Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleCreative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported Licence
Correction: Spatiotemporal distribution and speciation of silver nanoparticles in the healing wound
Marco
Roman
 *a,
Chiara
Rigo
a,
Hiram
Castillo-Michel
*a,
Chiara
Rigo
a,
Hiram
Castillo-Michel
 b,
Dagmar S.
Urgast
c,
Jörg
Feldmann
b,
Dagmar S.
Urgast
c,
Jörg
Feldmann
 cd,
Ivan
Munivrana
e,
Vincenzo
Vindigni
cd,
Ivan
Munivrana
e,
Vincenzo
Vindigni
 e,
Ivan
Mičetić
e,
Ivan
Mičetić
 f,
Federico
Benetti
f,
Federico
Benetti
 g,
Carlo
Barbante
g,
Carlo
Barbante
 ah and
Warren R. L.
Cairns
ah and
Warren R. L.
Cairns
 h
h
aCa’ Foscari University of Venice, Department of Environmental Sciences, Informatics and Statistics (DAIS), Via Torino 155, 30172 Venice Mestre, Italy. E-mail: marco.roman@unive.it; Tel: +0039 041 234 7731
bEuropean Synchrotron Radiation Facility (ESRF), 71 avenue des Martyrs, 38000 Grenoble, France
cUniversity of Aberdeen, Trace Element Speciation Laboratory, Aberdeen AB24 3UE, Scotland, UK
dUniversity of Graz, Institute of Chemistry, Universitätsplatz 1, 8010 Graz, Austria
eUniversity Hospital of Padua, Burns Centre, Division of Plastic Surgery, Via Giustiniani 2, 35128 Padua, Italy
fUniversity of Padua, Department of Biomedical Sciences, Via Ugo Bassi 58/B, 35131 Padua, Italy
gEcamRicert Srl, European Centre for the Sustainable Impact of Nanotechnology (ECSIN), Corso Stati Uniti 4, 35127 Padua, Italy
hInstitute for Polar Sciences (ISP-CNR), Via Torino 155, 30172 Venice Mestre, Italy
First published on 24th September 2021
Abstract
Correction for ‘Spatiotemporal distribution and speciation of silver nanoparticles in the healing wound’ by Marco Roman et al., Analyst, 2020, 145, 6456–6469, DOI: 10.1039/D0AN00607F.
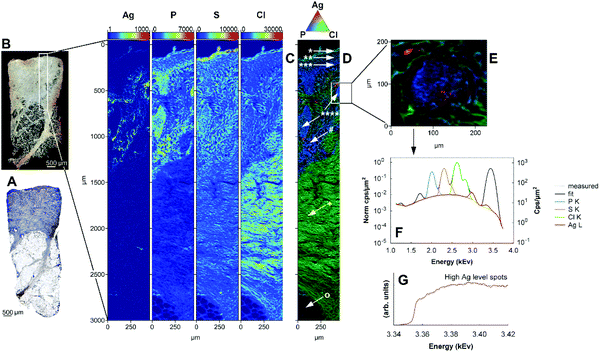
The authors regret that Fig. 3D, 5F and 7 were shown incorrectly in the original article. The correct versions of Fig. 3D, 5F and 7 are shown below.
The Royal Society of Chemistry apologises for these errors and any consequent inconvenience to authors and readers.
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2021 |