Open Access Article
Open Access Article“Visualizing” the partially reversible conversion of gold nanoclusters via the Au23(S-c-C6H11)17 intermediate†
Saniya
Gratious
 a,
Afreen‡
b,
Eti
Mahal‡
a,
Afreen‡
b,
Eti
Mahal‡
 c,
Jibin
Thomas
c,
Jibin
Thomas
 a,
Shubhadeep
Saha
a,
Akhil S.
Nair
a,
Shubhadeep
Saha
a,
Akhil S.
Nair
 c,
K. V.
Adarsh
b,
Biswarup
Pathak
c,
K. V.
Adarsh
b,
Biswarup
Pathak
 c and
Sukhendu
Mandal
c and
Sukhendu
Mandal
 *a
*a
aSchool of Chemistry, Indian Institute of Science Education and Research Thiruvananthapuram, Kerala 695551, India. E-mail: sukhendu@iisertvm.ac.in
bDepartment of Physics, Indian Institute of Science Education and Research Bhopal, Madhya Pradesh 462066, India
cDepartment of Chemistry, Indian Institute of Technology, Indore, Madhya Pradesh 453552, India
First published on 16th May 2024
Abstract
Transformation chemistry of atomically precise metal nanoclusters has emerged as a novel strategy for fundamental research on the structure–property correlations of nanomaterials. However, a thorough understanding of the transformation mechanism is indeed necessary to understand the structural growth patterns and corresponding property evolutions in nanoclusters. Herein, we present the ligand-exchange-induced transformation of the [Au23(SR)16]− (8e−) nanocluster to the [Au25(SR′)18]− (8e−) nanocluster, through the Au23(SR)17 (6e−) intermediate species. Identification of this key intermediate through a partially reversible transformation helped in a detailed investigation into the transformation mechanism with atomic precision. Moreover, photophysical studies carried out on this Au23(SR)17 species, which only differs by a single ligand from that of the [Au23(SR)16]− nanocluster reveal the property evolutions at the slightest change in the nanocluster structure.
Introduction
Ligand-protected gold nanoclusters (Au NCs), with their definite structure and molecule-like properties, have attracted extensive research over the last few decades, which has greatly enriched our fundamental understanding of nanomaterials.1–4 The versatility of these atomically precise NCs, such as their size, self-assembly behavior, physicochemical properties, stability, etc., can be tuned immensely by tailoring the surface ligands.5–8 Of ligands such as alkynyls, phosphines and thiolates, thiol-based molecules serve as stronger surface-protecting ligands for Au NCs owing to the larger orbital overlap of Au with S as well as their soft–soft interaction.9 Several reports on thiolate-protected Au NCs show that ligand engineering enables the fabrication of these nanomaterials for tremendous applications like bio-imaging, drug delivery, sensing, catalysis, etc.10–13Ligand-exchange-induced size/structure transformation, abbreviated as LEIST, stands as an accomplished strategy to engineer the surface protecting ligands on Au NCs and to unleash the transformation mechanism for a deeper understanding of the process.14–17 Furthermore, this method of NC synthesis gives rise to the most stable species with high molecular purity, as opposed to the bottom-up synthesis of Au NCs, which is just about “trial and error”.18–23 Despite these achievements, nanochemists are still unable to design and predict LEIST products and comprehend the detailed transformation mechanism, which precludes us from tailoring these nanomaterials for desired applications. Furthermore, a complete correlation of the optical/electronic properties with the NC structure remains only vaguely understood. To attain this atomic-level manipulation of NCs, detailed studies into the mechanistic insights of NC transformations should be carried out. Identifying the key intermediates and understanding their role in the ligand exchange-induced structural transformation of NCs allows us to comprehend the structural growth patterns and corresponding property evolutions and thereby, “visualize” the NC transformations. However, the high reactivity and labile nature of the transformation intermediates make their isolation and characterization far-fetched and reports on the same are seldom found.24–27 Additionally, understanding the intriguing ligand effects on the atomically precise metal NCs has always been at the forefront of comprehending the structure–property correlation in these nanomaterials. Even the slightest change in the surface protecting motifs has shown to cause radical changes in the electronic structure and thereby the core-to-shell electronic coupling in metal NCs. Jin et al. have shown the effect of atomic structure isomerism on the excited-state dynamics of two same-sized Au38(SC2H4Ph)24 NCs.28 Moreover, the role of core–shell electron–phonon interactions on the optical properties of NCs has been investigated by conducting ultrafast transient absorption studies on Au25(SR)18 NCs.29–33 In another study, the evolution of excited-state dynamics in the Au28+8n (n = 0–3) series of NCs was probed to understand the core–shell relaxations in these periodic FCC NCs.34 Nevertheless, more studies revealing the effect of protecting ligands and how these affect the transformation, stability, and photophysical properties of atomically precise NCs need to be carried out to achieve precise perceptions and intuitive designs for applications in optics, solar energy harvesting, thermoelectric applications, catalysis, etc.
Herein, we have employed the LEIST methodology to surface engineer the [Au25(SR)18]− NCs through the structural transformation of [Au23(S-c-C6H11)16]− NCs by changing the electronegativity of the substituents of incoming thiol ligands. In our previous work, we have shown that electron-donating substituents on aromatic thiols produced Au28(SR)20 and Au36(SR)24 as products from the [Au23(S-c-C6H11)16]− precursor.35 We tracked this transformation of [Au23(S-c-C6H11)16]− to [Au25(SR)18]− NCs through time-dependent UV-vis absorption and MALDI-MS measurements and identified the key intermediate, that is, Au23(S-c-C6H11)17. The isolation of the Au23(S-c-C6H11)17 intermediate was accomplished through a partial reverse LEIST strategy and was successfully characterized using various techniques. The precursor [Au23(S-c-C6H11)16]− NC along with the Au23(S-c-C6H11)17 intermediate serve as ideal candidates to study the structure–property correlations in atomically precise metal NCs at the slightest change in their structure. The excited-state evolution dynamics of these surface-modulated product NCs as well as the intermediate species were probed using ultrafast transient absorption studies to understand the evolution of core–shell electron–phonon interactions. These studies on the series of [Au25(SR)18]− NCs with minute changes in their surface functionality will enable us to fathom the structure-property correlation in atomically precise NCs in a superior way.
Results and discussion
The [Au23(S-c-C6H11)16]− (hereafter, Au23) NC has been synthesized and characterized by following the reported procedure.36 The characteristic peak at 570 nm and the shoulder peak at 460 nm in the UV-vis absorption spectrum were matched with the reported spectrum (Fig. S1a†). The MALDI-MS data showed a single peak at m/z = 6373.13, corresponding to the molecular ion peak of the [Au23(S-c-C6H11)16]− NCs (Fig. S1b†). The transformation reaction was carried out on a 5 mg per mL DCM solution of molecularly pure Au23 NC and 2 mmol of p-fluorobenzenethiol (FBT) at 40 °C under ambient conditions. The same reaction was carried out at 20 °C to slow down the reaction kinetics and track the transformation mechanism. Aliquots were taken at regular time intervals from the reaction mixture to monitor the transformation using UV-vis absorption spectroscopy and MALDI-MS spectrometry. Fig. 1 shows the time-dependent UV-vis absorption spectra collected at various time intervals during the reaction. The Au23 NC shows a prominent absorption peak at 570 nm, whereas in the presence of FBT, the intensity of the peak gradually reduced and new absorption features started arising at 425 and 690 nm in less than 10 min. As time proceeded, the 570 nm peak completely disappeared, indicating the complete transformation of the Au23 NC. The transformation reaction was continued for 4 h, during which the absorption spectra showed prominent features at 425, 465, 695, and 795 nm. These features in the UV-vis absorption spectra resembled the characteristic absorption peaks of previously reported [Au25(SR)18]− NCs.37–39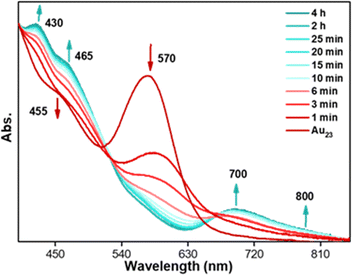 | ||
| Fig. 1 Time-dependent UV-vis absorption spectra of the aliquots taken during the transformation reaction of Au23 NCs with excess XBT, X = F, Cl, and Br. | ||
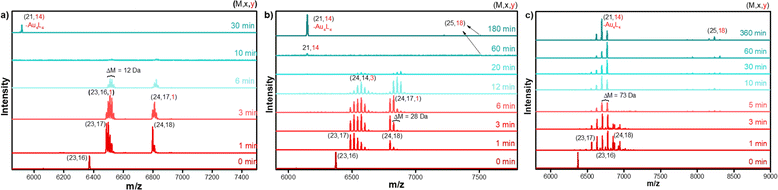
Time-dependent MALDI-MS confirmed the transformation reaction and the formation of [Au25(FBT)18]− NC. The spectral evolution of the reaction mixture during the transformation reaction is shown in Fig. 2a. At 0 min, a single peak at m/z = 6373 was observed which corresponds to the intact [Au23(S-c-C6H11)16]− NC, whereas after 1 min of addition of excess FBT, two peaks evolve at m/z = 6487 and 6798, which correspond to Au23(S-c-C6H11)17 and Au24(S-c-C6H11)18 species, respectively. Each of these species undergoes subsequent ligand-exchange with incoming FBT ligands to give rise to two sets of peaks which belong to Au23(S-c-C6H11)17−x(FBT)x and Au24(S-c-C6H11)18−x(FBT)x. This set of peaks with an equal spacing of 12 Da corresponds to the difference between the incoming FBT (MW = 128 Da) and the existing cyclohexane thiol (MW = 116 Da). As time proceeds, both these sets of peaks shift towards the right, indicating more cyclohexanethiol being replaced by the incoming FBT ligands. After 15 min of the LEIST reaction, both these peaks gradually reduced in intensity and an intense peak at m/z = 5916 corresponding to Au21(FBT)14 and a less intense peak at m/z = 7212 corresponding to Au25(FBT)18 appeared, indicating the formation of Au25(FBT)18 NC. The obtained product was washed several times with methanol to remove excess thiol and purified using Size Exclusion Chromatography (SEC) for further characterization. The overall yield of the obtained Au25(FBT)18 NC was determined to be close to ∼90%. Similarly, LEIST reactions were carried out on Au23 NC using p-chlorobenzenethiol (CBT) and p-bromobenzenethiol (BBT) as incoming ligands. Similar features were observed in the time-dependent UV-vis and MALDI-MS measurements for the LEIST using the CBT ligand (Fig. 2b), whereas, the LEIST using BBT showed the overlap of the Au23(SR)17 and Au24(SR)18 set of peaks from the very beginning of the reaction (Fig. 2c). Furthermore, in the case of BBT, the final product formation took a longer time compared to the FBT and CBT ligands.
The as-obtained Au25(SR)18 NCs were characterized using UV-vis absorption spectroscopy (Fig. S2†), electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (ESI-MS) (Fig. S3†) and single crystal X-ray diffraction (SCXRD) (Fig. 3). The UV-vis absorption spectrum showed intense absorption around 345, 430, 470, 700, and a shoulder band around 800 nm, which are the characteristic features of [Au25(SR)18]− NC. The negative-ion mode ESI mass spectra showed peaks at m/z = 7212.14, 7508.37, and 8308.96 with an isotopic pattern spacing of 1 Da, which corresponds to the molecular ion peaks of [Au25(FBT)18]−, [Au25(CBT)18]−, and [Au25(BBT)18]− NCs, respectively (Fig. S3†). The positive-ion mode ESI-MS spectra showed an intense peak at m/z = 466.57, corresponding to the mass of tetraoctyl ammonium (TOA+) ion, which serves as the stabilizing counter cation for [Au25(XBT)18]−, X = F, Cl, and Br NCs (Fig. S4†). We have obtained dark-red block-like single crystals of [Au25(FBT)18]− NCs by layering the DCM solution of the NC with hexane solvent (Fig. S5a†). The SCXRD analysis revealed a centered Au13 icosahedron core for the [Au25(FBT)18]− NC with six dimeric staple motifs arranged in three mutually perpendicular 2-fold axes of the icosahedron, as shown in Fig. 3 (Table S1†). The Au–Au bond distances in the icosahedral core range from 2.75–3.06 Å, while the Aucore–S and Aushell–S ranged from 2.38–2.42 Å and 2.24–2.66 Å, respectively (Table S2†). The total structure (Fig. S5b†) was in good agreement with the formula obtained from the ESI-MS spectrum and matched with previously reported [Au25(SR)18]− NCs.40–48 We optimized the structure and calculated the density of states using the single crystal data (Fig. S6, S7 and Table S3†).
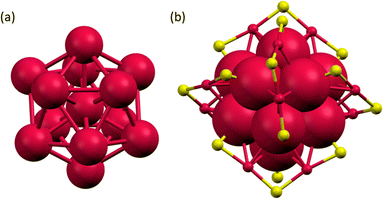 | ||
| Fig. 3 (a) The centered Au13 icosahedron core and (b) Au25S18 framework of the [Au25(FBT)18]− NC. Colour code: red, Au; yellow, S. | ||
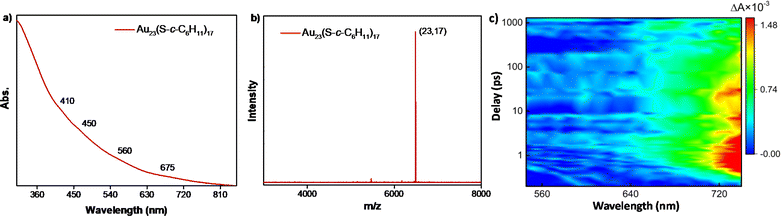
To attain a deeper understanding of the mechanical insights of the transformation, several attempts were made to isolate the key intermediate, Au23(S-c-C6H11)17 of the conversion reaction. However, the intermediate was found to be extremely reactive in the presence of an excess amount of incoming halobenzenethiols. However, this Au23(S-c-C6H11)17 was formed with high molecular purity and stability through the partially reversible transformation of the [Au25(XBT)18]− NCs in the presence of excess cyclohexanethiol at 55 °C in less than 2 h. This species was purified and characterized using UV-vis spectroscopy and MALDI-MS, where the molecular ion peak was obtained at m/z = 6489 (Fig. 4a and b). The UV-vis spectrum showed drastic changes in the absorption features as compared to the parent NC, even though they differed only by an extra cyclohexanethiolate ligand. The [Au23(S-c-C6H11)16]− NC shows a prominent peak at 570 nm; whereas, the Au23(S-c-C6H11)17 intermediate showed broad absorption features with small peaks at around 410, 450, 560, and 675 nm.
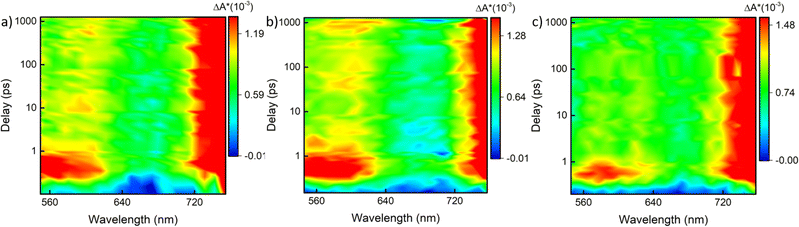
Correlating the atomic structure and optical properties of NCs is essential for their manipulation for various applications in optics and light harvesting. Herein, the identification of the Au23(S-c-C6H11)17 intermediate, which differs only by a ligand from the parent NC – [Au23(S-c-C6H11)16]−, paved the way towards elucidating the structure–property correlation with the slightest change in the structure. Moreover, the transformation reaction yielded a series of surface modulated [Au25(XBT)18]− NCs with minute changes in their carbon tails substituents, which serve as ideal candidates to understand how tailoring the surface functionalities affect the photophysics of these structures. In this regard, we have carried out femtosecond measurements on the parent [Au23(S-c-C6H11)16]− NC, the Au23(S-c-C6H11)17 intermediate and the series of [Au25(XBT)18]− NCs. This also helped us understand how the excited-state dynamics evolve throughout the transformation. All these NCs were dissolved in DCM and then excited with a 400 nm pump with a fluence of 490 nJ cm−2 and a white light probe (460–760 nm) was used to measure the absorption in the excited state. The transient absorption (ΔA = Aexcited − Aground difference in absorbance in the excited and ground states) was measured at different pump-probe delay times. The contour plot of transient absorption and selected cross sections at different pump-probe delay times for [Au23(S-c-C6H11)16]− revealed a broad featureless transient photobleaching feature (550–630 nm) of short duration, indicative of ground-state bleaching and an intense photo-induced absorption (PIA) feature from 650–720 nm, originating from excited-state absorption (Fig. S8a and b†). The photo bleaching coincided with the wavelengths observed in ground-state optical absorption measurements, confirming its association with ground-state bleaching. The PIA is attributed to the excited-state absorption since we have not seen any ground-state optical absorption in these wavelengths. Fig. 4c shows the ultrafast transient absorption studies conducted on the Au23(S-c-C6H11)17 species to understand the evolution of excited-state dynamics. As opposed to the ground-state absorption features, the excited-state absorption showed similar features to that of the parent [Au23(S-c-C6H11)16]− NC (Fig. S8c, d and S9†). Moving on to the [Au25(XBT)18]− NCs (Fig. 5), they showed a dramatic change compared to [Au23(S-c-C6H11)16]− NCs. Fig. 5a shows the transient absorption feature of [Au25(FBT)18]− NC, where the photo bleaching is entirely suppressed and replaced by two robust PIA features centered around 560 and 720 nm, indicating a distinctive response to excited state absorption. We repeated similar measurements on [Au25(CBT)18]− and [Au25(BBT)18]− NCs (Fig. 5b and c). Similar observations were acquired on these Au25 NCs, emphasizing the universality of these features. The photo bleaching is completely suppressed and we could observe two intense PIA features centered around 560 and 720 nm linked to the excited-state absorption. However, [Au25(CBT)18]− NC exhibits the highest PIA amplitude compared to the Au25 NCs protected by FBT and BBT, indicative of a substantial excited-state transition cross-section (Fig. S10†). These dramatic changes observed in the transient absorption features of [Au25(XBT)18]−, X = F, Cl, and Br, NCs point towards tailoring the optical properties of Au NCs for potential applications. Upon detailed examination of the temporal dynamics depicted in Fig. S11a and b†, it becomes evident that in [Au25(FBT)18]− (Fig. S11a†), the PIA at 560 nm attains its maximum within 1 ps, experiences a slight decay, and then stabilizes. This can be attributed to the inter-conversion (Sn to S1), vibrational relaxation, intersystem crossing, and core–shell charge transfer.49 However, the PIA at approximately 750 nm is not decaying within the limited instrumental time window (Fig. S11b†). It has not shown any signature of decay in [Au25(CBT)18]− and [Au25(BBT)18]− either. Conversely, in [Au23(S-c-C6H11)16]−, the PIA reaches its peak around 1 ps and subsequently starts decaying. It completely vanishes within 1 ns and is finally replaced by bleaching. Therefore, we performed the nanosecond flash photolysis to analyze the complete decay kinetics by exciting the [Au25(XBT)18]− NCs with a 532 nm pulsed laser. Fig. S12a† shows the decay kinetics of the first PIA at 560 nm and Fig. S12b† shows the decay kinetics of the second PIA at 750 nm wavelength of the [Au25(FBT)18]− NC. All the [Au25(XBT)18]− NCs show single exponential decay of a few hundred nanoseconds, corresponding to the ground-state relaxation of the electrons (Fig. S12c–f†). Here, at 560 nm, the [Au25(BBT)18]− (235 ± 5 ns) has the most extended lifetime, followed by [Au25(CBT)18]− (169 ± 20 ns), and [Au25(FBT)18]− (122 ± 6 ns) has the shortest lifetime. Decay kinetics at 750 nm show that again [Au25(BBT)18]− (273 ± 7 ns) has the most extended lifetime, followed by [Au25(CBT)18]− (220 ± 13 ns), and [Au25(FBT)18]− (182 ± 9 ns) has the shortest lifetime. We observed that these lifetime trends associated with the PIA are just opposite to the trend of the electronegativity of the ligands (F > Cl > Br). Therefore, we can tune the ground-state relaxation of the system by changing the electronegativity of the carbon tail substituents of the thiolate ligands.
To gain further insights into the mechanistic pathway of the transformation, we performed the ligand-exchange reaction on the key intermediate, Au23(S-c-C6H11)17 (hereafter Au23(SCy)17) with BBT as the incoming ligand. Fig. S13a† shows the time-dependent MALDI-MS measurements carried out on aliquots taken out during the transformation reaction. A plausible transformation pathway (Scheme 1) has been proposed based on the mass spectrometric analysis and the DFT calculations as implemented in the VASP (Vienna Ab Initio Simulation Package) software (Table S4†).50 The calculated cohesive energy of the core (−2.69 eV) and shell-to-core binding energy (−3.20 eV) for the Au23(SCy)17 species indicate that its lower stability compared to the [Au23(SCy)16]− NC acts as the driving force for undergoing subsequent ligand-exchange reactions. As shown in Fig. S13a,† the initial MALDI spectrum taken at 0 min shows the molecular-ion peak corresponding to the Au23(SCy)17 intermediate species before the reaction, whereas the addition of BBT ligand to the Au23(SCy)17 solution initiated the ligand-exchange reaction on the intermediate causing the formation of several mixed ligand species, Au23(SCy)17−x(BBT)x, x ∼0–4. As time proceeds, one can see that more SCy ligands are being replaced by BBT and a set of peaks corresponding to Au23(SCy)17−x(BBT)x, x ∼2–6 were observed. This conclusion was supported by the DFT calculations, which showed the thermodynamic feasibility of the ligand-exchange on the Au23(SCy)17 species (Scheme 1a). Subsequent ligand-exchange with BBT and attachment of an Au(SCy)2 complex (sourced from the synthesis of the starting material Fig. S13b†)51 to the Au23(SCy)17−x(BBT)x, x ∼2–6 gave rise to the formation of Au24(SCy)18−x(BBT)x, x ∼16 species as observed in MS spectrum. Owing to the significant structural transformation involved, this step is energy-demanding (Scheme 1b). As the reaction moves further, another Au(SCy)2 unit attaches to give the Au24(SCy)18−x(BBT)x, x ∼16 mixed ligand species (Scheme 1c), which eventually undergoes complete ligand-exchange to give the [Au25(BBT)18]− NC (Scheme 1d). This was indicated by the presence of an intense peak corresponding to Au21(BBT)14, which is a stable fragment of the [Au25(BBT)18]− NC.52 This transformation from Au24 to Au25 is energetically feasible probably due to the exceptional stability of the highly symmetric [Au25(SR)18]− NC. Overall, it can be concluded that the transformation of [Au23(S-c-C6H11)16]− NC could be triggered by the presence of Au(I)-SR complexes, where the squeezed double layer of the [Au23(S-c-C6H11)16]− NC could weaken its electrostatic repulsion with the negatively-charged Au(I)-SR complex species, facilitating their collision followed by ligand-exchange and size conversion reactions.51
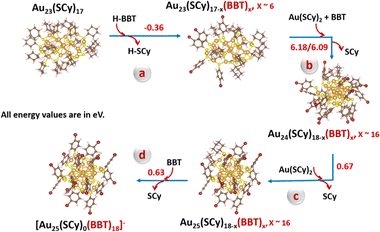 | ||
| Scheme 1 A proposed mechanism for the transformation of Au23(SCy)17 species to the [Au25(BBT)18]− NC. Colour code: golden yellow, Au; yellow, S; red, Br; brown, C and pink, H. | ||
Conclusions
In summary, detailed investigation into the mechanistic insights along with isolation of the key intermediate enabled “visualization” of the transformation of [Au23(S-c-C6H11)16]− NC to [Au25(XBT)18]− NCs (where, X = F, Cl, and Br). Meticulous investigation into the time-dependent UV-vis absorption and MALDI-MS studies carried out during the transformation of the parent NC as well as the intermediate Au23(S-c-C6H11)17 species helped in mapping out the mechanistic pathway with atomic precision. An elaborate study on the excited-state evolution dynamics of the transformation was carried out using ultrafast transient absorption studies conducted on the precursor and product NCs along with the intermediate. Moreover, this precise understanding of the transformation reaction will henceforth benefit us in manipulating NC structures and properties at an atomic level.Data availability
The ESI† contains experimental details, ESI-MS data and measurement details, theoretical calculation details, crystal structure parameters, selected bond lengths, theoretically optimized structures, density of states calculations, ultrafast transient spectroscopy data and parameters.Author contributions
S. G. performed the synthesis, characterization and data interpretation with assistance from J. T. and S. S. Afreen and A. K. V. conducted the ultrafast transient absorption measurements. E. M., A. S. N. and B. P. performed the theoretical calculations. S. M conceived the project, analysed the data and was involved in manuscript preparation. All authors were involved in discussion of results and manuscript writing.Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no competing interest.Acknowledgements
We thank Dr Prathap S. J, Dr Anish Kumar Das and Dr Noohul Alam for their help solving the single crystal structure. We acknowledge funding from the Science and Engineering Research Board (SERB) through the grant CRG/2022/000984.References
- R. Jin, C. Zeng, M. Zhou and Y. Chen, Chem. Rev., 2016, 116, 10346–10413 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- I. Chakraborty and T. Pradeep, Chem. Rev., 2017, 117, 8208–8271 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- Y. Du, H. Sheng, D. Astruc and M. Zhu, Chem. Rev., 2020, 120, 526–622 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- L. Liu and A. Corma, Chem. Rev., 2018, 118, 4981–5079 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- R. Jin, G. Li, S. Sharma, Y. Li and X. Du, Chem. Rev., 2021, 121, 567–648 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- X. Kang and M. Zhu, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2019, 48, 2422–2457 RSC
.
- J. Huang, L. Lin, D. Sun, H. Chen, D. Yang and Q. Li, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2015, 44, 6330–6374 RSC
.
- L. Tang, X. Kang, S. Wang and M. Zhu, Langmuir, 2019, 35, 12350–12355 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- N. Goswami, Q. Yao, T. Chen and J. Xie, Coord. Chem. Rev., 2016, 329, 1–15 CrossRef CAS
.
- H. Shen, G. Deng, S. Kaappa, T. Tan, Y. Han, S. Malola, S. Lin, B. K. Teo, H. Häkkinen and N. Zheng, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2019, 58, 17731–17735 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- S. Wang, L. Tang, B. Cai, Z. Yin, Y. Li, L. Xiong, X. Kang, J. Xuan, Y. Pei and M. Zhu, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2022, 144, 3787–3792 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- Y. Song, J. Zhong, S. Yang, S. Wang, T. Cao, J. Zhang, P. Li, D. Hu, Y. Pei and M. Zhu, Nanoscale, 2014, 6, 13977–13985 RSC
.
- H. Shen, Q. Wu, S. Malola, Y. Z. Han, Z. Xu, R. Qin, X. Tang, Y. B. Chen, B. K. Teo, H. Häkkinen and N. Zheng, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2022, 144, 10844–10853 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- X. Kang and M. Zhu, Chem. Mater., 2019, 31, 9939–9969 CrossRef CAS
.
- C. Zeng, Y. Chen, A. Das and R. Jin, J. Phys. Chem. Lett., 2015, 6, 2976–2986 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- A. Dass, T. C. Jones, S. Theivendran, L. Sementa and A. Fortunelli, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2017, 121, 14914–14919 CrossRef CAS
.
- M. P. Maman, A. S. Nair, H. Cheraparambil, B. Pathak and S. Mandal, J. Phys. Chem. Lett., 2020, 11, 1781–1788 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- C. Zeng, C. Liu, Y. Pei and R. Jin, ACS Nano, 2013, 7, 6138–6145 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- Z. Gan, J. Chen, J. Wang, C. Wang, M. B. Li, C. Yao, S. Zhuang, A. Xu, L. Li and Z. Wu, Nat. Commun., 2017, 8, 14739–14745 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- C. Zeng, T. Li, A. Das, N. L. Rosi and R. Jin, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2013, 135, 10011–10013 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- Y. Chen, C. Liu, Q. Tang, C. Zeng, T. Higaki, A. Das, D. E. Jiang, N. L. Rosi and R. Jin, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2016, 138, 1482–1485 CrossRef CAS
.
- S. Gratious, A. S. Nair, S. Mukherjee, N. Kachappilly, B. Pathak and S. Mandal, J. Phys. Chem. Lett., 2021, 12, 10987–10993 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- S. Gratious, S. Mukherjee and S. Mandal, J. Phys. Chem. Lett., 2022, 13, 9014–9027 CrossRef CAS
.
- Z. Luo, V. Nachammai, B. Zhang, N. Yan, D. T. Leong, D. Jiang and J. Xie, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2014, 136, 10577–10580 CrossRef CAS
.
- Q. Li, Y. Tan, B. Huang, S. Yang, J. Chai, X. Wang, Y. Pei and M. Zhu, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2023, 145, 15859–15868 CrossRef CAS
.
- X. Wei, H. Li, H. Li, Z. Zuo, F. Song, X. Kang and M. Zhu, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2023, 145, 13750–13757 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- M. Cui, Y. Shi, X. Ma, Q. Li, L. Chen, L. Zhang, J. Wu, H. Yu and M. Zhu, ACS Nano, 2024, 18, 6591–6599 CrossRef CAS
.
- M. Zhou, S. Tian, C. Zeng, M. Y. Sfeir, Z. Wu and R. Jin, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2017, 121, 10686–10693 CrossRef CAS
.
- T. D. Green and K. L. Knappenberger, Nanoscale, 2012, 4, 4111–4118 RSC
.
- H. Qian, M. Y. Sfeir and R. Jin, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2010, 114, 19935–19940 CrossRef CAS
.
- M. Zhou, H. Qian, M. Y. Sfeir, K. Nobusada and R. Jin, Nanoscale, 2016, 8, 7163–7171 RSC
.
- M. S. Devadas, J. Kim, E. Sinn, D. Lee, T. Goodson and G. Ramakrishna, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2010, 114, 22417–22423 CrossRef CAS
.
- M. S. Devadas, V. D. Thanthirige, S. Bairu, E. Sinn and G. Ramakrishna, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2013, 117, 23155–23161 CrossRef CAS
.
- M. Zhou, C. Zeng, M. Y. Sfeir, M. Cotlet, K. Iida, K. Nobusada and R. Jin, J. Phys. Chem. Lett., 2017, 8, 4023–4030 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- M. P. Maman, E. N. Nahan, K. G. Suresh, A. Das, A. S. Nair, B. Pathak and S. Mandal, Nanoscale, 2023, 15, 13102–13109 RSC
.
- A. Das, T. Li, K. Nobusada, C. Zeng, N. L. Rosi and R. Jin, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2013, 135, 18264–18267 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- J. F. Parker, J. E. F. Weaver, F. McCallum, C. A. Fields-Zinna and R. W. Murray, Langmuir, 2010, 26, 13650–13654 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- Z. Wu, J. Suhan and R. Jin, J. Mater. Chem., 2009, 19, 622–626 RSC
.
- X. Kang, H. Chong and M. Zhu, Nanoscale, 2018, 10, 10758–10834 RSC
.
- M. Zhu, C. M. Aikens, F. J. Hollander, G. C. Schatz and R. Jin, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2008, 130, 5883–5885 CrossRef CAS
.
- M. Waszkielewicz, J. Olesiak-Banska, C. Comby-Zerbino, F. Bertorelle, X. Dagany, A. K. Bansal, M. T. Sajjad, I. D. W. Samuel, Z. Sanader, M. Rozycka, M. Wojtas, K. Matczyszyn, V. Bonacic-Koutecky, R. Antoine, A. Ozyhar and M. Samoc, Nanoscale, 2018, 10, 11335–11341 RSC
.
- M. A. MacDonald, D. M. Chevrier, P. Zhang, H. Qian and R. Jin, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2011, 115, 15282–15287 CrossRef CAS
.
- Z. Luo, V. Nachammai, B. Zhang, N. Yan, D. T. Leong, D. E. Jiang and J. Xie, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2014, 136, 10577–10580 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- M. Agrachev, S. Antonello, T. Dainese, J. A. Gascón, F. Pan, K. Rissanen, M. Ruzzi, A. Venzo, A. Zoleo and F. Maran, Chem. Sci., 2016, 7, 6910–6918 RSC
.
- Y. Cao, V. Fung, Q. Yao, T. Chen, S. Zang, D. en Jiang and J. Xie, Nat. Commun., 2020, 11, 5498–5505 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- G. Li, H. Abroshan, C. Liu, S. Zhuo, Z. Li, Y. Xie, H. J. Kim, N. L. Rosi and R. Jin, ACS Nano, 2016, 10, 7998–8005 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- S. Wang, Y. Song, S. Jin, X. Liu, J. Zhang, Y. Pei, X. Meng, M. Chen, P. Li and M. Zhu, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2015, 137, 4018–4021 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- Z. Liu, Y. Li, E. Kahng, S. Xue, X. Du, S. Li and R. Jin, ACS Nano, 2022, 16, 18448–18458 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- S. Kolay, S. Maity, S. Chakraborty, S. Ghosh and A. Patra, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2023, 127, 3769–3777 CrossRef CAS
.
- G. Kresse and J. Hafner, Phys. Rev. B: Condens. Matter Mater. Phys., 1994, 49, 14251–14269 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- Q. Yao, V. Fung, C. Sun, S. Huang, T. Chen, D. Jiang, J. Y. Lee and J. Xie, Nat. Commun., 2018, 9, 1979–1990 CrossRef PubMed
.
- Y. Lu and W. Chen, Anal. Chem., 2015, 87, 10659–10667 CrossRef CAS
.
Footnotes |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available. CCDC 2334107. For ESI and crystallographic data in CIF or other electronic format see DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/d4sc01225a |
| ‡ These authors contributed equally to this work. |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2024 |