Surfactant assisted synthesis of strontium hexaferrite microspheres for the fabrication of high-performance asymmetric supercapacitors†
Abstract
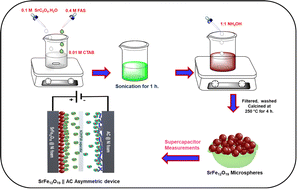
In this work, we describe a surfactant-assisted chemical co-precipitation methodology for the synthesis of strontium hexaferrite (SrFe12O19). Various physicochemical techniques were used to confirm the formation of SrFe12O19 particles. XRD and SEM analyses confirmed the formation of M-type strontium hexaferrite spheres. The as-prepared SrFe12O19 particles were utilized as an electrode material in supercapacitors. As a result, SrFe12O19 delivered a maximum specific capacity (Csp) of 1085 C g−1 at 1 A g−1, and retained 96.0% of its specific capacity even after 6000 GCD cycles. As a consequence, the SrFe12O19 sample was used to construct an asymmetric SrFe12O19//AC device, which exhibited an energy density of 13.8 W h kg−1 at a power density of 496.8 W kg−1. The unique structural features and multiple redox sites and increased electrical conductivity of SrFe12O19 are responsible for its excellent capacity behavior. Thus, it is clear that SrFe12O19 microspheres can be exploited as an electrode material in high-performance supercapacitor devices for real-time applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...