Multiscale polarizable coarse-graining water models on cluster-level electrostatic dipoles†
Abstract
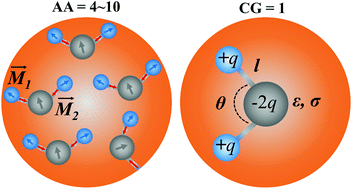
The development of a coarse-grained (CG) water model is increasingly important in CG studies of biological processes. In this work, we developed a generic CG force field of liquid water on cluster-level electrostatic dipoles. An exponential term is introduced in the non-bonded potential to adjust the well depth. The whole force field is parametrized on the AMOEBA simulation and then refined on the experimental density, dielectric permittivity and isothermal compressibility. The new CG water force field is suitable for the construction of multi-resolution water models and here the NC = 4/5/10 systems are taken as examples. The results show that the NC = 4/5/10 models can correctly reproduce the density and relative dielectric permittivity. The models can well predict the pressure–density/density–temperature relationships close to the all-atom or experiment results. However, the new models behave differently from other CG models in several water properties such as the air–water surface tension. Through dipole distributions, two representative polarizable configurations are captured after the NC = 4/5/10 systems are dynamically equilibrated. Besides, the NC = 4 model is coupled with the Martini Na+/Cl− models to predict ion-relevant radial distribution functions in comparison to the Martini result. Lastly, CPU tests suggest that the new CG models can enhance simulation efficiency by factors of 20–42, compared to the TIP3P force field. The newly proposed polarizable water force field is practical and transferable and can be flexibly extended to higher coarse-graining of liquid water.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...