 Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleImproved thermoset materials derived from biobased terpene macromolecules via photo-crosslinking†
Dimitrios
Skoulas
 a,
Fernando
Bravo
a,
Fernando
Bravo
 a and
Arjan W.
Kleij
a and
Arjan W.
Kleij
 *ab
*ab
aInstitute of Chemical Research of Catalonia (ICIQ-CERCA), Barcelona Institute of Science & Technology (BIST), Av. Països Catalans 16, 43007 – Tarragona, Spain. E-mail: akleij@iciq.es
bCatalan Institute of Research and Advanced Studies (ICREA), Pg. Lluís Companys 23, 08010 – Barcelona, Spain
First published on 24th May 2024
Abstract
A series of cross-linked materials was prepared via photo-induced reactions involving olefin-containing precursors and dithiols. The resultant materials (M1–M6) combine conventional feedstock with biobased ones and allow to forge hybrid thermosets whose properties were investigated by a range of analytical methods. Materials M1 and M2 served as references to compare with the biohybrid ones (M3–M6), whose thermal, spectra and mechanical properties can be easily regulated by the type of bio-component added to the overall composition. The biobased compositions allowed to expand the range of thermal properties and the degree of stiffness as measured by TGA, DSC and DMA, with the overall material morphology not being significantly altered as evidenced by SEM.
Novel materials that are able to combat the negative side-effects of climate change and shortage of petroleum-based resources contribute to a more sustainable future. In parallel, if such materials can be forged with improved and more modular properties, and with significantly reduced carbon footprints compared to purely fossil-fuel derived ones, they will undoubtedly create a vast interest from both academic and industrial laboratories.1–4
One of the most promising strategies towards the establishment of new materials is the construction of novel plastics with improved and/or expanded properties. Plastic materials combine a plethora of features that render them of great use in every-day life and in industrial applications. Furthermore, they exhibit advanced material properties and can be easily formulated, while they are typically cheap to manufacture. Depending on their composition and behavior, they are categorized into two main groups viz. thermoplastics, which can be reprocessed again, and thermosets which cannot.5 Current and future efforts to produce better plastics are inspired by practices that lead to a circular use of macromolecules.6,7 Additionally, a lower dependence on petroleum-based chemicals can favorably affect the overall carbon footprint of polymeric materials.8
In this respect, biomass-based raw materials have shown to act as feedstock for the preparation of polymers that can (partially) replace or reduce the utilization of the traditional petroleum-based polymers highlighting an important breakthrough in the field of sustainable chemistry.9 Cross-linked polymers, that combine the advantages of thermoset and thermoplastic polymers while originating from renewable sources, have sparked increasing scientific interest surrounding their potential applications.10 Biobased polymers can be categorized mainly into two groups being either natural polymers or synthetic ones.11 Cellulose, lignin, starch are the most prominent examples of the first group, while synthetic biobased polymers can be derived from biobased precursors such as plant oils and amino acids.
One particular class of structurally diverse biomass-derived, chemical compounds are terpenes. Their relative abundance in nature combined with their chemical functionality makes them attractive for the design of materials with tunable mechanical, optical and thermal properties. In addition, many of these terpenes feature double bond functionalities which are suitable for epoxidation thereby furnishing new types of epoxy monomers, which serve towards the preparation of biobased polymers.12–16
A prominent and well-studied example within the known family of terpene oxides is limonene oxide (LO), which can be copolymerized with CO2 yielding poly(limonene carbonate)s (PLC) with high glass transitions.17–20 The advantages of its bio-origin, high level of functionality and depolymerization potential of PLC explain the increased efforts in using this polymer for various applications.21–23 Moreover, recently it was reported that the estimated cost for PLC production is similar to the production cost of the petroleum-based polystyrene adding further to its potential use beyond academia.24
Catalytic ring-opening copolymerization (ROCOP) of LO and carbon dioxide is the main method for the synthesis of PLC, while ring-opening polymerization (ROP) of its trans-cyclic carbonate is also feasible.23,25–28 In the ROCOP route, CO2 offers a an additional renewable C1 building block for the synthesis of PLC being both highly available and cheap. A crucial parameter for the successful polymerization of PLC is the presence of a suitable catalyst due to the sterically demanding nature of the terpene oxide monomers. Until now, only two effective catalysts have been reported in literature. In 2004, Coates reported Zn(II)BDI based catalysts that efficiently copolymerize LO and CO2.29 Further progress was achieved by our group when reporting the development of a binary Al(III) aminotriphenolate complex/PPNCl catalyst [PPNCl = bis(triphenylphosphine)iminium chloride], as high conversion of both stereoisomers of LO (cis and trans) could be achieved.30,31
The existence of pendent double bond in each monomeric unit of PLC offers a possibility for post-modification using thiol–ene click chemistry for cross-linking reactions changing the final properties of the material.18,32,33 This underlines the use of PLC for preparing new types of materials. Further to this, Greiner et al. investigated materials resulting from blending PLC with commodity polymers in order to explore the possibility of new materials.34 However, a broader study centered on the covalent incorporation of PLC into other petroleum- or plant-based materials would be useful in this respect.
Herein we present novel plastic materials based on the covalent incorporation of PLC within either petroleum-based or plant-based matrices without changing the application potential to create thermoset materials. We considered both divinylbenzene (DVB) and 1,7-octadiene as fossil-fuel feedstock (Scheme 1) as these have been frequently used as cross-linking agents and would a priory be suitable co-reagents for PLC (Scheme 1) thereby increasing the overall bio-content of such hybrid structures. Second, we also wished to evaluate combinations of PLC with either geraniol or limonene (having a plant-based origin) to forge materials with a higher degree of bio-content. To this end, we thus examined well-established radical-initiated copolymerization of both of these aforementioned substrate combinations in the presence of phenyl-bis(2,4,6-trimethylbenzoyl)phosphine oxide (BAPO) as photo-initiator with a constant 20 wt% of PLC in each of the resultant materials. The cured plastic materials (through thiol–ene chemistry except for the DVB-based materials) were examined by different analytical methods investigating their thermal and mechanical properties, and the results demonstrate that the properties of fossil-fuel commercial matrices can be improved and expanded. In parallel, we here also report novel bioplastics with plant-based feedstock that form rubber-like materials with superior mechanical and thermal properties compared to their parent materials.
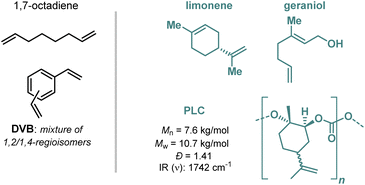 | ||
| Scheme 1 Substrates used in this work to create cross-linked biobased matrices. PLC stands for poly(limonene carbonate), DVB is divinyl benzene. | ||
Our overall objective is to exhibit the successful preparation of more sustainable bioplastics, in comparison with the 100% petroleum-based, existing ones. This emphasizes the potential of PLC to be used as an additive for the synthesis of cross-linked thermoset materials by covalent anchoring to existing fossil-fuel derived matrices. The combined advantageous features of PLC, being its bio-origin and chemical functionality (cf., pendent double bonds), make it an attractive choice as an additive for new, sustainable polymer and material development. DVB and 1,7-octadiene were chosen as representative examples of petroleum-based feedstock, while limonene and geraniol were also examined due to their related chemical structure and functionality compared to PLC and being characteristic examples of plant-based monomers. The overall approach should open up new avenues for the use of PLC and other types of bio-polycarbonates towards the creation of more sustainable thermosets.
Results and discussion
A standard procedure (see the Experimental section and ESI,† for details) for the cross-linking of all olefin-containing precursors and mixtures was used. As reference materials, cross-linked DVB and 1,7-octadiene (M1 and M2, respectively) were prepared, while combinations of DVB–PLC (M3), 1,7-octadiene–PLC (M4), limonene–PLC (M5) and geraniol–PLC (M6) were also investigated (Scheme 2). | ||
| Scheme 2 Schematic structures of the materials M1–M6 produced via direct or ethane-1,2-dithiol mediated photo-crosslinking. | ||
In order to prepare the different materials, all the components were mixed in a vial prior to their exposure to a lamp. The same preparation protocol was followed for all materials with the exception of M1 and M3, that did not require a crosslinker (i.e., ethane-1,2-dithiol) since it was possible to perform the cross-linking reaction without this additive. It is important to emphasize that in order to start the photo-initiated crosslinking, the overall reaction mixture needs to be homogeneous and PLC has to be fully dissolved into the mixture. In this respect, we found that a 20 wt% of PLC in the respective mixture was the highest possible amount to retain full homogeneity, as percentages such as 30% of PLC in all the studied matrices (see the ESI for details; Fig. S25–S28†) resulted in partially heterogeneous/insoluble mixtures, likely leading to unpredictable and non-reproducible photo-polymerizations. Thus, we selected 20 wt% of PLC for the each of the envisioned materials to reach the highest possible bio-content within the final bio-composites.
The double bond functionalities present in PLC and the other starting materials offers the possibility for photo-induced, random radical polymerization with or without the presence of an appropriate crosslinker (ethane-1,2-dithiol), thereby leading to cross-linked materials M1–M6. The covalently incorporation of PLC into the respective materials can be easily followed through IR spectroscopy (vide infra). BAPO was used as a reliable photo initiator since it undergoes homolytic α-cleavage at the carbonyl–phosphorus bond upon exposure to LED light at 405 nm![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 35,36 and it produces free-radicals with high efficiency, which promotes polymerization of vinyl monomers and double bond-containing compounds.37
35,36 and it produces free-radicals with high efficiency, which promotes polymerization of vinyl monomers and double bond-containing compounds.37
Another challenge is the characterization of the final materials in terms of their structure. All the synthesized bioplastics are insoluble in the typical organic solvents, which limited the in-depth characterization of their structure by standard spectral and chromatographic techniques. Despite this general observation, the insoluble character of the obtained materials M1–M6 offers as a possible advantage their exploitation in applications for which hydrophobic and/or insoluble materials are required such as in sealants or rubbers.
The cross-linking reactions were typically followed by IR spectroscopy as the absorption bands related to the double bonds of the involved substrates are highly diagnostic. Furthermore, in the hybrid materials with an increase bio-content (with PLC, limonene and/or geraniol), IR spectroscopy also allows to examine the stability of the polycarbonate as the linear carbonate group absorption typically falls in the region 1740–1760 cm−1.26,38,39
Fig. 1 shows two representative cases involving the synthesis of cross-linked materials M3 and M4 containing a DVB–PLC and 1,7-octadiene–PLC combination, respectively. In Fig. 1a, a comparative IR spectral analysis between the parent DVB and PLC, and the hybrid cross-linked M3 (DVB–PLC) shows that upon cross-linking the two components via photo-initiated radical addition, the main polycarbonate chain is unaffected as shown by a clear carbonate band at ν = 1744 cm−1 in the blue trace. Furthermore, the double bond absorption of the PLC around 1650 cm−1 (Fig. 1b, orange trace) for a larger part disappeared upon reaction, indicating a good-to-high level of C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C conversion. Both observations are in line with a successful cross-linking process.
C conversion. Both observations are in line with a successful cross-linking process.
The second case (Fig. 1c and d, M4) illustrates the cross-linking between 1,7-octadiene and PLC, with a clear presence of carbonate groups in the hybrid cross-linked material M4 after photo-irradiation (Fig. 1c, absorption at 1744 cm−1). In addition, C–H wagging peaks in the region 750–900 cm−1 can be found for parent PLC (Fig. 1d; orange trace), which after the cross-linking process are virtually lost. This is a strong indication that high C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C bond conversion in PLC had taken place.
C bond conversion in PLC had taken place.
Similar IR spectroscopic changes were observed for materials M5 and M6 (see the ESI† for details), and combined together it supports the overall efficacy of the used photo-induced cross-linking of various combinations of substrates with PLC to afford the partially biobased matrices M1–M6 under user-friendly process conditions. It should be noted that the attempted cross-linking of limonene and geraniol in the absence of PLC as co-substrate led to materials with lower cross-linking degrees and typically required longer reaction times as evidenced by their physical appearance and IR analysis, thus pointing at a beneficial effect of adding PLC as a promoting cross-linking agent (see the ESI† for further details).
Next, we turned our attention to characterize the different materials using other techniques. First, photos of M3–M6 show the different textures that are obtained after photo-cross-linking (Fig. 2a). The hybrids M3–M5 display solid materials with different degrees of flexibility and hardness (discussed further below), while M6 represents a softer and more bendable material. Since the prepared solutions were transferred in a Teflon based mould, the final biomaterials obtained their shape after light exposure. However, M6 was much softer, rubbery-like material (as indicated by DMA analysis, see Fig. S19 and S20 in the ESI†) and it was thus prepared inside the vial upon exposure to light. The other materials were processed in a complete “dog bone” shape (details in the ESI†). In order to investigate the influence of incorporating PLC into the cross-linked matrix, thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) was carried out for M1–M6 (selected and typical examples for M3 and M4 are shown in Fig. 2b–d). It is clear that pristine PLC has the lowest thermal stability with an onset decomposition at around 200 °C (orange traces in Fig. 2b). An earlier thermal transition (>70 °C) present in cross-linked DVB is retained in the DVB–PLC hybrid, while two further transitions (not present in cross-linked DVB) occur at around 245 and 390 °C.
These data seem to indicate a higher stability of the cross-linked PLC in M3 compared to the parent polymer. These transitions are not equally observed for M4–M6 (Fig. 2c and d), and for M4 a first onset is observed at 245 °C with a second one initiating at 330 °C. For M5 and M6, a first onset decomposition starts around 120 °C but compared with the parent PLC (Fig. 2d, orange trace) the rate of decomposition is much slower and requires a higher temperature to proceed. Thus, these latter data indicate as well that the hybrid structures M3–M6 show better overall thermal endurance than the polycarbonate PLC reference.
We also examined the materials M1–M6 by differential scanning calorimetry (DSC, see Fig. 3 for selected examples and the ESI† for further details). In all cases studied, we observed typical melting points for the cross-linked, hybrid polymer samples. For M4 (the 1,7-octadiene–PLC hybrid; Fig. 3a; data from the 3rd heating curve), the observed Tm was located at 79 °C, while for M6 (geraniol–PLC hybrid; Fig. 3b), a Tm at 91 °C was observed. For M3 based on DVB and PLC, an even higher and single Tm of 154 °C was detected (see the ESI†), while for M5 (the limonene–PLC hybrid, ESI†), a Tm was noted at 133 °C. Additionally, for M4 and M5 a second peak at lower temperature was noted (49.8 °C and 73.3 °C, respectively), which could suggest a separate, second phase or an additional structural change occurring at higher temperature.
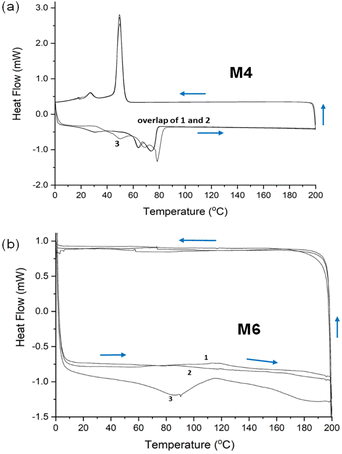 | ||
| Fig. 3 (a and b) Selected DSC traces for materials M4 and M6, respectively. The indices 1–3 refer to the consecutive heating curves in these DCS analyses. | ||
In order to gather information on the viscoelastic behavior of the newly prepared materials M1–M6, we carried out dynamic mechanical analysis (DMA). An example DMA result is provided in Fig. 4, for all other DMA results see the ESI† and Table 1. From a comparative analysis of the storage modulus E′ measured for M3 (DVB–PLC hybrid) and the parent M1 (Table 1, entries 1 vs. 3), a clear and significant increase in the stiffness of the hybrid material can be noted (269.0 → 482.2 MPa), being an increase of nearly 80%. An even larger effect was detected for the hybrid M4 (1,7-octadiene–PLC) compared to 1,7-octadiene itself (Table 1, entries 2 vs. 4), showing an increase of the storage modulus from 84.2 to 200.8 MPa (a 138% increase).
| M | Bio%a (wt%) | IRb (cm−1) |
T
d
5![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) c (°C) c (°C) |
T
m![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) d (°C) d (°C) |
T
g![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) e (°C) e (°C) |
E′![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) e (MPa) e (MPa) |
M c (g mol−1) | CDg (mol cm−3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a Calculated from the mass of each component introduced in the cross-linking experiment. Note that here no correction for the oxidation of the monomer LO in the case of PLC-based materials was applied. b Determined by IR spectroscopy (neat) providing the most diagnostic absorption bands. c Determined by TGA analysis, the Td5 stands for the decomposition temperature at 5 wt% loss. d Obtained from DSC analysis using the data from the 3rd heating curve. e Data extracted from the dynamic mechanical analysis (DMA) curves, see the ESI† for details. E′ is the he storage modulus expressed in MPa at 25 °C. f Molecular weight between crosslinks (Mc). g Crosslinking density (CD) was calculated by dividing the polymer density by Mc. | ||||||||
| M1 | 0 | 1630 | 419 | 149.3 | 122.5 | 269.0 | — | — |
| M2 | 0 | 920, 1640 | 297 | 87 | 69.2 | 84.2 | — | — |
| M3 | 13 | 1630, 1744 | 251 | 154.3 | 74.1 | 482.2 | 64 | 0.0166 |
| M4 | 12 | 788, 822, 887, 920, 1640, 1745 | 277 | 49.8, 78.5 | 56.9 | 200.8 | 5184 | 0.0002 |
| M5 | 65 | 1744 | 266 | 73.3, 133.3 | −1.8 | 26.3 | 317 | 0.0034 |
| M6 | 68 | 1744 | 201 | 90.5 | −28.6 | 0.034 | 173![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 220 220 |
6.5 × 10−6 |
For materials M5 and M6 based on combination of biocomponents PLC with limonene and geraniol, respectively, such comparisons were not feasible as the level of cross-linking did not provide materials useful for DMA analysis as evidenced by their physical inspection and IR spectroscopy (see the ESI†). For both M5 and M6 (Table 1, entries 5 and 6), the measured E′ values were substantially lower than those collected for M3 and M4, pointing at relatively flexible materials and indeed both were rubbery-like. The different relaxation processes in comparison to samples M3 and M4 indicates the high structural flexibility of the PLC/limonene-based material. Altogether, these different combinations of (bio)components with PLC allow to modulate the storage moduli over a wider range of values compared to their parent cross-linked materials, while introducing different degrees of bio-content of up to 68 wt%.
Additionally, it is important to stress the nature of the respective starting materials in relation to the properties of the final cross-linked materials, as these had markedly different mechanical properties despite adding the same amount of PLC. This agrees with the physical appearance of the final biohybrids, since M2 and M4 are opaque similar to M1 and M3, showing the strong influence of their crosslinked matrix. A direct relative comparison involving M5 and M6 is impossible since limonene and geraniol themselves could not be obtained as crosslinked materials without the addition of PLC, emphasizing the importance of its presence in the final composition.
Further to this, DMA analysis offers the opportunity to gather insight information about the molecular weight between crosslinks (Mc) and the crosslinking density (CD), exploiting the obtained data of the storage modulus at the rubbery state.40,41 A quantitative calculation of those parameters was processed for all the samples that had PLC crosslinked to the petroleum- or plant-based precursors (i.e., M3–M6) to investigate its crosslinking density. For M1 and M2, it was not possible to detect the plateau zone at the rubbery state. Comparison of the crosslinking densities between materials M3 and M4 (petroleum-based matrix) and M5 and M6 (plant-based matrix), can shed light on the relationship between this parameter with the viscoelastic behavior of the respective samples.
From Table 1 it is clear that material M3 has the highest crosslinking density at the lowest molecular weight between the crosslinks. This seems to relate well with the storage modulus data, as M3 also possesses the highest value among the series M3–M6. Comparatively, M6 has both the lowest crosslinking density and the lowest storage modulus, while having the highest molecular weight between the crosslinks. The cyclic nature of DVB and limonene, and the different, linear structure of 1,7-octadiene and geraniol may be partially responsible for the noted differences in the series M3–M6.
Finally, we evaluated the overall morphology of the materials by scanning electron microscopy (SEM, Fig. 5). Selected SEM images are presented for the parent material M1 and its co-cross-linked biohybrid M3. Judging from the representative images in Fig. 5, the overall crosslinked structures do not show significant changes when adding PLC as a component, which suggest that the use of PLC should not imply any practical objection when combined with typical fossil-fuel based substrates such as DVB and 1,7-octadiene (or others) to create new types of hybrid materials. Furthermore, the combination of PLC with the other biobased precursors upon crosslinking results into a uniformal surface of the final materials. Careful examination of the SEM photos shows no visible indication of porosity and a smooth surface area in the networks for all samples. In addition, the SEM photos reveal a homogenous network for all the samples M1–M6 with and without the presence of PLC. The observation of dense polymer networks is made for all the samples independently of the presence of PLC.
 | ||
| Fig. 5 Selected SEM images of the materials M1 and M3 with an inserted scale. For more details and images, see the ESI.† | ||
Conclusions
In summary, we have prepared a family of new hybrid materials by using a practical and straightforward photo-cross-linking approach. The hybrid materials contain different degrees of biobased content (PLC, geraniol, limonene; 12–68%) and were analysed by a range of techniques with their data compared to the parent cross-linked materials where possible. From the data obtained, we conclude that the addition of PLC and its cross-linking proceeds with success and the storage modulus (E′) can be markedly improved as shown in materials M3 and M4. Biobased combinations of PLC with limonene and geraniol offer additional possibilities to access materials with a lower stiffness (rubbery-like), and higher degrees of overall bio-content. This work further demonstrates the potential of biobased polycarbonates such as PLC42 as possible drop-in additives towards the creation of more sustainable thermoset materials.Experimental section
Typical cross-linking experiment
0.80 g of substrate (DVB technical grade 80% Sigma-Aldrich; mixture of regio-isomers, 1,7-octadiene, limonene or geraniol) and 0.20 g of PLC were weighed into a screw-capped glass vial. Note that in the case of DVB-containing reaction mixtures, the cross-linking was done in the absence of ethane-1,2-dithiol, while in all other cases this cross-linking agent was added in stoichiometric amount with respect to the double bonds present (ratio 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1). Then 0.010 g of BAPO was added following vigorous stirring, and the content of the vial was transferred in a Teflon based mould and a 405 nm (0.5 mW cm−2) lamp was used to apply light over the mould. After 20 minutes, the final composite material was formed (M3–M6), and removed from the mould. DVB and 1,7-octadiene were also separately cross-linked for comparative reasons following the same protocol without adding PLC, providing as such cross-linked reference materials M1 and M2.
1). Then 0.010 g of BAPO was added following vigorous stirring, and the content of the vial was transferred in a Teflon based mould and a 405 nm (0.5 mW cm−2) lamp was used to apply light over the mould. After 20 minutes, the final composite material was formed (M3–M6), and removed from the mould. DVB and 1,7-octadiene were also separately cross-linked for comparative reasons following the same protocol without adding PLC, providing as such cross-linked reference materials M1 and M2.
Author contributions
DS carried out all the experiments and the analytical interpretation, AWK assisted DS during the project with feedback and scientific input, DS and AWK designed the project, while FB provided feedback on the results and wrote the manuscript in collaboration with DS and AWK.Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.Acknowledgements
The authors thank the Cerca Program/Generalitat de Catalunya, ICREA, MINECO (PID2020-112684GB-100 and Severo Ochoa Excellence Accreditation 2020–2023 CEX2019-000925-S) and AGAUR (2021-SGR-00853) for support. This work has further received funding from the European Union's Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under Marie Skłodowska-Curie grant agreement no. 801342 (Tecniospring INDUSTRY) and the Government of Catalonia's Agency for Business Competitiveness (ACCIÓ: COMBILOOP, ACE026/21/000087). We thank Prof. Silvia de la Flor from the Universitat Rovira i Virgili (Tarragona; Spain) for the DMA analyses and interpretation. The CTD unit of ICIQ is acknowledged for the TGA and DSC analyses.Notes and references
- M. Yang, L. Chen, J. Wang, G. Msigwa, A. I. Osman, S. Fawzy, D. W. Rooney and P. S. Yap, Circular economy strategies for combating climate change and other environmental issues, Environ. Chem. Lett., 2023, 21, 55–80 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Chen, L. Wang, D. W. Cho, D. C. W. Tsang, L. Tong, Y. Zhou, J. Yang, Q. Hu and C. S. Poon, Sustainable stabilization/solidification of municipal solid waste incinerator fly ash by incorporation of green materials, J. Cleaner Prod., 2019, 222, 335–343 CrossRef CAS.
- R. W. Bentley, Global oil and gas depletion: An overview, Energy Policy, 2002, 30, 189–205 CrossRef.
- G. Chyr and J. M. DeSimone, Review of high-performance sustainable polymers in additive manufacturing, Green Chem., 2023, 25, 453–466 RSC.
- S.-A. Park, H. Jeon, H. Kim, S.-H. Shin, S. Choy, D. S. Hwang, J. M. Koo, J. Jegal, S. Y. Hwang, J. Park and D. X. Oh, Sustainable and recyclable super engineering thermoplastic from biorenewable monomer, Nat. Commun., 2019, 10, 2601 CrossRef PubMed.
- J. G. Rosenboom, R. Langer and G. Traverso, Bioplastics for a circular economy, Nat. Rev. Mater., 2022, 7, 117–137 CrossRef PubMed.
- T. Keijer, V. Bakker and J. Chris Slootweg, Circular chemistry to enable a circular economy, Nat. Chem., 2019, 11, 190–195 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J.-G. Rosenboom, R. Langer and G. Traverso, Bioplastics for a circular economy, Nat. Rev. Mater., 2022, 7, 117–137 CrossRef PubMed.
- R. A. Sheldon, Green and sustainable manufacture of chemicals from biomass: State of the art, Green Chem., 2014, 16, 950–963 RSC.
- S. Kamarulzaman, Z. M. Png, E. Q. Lim, I. Z. S. Lim, Z. Li and S. S. Goh, Covalent adaptable networks from renewable resources: Crosslinked polymers for a sustainable future, Chem, 2023, 9, 2771–2816 CAS.
- Z. Wang, M. S. Ganewatta and C. Tang, Sustainable polymers from biomass: Bridging chemistry with materials and processing, Prog. Polym. Sci., 2020, 101, 101197 CrossRef CAS.
- F. Della Monica and A. W. Kleij, From terpenes to sustainable and functional polymers, Polym. Chem., 2020, 11, 5109–5127 RSC.
- C. Wahlen and H. Frey, Anionic Polymerization of Terpene Monomers: New Options for Bio-Based Thermoplastic Elastomers, Macromolecules, 2021, 54, 7323–7336 CrossRef CAS.
- M. F. M. G. Resul, A. Rehman, A. M. L. Fernández, V. C. Eze and A. P. Harvey, Continuous process for the epoxidation of terpenes using mesoscale oscillatory baffled reactors, Chem. Eng. Process., 2022, 177, 108998 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. M. Ahmat, S. Madadi, L. Charbonneau and S. Kaliaguine, Epoxidation of terpenes, Catalysts, 2021, 11, 847 CrossRef.
- A. Brandolese, D. H. Lamparelli, M. A. Pericàs and A. W. Kleij, Synthesis of Biorenewable Terpene Monomers Using Enzymatic Epoxidation under Heterogeneous Batch and Continuous Flow Conditions, ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng., 2023, 11, 4885–4893 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- F. Parrino, A. Fidalgo, L. Palmisano, L. M. Ilharco, M. Pagliaro and R. Ciriminna, Polymers of Limonene Oxide and Carbon Dioxide: Polycarbonates of the Solar Economy, ACS Omega, 2018, 3, 4884–4890 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- O. Hauenstein, S. Agarwal and A. Greiner, Bio-based polycarbonate as synthetic toolbox, Nat. Commun., 2016, 7, 11862 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- O. Hauenstein, M. Reiter, S. Agarwal, B. Rieger and A. Greiner, Bio-based polycarbonate from limonene oxide and CO2 with high molecular weight, excellent thermal resistance, hardness and transparency, Green Chem., 2016, 18, 760–770 RSC.
- C. Li, R. J. Sablong and C. E. Koning, Synthesis and characterization of fully-biobased α,ω-dihydroxyl poly(limonene carbonate)s and their initial evaluation in coating applications, Eur. Polym. J., 2015, 67, 449–458 CrossRef CAS.
- V. B. Moreira, C. Alemán, J. Rintjema, F. Bravo, A. W. Kleij and E. Armelin, A Biosourced Epoxy Resin for Adhesive Thermoset Applications, ChemSusChem, 2022, 15, e202102624 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- V. Bonamigo Moreira, J. Rintjema, F. Bravo, A. W. Kleij, L. Franco, J. Puiggalí, C. Alemán and E. Armelin, Novel Biobased Epoxy Thermosets and Coatings from Poly(limonene carbonate) Oxide and Synthetic Hardeners, ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng., 2022, 10, 2708–2719 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. H. Lamparelli, A. Villar-Yanez, L. Dittrich, J. Rintjema, F. Bravo, C. Bo and A. W. Kleij, Bicyclic Guanidine Promoted Mechanistically Divergent Depolymerization and Recycling of a Biobased Polycarbonate, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2023, 62, e202314659 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. Zhang, E. A. del Rio-Chanona, J. L. Wagner and N. Shah, Life cycle assessments of bio-based sustainable polylimonene carbonate production processes, Sustainable Prod. Consumption, 2018, 14, 152–160 CrossRef.
- M. Lanzi and A. W. Kleij, Recent advances in the synthesis and polymerization of new CO2-based cyclic carbonates, Chin. J. Chem., 2024, 42, 430–443 CrossRef CAS.
- A. J. Kamphuis, F. Picchioni and P. P. Pescarmona, CO2-fixation into cyclic and polymeric carbonates: Principles and applications, Green Chem., 2019, 21, 406–448 RSC.
- S. Paul, Y. Zhu, C. Romain, R. Brooks, P. K. Saini and C. K. William, Ring-opening copolymerization (ROCOP): synthesis and properties of polyesters and polycarbonates, Chem. Commun., 2015, 51, 6459–6479 RSC.
- S. J. Poland and D. J. Darensbourg, A quest for polycarbonates provided: Via sustainable epoxide/CO2 copolymerization processes, Green Chem., 2017, 19, 4990–5011 RSC.
- C. M. Byrne, S. D. Allen, E. B. Lobkovsky and G. W. Coates, Alternating copolymerization of limonene oxide and carbon dioxide, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2004, 126, 11404–11405 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. Peña Carrodeguas, J. González-Fabra, F. Castro-Gómez, C. Bo and A. W. Kleij, AlIII-Catalysed Formation of Poly(limonene)carbonate: DFT Analysis of the Origin of Stereoregularity, Chem. – Eur. J., 2015, 21, 6115–6122 CrossRef PubMed.
- N. Kindermann, A. Cristòfol and A. W. Kleij, Access to Biorenewable Polycarbonates with Unusual Glass-Transition Temperature (Tg) Modulation, ACS Catal., 2017, 7, 3860–3863 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Stößer, C. Li, J. Unruangsri, P. K. Saini, R. J. Sablong, M. A. R. Meier, C. K. Williams and C. Koning, Bio-derived polymers for coating applications: Comparing poly(limonene carbonate) and poly(cyclohexadiene carbonate), Polym. Chem., 2017, 8, 6099–6105 RSC.
- C. Martín and A. W. Kleij, Terpolymers Derived from Limonene Oxide and Carbon Dioxide: Access to Cross-Linked Polycarbonates with Improved Thermal Properties, Macromolecules, 2016, 49, 6285–6295 CrossRef.
- S. Neumann, P. Hu, F. Bretschneider, H. Schmalz and A. Greiner, Blends of Bio-Based Poly(Limonene Carbonate) with Commodity Polymers, Macromol. Mater. Eng., 2021, 306, 2100090 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Li, Y. Chen, H. Wu, B. Chen, W. Li, X. Zhu and J. Nie, Enhancement in the Light-Stability of BAPO and ITX-based Photo-Curable Materials via Photobleaching of Pyrrolidene Cyclohexanone, Prog. Org. Coat., 2024, 186, 108027 CrossRef CAS.
- B. Steyrer, P. Neubauer, R. Liska and J. Stampfl, Visible Light Photoinitiator for 3D-Printing of Tough Methacrylate Resins, Materials, 2007, 10, 1445 CrossRef PubMed.
- P. Fouassier and J. Lalevée, Three-Component Photoinitiating Systems: Towards Innovative Tailor-Made High-Performance Combinations, RSC Adv., 2012, 2, 2621–2629 RSC.
- J. Ni, M. Lanzi, D. H. Lamparelli and A. W. Kleij, Ring-Opening Polymerization of Functionalized Aliphatic Bicyclic Carbonates, Polym. Chem., 2023, 14, 4748–4753 RSC.
- T. M. McGuire, E. M. López-Vidal, G. L. Gregory and A. Buchard, Synthesis of 5- to 8-Membered Cyclic Carbonates from Diols and CO2: A One-Step, Atmospheric Pressure and Ambient Temperature Procedure, J. CO2 Util., 2018, 27, 283–288 CrossRef CAS.
- I. M. Barszczewska-Rybarek, A. Korytkowska-Wałach, M. Kurcok, G. Chladek and J. Kasperski, DMA Analysis of the Structure of Crosslinked Poly(methyl methacrylate)s, Acta Bioeng. Biomech., 2017, 19, 47–53 Search PubMed.
- K. P. Menard and N. R. Menard, Dynamic Mechanical Analysis, CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, 2020 Search PubMed.
- For a recent example see: A. Wambach, S. Agarwal and A. Greiner, Synthesis of Biobased Polycarbonate by Copolymerization of Menth-2-ene Oxide and CO2 with Exceptional Thermal Stability, ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng., 2020, 8, 14690–14693 CrossRef CAS.
Footnote |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available: Experimental details, characterization data for all materials, and copies of relevant spectra and chromatograms. See DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/d4py00381k |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2024 |



