduction band minimum (CBM), then the DOS at these band edges gets smaller. The bandgap value increases to 1.02 eV using the HSE06 functional together with SOI (HSE + SOI), close to the reported value.15 Such a bandgap value will meet the requirements of narrow-bandgap semiconductors for thermoelectric applications.
The electron localization function (ELF) and charge density help to visualize the electronic structure more clearly. There are electrons distributed at the geometric center of the hexagon as shown in the ELF results in Fig. 2c, which indicates that the electrene HfI2 is a 0D electride. The interstitial electrons are the intrinsic reasons for the sharp DOS peak near the VBM. The perturbation on the interstitial electrons from the lattice vibration is weaker compared with that on electrons close to the atoms due to the longer carrier–lattice distance. The VBM is occupied by the interstitial electrons as indicated by the decomposed charge density in Fig. 2d. Hence, the hole will transport much more easily, consistent with the large curvature of the highest valence band (small effective mass) and the reported high hole mobility results.15
3.2 Electron transport properties
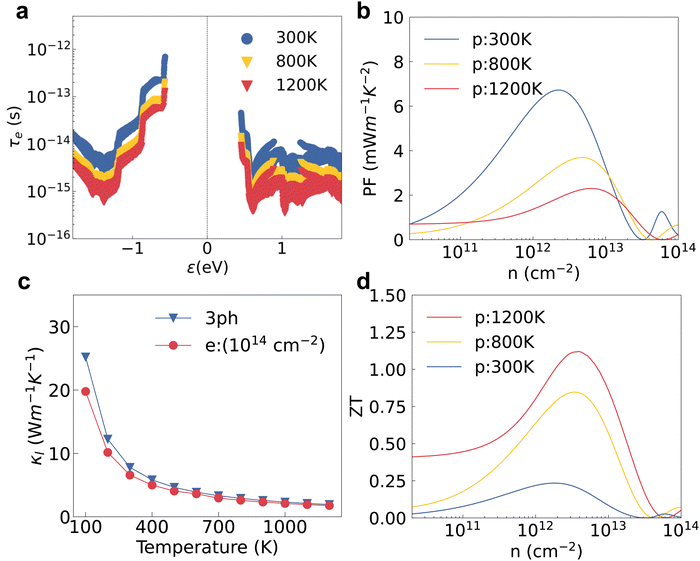
We studied the EPI and obtained the carrier relaxation time based on the calculated electron and phonon band structures, as shown in Fig. 3a. The Fröhlich interaction greatly decreases the hole relaxation time near the VBM as shown in Fig. S1a (ESI†), which indicates that the interstitial charge is quite sensitive to the macroscopic electric field induced by longitudinal optical (LO) phonons.41 Contrary to the holes, the relaxation time of electrons near the CBM is almost the same regardless of whether the Fröhlich interaction is included or not. τe near the VBM is reasonably higher than the value near the CBM because the interstitial charge near the VBM undergoes a weaker lattice perturbation. The τe near the VBM of HSE + SOI is almost the same compared with the value of PBE + SOI, although the electron bandgap calculated by the hybrid functional is larger (see Fig. 2). The hole mobility of 2D HfI2 reaches 4854 cm2 V−1 s−1 close to the published value (4782 cm2 V−1 s−1) as shown in Fig. S1b (ESI†), indicating that our calculations are reasonable.Then, the electron BTE is solved based on the energy dependent carrier relaxation time. The carrier concentration is evaluated based on the rigid band approximation, which means the doping does not change the electron band structure strongly.42 The transport properties at a smaller doping concentration are closer to the actual results. The transport properties for the 2H phase hexagonal HfI2 structure are isotropic in-plane. Hence, there are no direction dependent values. The Seebeck coefficient value under p-type doping is around 300 μV K−1 at a carrier concentration of 1012 cm−2 under the PBE functional as shown in Fig. 3b, which is higher than the values of some other high mobility 2D materials like BSb.44 The high S value under p-type doping is closely related to the VBM states occupied by interstitial electrons with a relatively sharp DOS peak. The S value under n-type doping is even higher due to the rapid change of DOS near the CBM. The SOI decreases the DOS near the VBM and the CBM due to the band splitting and the Seebeck coefficient value with SOI gets smaller than the value with only PBE as a result. The Seebeck coefficient under the hybrid functional is close to that under the PBE functional as the 0.77 eV bandgap of the PBE functional is already large enough to maintain the imbalance of charge carriers below and above the Fermi level. Unlike the Seebeck coefficient, the electrical conductivity is dominated by τe. The p-type σ is much higher than the n-type one as shown in Fig. 3c, consistent with the higher τe near the VBM. σ calculated by HSE + SOI is also close to that calculated by PBE + SOI due to similar τe. The n-type Seebeck coefficients and electrical conductivity exhibit similar trends, i.e. SOI leads to a smaller Seebeck coefficient and larger electrical conductivity as shown in Fig. S2a and b (ESI†).
The power factor under p-type doping is much higher than that under n-type dominated by the higher p-type σ as shown in Fig. 3d. The PF values with SOI are higher than those without SOI, consistent with the larger electron relaxation time and electrical conductivity calculated using PBE + SOI and HSE + SOI. We also notice that the carrier concentration with peak PF value gets larger as the electrical conductivity gets smaller. With the full consideration of the EPI, SOI and hybrid functional, the maximum PF of HfI2 reaches 6.72 mW m−1 K−2 under p-type doping at 300 K, while the corresponding n-type value is only 1.00 mW m−1 K−2 (Fig. S2c, ESI†). The carrier relaxation time has the greatest impact on the power factor values. The larger n-type Seebeck coefficient does not compensate for the small electrical conductivity which is mainly determined by the carrier relaxation time. The n-type PF value is much smaller than the p-type one as a result. We also calculated the electron band structure, ELF, carrier relaxation time, and p-type power factor of ZrI2 for comparison. The electron properties of ZrI2 are similar to those of HfI2. Only the hole relaxation time and p-type power factor are slightly higher than the values of HfI2 as shown in Fig. S3 (ESI†). The p-type PF value of HfI2 is obviously higher than the values of 2D transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDCs) with MoS2-like structures.45 For example, the experimentally measured PF of PtSe2 is only 0.245 mW m−1 K−2, highest among the reported PF values of TMDCs.46 The electron thermal conductivity in Fig. S2d and S4 (ESI†) is proportional to the electrical conductivity according to the Wiedemann–Franz law.47
3.3 Phonon transport properties
The lattice thermal conductivity is another key factor for the thermoelectric properties, and is mainly determined by the phonon properties. From the calculated intermediate properties, the group velocity (vg) of low-frequency phonons, or acoustic phonons, is obviously larger than that of high-frequency optical phonons, as shown in Fig. 4a. The Grüneisen parameters (γ) of low frequency phonons are quite large indicating a stronger lattice anharmonicity as shown in Fig. 4b. The lattice with a stronger anharmonicity usually exhibits lower thermal conductivity.48,49 The loosely bound charge as indicated in Fig. 2d will soften the phonon modes and enhance the phonon anharmonicity, thereby decreasing the κl. Overall, the acoustic phonons will have a more dominant effect on the lattice thermal conductivity.In the doped semiconductors, the phonons will interact with both other phonons and electrons. The phonon–phonon interaction is usually dominated by the three-phonon interaction (3ph) if the frequency gap between the acoustic and optical modes is not large enough.50 The lattice thermal conductivity of HfI2 reaches 7.80 W m−1 K−1 at 300 K if only the second and third order force constants are considered. The room temperature κl of HfI2 is reasonably lower than the value of ZrI2, 20.30 W m−1 K−1,21 due to the heavier atomic weight of the Hf element. Limited by the higher lattice thermal conductivity, the final figure of merit of ZrI2 will not be superior to HfI2 as the power factor values of these two structures are similar. We notice the phonon scattering rate of the electron–phonon interaction under electron doping is even larger than that of the 3ph interaction for the phonon modes with frequencies around 50 cm−1 as shown in Fig. 4c. The electron doping will scatter the phonons and enhance the phonon scattering rate due to the enhanced electron–phonon interaction by the high DOS near the CBM. Hence, the effect of EPI on the phonon transport should not be neglected especially under electron doping. The phonon scattering rate of 3ph and electron–phonon interaction is summed using the Matthiessen's rule. With the phonon frequencies, group velocity, and relaxation time from 3ph and EPI, we further calculate the lattice thermal conductivity with the contribution from EPI under electron doping. The electron doping with a concentration of 1014 cm−2 decreases the lattice thermal conductivity by 1.22 W m−1 K−1 at room temperature as shown in the cumulative κl in Fig. 4d. Contrary to the electron doping, the hole doping hardly affects the phonon scattering rate as shown in Fig. S5 (ESI†) as the interstitial electrons induce a weak hole–phonon interaction.
3.4 Thermoelectric figure of merit
We also investigated the temperature effect on the electron–phonon and phonon–phonon interaction to evaluate the ZT. The lattice perturbation on the electron becomes stronger at higher temperature; then the electron relaxation time calculated by HSE + SOI gradually decreases as a result (see Fig. 5a). The hole mobility also decreases with the increasing temperature in an exponential trend as shown in Fig. S6a (ESI†). Contrary to the decreasing electron relaxation time and mobility, the Seebeck coefficient increases at higher temperatures as shown in Fig. S6b (ESI†). The electrical conductivity and electron thermal conductivity are dominated by the carrier relaxation time, which also decrease with increasing temperatures as shown in Fig. S6c and d (ESI†). The peak value of the p-type power factor at 1200 K is the smallest compared with the values at lower temperatures, which is consistent with the variation of τe and σ as shown in Fig. 5b. Meanwhile, the lattice thermal conductivity decreases with increasing temperature as shown in Fig. 5c. The effect of EPI on phonon transport is less sensitive to the temperature, and the κl value with only the 3ph interaction is almost the same compared with the value with both the 3ph and e–ph interaction at temperatures higher than 900 K.The final thermoelectric figure of merit was evaluated with all the electron and phonon properties elaborated. Due to the decreasing of both the power factor and thermal conductivity, the ZT value increases with the increasing temperature. The decreasing κl under electron doping definitely does not contribute to improve the ZT under hole doping. The n-type ZT value at room temperature is only 0.041 at an electron concentration of 1013 cm−2 as shown in Fig. S7 (ESI†) even though κl is slightly smaller than the p-type one caused by the stronger EPI. The n-type Seebeck coefficient and electrical conductivity at 1200 K exhibit a strong bipolar effect and the peak ZT value is only 0.24 at an electron concentration of 1014 cm−2 (see Fig. S7d, ESI†). For p-type doping, we also calculate the bipolar thermal conductivity (κbi) based on the electron and hole electrical conductivity and Seebeck coefficient.51κbi is just slightly smaller than the p-type κe and the final p-type ZT at 1200 K decreases from 1.19 to 1.12 when the bipolar thermal process is included as shown in Fig. S8 (ESI†). The p-type ZT value at 1200 K is still higher than those at 800 K and 300 K as shown in Fig. 5d. The final ZT with a value of 1.12 at 1200 K is comparable to those of some 2D TMDCs like PtSe2.45 Although the calculated ZT value of PtSe2 reaches 0.84, the experimentally measured value is only 0.1 at room temperature.46,52 Since our calculation method is high-fidelity, we believe the experimental ZT value of HfI2 will be close to our calculated one. The ZT value can be further improved using several engineering approaches like doping, nanostructuring and interface engineering.53–56
4 Conclusion
In summary, we investigated the electron–phonon interaction and the thermoelectric properties of electrene HfI2. Its loosely bound interstitial electrons exhibit a high carrier relaxation time near the valence band maximum due to a weak lattice perturbation. The p-type Seebeck coefficient, although smaller than the n-type ones, is still relatively large due to the sharp DOS peak at the VBM occupied by the interstitial electrons. The hole mobility, p-type electrical conductivity, and power factor are much higher than those of n-type. The inclusion of the spin orbital interaction and hybrid functional provides an accurate prediction of the Seebeck coefficient and electrical conductivity. The electron doping with a concentration of 1014 cm−2 decreases the lattice thermal conductivity by 16%. The final thermoelectric figure of merit reaches 1.12 at 1200 K under p-type doping. Our work suggests that electrenes, a new class of 2D materials, will be promising thermoelectric materials due to their unique electronic and phonon properties.Data availability
The data supporting this article have been included as part of the ESI.†Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest to declare.Acknowledgements
The authors thank Dr Jiaren Yuan, Dr Xiwen Zhang, and Dr Yongchao Rao for their helpful discussion. Y. M. Z. gratefully acknowledges the support of China Scholarship Council (No. CSC202104910079). L. S. thanks the support from the Ministry of Education, Singapore, under its MOE Tier 1 (grant no. A-8001194-00-00). The computational work for this article was performed on resources of the National Supercomputing Centre, Singapore (https://www.nscc.sg) and the High Performance Computing of National University of Singapore (HPC@NUS IT).Notes and references
- F. J. DiSalvo, Science, 1999, 285, 703–706 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. Xie, L. Yin, Y. Yu, G. Peng, S. Song, P. Ying, S. Cai, Y. Sun, W. Shi, H. Wu, N. Qu, F. Guo, W. Cai, H. Wu, Q. Zhang, K. Nielsch, Z. Ren, Z. Liu and J. Sui, Science, 2023, 382, 921–928 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X.-L. Shi, J. Zou and Z.-G. Chen, Chem. Rev., 2020, 120, 7399–7515 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Zhou and L.-D. Zhao, Adv. Mater., 2017, 29, 1702676 CrossRef PubMed.
- M. Mukherjee, A. Srivastava and A. K. Singh, J. Mater. Chem. C, 2022, 10, 12524–12555 RSC.
- H. Shao, D. Ding, L. Zhang, C.-K. Dong and H. Zhang, Mater. Today Phys., 2022, 27, 100756 CrossRef CAS.
- K. Kanahashi, J. Pu and T. Takenobu, Adv. Energy Mater., 2020, 10, 1902842 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Huang, W. Li, C. Hu and X. Fan, J. Mater. Chem. C, 2023, 11, 9449–9464 RSC.
- L. Cheng, C. Zhang and Y. Liu, Phys. Rev. Lett., 2020, 125, 177701 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Li, T. Ding, D. K. Sang, M. Wu, J. Li, C. Wang, F. Liu, H. Zhang and H. Xie, J. Mater. Chem. C, 2020, 8, 4181–4191 RSC.
- W. Li, S. Poncé and F. Giustino, Nano Lett., 2019, 19, 1774–1781 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- G. Fugallo, A. Cepellotti, L. Paulatto, M. Lazzeri, N. Marzari and F. Mauri, Nano Lett., 2014, 14, 6109–6114 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. Lindsay and D. A. Broido, Phys. Rev. B: Condens. Matter Mater. Phys., 2012, 85, 035436 CrossRef.
- W. G. Zeier, A. Zevalkink, Z. M. Gibbs, G. Hautier, M. G. Kanatzidis and G. J. Snyder, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2016, 55, 6826–6841 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Zhang, R. Wang, H. Mishra and Y. Liu, Phys. Rev. Lett., 2023, 130, 087001 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. He, Y. Chen, Z. Wang, M. Yang, T. Yang, L. Shen, X. Xu, Y. Jiang, J. Chai, L. M. Wong, S. Wang, Y. P. Feng and J. Zhou, J. Mater. Chem. C, 2022, 10, 7674–7679 RSC.
- J. Zhou, Y. P. Feng and L. Shen, Phys. Rev. B, 2020, 102, 180407 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Zhou, L. Shen, M. Yang, H. Cheng, W. Kong and Y. P. Feng, Chem. Mat., 2019, 31, 1860–1868 CrossRef CAS.
- M. S. Dresselhaus, G. Chen, M. Y. Tang, R. G. Yang, H. Lee, D. Z. Wang, Z. F. Ren, J. P. Fleurial and P. Gogna, Adv. Mater., 2007, 19, 1043–1053 CrossRef CAS.
- R. Sarabia Riquelme, Doctoral Dissertation, University of Kentucky, 2020.
- J. Wen, J. Peng, B. Zhang and Z.-Y. Wang, Nanoscale, 2023, 15, 4397–4407 RSC.
- S.-Y. Yue, R. Yang and B. Liao, Phys. Rev. B, 2019, 100, 115408 CrossRef CAS.
- S. W. Kim, R. Tarumi, H. Iwasaki, H. Ohta, M. Hirano and H. Hosono, Phys. Rev. B: Condens. Matter Mater. Phys., 2009, 80, 075201 CrossRef.
- Z. Liu, J. Mao, S. Peng, B. Zhou, W. Gao, J. Sui, Y. Pei and Z. Ren, Mater. Today Phys., 2017, 2, 54–61 CrossRef.
- S. Kanno, T. Tada, T. Utsumi, K. Nakamura and H. Hosono, J. Phys. Chem. Lett., 2021, 12, 12020–12025 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. L. Druffel, K. L. Kuntz, A. H. Woomer, F. M. Alcorn, J. Hu, C. L. Donley and S. C. Warren, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2016, 138, 16089–16094 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. Lee, S. W. Kim, Y. Toda, S. Matsuishi and H. Hosono, Nature, 2013, 494, 336–340 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. C. Dhanabalan, J. S. Ponraj, Z. Guo, S. Li, Q. Bao and H. Zhang, Adv. Sci., 2017, 4, 1600305 CrossRef PubMed.
- P. Giannozzi, O. Andreussi and T. Brumme, et al. , J. Phys.: Condens. Matter, 2017, 29, 465901 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. P. Perdew, K. Burke and M. Ernzerhof, Phys. Rev. Lett., 1996, 77, 3865–3868 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. R. Hamann, Phys. Rev. B: Condens. Matter Mater. Phys., 2013, 88, 085117 CrossRef.
- J. Li, Q. Yao, L. Wu, Z. Hu, B. Gao, X. Wan and Q. Liu, Nat. Commun., 2022, 13, 919 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Yuan, Y. Cai, L. Shen, Y. Xiao, J.-C. Ren, A. Wang, Y. P. Feng and X. Yan, Nano Energy, 2018, 52, 163–170 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Heyd, G. E. Scuseria and M. Ernzerhof, J. Chem. Phys., 2003, 118, 8207–8215 CrossRef CAS.
- G. Kresse and J. Furthmüller, Phys. Rev. B: Condens. Matter Mater. Phys., 1996, 54, 11169 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Baroni, S. de Gironcoli, A. Dal Corso and P. Giannozzi, Rev. Mod. Phys., 2001, 73, 515–562 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Zhou, B. Liao and G. Chen, Semicond. Sci. Technol., 2016, 31, 043001 CrossRef.
- Z. Bai, D. He, S. Fu, Q. Miao, S. Liu, M. Huang, K. Zhao, Y. Wang and X. Zhang, Nano Sel., 2022, 3, 1112–1122 CrossRef CAS.
- G. Samsonidze and B. Kozinsky, Adv. Energy Mater., 2018, 8, 1800246 CrossRef.
- S. Poncé, E. R. Margine, C. Verdi and F. Giustino, Comput. Phys. Commun., 2016, 209, 116–133 CrossRef.
- C. Verdi and F. Giustino, Phys. Rev. Lett., 2015, 115, 176401 CrossRef PubMed.
- G. K. H. Madsen, J. Carrete and M. J. Verstraete, Comput. Phys. Commun., 2018, 231, 140–145 CrossRef CAS.
- W. Li, J. Carrete, N. A. Katcho and N. Mingo, Comput. Phys. Commun., 2014, 185, 1747–1758 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Ahmadi, M. Raeisi, L. Eslami and A. Rajabpour, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2021, 125, 14525–14537 CrossRef CAS.
- R. Rani and M. M. Sinha, Phys. Scr., 2024, 99, 032002 CrossRef.
- T.-Y. Su, T.-H. Wang and D. P. Wong, et al. , Chem. Mater., 2021, 33, 3490–3498 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Yadav, P. C. Deshmukh, K. Roberts, N. M. Jisrawi and S. R. Valluri, J. Phys. Commun., 2019, 3, 105001 CrossRef CAS.
- G. Qin, X. Zhang, S.-Y. Yue, Z. Qin, H. Wang, Y. Han and M. Hu, Phys. Rev. B, 2016, 94, 165445 CrossRef.
- F. Duan, C. Shen, H. Zhang and G. Qin, Phys. Rev. B, 2022, 105, 125406 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Qian, J. Zhou and G. Chen, Nat. Mater., 2021, 20, 1188–1202 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J.-H. Bahk and A. Shakouri, Appl. Phys. Lett., 2014, 105, 052106 CrossRef.
- J. Zhang, Y. Xie, Y. Hu and H. Shao, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2020, 532, 147387 CrossRef CAS.
- G. Wang, F. Meng, Y. Chen, A. Lotnyk and X. Shen, Adv. Sci., 2024, 11, 2308056 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Guo, Q. Ma, K. Luo, W. Qiu, H. Chen, P. Qian, Y. Deng, X. Wu, L. Yang and J. Tang, Ceram. Int., 2024, 50(9), 15209–15217 CrossRef CAS.
- V. C. S. Theja, V. Karthikeyan, D. S. Assi, H. Huang, V. Kannan, Y. Chen, C.-H. Shek and V. A. L. Roy, Adv. Mater. Technol., 2024, 2301722 CrossRef.
- J. Kim, W. Shim and W. Lee, J. Mater. Chem. C, 2015, 3, 11999–12013 RSC.
Footnote |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available. See DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/d4tc01927j |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2024 |