The growing metaverse sector can reduce greenhouse gas emissions by 10 Gt CO2e in the united states by 2050†
Abstract
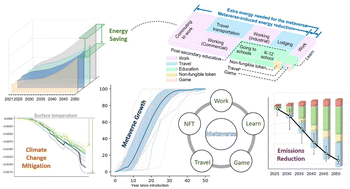
The metaverse, an immersive combination of the physical and digital world, is becoming a booming industry with the potential to reach billions of users before 2030, but the climate impacts due to its rapid expansion have not been quantitatively understood. Here we show that the growing metaverse sector will facilitate climate change mitigation, through prospective analyses that systematically investigate five prominent metaverse-based applications for working, traveling, education, non-fungible token, and gaming. We find that the increasing metaverse adoption can reduce the global surface temperature by up to 0.02 °C before the end of this century and lower the greenhouse gas emissions by 10 Gt CO2e throughout the expansion period, based on different metaverse growth projections in the United States. The metaverse growth accelerates decarbonization and improves air quality, through alleviating air pollutant emissions by 10–23% and saving 10% of nationwide energy use by 2050 compared to the projections without further metaverse sector expansion. Therefore, it is suggested that the environmentally responsible adaptation of the metaverse growth requires transformations of domestic energy supply and benefits implementation of less aggressive climate policies.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...