Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleCreative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported Licence
Zinc metal complexes synthesized by a green method as a new approach to alter the structural and optical characteristics of PVA: new field for polymer composite fabrication with controlled optical band gap
Dana S. Muhammada,
Dara M. Aziz b and
Shujahadeen B. Aziz
b and
Shujahadeen B. Aziz *cd
*cd
aDepartment of Physics, College of Education, University of Sulaimani, Old Campus, Kurdistan Regional Government, Sulaimani 46001, Iraq
bDepartment of Chemistry, College of Science, University of Raparin, Kurdistan Region, Ranya 46012, Iraq
cResearch and Development Center, University of Sulaimani, Qlyasan Street, Kurdistan Regional Government, Sulaymaniyah, 46001, Iraq. E-mail: shujahadeenaziz@gmail.com
dDepartment of Physics, College of Science, Charmo University, Chamchamal 46023, Sulaymaniyah, Iraq
First published on 20th August 2024
Abstract
The current study employed a novel approach to design polymer composites with modified structural and declined optical band gaps. The results obtained in the present work for polymer composites can be considered an original method to make a new field for research based on green chemistry. Natural dyes extracted from green tea were mixed with hydrated zinc acetate (Zn(CH3COO)2·2H2O) to produce a metal complex. FTIR results comprehensively established the formation of the Zn-metal complex. The interaction among various components of PVA![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) Zn-metal complex composite was investigated using FTIR spectroscopy. The non-existence of anion bands of acetate in the Zn-metal complex spectrum confirms the formation of the Zn-metal complex. XRD analysis reveals that the Zn-metal complex improves the amorphous phase of the PVA-based composites. The absorption edge of the doped films shifted towards the lower photon energies. Optical dielectric properties were used to determine N/m*, ε∞, τ, μopt, ωp, and ρopt; the W–D model was used to calculate Ed, Eo and no parameters. The optical dielectric loss parameter was used to determine the optical band gap while the Tauc model was employed to identify various types of electron transitions. The optical energy band gap was 6.05 eV for clean PVA while it decreased to 1 eV for PVA inserted with the Zn-metal complex. The increase in Urbach energy from 0.26 eV to 0.45 eV is an evidence of the boost of amorphous phases in PVA
Zn-metal complex composite was investigated using FTIR spectroscopy. The non-existence of anion bands of acetate in the Zn-metal complex spectrum confirms the formation of the Zn-metal complex. XRD analysis reveals that the Zn-metal complex improves the amorphous phase of the PVA-based composites. The absorption edge of the doped films shifted towards the lower photon energies. Optical dielectric properties were used to determine N/m*, ε∞, τ, μopt, ωp, and ρopt; the W–D model was used to calculate Ed, Eo and no parameters. The optical dielectric loss parameter was used to determine the optical band gap while the Tauc model was employed to identify various types of electron transitions. The optical energy band gap was 6.05 eV for clean PVA while it decreased to 1 eV for PVA inserted with the Zn-metal complex. The increase in Urbach energy from 0.26 eV to 0.45 eV is an evidence of the boost of amorphous phases in PVA![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) Zn-metal complex composites. The nonlinear refractive index and the first-order and second-order nonlinear optical susceptibilities were determined. The value of Eo obtained from the W–D model closely matches the optical energy band gap obtained from the Tauc model, which indicates the precision of the analysis in the present study. The increase in SELF and VELF in the composite films establishes that new energy states assigned to the added Zn-metal complex amplify the probability of light–matter interaction.
Zn-metal complex composites. The nonlinear refractive index and the first-order and second-order nonlinear optical susceptibilities were determined. The value of Eo obtained from the W–D model closely matches the optical energy band gap obtained from the Tauc model, which indicates the precision of the analysis in the present study. The increase in SELF and VELF in the composite films establishes that new energy states assigned to the added Zn-metal complex amplify the probability of light–matter interaction.
1. Introduction
Recently, research interests in polar organic polymers such as polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) have been in progress due to their strong chemical and thermal stabilities, affordability, mechanical flexibility, high biocompatibility, and transparency. Because PVA chains are hydrogen bonded, they are a synthetic semicrystalline structured polymer.1–4 The most pertinent feature of PVA is that, in addition to being non-toxic, it is also a readily degradable and water-soluble crystalline polymer.5,6 PVA is a biodegradable substance used in paper coating and textile sizing. This particular polymer is typically employed in the pharmaceutical and chemical industries after being blended with other polymers.7,8 Additionally, PVA possesses hydrophilic properties, the ability to form films, and a high density of reactive chemical functional groups. These functional (OH) groups facilitate the cross-linking of PVA with doping materials.9Wastewater has emerged as a significant source of pollution and a serious threat to human health in recent years.10 Water pollution caused by persistent, hazardous, and bio-accumulative organic and inorganic contaminants has been linked to several environmental issues.11 Consequently, using natural materials made from renewable resources is one of the strategies used to address these challenges. It concerns the advancement of green chemistry, which is centred on employing biopolymers and natural dyes.12 Dye-doped polymers have gained popularity due to their numerous advantages. Their versatility makes them useful in photonic devices, both linear and nonlinear.13 Novel optical telecommunication devices, cutting-edge nanoscale lasers, and chip-integrated photonic biosensors all use dye-doped polymers.14 Electronic sensors, optical fibers, solar cells, optophotonic devices, and dye-doped polymeric materials are some of the promising new uses of these materials.15 Optical characterization of polymer films provides a wealth of significant physical data (refractive index n, extinction coefficient k, optical energy gap Eg, and dielectric constant ε) that are critical for various applications.16
Examining the absorption edge and refractive index can help us understand the type of transitions that occurs between the highest occupied molecular orbital (HOMO) and the lowest unoccupied molecular orbital (LUMO).17 To our understanding, metal complexes can be inserted into polymers to create polymer composite films with the desired optical properties. Researchers have made great strides in the field of organic-inorganic hybrid materials over the past 20 years; this is an intriguing and potentially pivotal area of study. The optical characteristics of PVA mixed with metal complexes have been studied in the literature. Transition metal complexes are a varied group of compounds that encompasses bioinorganic, Werner, and organometallic complexes. They have significant uses in various fields, such as catalysis, nanomaterials (such as electronic devices), medicinal chemistry, and renewable energies.18,19 Because of their high surface-to-bulk ratio, inorganic particles inserted into the host polymer may cause considerable changes in the host's properties.20–22 Previous studies employed many methods for the production of ligands to produce metal complexes, such as (C15H10N4O7SCl),23 4-[(2-amino-4-phenylazo)-methyl]N-[(benzoyl amino)-thioxo methyl]-cyclohexane carboxylic acid,24 N-[(benzoyl amino)-thioxo methyl], the benzoyl isothiocyanate–proline reaction,25 and 4-[(2-amino-4-phenylazo)-methyl]-cyclohexane carboxylic acid.26 According to Samuel et al., there are several issues with the ligand method for synthesizing metal complexes using organic solvents under reflux. These issues encompass excessive use of organic solvents, prolonged reaction times, environmentally harmful solvents, reduced product yields, and harsh reflux conditions.27 In the present study, we offer a new technique for preparing metal complexes, namely the synthesis of Zinc metal complex (Zn-metal complex) using green tea (GT) dye and Zn(CH3COO)2 salt. The GT dye is renowned for its significant phytochemical components in metallic ion reduction.28,29 The composition of fresh, young green tea leaves when analyzed for dry weight is generally as follows: Polyphenols comprise 20–35% of the composition, while cellulose, lignin, starch, and other substances account for 20–30%. Proteins make up 10–20%, fats make up 3–9%, mineral substances make up 4–8%, polysaccharides make up 4–7%, amino acids make up 3–4%, caffeine makes up 2–4%, chlorophyll and carotenoids make up 2–3%, and volatile chemicals are also present.30,31 The polyphenolic level in green tea types varies depending on factors such as the harvesting season, cultivars, cultivation circumstances, and manufacturing procedure. The main catechins found in tea leaves include (–)-epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), (–)-epi-gallocatechin (ECC), (–)-epicatechin gallate (ECG), and (–)-epicatechin (EC);20,32 it has also been demonstrated that dyes derived from tea, specifically black tea (BT), contain sufficient ligands with functional groups, such as OH, NH, NH2, and C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O. Based on Aziz's approach, tea dyes are an environmentally friendly approach to producing Sn2+-PPH metal–organic frameworks.
O. Based on Aziz's approach, tea dyes are an environmentally friendly approach to producing Sn2+-PPH metal–organic frameworks.
According to previous studies, several approaches have been carried out to modify the optical properties of PVA, such as the insertion of nanofillers, polymer blending, ceramic filler, and salt addition. It was found that nano-Ag insertion into PVA decreased the optical band gap from 4.92 to 3.93 eV.33 Abdelrazek et al.34,35 and Barzic et al. studied the blends of PVA/PVP (50/50) with different amounts of LiBr. They observed that Eg reduced from 5.10 to 4.40 eV.35 The Eg value of PVA can decrease from 3.448 eV to 2.605 eV in a system containing 2 wt% barium titanate. Moreover, the PVA doped with LiAsF6 showed a band gap reduction from 5.76 to 4.7 eV.36 An intensive literature survey revealed that the optical band gap of PVA did not change noticeably. In the current study, the metal complex was examined as an alternative to all the traditional approaches examined in the literature. The advantages of this approach are that it is environmentally friendly, economically feasible, and a moderate method for preparing the Zn-metal complexes, including an uncomplicated purification process, high product output, and quick reaction times.37,38 The literature review has shown that it is difficult to decrease the optical band of PVA to an appropriate value to be eligible for various applications. The present research investigates PVA's optical and structural characteristics incorporated with the Zn-metal complex. The current study's findings suggest that using environmentally friendly methods to create metal complexes is innovative and unique in reducing the optical band gap of biopolymers. This could have significant implications for photonics and optoelectronic devices and applications. This work employed numerous models and methodologies to accurately compute the optical band gap.
2. Methodology
2.1. Materials
Molecular weights of 12![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000–18
000–18![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 were supplied by Sigma-Aldrich for the PVA powder. HOPKIN & WILLIAMS Zn(CH3COO)2 was also provided. The GT leaf was acquired from a marketplace located in London.
000 were supplied by Sigma-Aldrich for the PVA powder. HOPKIN & WILLIAMS Zn(CH3COO)2 was also provided. The GT leaf was acquired from a marketplace located in London.
2.2. Metal complex preparation
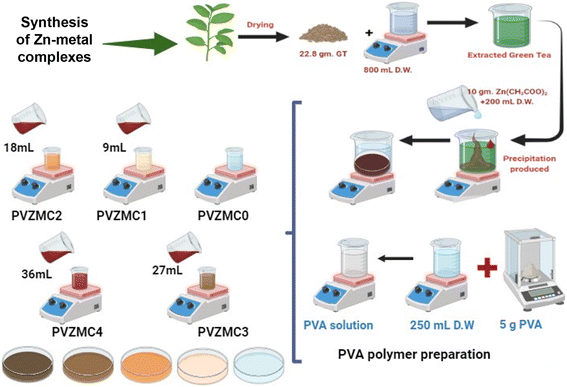
A 22.8 g of Green Tea GT leaf and 800 mL of water (D.W.) mixture were prepared at approximately 95 °C without sunshine. After standing for thirty minutes, the extracted green tea solution was filtered (W. man paper 41, cat. no. 1441) with a pore radius of 20 μm comprehensive residue removal. Within an individual flask, 200 mL of D.W. was diluted by dissolving 10 g of Zinc Acetate Zn(CH3COO)2 salt. The structure of zinc acetate and the main catechins found in tea leaves are shown in Scheme 1a and b. It produced polyphenols (PPHs) in green tea (GT); the Zn2+–PPHs metal complex was then created by adding zinc acetate into the extracted green tea solution at 70 °C and stirring for sixty minutes. At the bottom of the tube, the extract solution's color changed from light green to dark green, confirming that Zn2+–metal ions and PPHs had complexed.When the green tea solution progressed from light green to dark green and a cloud of precipitate developed at the bottom of the beaker, it was a sure sign that the Zn2+–polyphenol complex had formed. The complex mixture was allowed to settle down at room temperature. These complexes were extracted in 200 mL; after five days of washing, the Zn2+–PPHs metal complexes with D.W. Simplified PVA composite samples filled with Zn2+ metal complex were cast using the solution cast technique.
2.3. Sample preparation
The solution casting method produced composite samples using PVA doped with a Zn2+–polyphenol combination. The PVA solution, acting as the main polymer material, was created by thoroughly combining 5 g of pure PVA powder (with an average molecular weight of 18![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 g mol−1) with 250 mL of distilled water at 90 °C. The mixture was stirred for approximately one hour using a magnetic stirrer, resulting in an evenly distributed solution. It was then allowed to cool to room temperature. In 9 mL increments, different quantities of the zinc metal complex (Zn-metal complex) solution ranging from 0 to 36 mL were incorporated into the identical host polymer PVA solution. The solutions produced (extracted green tea and zinc acetate) were agitated for around 40 minutes. PVZMC0, PVZMC1, PVZMC2, PVZMC3, and PVZMC4 were utilized to represent 0 mL, 9 mL, 18 mL, 27 mL, and 36 mL of the Zn-metal complex, respectively, of the loaded metal complex solution.
000 g mol−1) with 250 mL of distilled water at 90 °C. The mixture was stirred for approximately one hour using a magnetic stirrer, resulting in an evenly distributed solution. It was then allowed to cool to room temperature. In 9 mL increments, different quantities of the zinc metal complex (Zn-metal complex) solution ranging from 0 to 36 mL were incorporated into the identical host polymer PVA solution. The solutions produced (extracted green tea and zinc acetate) were agitated for around 40 minutes. PVZMC0, PVZMC1, PVZMC2, PVZMC3, and PVZMC4 were utilized to represent 0 mL, 9 mL, 18 mL, 27 mL, and 36 mL of the Zn-metal complex, respectively, of the loaded metal complex solution.
The solution cast method created composite films from PVA impregnated with a foreign substance Zn2+–polyphenol complex. The mixture's contents were put into Petri dishes and left to dry at room temperature. Finally, the homogeneous solutions were cast into plastic Petri dish plates, and the water in this homogeneous solution gradually evaporated during the drying process at room temperature. The samples are ready for characterization after two weeks. Table 1 lists the pure polymer and doped PVA with a coordination metal complex. The methodology employed for preparing the metal complex (Scheme 2).
| Identifying a sample | PVA (g mL−1) | Metal complex solution (mL) |
|---|---|---|
| PVZMC0 | 1/50 | 0 |
| PVZMC1 | 1/50 | 9 |
| PVZMC2 | 1/50 | 18 |
| PVZMC3 | 1/50 | 27 |
| PVZMC4 | 1/50 | 36 |
3. Characterization techniques
3.1. X-ray diffraction
The structural characterization and impact of the polymer complexation materials were evaluated using X-ray diffraction (XRD). The X-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns were obtained using a PANalytical X-ray diffractometer (model: 40 mA/40 kV) produced by PANalytical in Almelo, Netherlands. This study used a monochromatic X-ray beam with a wavelength of 1.5406 Å, specifically CuKα, to analyze the studied materials. The glancing angle (2θ) ranged from 5° to 50°, with a step size of 0.1°. All measurements were conducted at an ambient temperature.3.2. FTIR study
The spectrophotometer operated in the range of 4000–400 cm−1, with a resolution of 4 cm−1 and 32 scans were accumulated. The samples were produced as KBr pellets, with a sample-to-KBr ratio of 1% w/w. A pure KBr disk was used as a reference.3.3. UV-vis measurement
The UV-visible spectrometer is a scientific apparatus employed to quantify the absorption and transmission of light in liquid and solid samples within the ultraviolet (UV) and visible portions of the electromagnetic spectrum. The pure PVA and composite PVA were analyzed using UV-vis spectroscopy for absorption with a Jasco V-570 UV-vis-NIR spectrophotometer (manufactured by Jasco, Japan, model SLM-468). The spectra were recorded in absorbance mode within the 190–1100 nm wavelength range. The thicknesses of the samples were measured in the range of 100–145 μm.4. Results and discussions
4.1. Structural analysis
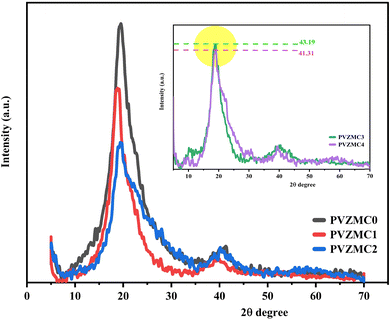
Fig. 1 displays the patterns created by XRD of the Zn2+–PPL complex, pure PVA, and the PVA/Zn-metal complex. According to Achilles et al. (2018), larger peaks are associated with the amorphous phase, whereas sharper peaks distinguish the crystalline phase.39 A sharp peak with a wide distribution centered at 19.54 was detected in the X-ray diffraction (XRD) of pure PVA (see Fig. 1). However, in the PVZMC1, PVZMC2, PVZMC3, and PVZMC4 composite films, the peak corresponding to pure PVA (19.54) exhibited a broader shape and decreased intensity. The expanding shape of the peak demonstrates the lack of a defined structure in the complex system. The interpretation of these data might be based on Hema M. et al.40 The guideline establishes a direct relationship between the height of the highest point and the degree of crystallinity. The inset plots in Fig. 1 represent the XRD curves of PVZMC3 and PVZMC4, which have similar intensity values. The purpose of the inset is to distinguish between the two samples.The XRD spectra of the polymer composite broadening films show a notable decrease in intensity and signal inside the range of 2θ = 40–55, which is considered the most valuable area. This phenomenon suggests a rise in the amorphous configuration inside the resulting hybrid films. The observed change is most likely due to substituting the typical intermolecular hydrogen bonding seen in pure polymers with unpredictable intermolecular hydrogen bonding in composite films. Hydrogen bonds, which are directed intermolecular contacts, substantially impact the conformation of polymers and their optical and physical properties. As the concentration of the Zn-metal complex increases, the crystallinity of the PVA decreases. The XRD measurements verified the presence of distinct complex coordination between PVA and Zn-metal complexes. The strong interactions between the polar functional group, OH of PVA, and metal complex OH and NH groups reveal the excellent compatibility and miscibility of the polymer and metal complex components. This complex formation reduces the degree of crystallinity of the composite.41
4.2. Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) analysis
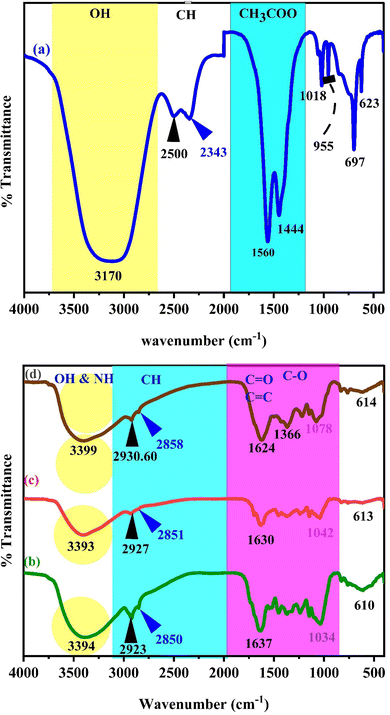
Fig. 2a–d illustrates the FTIR bands of the zinc acetate salt, green tea powder, extracted green tea dye, and Zn-metal complexes, respectively. From Fig. 2a, the final two bands are detected in the range of 1600–1350 cm−1, which acts as a distinctive characteristic of the acetate anion group present in the compounds. The carboxyl acetate groups in basic metal salts typically form coordination bonds with specific cations.42 The vibrational modes of the carbonyl group (C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O) are influenced by the coordination formed by the inserted acetate. Acetate with zinc is associated with three well-known coordination types. The two bands detected at 1560 and 1444 cm−1 were observed phenomena that can be attributed to the asymmetric stretching vibrations of the C
O) are influenced by the coordination formed by the inserted acetate. Acetate with zinc is associated with three well-known coordination types. The two bands detected at 1560 and 1444 cm−1 were observed phenomena that can be attributed to the asymmetric stretching vibrations of the C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O bond.43
O bond.43
 | ||
| Fig. 2 FT-IR spectra of (a) zinc acetate, (b) green tea powder, (c) extracted green tea dye, and (d) Zn-metal complex. | ||
Fig. 2b and c display the transmission spectrum as a function of wavenumber for the green tea powder and extracted GT dyes, specifically in the 400 to 4000 cm−1 range. The broad peak presence of phenolic hydroxyl groups is responsible for this peak. Each infusion displayed a distinct and wide peak between 3000 and 3600 cm−1, suggesting the presence of hydroxyl groups (alcoholic substances or phenols), C–H stretching (alkenes or arenes), and N–H stretching (amine groups) that intersected. The infrared spectrum of the GT sample showed absorption peaks in specific regions: between 2850 and 3600 cm−1 (which indicates the stretching of O–H bonds in carboxylic acids and C–H bonds in alkanes), 1500–1750 cm−1 (indicating the stretching of C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O bonds in carbonyl acids and esters, bending of N–H bonds in amides, stretching of C
O bonds in carbonyl acids and esters, bending of N–H bonds in amides, stretching of C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C bonds in alkenes and aromatic groups, and stretching of C
C bonds in alkenes and aromatic groups, and stretching of C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N bonds in aromatic groups), 1250–1500 cm−1 (indicating the stretching of C–O bonds in carboxylic acids, bending of C–H bonds in alkanes, and bending of O–H bonds in alcohols/phenols), 930–1200 cm−1 (which indicates the stretching of C–O bonds in alcohols/phenols/esters, stretching of C–N bonds in amines, and bending of
N bonds in aromatic groups), 1250–1500 cm−1 (indicating the stretching of C–O bonds in carboxylic acids, bending of C–H bonds in alkanes, and bending of O–H bonds in alcohols/phenols), 930–1200 cm−1 (which indicates the stretching of C–O bonds in alcohols/phenols/esters, stretching of C–N bonds in amines, and bending of ![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C–H bonds in alkenes), and numerous points in the region 800–930 cm−1 (indicating the bending of
C–H bonds in alkenes), and numerous points in the region 800–930 cm−1 (indicating the bending of ![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C–H bonds in alkenes and bending of C–H bonds in aromatic groups) in the GT sample. The GT had a prominent and wide peak across the 3000–3600 cm−1 range.44–47 The FTIR spectra of powder GT and GT dye extracts are almost the same. Widatalla et al.48 also discovered that GT dye has distinct peaks at specific wavenumbers: 3566.3, 2918, 2850.7, 1653.9, 1384, 1107, 1053, and 997.2 cm−1. These peaks correspond to O–H bond stretching in alcohol present in polyphenols and amines, as shown in Table 2.
C–H bonds in alkenes and bending of C–H bonds in aromatic groups) in the GT sample. The GT had a prominent and wide peak across the 3000–3600 cm−1 range.44–47 The FTIR spectra of powder GT and GT dye extracts are almost the same. Widatalla et al.48 also discovered that GT dye has distinct peaks at specific wavenumbers: 3566.3, 2918, 2850.7, 1653.9, 1384, 1107, 1053, and 997.2 cm−1. These peaks correspond to O–H bond stretching in alcohol present in polyphenols and amines, as shown in Table 2.
| Samples | OH & NH | CH | C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O O |
C–O | C–O–C | (CH3COO)2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zn(CH3COO)2 | 3170 | 2500 | 1560 | |||
| 2343 | 1444 | |||||
| G.T. powder | 3394 | 2923 | 1637 | 1034 | ||
| 2850 | ||||||
| Extracted G.T. | 1630 | 1042 | ||||
| Zn-metal complex | 1624 | 1078 | ||||
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) |
||||||
| Composite samples | ||||||
| PVZMC0 | 3302 | 2941 | 1729.86 | 1086.50 | 1246 | |
| 2910.36 | ||||||
| PVZMC1 | 3299 | 2943.40 | 1722.30 | 1086 | 1244 | |
| 2913.23 | ||||||
| PVZMC2 | 3295 | 2941.96 | 1721.36 | 1086 | 1242.50 | |
| 2911.97 | ||||||
| PVZMC3 | 3295 | 2940.56 | 1718.60 | 1084 | 1239.70 | |
| 2910.36 | ||||||
| PVZMC4 | 3289 | 2940.53 | 1713.75 | 1080 | 1239.70 | |
| 2910.36 | ||||||
The stretching of carbon–hydrogen (C–H) bonds in alkaline substances and carboxylic acids, the presence of carbon–carbon double (C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C) bonds in aromatic compounds and primary amide groups in proteins (–CO–NH2), the stretching of carbon–oxygen–carbon (C–O–C) bonds, and the bending of C
C) bonds in aromatic compounds and primary amide groups in proteins (–CO–NH2), the stretching of carbon–oxygen–carbon (C–O–C) bonds, and the bending of C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C bonds were observed. The aqueous extract of GT (green tea) was analyzed for phytochemicals, revealing the presence of various polyphenols, such as gallic acid (GA), gallocatechin (GC), catechin (CE), and epigallocatechin (ECC), together with proteins, flavonoids, saponins, and glycosides. Catechins, a type of polyphenol, make up the majority of GT, accounting for 24–36% of its dry weight. However, based on Fig. 2d of the Zn-metal complex, the absence of acetate peaks in the range of 1350–1600 cm−1 indicates that no acetate is present in the metal complex. The peaks observed at 1366 cm−1 and 1624 cm−1 in Fig. 2d are not due to acetate salt because these peaks exist in the GT dye, and the development of metal complexes is now established.
C bonds were observed. The aqueous extract of GT (green tea) was analyzed for phytochemicals, revealing the presence of various polyphenols, such as gallic acid (GA), gallocatechin (GC), catechin (CE), and epigallocatechin (ECC), together with proteins, flavonoids, saponins, and glycosides. Catechins, a type of polyphenol, make up the majority of GT, accounting for 24–36% of its dry weight. However, based on Fig. 2d of the Zn-metal complex, the absence of acetate peaks in the range of 1350–1600 cm−1 indicates that no acetate is present in the metal complex. The peaks observed at 1366 cm−1 and 1624 cm−1 in Fig. 2d are not due to acetate salt because these peaks exist in the GT dye, and the development of metal complexes is now established.
Fig. 2d illustrates the characteristic frequencies of Zn-metal complexes in both the infrared (IR) and far infrared (far IR) regions. The infrared spectrum of the bound ligand has a distinct peak at 2930.60 and 2858 cm−1, which is attributed to the presence of methyl (CH). A wide band is also observed at 3411 cm−1, corresponding to the hydroxyl group (OH) in its phenolic form. Nevertheless, the infrared spectra of the Zn-metal complex indicate the existence of a novel wide band in the range of 3000–3750 cm−1, which can be ascribed to a combination of (NH) and (OH) vibrations originating from the coordinated or lattice water. The alterations in stretching frequencies associated with (NH) and (OH) cannot be discerned due to the merging of that region with m(OH) of water, resulting in a broad band in the complexes.49 A typical instance of a C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O stretching vibration, commonly observed in ketones and aldehydes, occurs at around 1624 cm−1. The compound's molecular structure is characterized by very particular and unique patterns in the ∼1500–400 cm−1 range. Nevertheless, the positions of peaks might differ because of various factors, including the molecular surroundings, the way the sample is prepared, and the instrument's parameters. This emphasizes the significance of referring to dependable databases and literature to ensure precise peak assignments.50 In the present situation, specific peaks are observed within the range of 600–850 cm−1 during the creation of the Zn-metal complex. However, in the case of green tea, there is no discernible peak in the range mentioned above. Following the complexation process, a band emerged, accompanied by the discovery of additional bands at 830, 765, and 614 cm−1 in the zinc metal complex. Fig. 2a shows a distinct peak corresponding to the Zn(II) at 697 cm−1, which displays higher intensity. However, in Fig. 2d, the strength of this peak vanished due to the formation of coordination between zinc and polyphenols in GT, facilitated by the acceptance of a pair of electrons by the zinc metal ion. This is related to the metal ion being more stable. The prepared dye and proposed Zn-metal complex structure are illustrated in Schemes 3 and 4, respectively. The metal complex leads to a decrease in the frequency and intensity of most peaks in the FTIR pattern of the Zn-metal complex compared to the corresponding GT ligands. This decrease depends on factors such as the specific metal cation mass, the kind of ligands (GT), and the oxidation state of the metal. In PVA polymers, intramolecular hydrogen bonding occurs between OH groups on the same polymer chain, while intermolecular hydrogen bonding occurs between the OH functional groups in different polymer chains. Introducing the Zn-metal complex into the PVA polymer disturbs the intermolecular hydrogen bonding among polymer chains, thereby reducing the extent of intermolecular hydrogen bonding. Incorporating the Zn-metal complex into PVA polymer creates a powerful link between the metal complex's OH or NH functional groups and the hydroxyl OH group of PVA. This interaction creates a space between these functional groups and reduces the degree of crystallinity.51,52
O stretching vibration, commonly observed in ketones and aldehydes, occurs at around 1624 cm−1. The compound's molecular structure is characterized by very particular and unique patterns in the ∼1500–400 cm−1 range. Nevertheless, the positions of peaks might differ because of various factors, including the molecular surroundings, the way the sample is prepared, and the instrument's parameters. This emphasizes the significance of referring to dependable databases and literature to ensure precise peak assignments.50 In the present situation, specific peaks are observed within the range of 600–850 cm−1 during the creation of the Zn-metal complex. However, in the case of green tea, there is no discernible peak in the range mentioned above. Following the complexation process, a band emerged, accompanied by the discovery of additional bands at 830, 765, and 614 cm−1 in the zinc metal complex. Fig. 2a shows a distinct peak corresponding to the Zn(II) at 697 cm−1, which displays higher intensity. However, in Fig. 2d, the strength of this peak vanished due to the formation of coordination between zinc and polyphenols in GT, facilitated by the acceptance of a pair of electrons by the zinc metal ion. This is related to the metal ion being more stable. The prepared dye and proposed Zn-metal complex structure are illustrated in Schemes 3 and 4, respectively. The metal complex leads to a decrease in the frequency and intensity of most peaks in the FTIR pattern of the Zn-metal complex compared to the corresponding GT ligands. This decrease depends on factors such as the specific metal cation mass, the kind of ligands (GT), and the oxidation state of the metal. In PVA polymers, intramolecular hydrogen bonding occurs between OH groups on the same polymer chain, while intermolecular hydrogen bonding occurs between the OH functional groups in different polymer chains. Introducing the Zn-metal complex into the PVA polymer disturbs the intermolecular hydrogen bonding among polymer chains, thereby reducing the extent of intermolecular hydrogen bonding. Incorporating the Zn-metal complex into PVA polymer creates a powerful link between the metal complex's OH or NH functional groups and the hydroxyl OH group of PVA. This interaction creates a space between these functional groups and reduces the degree of crystallinity.51,52
 | ||
Scheme 3 Components present in extracting the green tea dye enriched with NH and C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O functional groups. O functional groups. | ||
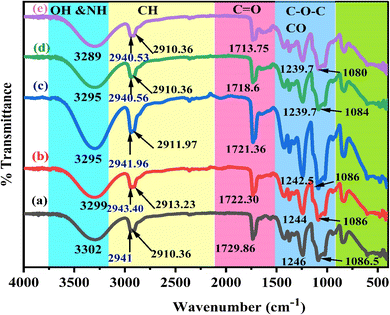
Fig. 3a depicts the FTIR spectrum of pure polymer PVA. Upon comparing the spectral properties of complex PVA with those of pure PVA, GT, and Zn-metal complex, the following modifications were observed. The frequency with which the OH groups in PVA form intermolecular hydrogen bonds, initially observed at 3302 cm−1, is moved to 3289 cm−1 when PVA forms a complex film. Furthermore, the CH stretching of CH2 in pure PVA, which is initially seen at 2941 cm−1, is shifted to 2943.40, 2941.96, 2940.56, and 2940.53 cm−1.53 The peak observed at 1729.86 cm−1 refers to the stretching vibration of the C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O bond in the carboxylic groups (COOH) in pure PVA. The stretching modes of C–O and C–C are responsible for the peaks at 1087 and 1571 cm−1, respectively, in the PVA backbone. The stretch C–C vibrations of the planar zigzag structure of the carbon backbone show moderate absorption at 836 cm−1. The peak at 651 cm−1 corresponds to the wagging mode of (OH) groups.54
O bond in the carboxylic groups (COOH) in pure PVA. The stretching modes of C–O and C–C are responsible for the peaks at 1087 and 1571 cm−1, respectively, in the PVA backbone. The stretch C–C vibrations of the planar zigzag structure of the carbon backbone show moderate absorption at 836 cm−1. The peak at 651 cm−1 corresponds to the wagging mode of (OH) groups.54
 | ||
| Fig. 3 FTIR spectra of polar polymer PVA with zinc metal complexes in the region 400–4000 cm−1 for pure (a) PVZMC0 (b) PVZMC1 (c) PVZMC2 (d) PVZMC3 and (e) PVZMC4 films. | ||
The FITR spectrum of the polar polymeric metal complex reveals the presence of additional bands. Nagesh et al. observed that in the zinc complexes, the presence of Zn–nitrogen and Zn–oxygen bonds may be identified by low-intensity bands ranging from 420 to 450 cm−1.55 Although there are many possibilities, a general structure for the complexes is proposed based on the literature. As a result of extending the C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O bond in the acetate group of PVA, a peak at 1729.86 cm−1 was noted. This peak is displaced to 1722.30, 1721.36, 1718.60 and 1713.75 cm−1 in the polymer complexes, respectively, as depicted in Fig. 3b–e curves of the polymer composites, respectively, as shown in Table 2. In the pure PVA, the peak at 1087 cm−1 exhibited a decreased amplitude and shifted to 1086, 1086, 1084, and 1080 cm−1 when doped with 9, 18, 27, and 36 mL of Zn-metal complex, respectively, in the polymer complex. The polymer with a metal complex exhibits peaks in the 400 to 700 cm−1 range, which is attributed to the presence of Zn cations. This observation provides evidence of interactions between the polymer and the metal complex.56
O bond in the acetate group of PVA, a peak at 1729.86 cm−1 was noted. This peak is displaced to 1722.30, 1721.36, 1718.60 and 1713.75 cm−1 in the polymer complexes, respectively, as depicted in Fig. 3b–e curves of the polymer composites, respectively, as shown in Table 2. In the pure PVA, the peak at 1087 cm−1 exhibited a decreased amplitude and shifted to 1086, 1086, 1084, and 1080 cm−1 when doped with 9, 18, 27, and 36 mL of Zn-metal complex, respectively, in the polymer complex. The polymer with a metal complex exhibits peaks in the 400 to 700 cm−1 range, which is attributed to the presence of Zn cations. This observation provides evidence of interactions between the polymer and the metal complex.56
Fig. 3 depicts the FTIR spectra of pure PVA and PVA![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) Zn-metal complex composites. The hydroxyl groups exhibit broad and intense OH stretching absorption. The absorption peak of pure PVA is observed at 3302 cm−1. Curiously, the intensity of this peak varies and decreases as the Zn-metal complex increases. The intensity of this peak decreased significantly when 36 mL of Zn-metal complex was present, causing a shift to 3289 cm−1. The CH asymmetric stretching vibration band in pure PVA occurs at 2941 cm−1, as illustrated in Table 2. However, in the doped samples, there is an apparent change to 2940 cm−1, followed by a considerable decrease in the intensity of this band.
Zn-metal complex composites. The hydroxyl groups exhibit broad and intense OH stretching absorption. The absorption peak of pure PVA is observed at 3302 cm−1. Curiously, the intensity of this peak varies and decreases as the Zn-metal complex increases. The intensity of this peak decreased significantly when 36 mL of Zn-metal complex was present, causing a shift to 3289 cm−1. The CH asymmetric stretching vibration band in pure PVA occurs at 2941 cm−1, as illustrated in Table 2. However, in the doped samples, there is an apparent change to 2940 cm−1, followed by a considerable decrease in the intensity of this band.
4.3. Optical characterization
As shown in Fig. 4, decreasing the concentration (diluted) of a solute in a solution is referred to as dilution, and it is almost often accomplished by simply mixing with an additional solvent (in this process, D.W.). Fig. 4b illustrates the UV-vis. of zinc acetate ranging from 325 nm to 700 nm. Interestingly, no notable peak was observed in the absorbance of zinc acetate inside the visible area. No substantial fluctuations in the absorption properties of zinc acetate were detected in this area. However, based on Fig. 4c, the findings demonstrated that combining zinc acetate and green tea G.T. produced a Zn-metal complex.62,63
 | ||
| Fig. 4 Absorption spectra for (a) pure G.T., (b) zinc acetate salt, and (c) Zn-metal complex samples. | ||
The two (Fig. 4a and c) exhibit exponential curves in the visible region. UV-visible absorption spectroscopy can be utilized to investigate the interaction between metal complexes and PVA polymers. The investigation involved adding different concentrations of Zn-metal complex to PVA to observe how the position of the absorption bands changed due to the interaction between the metal complex and PVA. In addition to varying concentrations of Zn-metal complex to PVA, a noticeable shift to a high wavelength occurred in the absorption position; due to the color of the metal complex, this means that there is a good interaction between the metal complex and PVA.
During the process of absorption, an electron is elevated from a lower energy band to a higher energy band by the interaction with a photon possessing a specific energy concept of absorption, which is quantified by a coefficient (α), the ratio of the initial light intensity to the light intensity after a reduction.64 Using Lambert Beer's relation, the absorption coefficient (α) for a specific film thickness (d) was computed. An essential variable in this context is the optical absorbance (A). The correlation between the energy of the incident photons (hv) and the coefficient of absorption (α) was shown by a drawn graph. The linear section of the α-hv curves was extrapolated to the horizontal axis to calculate the absorption edges of the created samples.65,66
By incorporating Zn-metal complex molecules into the polar PVA polymer, the bandgap of the PVA-doped material was significantly reduced, resulting in a downward change in the location of the valence band. Furthermore, the electronic states at the Fermi level of the Zn-metal complex and PVA exhibit hybridization, indicating that combining Zn-metal complex molecules substantially impacts the electronic states below the Fermi level. Kalarani et al.67 utilized the Zn-metal complex of a bidentate Schiff base ligand (L) 2-((1H-benzo [d]imidazole-4ylimmino)). It was found that the HOMO and LUMO orbitals of the L-Zn2+ combination were mainly located on both the ligand and metal systems, and the band gap was 1.76 eV. This finding closely aligns with the energy gap of our hypothesized Zn-metal complex, as depicted in Fig. 5.
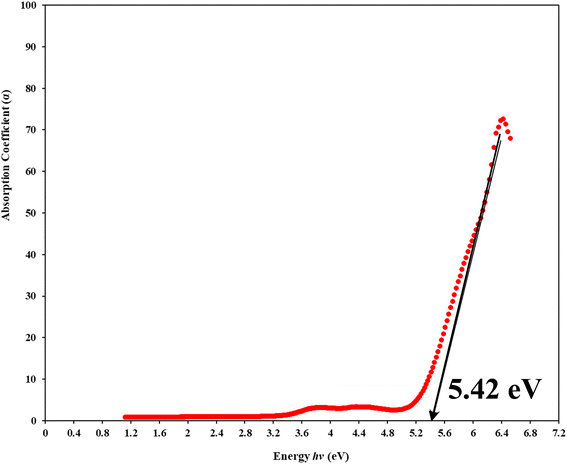
As illustrated in Fig. 5, the observed phenomenon is that the absorption edge of the hybrid films is moved towards lower photon energy compared to pure PVA, providing empirical support for the indispensability of metal complexes in doping functional polymers. The absorption edge values for metal complex PVA films with contents of 0, 9, 18, 27, and 36 mL were determined to be 6.05, 2.32, 2.27, 1.98, and 1 eV, respectively. The formation of novel localized states within the gap could cause these occurrences. This observation suggests that the integration of the Zn-metal complex into the PVA matrix results in a decrease in the band gap energy.68–70
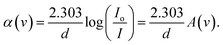 | (1) |
In the previous context, the amount of light that hits the object is depicted by the symbol Io; IT represents the transmitted light intensity, and the symbol (d) defines the thickness of the sample. This study investigates the relationship between the variation in α(ν) and photon energy (hν) in pure polymer PVA and PVA films doped with Zn-metal complexes samples.64,71
To understand how the variations between Zn-metal complexes and Zn polymer electrolytes affect the energy band gap, a solution casting process was used to make a polymer film of PVA/ZnAc electrolytes. This phenomenon is shown in Fig. 6. As depicted in Fig. 5 and 6, metal complexes have a more significant impact on energy band gaps than polymer electrolytes because the edge of absorption of PVA films shifts from 6.05 eV to 5.42 eV. Aziz et al.38 presented novel strategies that combine a green method of manufacturing metal complexes with a host PVA polymer.
| εr = n2 − k2. | (2) |
The refractive index, denoted as (n), is associated with the actual velocity, and an extinction coefficient (k) is related to loss. The Fresnel formulas are utilized to determine the refractive indices of pure polymer PVA and composite PVA films. This is achieved by analyzing the reflectance, R, and the optical loss coefficient, k, which can be calculated using the formula k = αλ/4πd. Here, α represents the absorption coefficient, λ denotes the wavelength, and d denotes the thickness of the sample.
 | (3) |
In the present study, practically, we can investigate the variations in the real (εr) and imaginary (εi) components of the dielectric constant for various films composed of (PVA) and PVA with a metal complex. Based on the analyses of (n) and (k), it is found that the magnitudes of the real components are greater than those of the imaginary parts. The refractive index of pure PVA increased from (1.1553 to 1.3569) by doped 36 mL Zn-metal complex. The optical data reveal an identical trend in the refractive index (n) and the real parts of the samples (εr). The real portion (εr) serves as an indicator of the degree of polarization. According to the reference, there is a positive correlation between the degree of polarization and the value of (εr).29
It is possible to determine the actual component of the real part of the dielectric constant from a theoretical perspective:
 | (4) |
Fig. 7 illustrates the imaginary component of the dielectric vs. photon energy (hv). A previous study demonstrated a significant association between the band structure and optical characteristics of materials. The detailed dielectric function affects the optical characteristics of absorbing isotropic substances depending upon the wavelength. The imaginary dielectric function (εi) is used to describe the electronic absorption of materials resulting from the interaction with an electromagnetic field, which induces dipole motion. The complex dielectric function is commonly utilized to provide insights into the optical characteristics.9,74 The complex dielectric function is a valuable parameter for precisely characterizing many optical features, such as the reflectivity ratio and absorption spectrum. Theoretically, the imaginary component of the dielectric function is determined by applying eqn (5), which considers interband transitions of active electrons between occupied (ik) and unoccupied electron states (fk).21,73
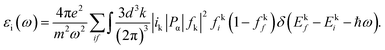 | (5) |
In eqn (5), the symbol ω represents the frequency of incident photons and Ω represents the crystal volume. The fundamental unit of electric charge is denoted as e, and the permittivity in the vacuum of space, denoted as εo, is the respective term used in scientific discourse. The terms (fki) and (fkf) denote the initial and final states of transition electrons, respectively. The electronic transitions between the occupied states ik, and unoccupied states fk wave functions cause photon absorption or emission. These transitions are accurately represented by the optical dielectric loss (εi). The optical band gap computation is based on the extrapolated linear intersection of (εi) in its place of (hv), as demonstrated. The following expression illustrates the practical relationship to determine the imaginary part of the optical dielectric constant. From the gained n and k data, the εi can be computed using the following equation:9
| εi = 2nk. | (6) |
Analyzing optical absorption spectra is crucial for determining the optical energy gap (Eg) in organic and inorganic materials. In numerous amorphous materials, photon absorption follows the Tauc relation, which can be expressed as follows:75
| (αhν) = B(hν − Eg)γ, | (7) |
 | ||
| Fig. 8 Direct allowed band gap energy plot of pure polymer PVA and composite PVA/Zn-metal complex films. | ||
 | ||
| Fig. 9 Indirect allowed band gap energy plot of pure polymer PVA and composite PVA/Zn-metal complex films. | ||
 | ||
| Fig. 10 Direct forbidden band gap energy plot of pure polymer PVA and composite PVA/Zn-metal complex films. | ||
 | ||
| Fig. 11 Indirect forbidden band gap energy plot of pure polymer PVA and composite PVA/Zn-metal complex films. | ||
| Sample designation | Eg (eV) for γ = 1/2 | Eg (eV) for γ = 3/2 | Eg (eV) for γ = 2 | Eg (eV) for γ = 3 | Eg from εi (hv) plot |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PVZMC0 | 6.21 | 5.95 | 5.85 | 5.22 | 6.05 |
| PVZMC1 | 2.52 | 2.18 | 1.84 | 1.55 | 2.35 |
| PVZMC2 | 2.45 | 1.94 | 1.74 | 1.17 | 2.26 |
| PVZMC3 | 2.35 | 1.59 | 1.62 | 0.84 | 1.95 |
| PVZMC4 | 1.98 | 1.24 | 1.35 | 0.38 | 1.74 |
The presence of the Zn-metal complex has an evident effect on the decrease in Eg values in such a way that clean PVA has wide Eg, while PVA composites, including PVZMC1, PVZMC2, PVZMC3, and PVZMC4, have small Eg values. The insertion of Zn-metal complexes into PVA composite films is responsible for the observed shift in the energy gap. Several OH, NH, and C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O functional groups around the Zn central metal help to interact with the OH groups of the PVA through hydrogen bonding. This produces a polymer–metal complex interaction and overlaps many orbitals, thus reducing the optical band gap.
O functional groups around the Zn central metal help to interact with the OH groups of the PVA through hydrogen bonding. This produces a polymer–metal complex interaction and overlaps many orbitals, thus reducing the optical band gap.
The direct incorporation of salt into a polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) polymer solution is called a polymer electrolyte. The results of the current study confirm that the polymer–salt system shows negligible optical band gap reduction (see Fig. 6). The novelty of the present work is that the transfer of metal salts into metal complexes and then their combination with polar polymers is surprising in delivering polymer composites with the desired optical band gap. The effect of metal complexes in PVA (complex polymer) on the energy band gap of polymers can depend on various factors, including the nature of the metal complex, coordination bonds between central metal and ligands and ligand functional groups, but in direct salts in PVA (polymer electrolyte) depend on the type of salt.36 Bhargav et al.53 studied the Eg values of PVA![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) NaI electrolytes, and they observed that absorption edges reduced from 5.80 to 4.90 eV. Gupta et al.79,80 observed that the metal complex (chloropentamminecobalt chloride [Co(NH3)5Cl]Cl2) decreased the energy band gap of PVA from 4.8 to 1.85 eV.
NaI electrolytes, and they observed that absorption edges reduced from 5.80 to 4.90 eV. Gupta et al.79,80 observed that the metal complex (chloropentamminecobalt chloride [Co(NH3)5Cl]Cl2) decreased the energy band gap of PVA from 4.8 to 1.85 eV.
Fig. 12 demonstrates the linearity of the graphs depicting the direct relationship between the real part of the dielectric constant and λ2 within specific ranges, confirming the validity of the Spiter–Fan equation.
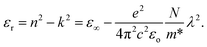 | (8) |
The material's dielectric response at high frequencies within the lattice, particularly at short wavelengths, is represented by the symbol ε∞. The speed of light (c), an electron's charge (e), the dielectric constant of the empty space region (εo), the concentration of charge carriers (N), and the electron effective mass (m*) are all defined in this context, and the constant values are shown in Table 4. The N/m* is the ratio of the free concentration of carriers to the effective mass of the electron.9,81 The parameters were derived by analyzing the slopes and intercepts of Fig. 12, as depicted in Table 5.
| Physical parameter constants | Values |
|---|---|
| Electron mass (me) | 9.109 × 10−31 kg1.602 × 10−19 ![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) C C |
| Electron charge (e) | |
| The dielectric constant of free space (εo) | 8.85 × 10−12 F m−1 |
| Speed of light (c) | 3 × 108 m s−1 |
| Π (Pi) | 3.1415 |
| Effective mass (m*) | 10.566 × 10−31 kg |
| Sample designation | N/m* × 1055 m3 kg−1 | ε∞ |
|---|---|---|
| PVZMC0 | 4.87 | 1.3515 |
| PVZMC1 | 21.9 | 1.6901 |
| PVZMC2 | 34.1 | 1.9872 |
| PVZMC3 | 36.5 | 2.0959 |
| PVZMC4 | 45 | 2.2155 |
The increased density of states within the valence band could be the outcome of adding a Zn-metal complex to the host polar PVA matrix. It is possible to create localized sub-bandgap states by introducing a metal complex. When metal complexes are added, the absorbed edge moves towards lower photon energies.82
 | (9) |
 | ||
| Fig. 13 ln(α) versus photon energy hv is used to calculate the Urbach energy for pure PVA and PVA/Zn-metal complex films. | ||
| Sample designation | Ed (eV) | Eo (eV) | no | Eu (eV) | Eg (eV) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PVZMC0 | 1.610106 | 5.903775 | 1.128151 | 0.2654 | 6.05 |
| PVZMC1 | 0.819452 | 2.272914 | 1.166417 | 0.4258 | 2.3 |
| PVZMC2 | 1.016202 | 2.152824 | 1.213273 | 0.4343 | 2.1 |
| PVZMC3 | 1.176863 | 2.186611 | 1.240247 | 0.4399 | 2.02 |
| PVZMC4 | 1.12438 | 2.074594 | 1.241763 | 0.4445 | 1 |
The values of the Eu increased from 0.2654 to 0.4445 eV as the Zn-metal complex amount increased from 9 to 36 mL. The increase in Eu value represents the growing amorphous nature of the PVA/Zn-metal complex matrix, leading to increased atomic and disorder defects in the structural bonding. Disorders and defects can result in localized states occurring at or near the connecting band level. The results of this study are consistent with the XRD results (see Fig. 1).
 | (10) |

The photon energy is denoted by hv. The electric-dipole oscillator strength, denoted by fk, is linked to transitions occurring at frequency ωp. The plasma frequency, ωp, is defined as 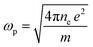 , where ne represents the effective electron density, and e and m represent the charges and mass of the electrons, respectively. According to the Wemple and DiDomenico (WD) hypothesis, one of the oscillators within the spectral range is believed to possess greater strength than the others.85 Fig. 14 shows the plot of 1/(n2 − 1) against (hv)2. The values of Ed and Eo were determined from both the slope and the intercept of the regression lines, respectively. The determined values are presented in Table 6. The Ed and Eo results exhibit a downward trend with increasing concentrations of Zn-metal complexes. The single effective oscillator energy, denoted as Eo, is close enough to the optical band gap achieved from the Taucs model. This establishes the fact that the data analysis was performed very carefully.
, where ne represents the effective electron density, and e and m represent the charges and mass of the electrons, respectively. According to the Wemple and DiDomenico (WD) hypothesis, one of the oscillators within the spectral range is believed to possess greater strength than the others.85 Fig. 14 shows the plot of 1/(n2 − 1) against (hv)2. The values of Ed and Eo were determined from both the slope and the intercept of the regression lines, respectively. The determined values are presented in Table 6. The Ed and Eo results exhibit a downward trend with increasing concentrations of Zn-metal complexes. The single effective oscillator energy, denoted as Eo, is close enough to the optical band gap achieved from the Taucs model. This establishes the fact that the data analysis was performed very carefully.
 | ||
| Fig. 14 Variant 1/(n2 – 1) against photon energy (hv)2 for pure polymer PVA and composite PVA/Zn-metal complex films. | ||
In this study, we examine the dielectric loss (εi) in relation to the wavelength of the incident photon to ascertain the relaxation time (τ).87 Fig. 15 illustrates the plot of (εi) as a function of the cubic of photon wavelength (λ3) for all films of polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) and PVA/Zn-metal complex composites. The time constant (relaxation time) τ can be ascertained by analyzing the gradient of the plot of εi against cubic wavelength λ3 and by utilizing the calculated value of N/m* derived from the following equation:
 | (11) |
In addition, the optical mobility parameter (μopt); optical resistivity, which refers to the measurement of the resistance of a material to the flow of light (ρopt); and the plasma frequency ωp using the Drude free electron model can be determined by considering the ratio term N/m*, the electronic charge e, and the electric permittivity of air εo.87 The calculated values of optical mobility refer to the ability of particles or molecules to move under the influence of light (μopt) and optical resistivity (ρopt), and the frequency of plasma ωp is illustrated in Table 7.
 | (12) |
 | (13) |
 | (14) |
| Sample designation | τ × 10−12 s | μopt | ρopt × 10−8 Ohm m | Nc × 1025 | ωp × 1029 Hz |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PVZMC0 | 2.6642 | 0.4 | 31.5772 | 4.89 | 1.4107 |
| PVZMC1 | 20.3978 | 3.64 | 0.7797 | 20.20 | 6.3482 |
| PVZMC2 | 10.6577 | 2.51 | 0.7250 | 30.43 | 9.8749 |
| PVZMC3 | 10.5985 | 2.42 | 0.7017 | 30.67 | 10.5803 |
| PVZMC4 | 0.9858 | 1.49 | 0.9226 | 40.53 | 13.0490 |
The light beam is slowed down through sheets of polymer composite with substantially greater refractive indices, leading to the low values of τ, μopt, and ρopt. After adding the Zn-metal complex, the electron's wp jumped from 1.41 × 1029 Hz to 1.304 × 1030 Hz. The plasma frequency similarly increases when the Zn-metal complex increases, which can be attributed to the increase in carrier concentration N, assuming that the effective mass m* remains constant.5,6 The quantitative measurements of these parameters for polymer composites are crucial for recognizing their suitability in optical devices.88
4.4. Non-linear optical (NLO) properties
Nonlinear optics is a modern and adaptable scientific area that explains how light interacts with matter by showing how induced polarization changes nonlinearly in response to external electric and magnetic fields. Nonlinear optical (NLO) phenomena occur when a substance emits electromagnetic radiation with different amplitudes, phases, and frequencies. Medium polarization (P) occurs when valence electrons transfer charges to atoms in the medium due to the induced electric field as light travels through the medium. The equation shows that an electric field's strength is directly proportional to the degree of polarization in a given medium.89| p = εoχ(1)E + εoχ(2)E2 + εoχ(3)E3 +… | (15) |
Vacuum dielectric constant (εo), applied electric field strength (E), and macroscopic polarization strength (P) are all used in the preview equation; χ(1), χ(2) and χ(3) are the first, second and third-order linear susceptibilities that refer to the measure of the response of a material to an applied electric field of EM radiation, which is directly proportional to the field strength.90 Fig. 16 shows the application of the nonlinear optics (NLO). From the figure, it can be understood that the NLO has impacted the development of many fields of science that are too crucial to be emphasized.91
Doping PVA with Zn-metal complex techniques can significantly improve the optical linear and non-linear characteristics of these composites. The variation in the band gap resulting from doping is caused by the creation of defect states within the band gap, which leads to a drop in the band gap or the elimination of inherent defect states in the samples, resulting in a decrease in the band gap.92 By analyzing the graphs, we can ascertain the values of χ(1) (linear optical susceptibility) and χ(3) (third-order nonlinear optical susceptibility) by drawing a straight line from the plateau region to the y-axis, as shown in Fig. 17. The values of χ(1) are illustrated in Table 8. The linear optical parameters χ(1) were also determined using the Wemple and DiDomenico (W–D) model for a PVA system doped with metal complexes. The increase in the value of χ(1) is correlated with the presence of transition metals in the PVA polymer matrix. This phenomenon is associated with the dependence of the refractive index on the energy of the incident photons.91
 | (16) |
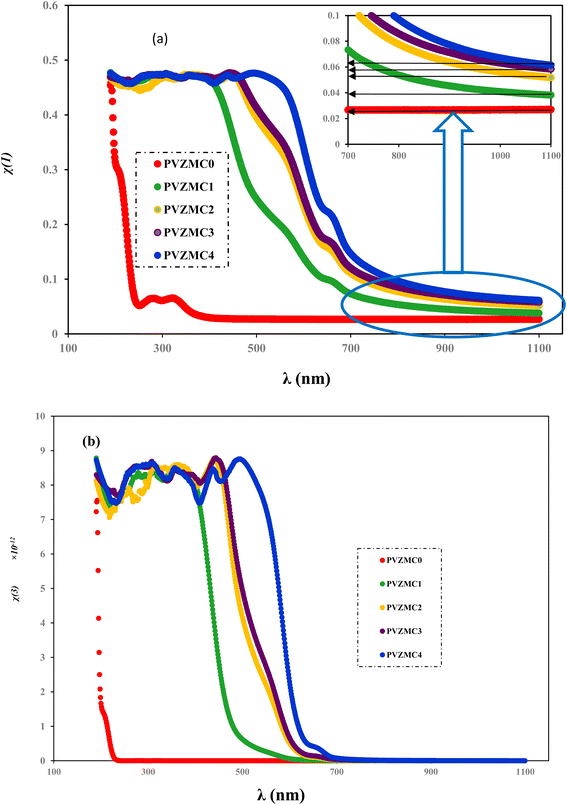 | ||
| Fig. 17 Linear and non-linear plots of (a) χ(1) and (b) χ(3) vs. λ for the pure PVA and PVA/Zn-metal complex films. | ||
| System designation | χ(1) (graph) | χ(1) (W–D) | nNL × 10−12 |
|---|---|---|---|
| PVZMC0 | 0.025 | 0.0217 | 0.011 |
| PVZMC1 | 0.043 | 0.0286 | 0.07 |
| PVZMC2 | 0.050 | 0.0375 | 0.125 |
| PVZMC3 | 0.055 | 0.0428 | 0.17 |
| PVZMC4 | 0.061 | 0.0431 | 0.185 |
The values of the linear parameter χ(1), the nonlinear parameter χ(3) and nNL are presented in Table 8. Higher values of χ(1) are observed for the PVA/Zn-metal complex, as depicted in Fig. 17a. Increased Zn-metal concentrations result in more particles that absorb electromagnetic waves, thus enhancing the polarization of the polymer sheets and improving the nonlinear characteristics. As the energy gap narrowed, the nonlinear characteristics of the polymeric composites may improve. The values of optical susceptibilities and nNL of composites are greater than those of pure PVA. Hence, the hybrid films could be utilized in nonlinear optoelectronic devices. It is interesting to mention that the higher values of nNL and χ(3) indicate the suitability of PVA![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) Zn-metal complex composites for utilization in nonlinear optical systems.93 Fig. 18 shows the relationship between the non-linear refractive index and photon energy.
Zn-metal complex composites for utilization in nonlinear optical systems.93 Fig. 18 shows the relationship between the non-linear refractive index and photon energy.
We employed two parameters to characterize the optical transitions of electrons in the PVA/Zn-metal complex composite films: the surface energy loss function (SELF) and the volume energy loss function (VELF), which show an electron transition at high and low wavelengths in bulk materials. The SELF and VELF are of high interest because they are related to microscopic phenomena inside the materials, and they can be deduced from optical dielectric parameters. The values of the SELF and VELF were determined utilizing detailed relationships with the εr and εi components of the dielectric constants:
 | (17) |
 | (18) |
Fig. 19 shows that the SELF and VELF are altered due to changes in Zn-metal complex concentrations, resulting in a modification of electron transition energy. The increase in SELF and VELF signifies a reduction in vacant energy levels produced within the host band gap of the PVA. Thus, the presence of many new energy states assigned to the added Zn-metal complex increases the probability of light–matter interaction. The VELF function values had greater magnitudes than the SELF values, as shown in Fig. 19, because the bulk contains more electrons than the surface. This demonstrated that doping can alter the transition energy of electrons.94
 | ||
| Fig. 19 (a) SELF and (b) VELF vs. photon energy functions for the PVA and PVA/Zn-metal complex films. | ||
5. Conclusions
The main findings of this study are that polymer composites based on green-synthesized metal complexes are guaranteed to reduce the optical band gap. Dyes from green tea are sufficient to capture dangerous heavy metal ions and transfer them to safe precipitated solid metal complexes. The FTIR results establish that Zn metal is surrounded by numerous functional groups that are suitable for complexation with polar groups of polar polymers. The XRD and FTIR outcomes confirm strong interaction among functional groups of the polymer and Zn-metal complex particles. The primary finding of this study is the production of amorphous polymer composites that closely align with the energy band gap of semiconductors. These composites have significant relevance for use in optoelectronic devices. The X-ray diffraction results and the Urbach energy parameter demonstrate the transition of the semicrystalline phase of PVA to an amorphous phase. The values of the Eu increased from 0.2654 to 0.4445 eV as the Zn-metal complex amount increased from 9 to 36 mL. The addition of metal complexes caused a shift in the dispersion behavior of the refractive index of PVA towards longer wavelengths. The refractive index, the static refractive index and non-linear refractive index increase from (1.1553 to 1.3569), (1.128 to 1.2417) and (0.011 to 0.185) by the incorporation of PVA with the metal complex. The Tauc model was employed to determine the most likely type of electron transition. Increased density of states N/m* within the valence band could result from adding a Zn-metal complex to the host PVA matrix. The dispersion energy, third-order optical susceptibility and nonlinear refractive index increased with the increase in Zn-metal complex concentration. The increase in SELF and VELF signifies that new energy states assigned to the added Zn-metal complex increase the probability of light–matter interaction; thus, more losses were expected in doped composite films. Due to advancements in enhanced linear and nonlinear optical characteristics, PVA composite films can be utilized in optical and optoelectronic devices.Data availability
Data will be available from the corresponding author upon request.Author contributions
Dana S. Muhammad: methodology, investigation, analysis, validation, writing – original draft. Dara M. Aziz: validation, supervision, project administration, writing – review & editing. Shujahadeen Aziz: conceptualization, writing – review & editing, supervision, project administration.Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support, facility and infrastructures provided for this study from the University of Sulaimani and the University of Raparin.References
- A. M. Abd-Elnaiem, M. Rashad, T. A. Hanafy and N. M. Shaalan, Improvement of Optical Properties of Functionalized Polyvinyl Alcohol-Zinc Oxide Hybrid Nanocomposites for Wide UV Optoelectronic Applications, J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater., 2023, 33, 2429–2444, DOI:10.1007/s10904-023-02616-w.
- R. Jansi, B. Vinay, M. S. Revathy, V. Aruna Janani, P. Sasikumar and M. Abbas, Investigation on polyvinyl alcohol and sodium alginate blend matrix with ammonium nitrate conducting electrolytes for electrochemical applications, J. Saudi Chem. Soc., 2023, 27, 101743, DOI:10.1016/j.jscs.2023.101743.
- M. Aslam, M. A. Kalyar and Z. A. Raza, Polyvinyl alcohol: a review of research status and use of polyvinyl alcohol based nanocomposites, Polym. Eng. Sci., 2018, 58, 2119–2132, DOI:10.1002/pen.24855.
- A. H. A. Darwesh, P. A. Mohammed, S. M. Mamand, S. A. Hussen, S. B. Aziz and M. A. Brza, et al., Investigation of Structural and Optical Characteristics of Biopolymer Composites Based on Polyvinyl Alcohol Inserted with PbS Nanoparticles, Coatings, 2023, 13, 578, DOI:10.3390/coatings13030578.
- K. A. Abdalkarim, S. B. Aziz, R. T. Abdulwahid, S. M. Alshehri, T. Ahamad and J. M. Hadi, et al., Synthesis of Hg metal complex and its application to reduce the optical band gap of polymer, Arabian J. Chem., 2021, 14, 103215, DOI:10.1016/j.arabjc.2021.103215.
- M. Bulinski, Metal doped PVA films for opto-electronics-optical and electronic properties, an overview, Molecules, 2021, 26(10), 2886, DOI:10.3390/molecules26102886.
- K. M. Gnana, N. Krishna Jyothi, K. Samatha, M. P. Rao and V. B. V. N. Prasad, Studies on optical properties of PVA based complex polymer electrolyte, Rasayan J. Chem., 2021, 14, 760–767, DOI:10.31788/RJC.2021.1425964.
- J. Gaume, P. Wong-Wah-Chung, A. Rivaton, S. Thérias and J. L. Gardette, Photochemical behavior of PVA as an oxygen-barrier polymer for solar cell encapsulation, RSC Adv., 2011, 1, 1471–1481, 10.1039/c1ra00350j.
- S. B. Aziz, Modifying Poly(Vinyl Alcohol) (PVA) from Insulator to Small-Bandgap Polymer: A Novel Approach for Organic Solar Cells and Optoelectronic Devices, J. Electron. Mater., 2016, 45, 736–745, DOI:10.1007/s11664-015-4191-9.
- M. E. Munawer, Human health and environmental impacts of coal combustion and post-combustion wastes, J. Sustain. Min., 2018, 17, 87–96, DOI:10.1016/j.jsm.2017.12.007.
- N. Zabat, Green complexation for removal of Ni2+ from synthetic effluents by a nanomaterial polyoxometalate, Curr. Res. Green Sustainable Chem., 2022, 5, 100243, DOI:10.1016/j.crgsc.2021.100243.
- A. M. Manea, I. Rau, F. Kajzar and A. Meghea, Fluorescence, spectroscopic and NLO properties of green tea extract in deoxyribonucleic acid, Opt. Mater., 2013, 36, 140–145, DOI:10.1016/j.optmat.2013.04.016.
- S. B. Aziz, O. G. Abdullah, A. M. Hussein and H. M. Ahmed, From Insulating PMMA Polymer to Conjugated Double Bond Behavior: Green Chemistry as a Novel Approach to Fabricate Small Band Gap Polymers Shujahadeen, Polymers, 2017, 9, 1–15, DOI:10.3390/polym9110626.
- A. Karabchevsky, A. Katiyi, A. S. Ang and A. Hazan, On-chip nanophotonics and future challenges, Nanophotonics, 2020, 9, 3733–3753, DOI:10.1515/nanoph-2020-0204.
- P. Maji, R. B. Choudhary and M. Majhi, Structural, optical and dielectric properties of ZrO2 reinforced polymeric nanocomposite films of polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA), Optik, 2016, 127, 4848–4853, DOI:10.1016/j.ijleo.2016.02.025.
- A. A. Ebnalwaled and A. Thabet, Controlling the optical constants of PVC nanocomposite films for optoelectronic applications, Synth. Met., 2016, 220, 374–383, DOI:10.1016/j.synthmet.2016.07.006.
- S. Mahendia, A. K. Tomar, R. P. Chahal, P. Goyal and S. Kumar, Optical and structural properties of poly(vinyl alcohol) films embedded with citrate-stabilized gold nanoparticles, J. Phys. D Appl. Phys., 2011, 44(20), 205105, DOI:10.1088/0022-3727/44/20/205105.
- H. Kneiding, R. Lukin, L. Lang, S. Reine, T. B. Pedersen and R. De Bin, et al., Deep learning metal complex properties with natural quantum graphs, Digital Discovery, 2023, 2, 618–633, 10.1039/d2dd00129b.
- E. Wächtler, R. Gericke, E. Brendler, B. Gerke, T. Langer and R. Pöttgen, et al., Group 10-group 14 metal complexes [E-TM]IV: the role of the group 14 site as an L, X and Z-type ligand, Dalton Trans., 2016, 45, 14252–14264, 10.1039/c6dt01621a.
- S. B. Aziz, M. M. Nofal, M. A. Brza, N. M. Sadiq, E. M. A. Dannoun and K. K. Ahmed, et al., Innovative Green Chemistry Approach to Synthesis of Sn2+-Metal Complex and Design of Polymer Composites with Small Optical Band Gaps, Molecules, 2022, 27(6), 1965, DOI:10.3390/molecules27061965.
- V. V. Vodnik, D. K. Božanić, E. Džunuzović, J. Vuković and J. M. Nedeljković, Thermal and optical properties of silver-poly(methylmethacrylate) nanocomposites prepared by in-situ radical polymerization, Eur. Polym. J., 2010, 46, 137–144, DOI:10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2009.10.022.
- A. P. Reverberi, M. Vocciante, E. Lunghi, L. Pietrelli and B. Fabiano, New trends in the synthesis of nanoparticles by green methods, Chem. Eng. Trans., 2017, 61, 667–672, DOI:10.3303/CET1761109.
- S. S. Hassan, S. K. Ibrahim, M. A. Mahmoud and M. F. Alias, Synthesis and characterization of some metal complexes with new ligand(C15H10N4O7SCl) & theoretical treatment, Syst. Rev. Pharm., 2020, 11, 747–753, DOI:10.31838/srp.2020.12.119.
- R. K. H. Al-Daffay and A. A. S. Al-Hamdani, Synthesis, Characterization, and Thermal Analysis of a New Acidicazo Ligand's Metal Complexes, Baghdad Sci. J., 2023, 20, 121–133, DOI:10.21123/bsj.2022.6709.
- E. J. Waheed, Synthesis and Characterization of Some Metals Complexes of {N-[(Benzoyl Amino)-Thioxo Methyl]Proline}, Al-Nahrain Journal of Science, 2012, 15(4), 1–10, DOI:10.22401/jnus.15.4.01.
- R. K. Hussain Al-Daffay and A. A. Salih Al-Hamdani, Synthesis and Characterization of Some Metals Complexes with New Acidicazo Ligand 4-[(2-Amino-4-Phenylazo)-Methyl]-Cyclohexane Carboxylic Acid, Iraqi J. Sci., 2022, 63, 3264–3275, DOI:10.24996/ijs.2022.63.8.2.
- S. A. Ajala, A. C. Tella, I. O. Adeoye, O. M. Olabemiwo, B. E. Abiola and S. A. Akintelu, Green and environmental friendly synthesis of copper (II) and nickel (II) complexes of rhodanine and its antibacterial effectiveness, Curr. Res. Green Sustainable Chem., 2022, 5, 100318, DOI:10.1016/j.crgsc.2022.100318.
- H. A. Widatalla, L. F. Yassin, A. A. Alrasheid, S. A. Rahman Ahmed, M. O. Widdatallah and S. H. Eltilib, et al., Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using green tea leaf extract, characterization and evaluation of antimicrobial activity, Nanoscale Adv., 2022, 4, 911–915, 10.1039/d1na00509j.
- D. S. Muhammed, M. A. Brza, M. M. Nofal, S. B. Aziz, S. A. Hussen and R. T. Abdulwahid, Optical dielectric loss as a novel approach to specify the types of electron transition: XRD and UV-vis as a non-destructive techniques for structural and optical characterization of peo based nanocomposites, Materials, 2020, 13, 1–15, DOI:10.3390/ma13132979.
- S. M. Chacko, P. T. Thambi, R. Kuttan and I. Nishigaki, Beneficial effects of green tea: A literature review, China's Med., 2010, 5, 1–9, DOI:10.1186/1749-8546-5-13.
- C. Das, B. Jain and K. Krishnamoorthy, Phenols from green tea as a dual functional coating to prepare devices for energy storage and molecular separation, Chem. Commun., 2015, 51, 11662–11664, 10.1039/c5cc03108g.
- S. Pradhan and R. C. Dubey, Beneficial Properties of Green Tea. Antioxidant Properties and Health Benefits of Green Tea, 2021, pp. 27–56 Search PubMed.
- S. Mahendia, A. K. Tomar and S. Kumar, Nano-Ag doping induced changes in optical and electrical behaviour of PVA films, Mater. Sci. Eng., B, 2011, 176, 530–534, DOI:10.1016/j.mseb.2011.01.008.
- E. M. Abdelrazek, I. S. Elashmawi, A. El-khodary and A. Yassin, Structural, optical, thermal and electrical studies on PVA/PVP blends filled with lithium bromide, Curr. Appl. Phys., 2010, 10, 607–613, DOI:10.1016/j.cap.2009.08.005.
- A. I. Barzic, M. Soroceanu, R. Rotaru, V. Harabagiu and R. C. Ciobanu, Optical dispersion characteristics of polyvinyl alcohol reinforced with a nanoceramic filler, Mater. Plast., 2020, 57, 1–7, DOI:10.37358/MP.20.1.5305.
- G. Hirankumar and N. Mehta, Effect of incorporation of different plasticizers on structural and ion transport properties of PVA-LiClO4 based electrolytes, Heliyon, 2018, 4(12) DOI:10.1016/j.heliyon.2018.e00992.
- S. B. Aziz, M. M. Nofal, M. A. Brza, N. M. Sadiq, E. M. A. Dannoun and K. K. Ahmed, et al., Innovative Green Chemistry Approach to Synthesis of Sn2+-Metal Complex and Design of Polymer Composites with Small Optical Band Gaps, Molecules, 2022, 27(6), 1965, DOI:10.3390/molecules27061965.
- M. A. Brza, S. B. Aziz, H. Anuar, F. Ali, E. M. A. Dannoun and S. J. Mohammed, et al., Tea from the drinking to the synthesis of metal complexes and fabrication of PVA based polymer composites with controlled optical band gap, Sci. Rep., 2020, 10, 1–17, DOI:10.1038/s41598-020-75138-x.
- C. N. Achilles, G. W. Downs, R. T. Downsl, R. V. Morris, E. B. Rampe, D. W. Ming and S. J. Chipera, et al., Amorphous phase characterization through X-ray diffraction profile modeling: Implications for amorphous phases in gale crater rocks and soils, in Lunar and Planetary Science Conference, no. JSC-E-DAA-TN53573, 20180002942, 2018 Search PubMed.
- M. Hema, S. Selvasekarapandian, D. Arunkumar, A. Sakunthala and H. Nithya, FTIR, XRD and ac impedance spectroscopic study on PVA based polymer electrolyte doped with NH4X (X = Cl, Br, I), J. Non-Cryst. Solids, 2009, 355, 84–90, DOI:10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2008.10.009.
- F. M. Ali, Structural and optical characterization of [(PVA:PVP)-Cu2+] composite films for promising semiconducting polymer devices, J. Mol. Struct., 2019, 1189, 352–359, DOI:10.1016/j.molstruc.2019.04.014.
- J. Zhao, D. Qian, L. Zhang, X. Wang and J. Zhang, Improved antioxidative and antibacterial activity of epigallocatechin gallate derivative complexed by zinc cations and chitosan, RSC Adv., 2024, 14, 10410–10415, 10.1039/d4ra00255e.
- Y. Wang, Y. Li, Z. Zhou, X. Zu and Y. Deng, Evolution of the zinc compound nanostructures in zinc acetate single-source solution, J. Nanopart. Res., 2011, 13, 5193–5202, DOI:10.1007/s11051-011-0504-y.
- M. Esteki, N. Memarbashi and J. Simal-Gandara, Classification and authentication of tea according to their harvest season based on FT-IR fingerprinting using pattern recognition methods, J. Food Compos. Anal., 2023, 115, 104995, DOI:10.1016/j.jfca.2022.104995.
- Y. J. Lee, E. Y. Ahn and Y. Park, Shape-dependent cytotoxicity and cellular uptake of gold nanoparticles synthesized using green tea extract, Nanoscale Res. Lett., 2019, 14, 1–14, DOI:10.1186/s11671-019-2967-1.
- S. Farooq and A. Sehgal, Scrutinizing antioxidant interactions between green tea and some medicinal plants commonly used as herbal teas, J. Food Biochem., 2019, 43, 1–12, DOI:10.1111/jfbc.12984.
- Y. Khan, A. Ahmad, N. Ahmad, F. R. Mir and G. Schories, Biogenic synthesis of a green tea stabilized PPy/SWCNT/CdS nanocomposite and its substantial applications, photocatalytic degradation and rheological behavior, Nanoscale Adv., 2020, 2, 1634–1645, 10.1039/d0na00029a.
- H. A. Widatalla, L. F. Yassin, A. A. Alrasheid, S. A. Rahman Ahmed, M. O. Widdatallah and S. H. Eltilib, et al., Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using green tea leaf extract, characterization and evaluation of antimicrobial activity, Nanoscale Adv., 2022, 4, 911–915, 10.1039/d1na00509j.
- N. Kavitha and P. V. Anantha Lakshmi, Synthesis, characterization and thermogravimetric analysis of Co(II), Ni(II), Cu(II) and Zn(II) complexes supported by ONNO tetradentate Schiff base ligand derived from hydrazino benzoxazine, J. Saudi Chem. Soc., 2017, 21, S457–S466, DOI:10.1016/j.jscs.2015.01.003.
- A. Kassem, L. Abbas, O. Coutinho, S. Opara, H. Najaf, D. Kasperek, K. Pokhrel, X. Li and S. Tiquia-Arashiro, Applications of Fourier Transform-Infrared spectroscopy in microbial cell biology and environmental microbiology: advances, challenges, and future perspectives, Front. Microbiol., 2023, 14, 1304081, DOI:10.3389/fmicb.2023.1304081.
- R. Zhang, Y. Wang, D. Ma, S. Ahmed, W. Qin and Y. Liu, Effects of ultrasonication duration and graphene oxide and nano-zinc oxide contents on the properties of polyvinyl alcohol nanocomposites, Ultrason. Sonochem., 2019, 59, 104731, DOI:10.1016/j.ultsonch.2019.104731.
- S. Mondal, S. Das and A. K. Nandi, A review on recent advances in polymer and peptide hydrogels, Soft Matter, 2020, 16, 1404–1454, 10.1039/c9sm02127b.
- P. B. Bhargav, V. M. Mohan, A. K. Sharma and V. V. R. N. Rao, Structural, electrical and optical characterization of pure and doped poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVA) polymer electrolyte films, Int. J. Polym. Mater. Polym. Biomater., 2007, 56, 579–591, DOI:10.1080/00914030600972790.
- R. Wahab, S. G. Ansari, Y. S. Kim, M. A. Dar and H. S. Shin, Synthesis and characterization of hydrozincite and its conversion into zinc oxide nanoparticles, J. Alloys Compd., 2008, 461, 66–71, DOI:10.1016/j.jallcom.2007.07.029.
- G. Y. Nagesh, K. Mahendra Raj and B. H. M. Mruthyunjayaswamy, Synthesis, characterization, thermal study and biological evaluation of Cu(II), Co(II), Ni(II) and Zn(II) complexes of Schiff base ligand containing thiazole moiety, J. Mol. Struct., 2015, 1079, 423–432, DOI:10.1016/j.molstruc.2014.09.013.
- B. Jinisha, A. F. Femy, M. S. Ashima and S. Jayalekshmi, Polyethylene oxide (PEO)/polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) complexed with lithium perchlorate (LiClO4) as a prospective material for making solid polymer electrolyte films, Mater. Today: Proc., 2018, 5, 21189–21194, DOI:10.1016/j.matpr.2018.06.518.
- A. Marzuki, V. Suryanti and A. Virgynia, Spectroscopic Study of Green Tea (Camellia sinensis) Leaves Extraction, IOP Conf. Ser.: Mater. Sci. Eng., 2017, 193(1), 012049, DOI:10.1088/1757-899X/193/1/012049.
- A. Sanaeifar, X. Huang, M. Chen, Z. Zhao, Y. Ji and X. Li, et al., Nondestructive monitoring of polyphenols and caffeine during green tea processing using Vis-NIR spectroscopy, Food Sci. Nutr., 2020, 8, 5860–5874, DOI:10.1002/fsn3.1861.
- Y. Huang, W. Dong, A. Sanaeifar, X. Wang, W. Luo and B. Zhan, et al., Development of simple identification models for four main catechins and caffeine in fresh green tea leaf based on visible and near-infrared spectroscopy, Comput. Electron. Agric., 2020, 173, 105388, DOI:10.1016/j.compag.2020.105388.
- M. Ranatunga, Y. Uwadaira, A. Ikehata and H. Ito, NIR Spectroscopic Determination of Polyphenol Content in Teas and Tea Extract at 2142 nm, Sens. Mater., 2021, 33, 4135–4145 CAS.
- G. Venkatesh, P. Vennila, S. Kaya, S. B. Ahmed, P. Sumathi and V. Siva, et al., Synthesis and Spectroscopic Characterization of Schiff Base Metal Complexes, Biological Activity, and Molecular Docking Studies, ACS Omega, 2024, 9(7), 8123–8138, DOI:10.1021/acsomega.3c08526.
- S. Basu, A. Hajra and A. Chattopadhyay, An ambient complexation reaction of zinc acetate and ascorbic acid leads to a new form of nanoscale particles with emergent optical properties, Nanoscale Adv., 2021, 3, 3298–3305, 10.1039/d1na00023c.
- H. Xu, M. Shi, C. Liang, S. Wang, C. Xia and C. Xue, et al., Effect of Zinc Acetate Concentration on Optimization of Photocatalytic Activity of p-Co3O4/n-ZnO Heterostructures, Nanoscale Res. Lett., 2018, 13, 1–16, DOI:10.1186/s11671-018-2604-4.
- Z. M. Elimat, A. M. Zihlif and M. Avella, Thermal and optical properties of poly(methyl methacrylate)/calcium carbonate nanocomposite, J. Exp. Nanosci., 2008, 3, 259–269, DOI:10.1080/17458080802603715.
- M. Aslam, M. A. Kalyar and Z. A. Raza, Fabrication of nano-CuO-loaded PVA composite films with enhanced optomechanical properties, Polym. Bull., 2021, 78, 1551–1571, DOI:10.1007/s00289-020-03173-9.
- S. B. Aziz, M. M. Nofal, H. O. Ghareeb, E. M. A. Dannoun, S. A. Hussen and J. M. Hadi, et al., Characteristics of poly(Vinyl alcohol) (PVA) based composites integrated with green synthesized Al3+-metal complex: Structural, optical, and localized density of state analysis, Polymers, 2021, 13(8), 1316, DOI:10.3390/polym13081316.
- R. Kalarani, M. Sankarganesh, G. G. V. Kumar and M. Kalanithi, Synthesis, spectral, DFT calculation, sensor, antimicrobial and DNA binding studies of Co(II), Cu(II) and Zn(II) metal complexes with 2-amino benzimidazole Schiff base, J. Mol. Struct., 2020, 1206, 127725, DOI:10.1016/j.molstruc.2020.127725.
- A. B. G. Trabelsi, A. M. Mostafa, F. H. Alkallas, W. B. Elsharkawy, A. N. Al-Ahmadi and H. A. Ahmed, et al., Effect of CuO Nanoparticles on the Optical, Structural, and Electrical Properties in the PMMA/PVDF Nanocomposite, Micromachines, 2023, 14(6), 1195, DOI:10.3390/mi14061195.
- S. B. Mallur, T. Czarnecki, A. Adhikari and P. K. Babu, Compositional dependence of optical band gap and refractive index in lead and bismuth borate glasses, Mater. Res. Bull., 2015, 68, 27–34, DOI:10.1016/j.materresbull.2015.03.033.
- S. Lorca, F. Santos and A. J. Fernández Romero, A review of the use of GPEs in zinc-based batteries. A step closer to wearable electronic gadgets and smart textiles, Polymers, 2020, 12(12), 2812, DOI:10.3390/polym12122812.
- S. B. Mallur, T. Czarnecki, A. Adhikari and P. K. Babu, Compositional dependence of optical band gap and refractive index in lead and bismuth borate glasses, Mater. Res. Bull., 2015, 68, 27–34, DOI:10.1016/j.materresbull.2015.03.033.
- H. M. Gayitri, M. Al-Gunaid and P. A. P. G. Siddaramaiah, Optical, structural and thermal properties of hybrid PVA/CaAl2ZrO6 nanocomposite films, Indian J. Eng. Mater. Sci., 2020, 27, 320–332, DOI:10.56042/ijems.v27i2.26781.
- M. Naseri, J. Jalilian and A. H. Reshak, Electronic and optical properties of paratellurite TeO2 under pressure: a first-principles calculation, Optik, 2017, 139, 9–15, DOI:10.1016/j.ijleo.2017.03.108.
- K. A. Abdalkarim, S. B. Aziz, R. T. Abdulwahid, S. M. Alshehri, T. Ahamad and J. M. Hadi, et al., Synthesis of Hg metal complex and its application to reduce the optical band gap of polymer, Arabian J. Chem., 2021, 14, 103215, DOI:10.1016/j.arabjc.2021.103215.
- A. G. Baker, The Study of Optical Energy Gap, Refractive Index, and Dielectric Constant of Pure and Doped Polyaniline with HCl and H2SO4 Acids, ARO-The Scientific Journal of Koya University, 2019, 7(1), 47–52, DOI:10.14500/aro.10483.
- E. Bacaksiz, M. Parlak, M. Tomakin, A. Özçelik, M. Karakiz and M. Altunbaş, The effects of zinc nitrate, zinc acetate and zinc chloride precursors on investigation of structural and optical properties of ZnO thin films, J. Alloys Compd., 2008, 466, 447–450, DOI:10.1016/j.jallcom.2007.11.061.
- V. Bhavsar and D. Tripathi, Study of biocompatible polymer blend films with tuneable band gap, Indian J. Pure Appl. Phys., 2020, 58, 795–803, DOI:10.56042/ijpap.v58i11.30235.
- M. Wang, J. Bai, K. Shao, W. Tang, X. Zhao and D. Lin, et al., Poly(vinyl alcohol) Hydrogels: The Old and New Functional Materials, Int. J. Polym. Sci., 2021, 2021(1), 2225426, DOI:10.1155/2021/2225426.
- A. Gupta, P. Caravan, W. S. Price, C. Platas-Iglesias and E. M. Gale, Applications for Transition-Metal Chemistry in Contrast-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging, Inorg. Chem., 2020, 59, 6648–6678, DOI:10.1021/acs.inorgchem.0c00510.
- N. K. Abbas, M. A. Habeeb and A. J. K. Algidsawi, Preparation of chloro penta amine cobalt(III) chloride and study of its influence on the structural and some optical properties of polyvinyl acetate, Int. J. Polym. Sci., 2015, 2015(1), 926789, DOI:10.1155/2015/926789.
- E. K. Shokr, W. S. Mohamed, A. G. Adam and H. M. Ali, Optical characterizations of lightly doped (PbS)1−xZnx thin films influenced by film thickness and annealing temperature for applications in highly intensive radiation systems, J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron., 2023, 34, 1–15, DOI:10.1007/s10854-023-11274-0.
- P. Sharma and S. C. Katyal, Effect of Ge addition on the optical band gap and refractive index of thermally evaporated As2Se3 thin films, Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng., 2008, 2008(1), 826402, DOI:10.1155/2008/826402.
- N. B. R. Kumar, V. Crasta and B. M. Praveen, Advancement in microstructural, optical, and mechanical properties of PVA (Mowiol 10-98) doped by ZnO nanoparticles, Phys. Res. Int., 2014, 2014(1), 742378, DOI:10.1155/2014/742378.
- A. Lukyanov, J. C. Golden and V. Lubchenko, Structural origin of the midgap electronic states and the Urbach tail in pnictogen-chalcogenide glasses, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2018, 122(33), 8082–8097, DOI:10.1021/acs.jpcb.8b05204.
- J. M. González-Leal, The Wemple-DiDomenico model as a tool to probe the building blocks conforming a glass, Phys. Status Solidi B, 2013, 250, 1044–1051, DOI:10.1002/pssb.201248487.
- E. W. Aslaksen, Optical Dispersion and the Structure of Solids, Phys. Rev. Lett., 1970, 24, 767–768, DOI:10.1103/PhysRevLett.24.767.
- A. M. Alsaad, Q. M. Al-Bataineh, A. A. Ahmad, Z. Albataineh and A. Telfah, Optical band gap and refractive index dispersion parameters of boron-doped ZnO thin films: A novel derived mathematical model from the experimental transmission spectra, Optik, 2020, 211, 164641, DOI:10.1016/j.ijleo.2020.164641.
- I. Saini, J. Rozra, N. Chandak, S. Aggarwal, P. K. Sharma and A. Sharma, Tailoring of electrical, optical and structural properties of PVA by addition of Ag nanoparticles, Mater. Chem. Phys., 2013, 139, 802–810, DOI:10.1016/j.matchemphys.2013.02.035.
- T. S. Soliman, S. A. Vshivkov and S. I. Elkalashy, Structural, linear and nonlinear optical properties of Ni nanoparticles – Polyvinyl alcohol nanocomposite films for optoelectronic applications, Opt. Mater., 2020, 107, 110037, DOI:10.1016/j.optmat.2020.110037.
- E. F. M. El-Zaidia, H. A. M. Ali, T. A. Hamdalla, A. A. A. Darwish and T. A. Hanafy, Optical linearity and bandgap analysis of Erythrosine B doped in polyvinyl alcohol films, Opt. Mater., 2020, 100, 109661, DOI:10.1016/j.optmat.2020.109661.
- E. Garmire, Nonlinear optics in daily life, Opt. Express, 2013, 21, 30532, DOI:10.1364/oe.21.030532.
- R. Bano, M. Asghar, K. Ayub, T. Mahmood, J. Iqbal and S. Tabassum, et al., A Theoretical Perspective on Strategies for Modeling High Performance Nonlinear Optical Materials, Front. Mater., 2021, 8, 1–24, DOI:10.3389/fmats.2021.783239.
- M. Sharma and S. K. Tripathi, Preparation and nonlinear characterization of zinc selenide nanoparticles embedded in polymer matrix, J. Phys. Chem. Solids, 2012, 73, 1075–1081, DOI:10.1016/j.jpcs.2012.04.007.
- M. I. A. Abdel Maksoud, A. S. Awed, R. Sokary and M. Bekhit, Effect of gamma irradiation on the free-standing polyvinyl alcohol/chitosan/Ag nanocomposite films: insights on the structure, optical, and dispersion properties, Appl. Phys. A: Mater. Sci. Process., 2021, 127(8), 619, DOI:10.1007/s00339-021-04776-3.
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2024 |