DOI:
10.1039/D2RA00034B
(Paper)
RSC Adv., 2022,
12, 7433-7445
Novel magnetic nickel ferrite nanoparticles modified with poly(aniline-co-o-toluidine) for the removal of hazardous 2,4-dichlorophenol pollutant from aqueous solutions†
Received
4th January 2022
, Accepted 23rd February 2022
First published on 7th March 2022
Abstract
Chlorinated organic and phenolic compounds are still purely studied by many researchers because of their severe damage to the aquatic environment and their carcinogenic effect on many living organisms. Therefore, there is a great interest in removing these environmental pollutants from aqueous mediums by easy and inexpensive methods. Herein, novel nickel ferrite (NiFe2O4) nano composite modified with poly(aniline-co-o-toluidine) (PAOT) is prepared, characterized, and used for the removal of 2,4-dichlorophenol (2,4-DCP) as an organic chlorinated environmental pollutant. The morphological properties of the composite are characterized by Fourier transform infrared spectrometry (FTIR), X-ray diffraction (XRD), high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HR-TEM), and Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) methods. The prepared composite is tested for the removal of the hazardous dichlorophenol pollutant from aqueous solutions. Under optimized conditions and with effective control of parameters including, contact time, pH of the test solution, adsorbent dose, and temperature, over 83% of the pollutant is adsorbed and removed. The adsorption capacity is 162 mg g−1. Adsorption kinetics, adsorption isotherm and some physicochemical parameters of the reaction are evaluated. The Redlich–Peterson isothermal model is the appropriate model for describing the adsorption process. These results indicate that NiFe2O4/PAOT nanocomposites are promising adsorbents for the removal of persistent organic pollutants (e.g., DCP) from aqueous solutions. The results also reveal that modification of NiFe2O4 particles with poly(aniline-co-o-toluidine) (PAOT) significantly enhances the adsorption capacity of the adsorbent. This is probably due to the electrostatic attraction and non-covalent interactions (e.g. π–π) between the aromatic rings in both dichlorophenol and poly(aniline-co-o-toluidine) copolymer. Advantages offered by using NiFe2O4/PAOT nanocomposites are the high stability, reasonable efficiency, reusability for at least five adsorption–desorption cycles and the ability to remove the adsorbent from aqueous solutions for reuse using an external magnetic field.
1. Introduction
Generation of hazardous pollutants by various industrial activities leads to the contamination of the environment, especially the aquatic and soil environments.1 For example, chlorophenols and their derivatives, are characterized by strong pungent odor, high toxicity, and carcinogenicity for various organisms, including humans. More seriously, their biodegradability is poor and depends on the number of chlorine atoms per mole and their position in the aromatic ring(s).2,3 Due to their antimicrobial properties, they are widely used as a raw material in the production of pesticides, herbicides, disinfectants, and preservatives, as well as dyes, phenolic resins, and paper.4,5 Their wide use has led to many environmental problems such as soil contamination and pollution of ground and surface water. Consequently, chlorophenols have become one of the leading causes of environmental pollution,6 and their removal using less complex methods and low-cost materials has become of paramount importance.
Methods in common use for the removal of chlorinated phenols from aqueous solutions include reverse osmosis,7 photo-Fenton degradation,8 membrane separation,9 sonochemical degradation,10 coagulation/flocculation,11 and electrochemical degradation.12 However, most of these methods require strictly controlled conditions, time-consuming with high operation cost.13 To date, adsorption techniques are the most widely method used for contaminants removal, due to their high efficiency, simplicity, low-cost, and regeneration ability and reusability of the adsorbent material.14,15 Conventional adsorbents have been used, such as carbon nanotubes,15 activated carbon,16 oxides,17 and microporous polymers,18 but these adsorbents have a practical major drawback related to the difficulty of their separation from the treated water. This issue is of a great challenge, especially on the large-scale systems. The difficulty of completely separating of these conventional adsorbents from the treated solution may lead to their accumulation in the environment and thus the creation of another pollutant (secondary pollution source).
Nowadays, this problem has been solved by using magnetic nano-adsorbent materials which have recently attracted research interest for organic pollutants removal from wastewater. Indeed, these nano-magnetic adsorbents have some distinctive characteristics such as high surface area, high absorption capacity, ease of separation by applying an external magnetic field, making them less likely to form a secondary pollutant and thus addressing the defects of conventional adsorbents that have difficulty separating them from contaminated solutions.19–23 In addition, there has been great interest in modifying these magnetic nano-adsorbents to increase their efficiency in removing some organic pollutants by using conductive polymers such as polyaniline (PANI)24 and polypyrrole (PPy).25 These polymer materials provide a high surface area with ductility and malleability, excellent mechanical rigidity,26 and unique electrical properties along with unique functional groups (e.g. –NH).27 Thus, the modification of magnetic nanoparticles with conductive polymers is characterized by its low cost, ease of synthesis, excellent environmental stability, and its ability to prevent agglomeration of magnetic nanomaterials.28
In the present work, NiFe2O4 nanoparticles are prepared, modified by poly(aniline-co-o-toluidine) polymer to form NiFe2O4/PAOT nanocomposite. The presence of the –CH3 group attached to the aromatic ring of o-toluidine increases its electron density therefore enhances the attachement of the nickel ferrite molecules to poly (aniline-co-o-toluidine) through the formation of a non-covalent bonding via the interaction of the metal complex hydrogen with the electron density in o-toluidine ring. Thus, it gives more stability to the prepared nanocomposite. In addition, its ability to increase the possibility of forming a non-covalent (π–π) bond between the aromatic rings of 2,4-DCP and o-toluidine, thus increasing its removal efficiency. The magnetic nanocomposite is characterized and used as adsorbent for the removal of chlorophenol from aqueous solutions. The present magnetic nanocomposite offered some advantages which are low-cost, high adsorption efficiency, ease of preparation, simple regeneration, recycling, and ease of completely separation from the treated solutions.
2. Experimental
2.1 Materials
2.1.1 Reagents. All reagents were used without further purifications. Ferric chloride hexahydrate (FeCl3·6H2O, 97%), nickel chloride hexahydrate (NiCl2·6H2O), ammonium persulfate ((NH4)2S2O8), aniline (C6H5NH2) and o-toluidine (C7H9N) were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA). Sodium hydroxide (NaOH) and hydrochloric acid (HCl) were obtained from Merck (Germany). 2,4-Dichlorophenol (2,4-DCP, C6H4Cl2O) was obtained from PubChem (St. Rockville Pike, Bethesda, USA). All chemicals were of analytical grade and used as received. Ultrapure water was used for the preparation of all solutions. Stock solutions and all dilute test solutions of 2,4-DCP were stored in brown bottles and kept in darkness to prevent degradation.
2.1.2 Synthesis of nano-sized nickel ferrite (NiFe2O4). Aqueous solutions of ferric chloride and nickel chloride in a 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 2 molar ratio was mixed with a constant stirring for 30 min at room temperature (22 °C ± 2 °C). An aqueous 2.0 M NaOH solution was added dropwise (1.0 mL min−1) to the mixture until reaching pH 11. The mixture was then heated to 100 °C with a constant stirring for 1 h where a brown precipitate was obtained. The mixture was allowed to stand for ageing overnight. The brown precipitate was washed several times with distilled water until the filtrate's pH became 7. The residue was collected and dried at 110 °C for 6 h. The obtained deep brown powder was calcinated at 600 °C for 5 h and kept in a desiccator after being grounded.
2 molar ratio was mixed with a constant stirring for 30 min at room temperature (22 °C ± 2 °C). An aqueous 2.0 M NaOH solution was added dropwise (1.0 mL min−1) to the mixture until reaching pH 11. The mixture was then heated to 100 °C with a constant stirring for 1 h where a brown precipitate was obtained. The mixture was allowed to stand for ageing overnight. The brown precipitate was washed several times with distilled water until the filtrate's pH became 7. The residue was collected and dried at 110 °C for 6 h. The obtained deep brown powder was calcinated at 600 °C for 5 h and kept in a desiccator after being grounded.
2.1.3 Synthesis of NiFe2O4/PAOT nanocomposite. Nickel ferrite polymeric nanocomposite was synthesized using the chemical polymerization method.29 A 4.5 g portion of NiFe2O4 nanoparticles was added to a mixture of 20 mL chloroform and 30 mL double-distilled water. The mixture was left in an ultrasonic bath for 1 h at room temperature (22 °C ± 2 °C). In a parallel step, equimolar amounts of aniline and o-toluidine monomers (0.05 mol each) were mixed with 200 mL of 1.0 M hydrochloric acid at a constant stirring for 30 min. The ferrite and monomers mixtures were mixed under sonication for another 30 min. A 20 mL aliquot of 0.1 M aqueous ammonium persulfate (APS) solution, as a polymerization initiator, was drop-wise added using a peristaltic pump with a rate of 0.5 mL min−1 to the mixture under sonication for 1 h. An intermediate black color was observed in the solution. The reaction mixture was kept overnight. Nickel ferrite modified with poly(aniline-co-o-toluidine) was separated from the reaction mixture using a filter holder set with vacuum pumps and washed several times with double-distilled water followed by methanol. Finally, the obtained black precipitated was dried at 60 °C and grounded to obtain fine particles.
2.2 Instruments measurements
The absorption spectra were recorded with Thermo UV-Visible double-beam spectrophotometer. The infrared spectra were measured with a Pye-Unicam Sp-3-300 Fourier-transform infrared spectrometer (FTIR) equipped with 8101 PC and KBr technique. X-ray diffraction (XRD) measurements were done with (Bruker AXS-D8, Germany) and CuKα radiation (λ = 1.5406 Å) in the 2θ range from 10 °C to 70 °C. High-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HR-TEM) was carried out using JEOL-JEM-2100 electron microscope (Osaka, Japan). Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) method was performed by adsorption and desorption of nitrogen gas at 77 K using BELSORP MINI X (Osaka, Japan) and automatic surface and pore size analyzer.
2.3 Investigation of adsorption
2.3.1 Adsorption techniques. The removal efficiency of the prepared nanocomposites was investigated using the batch equilibrium method. A series of concentrations (10–200 μg mL−1) of 2,4-dichlorophenols (2,4-DCP) solution was prepared. Different portions (ranged from 10 to 60 mg) of the prepared NiFe2O4/PAOT nanocomposite were dispersed in 50 mL of the test 2,4-DCP aqueous solution at pH 4. The mixtures were left in contact for a period varied from 10 min to 4 h at room temperature. The adsorbent particles were separated using a magnet bar. The concentration of 2,4-DCP in the filtrate was spectrophotometrically measured.30 A parallel similar series of experiment was made using non modified NiFe2O4 nano particles. After equilibrium, the removal efficiency and adsorption capacities (mg g−1) of the adsorbent were calculated by the following two eqn (1) and (2):31| | |
Removal efficiency (%) = ((Co − Ceq)/Co) × 100
| (1) |
| | |
Qeq = (Co − Ceq) × V/M
| (2) |
where, Co is the initial concentration of 2,4-DCP (μg mL−1), Ceq is the concentration of 2,4-DCP (μg mL−1) at equilibrium after time t, V is the initial volume of an aqueous 2,4-DCP solution, and M is the mass of adsorbent (g).
2.3.2 Adsorption kinetics. Kinetic studies of 2,4-DCP adsorption on non-modified NiFe2O4 nanoparticles and modified NiFe2O4/PAOT nanocomposite were investigated and compared. Portions of 40 mg of NiFe2O4 or 30 mg of NiFe2O4/PAOT were added to 50 mL aliquot of 30 μg mL−1 of aqueous 2,4-DCP solution at pH 4. The mixture was allowed in contact at different period of times. Pseudo-first order and second-order models were used to analyze the adsorption rate following eqn (3) and (4), respectively.31| |
ln(qeq − qt) = ln![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) qeq − k1t qeq − k1t
| (3) |
| | |
t/qt = (1/k2qe2) + (t/qeq)
| (4) |
where, qeq and qt are the adsorption capacity(mg g−1) of the adsorbents at equilibrium and at any time; respectively, t is the contact time (min), k1 (min−1) and k2 (g mg−1 min−1) are the rate constants of pseudo first order and second order adsorption, respectively.
2.3.3 Effect of pH. The pH effect of the aqueous 2,4-DCP test solution on the adsorption of both adsorbents (nano particles and nanocomposite) was investigated. Portions of 40 mg of NiFe2O4 and 30 mg of NiFe2O4/PAOT were added to 50 mL of 30 μg mL−1 2,4-DCP aqueous solutions adjusted at pH 2–11. The pH of 2,4-DCP test solutions was adjusted using dilute hydrochloric acid and/or sodium hydroxide.
2.3.4 Adsorption isotherms. 50 mL aliquots of aqueous 2,4-DCP solutions with different concentrations (10–200 μg mL−1) and fixed pH 4 were treated with 40 mg of NiFe2O4 nanoparticles and 30 mg of NiFe2O4/PAOT nanocomposite in separate runs. After a contact time of 2 h upon using NiFe2O4 nanoparticles and 4 h with NiFe2O4/PAOT nanocomposite, the adsorbent particles were separated using a magnet bar. The remaining concentration of 2,4-DCP in the solution was measured using the standard spectrophotometric method.30 The experimental data obtained were compared using Langmuir, Freundlich and Redlich–Peterson models.32,33 The Langmuir, Freundlich and Redlich–Peterson models were tested by applying eqn (5)–(7); respectively:| | |
qeq = (aLqmCeq)/(1 + bCeq)
| (5) |
| | |
qeq = (aRCeq)/(1 + KRCeqb)
| (7) |
where; Ceq is the 2,4-DCP concentration at equilibrium (mg L−1), qeq is the equilibrium adsorption capacity of sorbent (mg g−1), qm is the maximum adsorption capacity of adsorbent (mg g−1), aL (L mg−1) is the Langmuir constant related to the energy of sorption, KF (mg(1−1/n) L1/n g−1) and n are the Freundlich constants related to the adsorption density and adsorption intensity; respectively. KR, aR and b are the R–P isotherm constants, where KR is determined via trials and error to obtain the maximum linear regression value of the isotherm graph.
2.3.5 Reusability of NiFe2O4/PAOT nanocomposite. The usability of NiFe2O4/PAOT nanocomposite adsorbent for repeated removal of dichlorophenol in consecutive cycles was tested. Each cycle was performed as previously mentioned. After each cycle the adsorbent was isolated from the test solution using an external magnet bar. The adsorbent was dipped in 50 mL of 40 mg L−1 NaOH for 1 h, then washed with methanol followed by distilled water several times until the filtrate's pH became around 7 and dried. The regenerated adsorbent was used for sequential adsorption–desorption cycles. The adsorption efficiency and % 2,4-DCP removal after each cycle was calculated using eqn (2).
3. Results
3.1 Synthesis and characterization of adsorbent
3.1.1 FTIR spectral measurements. Fig. 1 shows IR spectra of both NiFe2O4 nanoparticles after calcination and NiFe2O4/PAOT nanocomposite after co-polymerization. The IR spectrum of NiFe2O4 nanoparticles after calcination shows small broad band at 3440 cm−1, attributed to the O–H stretching and vibrating modes of adsorbed water during preparation of the KBr disc. Another two bands appeared in the region of 1632–1382 cm−1 are assigned to asymmetric stretching mode of adsorbed carbonate groups.34 The two main bands appear between 585–453 cm−1 are assigned to the intrinsic stretching vibrations of Fe–O and Ni–O in the spinel structures.35 No other bands are detected in the spectrum of the calcinated NiFe2O4 nano-particles. On the other hand, the IR spectrum of NiFe2O4/poly(aniline-co-o-toluidine) composite shows a broad band in the range 3384–3230 cm−1 assigned to N–H stretching. The band is broad due to the presence of hydrogen bonding.36 The band appears in the region 2920–2852 cm−1 is due to the stretching vibration of –CH3 group of toluidine moiety. The band displayed in the region 1587–1485 cm−1 is assigned to N–H and C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N stretching vibrations. Furthermore, other bands in the region 1149–1006 cm−1 are noticed and assigned to C–H plane bending.37 Finally, two bands are detected between 572–415 cm−1, corresponding to metal–oxygen vibration bands in the spinel structure's crystal lattice.
N stretching vibrations. Furthermore, other bands in the region 1149–1006 cm−1 are noticed and assigned to C–H plane bending.37 Finally, two bands are detected between 572–415 cm−1, corresponding to metal–oxygen vibration bands in the spinel structure's crystal lattice.
 |
| | Fig. 1 FTIR spectra of NiFe2O4 nanoparticles and NiFe2O4/PAOT nanocomposite. | |
3.1.2 X-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns of analysis. The XRD patterns of both NiFe2O4 nanoparticles and NiFe2O4/PAOT nanocomposite were recorded with a powder X-ray diffractometer (PANalytical, Almelo, Netherlands) using CuKα (λ = 0.154 nm) radiation, and a diffraction angle between 10° and 70°. The XRD patterns (Fig. 2) indicate, the formation of cubic spinal crystal structure according to the standard of JCPDS (card no. 10-0325),38 with no diffraction peaks of other impurities such as Fe2O3 or NiO peaks. In case of NiFe2O4 nanoparticles, there is seven sharp diffraction peaks with 2θ values at 30.24°, 35.48°, 36.94°, 43.06°, 53.80°, 57.20° and 62.88° corresponding to the crystal planes (220), (311), (222), (400), (422), (511) and (440), respectively. While in case of the NiFe2O4/PAOT nanocomposite, the XRD pattern is similar to that of NiFe2O4 nanoparticles with the appearance of an additional broad diffraction band at 2θ around 15–25°, which is due to the amorphous nature of the copolymer matrix. The intensity of diffraction peaks of NiFe2O4/PAOT nanocomposites is appeared at a slightly lower diffraction than that of NiFe2O4 nanoparticles. This indicates doping of PAOT on the NiFe2O4 surface without affecting its crystalline structure. The average particles size of NiFe2O4 and NiFe2O4/PAOT was calculated using Scherrer's equation.39| |
D =(Kλ)/(β![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) cos cos![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) θ) θ)
| (8) |
where D is the crystalline size, λ is the X-ray wavelength (CuKα radiation and equals to 0.154 nm), θ is the Bragg diffraction angle (in radians), and β is the full width at half maximum (FWHM) of the XRD peak appearing at the most intense diffraction peak (3 1 1) and k = 0.9. The average particle size was found to be 12.3 and 16.7 nm for NiFe2O4 nanoparticles and NiFe2O4/PAOT nanocomposites, respectively.
 |
| | Fig. 2 X-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns of NiFe2O4 nanoparticles and NiFe2O4/PAOT nanocomposite. | |
3.1.3 High-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM). Size and morphology of the prepared NiFe2O4 nanoparticles (A) and NiFe2O4/PAOT nanocomposites (B) were characterized by high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HR-TEM). As shown in Fig. 3, the HR-TEM image of both compounds (A) and (B) show that the nanoparticles have a uniform, spherical structural morphology with narrow size distribution agglomeration to some extent. The nano size ranges from 12.66–29.87 nm, which is coincided with the XRD results. In Fig. 2(B), The HR-TEM image shows the poly(aniline-co-o-toluidine) layer covering the surface of the NiFe2O4 nanoparticles.
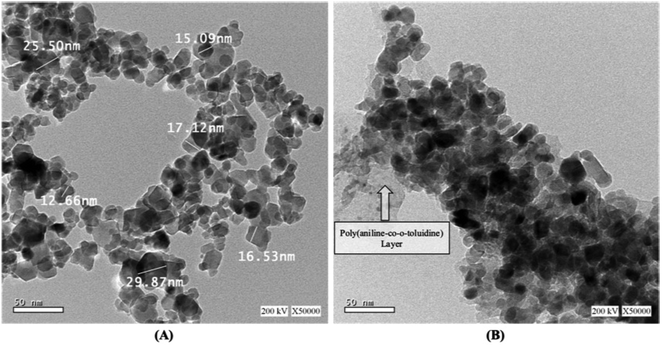 |
| | Fig. 3 High-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM) images of (A) NiFe2O4 nanoparticles and (B) NiFe2O4/PAOT nanocomposite. | |
3.2 Adsorption properties of magnetic composite
3.2.1 Nitrogen adsorption/desorption isotherm and pore structure. The nitrogen Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) method was employed to estimate the surface area, pore volume and pore diameter of both the nano and composite materials at 77 K. The N2 adsorption/desorption isotherms on both NiFe2O4 (A) and NiFe2O4/PAOT (A) (Fig. (S1, I)†) exhibit a IV type with H3 hysteresis loops. This suggests an adsorbents' mesoporous structure and indicates a monolayer-multilayer adsorption associated with capillary condensation and aggregates of plate-like particles (slit-shaped pores) according to IUPAC.40The BET surface area, pore-volume, pore diameter and particles size of NiFe2O4 nanoparticles and NiFe2O4/PAOT nano-composite data are presented in Table 1. The size distribution curves for both NiFe2O4 nanoparticles (A) and NiFe2O4/PAOT nanocomposite (B) (Fig. (S1, II)†), indicate that the majority of pores diameter are in the 0.4 to 50 nm range, characteristic of a mixture of micro and mesoporous materials.41 Simultaneously, the average pore diameters are 10.64 ± 2.80 and 14.59 ± 3.25 nm for (A) and (B), respectively. The t-plot of NiFe2O4 nanoparticles (A) and NiFe2O4/PAOT nanocomposite (B) (Fig. (S1, III)†) showed that at t-value of 0.9 nm and 1 nm for the two materials (A) and (B), the experimental curve deviates from the straight line, indicating that more nitrogen is taken up than the expected for multimolecular adsorption, the capillary condensation has set in at this point. At an average t-value of about 1.5 nm for both samples, the pores responsible for this phenomenon are filled. A new straight line shows the continuation of the multi-layer adsorption on the outer surface and/or side pores' surface.42
Table 1 Overall surface characteristic of the proposed adsorbents obtained by Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) method
| Sample |
Surface areaa (m2 g−1) |
Average pore volumea (cm3 g−1) |
Average pore diametera (nm) |
Average particle sizea (nm) |
| ± SD (n = 4 measurements); where SD is the standard deviation. |
| NiFe2O4 nanoparticles |
61 ± 1.86 |
0.240 ± 2.0 × 10−4 |
10.64 ± 2.80 |
14.35 ± 4.04 |
| NiFe2O4/PAOT nanocomposite |
39 ± 1.43 |
0.125 ± 8.2 × 10−3 |
14.59 ± 3.25 |
17.31 ± 1.07 |
3.3 Efficiency of magnetic composite
3.3.1 Adsorption kinetics. Fig. 4 shows the removal efficiently of 2,4-DCP onto both NiFe2O4 nanoparticles and NiFe2O4/PAOT nanocomposite as a function of contact time. With NiFe2O4 nanoparticles, the adsorption of 2,4-DCP increases gradually with time and reaches an equilibrium after 4 h with a low removal efficiency of around 24% ± 1.3. However, by using NiFe2O4/PAOT nanocomposite, the adsorption of 2,4-DCP increases quickly compared with NiFe2O4 nanoparticles reaching the equilibrium after only 2 h and the removal efficiency increased to about 83% ± 2.8.
 |
| | Fig. 4 Effect of contact time on 2,4-DCP removal from aqueous solutions by: (A) NiFe2O4 nanoparticles and (B) NiFe2O4/PAOT nanocomposite [conditions: initial conc. of 2,4-DCP solution = 30 mg L−1, adsorbent dose = 0.04 g for (A) and 0.03 g for (B), pH = 4, volume of solution = 50 mL]. | |
The adsorption kinetics were studied and used for identifying the adsorption mechanism. As shown in Fig. 5, the experimental kinetics data (Table 2) are fitted with pseudo-first and second-order models. The correlation coefficient (R2) using pseudo-second-order model is higher than that obtained using pseudo-first-order model, which means that both adsorbents obey pseudo-second-order model. The practical (qe) and calculated (qexpe) data for both adsorbents are also calculated.
 |
| | Fig. 5 Kinetics plot of pseudo first order (I) and second order (II) for adsorption of 2,4-DCP onto NiFe2O4 nanoparticles (a) and NiFe2O4/PAOT nanocomposite (b). | |
Table 2 Adsorption kinetics parameters achieved using pseudo first order and second order models
| Adsorbent |
Pseudo-first order |
Pseudo-second order |
| k1 × 10−2 (min−1) |
qe1 (mg g−1) |
R2 |
k2 × 10−4 (g (mg min)−1) |
qe2 (mg g−1) |
qexpe (mg g−1) |
R2 |
| NiFe2O4 nanoparticles |
1.6 ± 0.015 |
20.6 ± 1.14 |
0.959 |
6.3 ± 0.51 |
25.1 ± 1.10 |
20.1 |
0.987 |
| NiFe2O4/PAOT nanocomposite |
2.9 ± 0.060 |
32.4 ± 1.36 |
0.885 |
16.4 ± 3.20 |
72.2 ± 1.32 |
69.2 |
0.998 |
3.3.2 Effect of adsorbent dose. To optimize the appropriate amount of the adsorbent material for maximum pollutant removal, different quantities of the prepared adsorbents (10–60 mg) were used in 50 mL of 2.4-DCP aqueous solution (30 mg L−1) at pH 4, and contact time of 2 and 4 h for NiFe2O4 nanoparticles and NiFe2O4/PAOT nanocomposites, respectively. As shown in Fig. 6, the removal efficiency increases by increasing the adsorbent dose until reaching its maximum upon using 40 and 30 mg for NiFe2O4
 |
| | Fig. 6 Effect of adsorbent dose on 2,4-DCP removal from aqueous solutions using NiFe2O4 nanoparticles (a) and NiFe2O4/PAOT nanocomposite (b) [conditions: initial conc. of 2,4-DCP solution = 30 mg L−1, contact time = 4 h and 2 h for (a) and (b); respectively, pH = 4, volume of solution = 50 mL]. | |
3.3.3 Effect of pH. The adsorption efficiencies of 2,4-DCP onto both NiFe2O4 nanoparticles and NiFe2O4/PAOT nanocomposite were tested at various pH values ranging from 2 to 11 (Fig. 7). In case of NiFe2O4/PAOT nanocomposite, the removal efficiency at pH lower than 6 is higher than other pH values. These results demonstrate that the lower pH values are favorable for the adsorption of 2,4-DCP. Since 2,4-DCP has a pKa value of 7.8,43 it can exist in aqueous solutions in two forms (protonated and deprotonated) depending on the solution's pH.
 |
| | Fig. 7 Effect of pH on 2,4-DCP removal from aqueous solution using NiFe2O4 nanoparticles (a) and NiFe2O4/PAOT nanocomposite (b) [conditions: initial conc. of 2,4-DCP solution = 30 mg L−1, volume of solution = 50 mL, contact time = 4 h and 2 h, and adsorbent dose = 0.04 g and 0.03 g for (a) and (b); respectively]. | |
At pH < 6, the protonated (nonionized) form is predominant and at pH < 9, the deprotonated (dichlorophenate anions) form is predominant, while a mixture of the two forms exists in between.43 A pH 6 is chosen and used for the removal process by both sorbents.
Zeta potential measurements (Fig. 8) reveal, that the points of zero charge (PZC) for both NiFe2O4 nanoparticles and NiFe2O4/PAOT nanocomposites are 6.4 and 6.6, respectively. At pH < 6.4, the oxygen containing group in NiFe2O4 forms a positively charged aqua complex. At pH > 6.4, the oxygen containing group became ionized, forming a negative charge on its surface. In case of NiFe2O4/PAOT nanocomposite, at pH < 6.6, the nitrogen atoms of the amine and imine groups present in the poly(aniline-co-o-toluidine) composite undergoes protonation leading to the formation of a positive charge on the composite surface. At pH > 6.6, the composite surface becomes negatively charged due to the deprotonation of the amine groups. These data explain the high removal efficiency of both adsorbents at low pH values. The formation of positive charges on the surface of both adsorbents and the nonionized form of 2,4-DCP (pKa = 7.8), does not cause electrical repulsion. While at high pH values, both adsorbents' surface became negatively charged, leading to an electrostatic repulsion between the surface of the adsorbent and 2,4-DCP anion, in the test solutions.
 |
| | Fig. 8 Plots of zeta potential as a function of pH for NiFe2O4 nanoparticles and NiFe2O4/PAOT nanocomposite. | |
3.3.4 Effect of initial concentration of 2,4-DCP solutions. The removal efficiency and adsorption capacity (Qe) of NiFe2O4 nanoparticles and NiFe2O4/PAOT nano composite are tested using different initial concentrations of aqueous 2,4-DCP solutions (ranged from 10 to 200 mg L−1). The results are shown in Fig. 9. Using NiFe2O4 nanoparticles, the removal efficiency remains constant at 23% over the concentration range 10 to 30 mg L−1 2,4-DCP, then gradually declined to reach 14.5% at higher initial adsorbate concentrations (200 mg L−1). By using NiFe2O4/PAOT nanocomposite, on the other hand, the removal efficiency remains high and almost constant at 83% over the initial concentration range of 10 to 50 mg L−1 2,4-DCP. Further increase of 2,4-DCP concentration to 200 mg L−1 causes a slight decrease in the removal efficiency to reach 75%. The adsorption capacity of both adsorbents increases gradually with increasing the initial concentration of 2,4-DCP until all active sites of each adsorbent are occupied. The maximum adsorption capacity per unit mass (Qm) for NiFe2O4 nano particles and NiFe2O4/PAOT nanocomposite are found to be 36 ± 2 mg g−1 and 162 ± 3.8 mg g−1, respectively, indicating much higher efficiency of the nanocomposite over the nanoparticle's adsorbate for the removal of 2,4-DCP.
 |
| | Fig. 9 Effect of initial concentration of 2,4-DCP solution using NiFe2O4 nanoparticles (a) and NiFe2O4/PAOT nanocomposite (b) [conditions: adsorbent dose = 0.04 g for (a) and 0.03 g for (b), pH = 4, volume of solution = 50 mL, contact time = 4 h for (a) and 2 h for (b)]. | |
3.3.5 Adsorption isotherms. Langmuir (I), Freundlich (II) and Redlich–Peterson (III) adsorption isotherm models are used to fit the experimental data for NiFe2O4 nanoparticles and NiFe2O4/PAOT nanocomposite as shown in Fig. 10. The isotherm parameters of the three models, and the correlation coefficients (R2) are illustrated in Table 3. From the Langmuir model, the maximum capacity per unit mass (Qm) is 60.0 ± 4.9 and 245.8 ± 19.3 mg g−1 for NiFe2O4 nanoparticles and NiFe2O4/PAOT nanocomposite, respectively. According to the regression correlation coefficients (R2), it is observed that both adsorbents obey Redlich–Peterson model as the R2 of both are close to 1 and higher than that obtained using Langmuir and Freundlich models. This finding suggests that the adsorption mechanism is a mix of Langmuir and Freundlich isotherms and does not follow the ideal monolayer adsorption process.44
 |
| | Fig. 10 (I) Langmuir, (II) Freundlich, and (II) Redlich–Peterson isotherms for removal of 2,4-DCP using NiFe2O4 nanoparticles (a) and NiFe2O4/PAOT nanocomposite (b). | |
Table 3 Adsorption isotherm parameters achieved using Langmuir, Freundlich and Redlich–Peterson models
| Adsorbent |
Langmuir model |
Freundlich model |
Redlich–Peterson model |
| qm (mg g−1) |
aL ×10−2(L mg−1) |
R2 |
KF (mg(1−1/n) L1/ng−1) |
n |
R2 |
aR (L g−1) |
KR ×10−5 (L mg−1) |
b |
R2 |
| NiFe2O4 nanoparticles |
60.0 ± 4.9 |
1.18 ± 0.185 |
0.975 |
2.34 ± 0.62 |
1.77 ± 0.04 |
0.926 |
0.488 ± 0.0087 |
2.74 ± 0.14 |
2.09 ± 0.098 |
0.999 |
| NiFe2O4/PAOT nanocomposite |
245.8 ± 19.3 |
4.91 ± 0.783 |
0.972 |
23.06 ± 4.48 |
1.87 ± 0.05 |
0.911 |
8.384 ± 0.3280 |
119.72 ± 7.53 |
1.84 ± 0.151 |
0.998 |
3.3.6 Desorption and regeneration of NiFe2O4/PAOT nanocomposite. Regeneration of NiFe2O4/PAOT nanocomposite for re-using in multiple adsorption cycles was investigated (Fig. 11). After the first cycle, the adsorbent was collected, dipped in dilute sodium hydroxide solution, followed by washing with methanol and water and reused in the next adsorption cycle. This process was repeated several times until the % removal of dichlorophenol efficiency decreased. The results show that after five adsorption–desorption cycles, the removal efficiency for 2,4-DCP slightly declined from 83 to 80%.
 |
| | Fig. 11 2,4-DCP adsorption–desorption cycles on NiFe2O4/PAOT nanocomposite. | |
3.3.7 Adsorption mechanism. There are some possible explanations for the mechanism of 2,4-DCP adsorption on the proposed adsorbents (Fig. 12 and 13). With NiFe2O4 nanoparticles at low pH values, the aqua metal complex (i.e., M–OH2+) is formed. The hydrogen bonds formed between –Cl or –OH present in the 2,4-DCP aromatic ring and the hydrogen atom present in the aqua nickel ferrite complex facilitate the removal of the adsorbate. Alternatively, the formation of a weak non-covalent (M–OH2+⋯π) bonding between the hydrogen atom in the aqua complex and the electron density present on the 2,4-DCP aromatic ring45 enhances adsorbate removal.
 |
| | Fig. 12 3D-Simulation of the adsorption mechanism of 2,4-DCP on NiFe2O4 nanoparticles and NiFe2O4/PAOT nanocomposite. | |
 |
| | Fig. 13 Schematic 2D-Simulation for the adsorption mechanism of 2,4-DCP on NiFe2O4 nanoparticles and NiFe2O4/PAOT nanocomposite. | |
With NiFe2O4/PAOT nanocomposite, the nickel ferrite molecules attached to the poly(aniline-co-o-toluidine) through the formation of a hydrogen bonding between the hydrogen of the aqua metal complex and the nitrogen atom of the copolymer. Other possibility is the formation of non-covalent bonding (M–OH2+⋯π) by interaction of the metal complex hydrogen and the electron density of aromatic ring of o-toluidine in the copolymer which enhanced by the inductive effect of toluidine –CH3 group. Other possible mechanism and route of reaction involves the adsorption of the 2,4-DCP on the surface of NiFe2O4/PAOT nanocomposite and formation of a hydrogen bonding between –Cl, –OH and –H of 2,4-DCP with –NH2 and –N![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) , –NH– and
, –NH– and ![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) NH– groups of the copolymer. Formation of non-covalent bonding (H–π) between hydrogen atom (-OH) of 2,4-DCP and the electron density of the aromatic rings of the copolymer is another route of interaction.
NH– groups of the copolymer. Formation of non-covalent bonding (H–π) between hydrogen atom (-OH) of 2,4-DCP and the electron density of the aromatic rings of the copolymer is another route of interaction.
Other possible source of reaction involves the formation of non-covalent (π–π) interaction due to the dispersion forces between π electrons in 2,4-DCP aromatic ring and π electrons in o-toluidine (electro-rich) aromatic ring exist in the copolymer. The different and various possible modes of adsorbate/adsorbent interactions descried above (vide supra) support and confirm the high efficiency and superiority of NiFe2O4/PAOT nanocomposite over NiFe2O4 nanoparticles for the removal of 2,4-DCP from aqueous solutions.
Table 4 presents the main characteristics of some previously suggested adsorbents for removal of dichlorophenol from aqueous solutions. The proposed NiFe2O4/PAOT nanocomposite adsorbent offers the advantages of relative short contact time, high adsorption capacity, high removal efficiency, low cost, ease of preparation, regeneration, recycling, and reuse.
Table 4 Performance characteristics of some adsorbents used for the removal of 2,4-dichlorophenol
| Adsorbent type |
Maximum adsorption capacity (mg g−1) |
pH |
Contact time, hour |
Removal, (%) |
Ref. |
| Biocomposites of polypyrrole (PPY), polyaniline (PANI) and sodium alginate (NaAlg) with cellulosic biomass barley husk (BH) |
7.6–24.6 |
7–10 |
2 |
58 |
46 |
| Bamboo biochar-calcium sulphate |
16.4 |
6.5 |
3 |
60 |
47 |
| Cyclodextrin-ionic liquid polymer as a macro porous material |
29.6 |
6 |
3 |
83 |
48 |
| Activated carbon-impregnated alginate β-cyclodextrin/gelatin beads |
39.4 |
7 |
1 |
86 |
49 |
| Carbon dots modified mesoporous organosilica |
99.7 |
7 |
3 |
60 |
50 |
| β-cyclodextrin polymer (β-CDP) and γ-cyclodextrin polymer (γ-CDP) |
15.7 |
7 |
0.2 |
70 |
51 |
| Punica granatum (pomegranate) peel |
65.7 |
5.5–6.5 |
10 |
50 |
52 |
| NiFe2O4/PAOT nanocomposites |
162 |
6 |
2 |
83 |
This work |
4. Conclusions
Nickel ferrite nanoparticles were synthesized, characterized, and used before and after modification with poly(aniline-co-o-toluidine) to form NiFe2O4/PAOT nanocomposites. The composite is satisfactory used as adsorbent for the effective removal of 2,4-dichlorophenol (2,4-DCP) from aqueous solutions. The average sizes of the synthesized NiFe2O4 nanoparticles and NiFe2O4/PAOT nanocomposite are 12.3 and 16.7 nm, respectively. Under optimized conditions, NiFe2O4/PAOT nanocomposite efficiently adsorb and remove 2,4-DCP from aqueous solutions. At pH < 6, the removal efficiency and maximum adsorption capacity (Qm) are 24%, 36 mg g−1 for NiFe2O4 nanoparticles and 83%, 162 mg g−1 for NiFe2O4/PAOT nanocomposite, respectively. This is probably due to the electrostatic attractions between positively changed atoms located in the copolymer chain and 2,4-DCP molecules. Non-covalent π–π interactions between the aromatic ring of 2,4-DCP and aromatic rings of copolymer layer are also involved in the removal mechanism. Langmuir, Freundlich and Redlich–Peterson isotherm models were applied to fit the experimental data and Redlich–Peterson model is the most appropriate model for the adsorption process and both adsorbents followed the second order model. NiFe2O4/PAOT nanocomposite is stable and easily removed from aqueous solution after treatment by an external magnetic field and recycled for reuse for at least 5 cycles without loss of removal efficiency.
Author contributions
The listed authors contributed to this work are described as follows: S. S. M. H and A. H. K. contributed to the concepts of the work, interpretation of the results and prepared the manuscript. The experimental part was conducted by M. A. F. Preparation of the manuscript and the revision before submission were conducted by A. H. K., S. S. M. H. and M. A. F. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest. All authors have approved the manuscript and agree with the submission to your esteemed journal.
References
- W. Duan, F. Meng, H. Cui, Y. Lin, G. Wang and J. Wu, Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf., 2018, 157, 441–456 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- E. O. Igbinosa, E. E. Odjadjare, V. N. Chigor, I. H. Igbinosa, A. O. Emoghene, F. O. Ekhaise, N. O. Igiehon and O. G. Idemudia, Sci. World J., 2013, 2013, 1–12 Search PubMed.
- X. Li, M. Zhou, Y. Pan and L. Xu, Chem. Eng. J., 2017, 307, 1092–1104 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Zhang, M. Zhou, G. Ren, X. Yu, L. Ma, J. Yang and F. Yu, Water Res., 2015, 70, 414–424 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Ya, Y. Wu, Y. Li and X. Wang, Chemosphere, 2017, 170, 75–82 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- N. Aristov and A. Habekost, Chemosphere, 2010, 80, 113–115 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Al-Obaidi, C. Kara-Zaitri and I. M. Mujtaba, J. Water Proc. Eng., 2018, 22, 131–137 CrossRef.
- O. Ayodele, J. Lim and B. Hameed, Appl. Catal., A, 2012, 413, 301–309 CrossRef.
- M. Amini, M. Arami, N. M. Mahmoodi and A. Akbari, Desalination, 2011, 267, 107–113 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Abbasi and N. R. Asl, J. Hazard. Mater., 2008, 153, 942–947 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. B. Hadjltaief, A. Sdiri, W. Ltaief, P. Da Costa, M. E. Galvez and M. B. Zina, C. R. Chim., 2018, 21, 253–262 CrossRef.
- L. Fan, Y. Zhou, W. Yang, G. Chen and F. Yang, Dyes Pigm., 2008, 76, 440–446 CrossRef CAS.
- N. Singh, G. Nagpal and S. Agrawal, Environ. Technol. Innovation, 2018, 11, 187–240 CrossRef.
- I. Ali, M. Asim and T. A. Khan, J. Environ. Manage., 2012, 113, 170–183 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J.-G. Yu, X.-H. Zhao, H. Yang, X.-H. Chen, Q. Yang, L.-Y. Yu, J.-H. Jiang and X.-Q. Chen, Sci. Total Environ., 2014, 482, 241–251 CrossRef PubMed.
- S. Karthikeyan, V. Gupta, R. Boopathy, A. Titus and G. Sekaran, J. Mol. Liq., 2012, 173, 153–163 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Yang, Z. Chen, D. Zhang, Y. Liu, Y. Han and J. Shen, Water Sci. Technol., 2011, 63, 45–50 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Wang, L. Pan, W. Deng, G. Yang and X. Liu, Polym. J., 2016, 48, 787–792 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Chen, L. Di, H. Yang and T. Xian, J. Ceram. Soc. Jpn., 2019, 127, 221–231 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Homaeigohar, Nanomaterials, 2020, 10, 295 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Homaeigohar, N. K. Botcha, E. Zarie and M. Elbahri, Nanomaterials, 2019, 9, 250 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Homaeigohar and M. Elbahri, Water, 2019, 11, 2 CrossRef CAS.
- A. H Kamel, A. A. Hassan, A. E.-G. E. Amr, H. H. El-Shalakany and M. A. Al-Omar, Nanomaterials, 2020, 10, 586 CrossRef PubMed.
- A. Samadi, M. Xie, J. Li, H. Shon, C. Zheng and S. Zhao, Chem. Eng. J., 2021, 129425 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Hlekelele, N. E. Nomadolo, K. Z. Setshedi, L. E. Mofokeng, A. Chetty and V. P. Chauke, RSC Adv., 2019, 9, 14531–14543 RSC.
- E. N. Zare, A. Motahari and M. Sillanpää, Environ. Res., 2018, 162, 173–195 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Nasar and F. Mashkoor, Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res., 2019, 26, 5333–5356 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. Mylkie, P. Nowak, P. Rybczynski and M. Ziegler-Borowska, Materials, 2021, 14, 248 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. Kumar, Synth. Met., 2000, 114, 369–372 CrossRef CAS.
- R. B. Baird, Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 23rd, Water Environment Federation, American Public Health Association, American, 2017 Search PubMed.
- A. H. Kamel, Life Sci. J., 2013, 10, 1657–1664 Search PubMed.
- T. A. Osmari, R. Gallon, M. Schwaab, E. Barbosa-Coutinho, J. B. Severo Jr and J. C. Pinto, Adsorpt. Sci. Technol., 2013, 31, 433–458 CrossRef CAS.
- N. Ayawei, A. N. Ebelegi and D. Wankasi, J. Chem., 2017, 2017, 3039817 Search PubMed.
- S. Gunasekaran, G. Anbalagan and S. Pandi, J. Raman Spectrosc., 2006, 37, 892–899 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Joshi, M. Kumar, S. Chhoker, G. Srivastava, M. Jewariya and V. Singh, J. Mol. Struct., 2014, 1076, 55–62 CrossRef CAS.
- I. Kulszewicz-Bajer, A. Proń, J. Abramowicz, C. Jeandey, J.-L. Oddou and J. W. Sobczak, Chem. Mater., 1999, 11, 552–556 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Epstein, J. Ginder, F. Zuo, H.-S. Woo, D. Tanner, A. Richter, M. Angelopoulos, W.-S. Huang and A. MacDiarmid, Synth. Met., 1987, 21, 63–70 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Qu, J. Wang, J. Kong, P. Yang and G. Chen, Talanta, 2007, 71, 1096–1102 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. S. Hassan, A. H. Kamel, A. A. Hassan, A. E.-G. E. Amr, H. A. El-Naby and E. A. Elsayed, Nanomaterials, 2020, 10, 254 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Thommes, K. Kaneko, A. V. Neimark, J. P. Olivier, F. Rodriguez-Reinoso, J. Rouquerol and K. S. Sing, Pure Appl. Chem., 2015, 87, 1051–1069 CrossRef CAS.
- P. P. IUPAC, D. Everett, R. Haul, L. Moscou, R. Pierotti, J. Rouquerol and T. Siemieniewska, Chem, 1985, 57, 603 Search PubMed.
- J. De Boer, B. Lippens, B. Linsen, J. Broekhoff, A. Van den Heuvel and T. J. Osinga, J. Colloid Interface Sci., 1966, 21, 405–414 CrossRef CAS.
- J.-P. Wang, Y.-Z. Chen, H.-M. Feng, S.-J. Zhang and H.-Q. Yu, J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2007, 313, 80–85 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- F. Brouers and T. J. Al-Musawi, J. Mol. Liq., 2015, 212, 46–51 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Zhang, H. Dai, H. Yan, W. Zou and D. Cremer, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2016, 138, 4334–4337 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. N. Bhatti, Z. Mahmood, A. Kausar, S. M. Yakout, O. H. Shair and M. Iqbal, Int. J. Biol. Macromol., 2020, 153, 146–157 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. H. Alamin and L. Kaewsichan, Pol. J. Chem. Technol., 2016, 18, 59–67 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Raoov, S. Mohamad and M. R. Abas, J. Hazard. Mater., 2013, 263, 501–516 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- I. H. Alsohaimi, M. El-Aassar, A. A. Elzain, M. S. Alshammari and A. S. Ali, J. Mater. Res. Technol., 2020, 9, 5144–5153 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Wang, C. Cheng, S. Tapas, J. Lei, M. Matsuoka, J. Zhang and F. Zhang, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2015, 3, 13357–13364 RSC.
- N. Li, Z. Mei and S. Ding, J. Inclusion Phenom. Macrocyclic Chem., 2010, 68, 123–129 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Bhatnagar and A. Minocha, J. Hazard. Mater., 2009, 168, 1111–1117 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
Footnote |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available. See DOI: 10.1039/d2ra00034b |
|
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2022 |
Click here to see how this site uses Cookies. View our privacy policy here.  Open Access Article
Open Access Article a,
Ayman H. Kamel
a,
Ayman H. Kamel *ab and
Saad S. M. Hassan*a
*ab and
Saad S. M. Hassan*a
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 2 molar ratio was mixed with a constant stirring for 30 min at room temperature (22 °C ± 2 °C). An aqueous 2.0 M NaOH solution was added dropwise (1.0 mL min−1) to the mixture until reaching pH 11. The mixture was then heated to 100 °C with a constant stirring for 1 h where a brown precipitate was obtained. The mixture was allowed to stand for ageing overnight. The brown precipitate was washed several times with distilled water until the filtrate's pH became 7. The residue was collected and dried at 110 °C for 6 h. The obtained deep brown powder was calcinated at 600 °C for 5 h and kept in a desiccator after being grounded.
2 molar ratio was mixed with a constant stirring for 30 min at room temperature (22 °C ± 2 °C). An aqueous 2.0 M NaOH solution was added dropwise (1.0 mL min−1) to the mixture until reaching pH 11. The mixture was then heated to 100 °C with a constant stirring for 1 h where a brown precipitate was obtained. The mixture was allowed to stand for ageing overnight. The brown precipitate was washed several times with distilled water until the filtrate's pH became 7. The residue was collected and dried at 110 °C for 6 h. The obtained deep brown powder was calcinated at 600 °C for 5 h and kept in a desiccator after being grounded.![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) qeq − k1t
qeq − k1t
![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N stretching vibrations. Furthermore, other bands in the region 1149–1006 cm−1 are noticed and assigned to C–H plane bending.37 Finally, two bands are detected between 572–415 cm−1, corresponding to metal–oxygen vibration bands in the spinel structure's crystal lattice.
N stretching vibrations. Furthermore, other bands in the region 1149–1006 cm−1 are noticed and assigned to C–H plane bending.37 Finally, two bands are detected between 572–415 cm−1, corresponding to metal–oxygen vibration bands in the spinel structure's crystal lattice.
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) cos
cos![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) θ)
θ)




![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) , –NH– and
, –NH– and ![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) NH– groups of the copolymer. Formation of non-covalent bonding (H–π) between hydrogen atom (-OH) of 2,4-DCP and the electron density of the aromatic rings of the copolymer is another route of interaction.
NH– groups of the copolymer. Formation of non-covalent bonding (H–π) between hydrogen atom (-OH) of 2,4-DCP and the electron density of the aromatic rings of the copolymer is another route of interaction.










