Microfluidic post method for 3-dimensional modeling of platelet–leukocyte interactions
Abstract
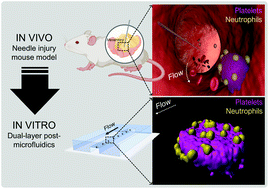
Microvascular thrombosis and inflammation (thromboinflammation) are major causes of morbidity and mortality in critically ill patients with limited therapeutic options. Platelets are central to thromboinflammation, and microvascular platelet thrombi are highly effective at recruiting and activating leukocytes at sites of endothelial injury. Whilst parallel-plate flow chambers, microslides and straight microchannel assays have been widely used to recapitulate leukocyte adhesive behavior on 2-dimensional (2D) surfaces, none of these methods achieve high fidelity 3-dimensional (3D) geometries emulating microvascular platelet thrombi. As a result, the role of hydrodynamic factors in regulating leukocyte interactions with platelet thrombi remains ill-defined. Here, we report a microfluidic post model that allows visualization and analysis of neutrophil–platelet interactions in a 3D flow field. We have utilized the unique mechanosensitive features of platelets to enable selective micropatterning of the 3D posts with human or mouse platelets. By modulating the activation status of platelets, our method enables precise control of platelet surface reactivity and neutrophil recruitment. In addition, our microfluidic post assay accurately recapitulated the rolling versus stationary adhesion behavior of single neutrophils and demonstrated the efficacy of the P-selectin and Mac-1 blocking antibodies to reduce neutrophil recruitment and stationary adhesion, respectively. Moreover, the geometry of posts had a major influence on the efficiency of neutrophil recruitment and adhesion stability. This new post method highlights the importance of platelet 3D geometries in facilitating efficient, localized neutrophil recruitment. These findings have potentially important implications for the potent proinflammatory function of microvascular platelet thrombi.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...