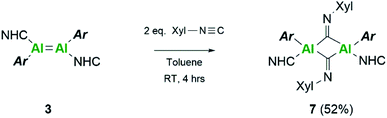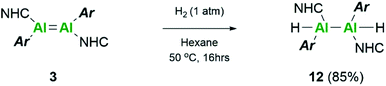Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleDialumenes – aryl vs. silyl stabilisation for small molecule activation and catalysis†
Catherine
Weetman
 ,
Amelie
Porzelt
,
Prasenjit
Bag
,
Franziska
Hanusch
and
Shigeyoshi
Inoue
,
Amelie
Porzelt
,
Prasenjit
Bag
,
Franziska
Hanusch
and
Shigeyoshi
Inoue
 *
*
Department of Chemistry, Catalysis Research Center and Institute of Silicon Chemistry, Technische Universität München, Lichtenbergstra βe 4, 85748, Garching bei München, Germany. E-mail: s.inoue@tum.de
First published on 21st April 2020
Abstract
Main group multiple bonds have proven their ability to act as transition metal mimics in the last few decades. However, catalytic application of these species is still in its infancy. Herein we report the second neutral NHC-stabilised dialumene species by use of a supporting aryl ligand (3). Different to the trans-planar silyl-substituted dialumene (3Si), compound 3 features a trans-bent and twisted geometry. The differences between the two dialumenes are explored computationally (using B3LYP-D3/6-311G(d)) as well as experimentally. A high influence of the ligand's steric demand on the structural motif is revealed, giving rise to enhanced reactivity of 3 enabled by a higher flexibility in addition to different polarisation of the aluminium centres. As such, facile activation of dihydrogen is now achievable. The influence of ligand choice is further implicated in two different catalytic reactions; not only is the aryl-stabilised dialumene more catalytically active but the resulting product distributions also differ, thus indicating the likelihood of alternate mechanisms simply through a change of supporting ligand.
Introduction
The ability to isolate and stabilise complexes containing metal–metal bonds is of fundamental interest, providing both experimental and theoretical insights into the intrinsic nature of the metal centre.1 Since the discovery that the so-called ‘double bond rule’ could be broken in the beginning of the last quarter of the 20th century,2–5 efforts within main group chemistry have strived towards isolating a plethora of both homo- and hetero-main group element multiply bonded compounds, which have been the subject of numerous reviews.6,7 Aside from curiosity, one of the driving forces behind this research area is the ability to use main group multiple bonds as transition metal mimics.8–10 This is possible due to similarly energetically accessible frontier molecular orbitals. Thus, reduction of small molecules, such as dihydrogen, under ambient conditions by sustainable main group metal centres is achievable.11Whilst the ability to mimic transition metals is now possible in regard to oxidative addition reactions, main group elements still fall short in terms of catalytic activity due to the resulting stability of the higher oxidation state complexes, i.e. the first step in a redox based catalytic cycle. In order to truly compete with transition metals that are currently employed in industry, the ability to influence the stability, and thus reactivity, of main group metal centres is paramount. One method of influencing stability is through choice of stabilising ligand. If you consider disilenes, the choice of silyl, aryl and nitrogen-based ligands has been shown to influence the structural parameters around the double bond,12,13 with silyl groups tending towards trans-planar geometries13 and aryl groups promoting trans-bent character. It was not until the use of an N-heterocyclic imine (NHI) based ligand, which results in a highly trans-bent and twisted geometry, that dihydrogen activation was achieved.14
An electropositive silyl supporting ligand was used to stabilise the first neutral aluminium–aluminium double bond, namely dialumene.15 DFT calculations found the HOMO to consist of a π-bond formed from almost pure Al p-orbitals and as such a planar geometry was observed. As predicted, the dialumene behaved as a transition metal mimic towards a variety of small molecules, as well as enabling catalytic reduction of CO2.16 Prior to the isolation of the first neutral dialumene, several compounds with Al–Al bond orders greater than 1 were isolated.17 These can be classed as radical monoanionic species, one electron π-bonded compounds, a dianionic complex and masked dialumenes. The stick with latter, reported independently by Power18 and Tokitoh,19 proposed the intermediacy of aryl-stabilised dialumenes, with the masked species being a result of [2 + 4]-cycloaddition reaction due to the use of aromatic solvent. This was additionally accounted for through a series of [2 + 2]-cycloaddition reactions with internal alkynes. Tokitoh further showed that the benzene derived masked species was capable of activating dihydrogen;20 however, upon switching to an anthracene derived masked species no reactivity towards dihydrogen was observed.
On descending group 13, heavier digallenes and dithallenes have been isolated which show notable trans-bent character and have been known to dissociate to their corresponding monomers in hydrocarbon solutions.21–25 However, digallanes have been shown to react as the double bonded species, rather than the monomer with regards to cycloadditions of unsaturated C–C bonds and even dihydrogen activation.26–28
Motivated by our group's previous efforts in dialumene chemistry, we targeted the isolation of a neutral aryl-stabilised dialumene to compare the intrinsic nature of the aluminium–aluminium double bond through the influence of ligand stabilisation. Whilst silyl and aryl groups have been routinely used in main group multiple bond chemistry, no direct comparisons of their influence on multiple bonds as reactive species have been drawn. As such, we proposed a systematic study of both dialumenes towards activation of a range of small molecules and their use in catalysis, with the aim of providing experimental and theoretical insight into the influence of these ligand classes on main group multiple bond reactivity.
Results and discussion
Synthesis of aryl-stabilised dialumene
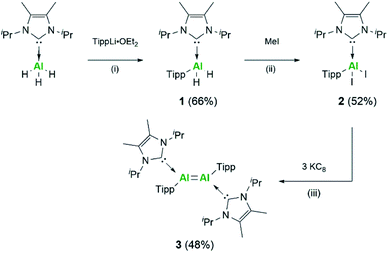
Following on from the successful isolation of the first neutral dialumene, we focused our attention on expanding the scope of this class of compounds towards aryl stabilised systems. As such, we targeted the use of the Tipp ligand (Tipp = 2,4,6-tri-iso-propylphenyl) for the stabilisation of a new dialumene. In keeping with the previous dialumene, the choice of N-heterocyclic carbene (NHC) remained the same, IiPr2Me2 (IiPr2Me2 = 1,3-di-iso-propyl-4,5-dimethyl-imidazolin-2-ylidene). Direct reaction of IiPr2Me2AlH3 and LiTipp at −78 °C resulted in formation of the monosubstituted aluminium dihydride complex IiPr2Me2Al(Tipp)H2 (1) (Scheme 1) in good yield (66%, 27Al: δ 112.9 ppm).29 The identity of compound 1 was confirmed upon inspection of the 1H NMR spectrum wherein three resonances for the iso-propyl groups were identified in a 2![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 2
2![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 ratio (NHC
1 ratio (NHC![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) o-Tipp
o-Tipp![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) p-Tipp iso-propyl signals) as well as a characteristic broad signal for the Al–H2 protons (1H: δ 5.11 ppm). Additionally, a sharp IR stretching band at 1711 cm−1 (Al–H) was observed in the IR spectrum.
p-Tipp iso-propyl signals) as well as a characteristic broad signal for the Al–H2 protons (1H: δ 5.11 ppm). Additionally, a sharp IR stretching band at 1711 cm−1 (Al–H) was observed in the IR spectrum.
Conversion of 1 towards formation of IiPr2Me2Al(Tipp)I2 (2) could be achieved through reaction with BI3·dms (dms = dimethyl sulfide) or with a small excess of methyl iodide, with the latter resulting in higher and cleaner conversion; moreover, the concomitant formation of methane allows for facile reaction monitoring. Loss of signals relating to Al–H were observed in both the 1H NMR and IR spectra, and further characterisation by single crystal XRD confirmed the identity of 2 (Fig. S54†). Compound 2 is structurally analogous to the corresponding silyl supported complex (2Si) with Al–CNHC bond lengths essentially the same (2: 2.0645(18) Å; 2Si: 2.0673(17) Å), indicating the dative nature of the NHC ligand. This is additionally confirmed on comparison with the Al–CTipp bond length (1.9887(19) Å), which is smaller than the sum of the covalent radii (RAl–C = 2.01 Å).30
Following the analogous synthetic protocol to the silyl dialumene, compound 2 was stirred vigorously with KC8 at room temperature (Scheme 1). Through monitoring the reaction by 1H NMR, it was found that this reaction requires 72 hours rather than the 24 hours required for the previous case. Compound 3 was isolated as a black solid, and in contrast to the silyl stabilised dialumene (3Si), 3 is highly soluble in a broad range of aromatic, alkyl and ethereal solvents. Both dialumenes are stable in the solid state in an inert atmosphere for prolonged periods; however, they decompose in solution after 24 hours. The 1H NMR spectrum of 3 shows a large broad signal at room temperature (∼7.0–5.5 ppm) which resolves into distinct signals at 228 K for the iso-propyl groups, indicating a degree of rotational fluxionality in this system (Fig. S11†).
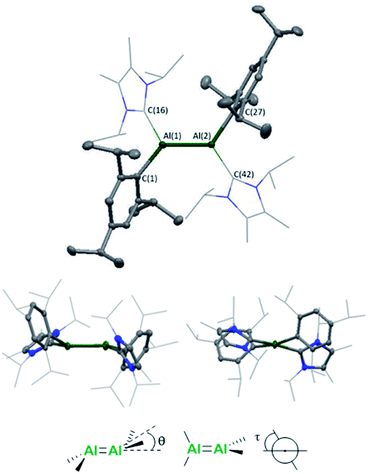
Single crystals were grown from a concentrated n-hexane solution at 5 °C and revealed a trans-bent and twisted geometry of the aryl stabilised dialumene (compound 3, Fig. 1) (θ = 17.25°, 23.70°, τ = 12.06°), which contrasts with the trans-planar geometry observed previously. Furthermore, in 3Si the NHC groups were found to be parallel to each other, whilst in 3 they are found to be almost perpendicular (85°). The change from a planar to a trans-bent and twisted geometry has also been observed in disilene chemistry on switching between aryl and silyl-based ligands.12,13 The Al–Al bond length is 2.4039(8) Å which is fractionally longer than that in the previous dialumene (3Si: 2.3943(16) Å). Another notable difference between the two systems lies in the Al–CNHC bond length (3: 2.0596(16), 2.0422(17); 3Si: 2.073(3) Å). The shorter bond length in the case of aryl stabilisation likely indicates a decrease in dative character and thus an increase in the covalent nature of the Al–CNHC bond (which is also supported by the calculated bond dissociation energy, see below).
Computational discussion of aryl-stabilised dialumene
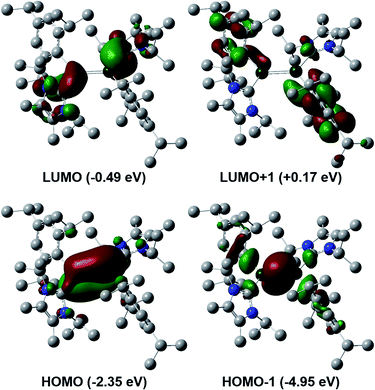
To gain a deeper insight into the differences between these two classes of dialumenes, we performed density functional theory (DFT) calculations at the B3LYP-D3/6-311G(d) level of theory (for detailed information see the ESI†). The optimised geometry of 3 is in good agreement with experimental values, with the addition of the dispersion required to account for the trans-bent and twisted geometry. For comparison, all calculated values for 3Si including dispersion are given in the ESI.† Analysis of the frontier orbitals of 3 revealed similar features to 3Si, in which the HOMO−1 and HOMO contain the Al–Al σ- and π-bonds, respectively, as well as the LUMO representing the Al–CNHC π bond (Fig. 2). The main difference to 3Si (see Fig. S57† for the corresponding orbitals) is the loss of uniform arrangement of the HOMO on the two aluminium centres as well as additional π-incorporation of the NHC present in 3. We attribute this to the different orientation of the NHCs in 3, enabling overlap with the p-orbital of the carbene carbon atom, which is experimentally observed as a shortened Al–CNHC bond in the SC-XRD structure and further evidenced by an increased Gibbs free energy of bond dissociation of 26.0 kcal mol−1 (cf.3Si = 16.9 kcal mol−1). The conjugation towards the Al–CNHC π-bond in 3 is also observed on inspection of the monomers (for further details see ESI Fig. S62†), which also gives rise to the decreased HOMO–LUMO gap in 3 compared to 3Si (3 = 1.86 eV, 3Si = 2.24 eV) based on decreased overlap of the monomers being possible.TD-DFT calculations corroborated the experimental UV/vis spectrum of 3. This showed an intense absorption band at 833 nm (ε = 6273 L mol−1 cm−1) (calc. value 794 nm), which can be assigned to the HOMO to LUMO transition and is responsible for the highly coloured compound.31 Natural bond orbital (NBO) analysis provided electronic insight into the nature of the Al–Al double bond. The Al–Al π-bond of 3 bears reduced p-character compared to 3Si. Moreover, this NBO orbital has a lower occupancy based on partial population of the π*-orbitals of the C–N bonds of the NHC, rationalising the increased interaction of the NHC for 3. This is based on its different orientation, which we mainly attribute to the reduced steric demand of the ligand. Furthermore, this is reflected in the decreased Wiberg bond index (WBI) of the Al–Al bond of 1.67 to 1.53 going from silyl to aryl (Fig. 3), yet still indicating a high degree of multiple bonding character in both systems.
Analysis of NPA charges clearly reflects the silyl effect (Fig. 3): the aluminium centres in 3Si bear a nearly neutral charge of +0.08, while in 3 they account for +0.48/+0.49. We attribute this to the silyl substituents, with their strong σ-donating properties, possessing a more effective orbital overlap with the aluminium centres in the σ(Al–Si) bonds. This also becomes evident upon examination of the results of NBO analysis for the Al–CTipp/Al–Si bonds: the Al–CTipp bonds are highly polarised (17% Al, 83% CTipp) compared to Al–Si bonds in 3Si (36% Al, 64% Si). This difference is also rationalised upon comparison of Al–C and Al–Si Pauling electronegativities (Δχ Al–C 0.94; Δχ Al–Si 0.29), thus resulting in less polarised Al–Si bonds.
To elucidate the effect of sterics around the aluminium centre, we initially compared the steric demand of the Tipp and SitBu2Me ligands, which revealed similar percentages of buried volume (% Vbur) of 29.9% (3) and 30.7% (3Si) (Fig. S58 and S59†). However, the shape and thus distribution of kinetic stabilisation vary. Further calculation and comparison of reduced model systems were performed with the IiPr2Me2 carbene replaced by IMe4 (IMe43 and IMe43Si, Fig. S60†).32
For IMe43Si the most stable isomer exhibits a strongly trans-bent and twisted geometry (θ = 42.1°, 30.4°, τ = 11.7°) with the NHC planes orientated almost parallel and a substantially elongated Al–Al bond length of 2.43 Å. In the Tipp-substituted IMe43 the trans-bent character is decreased compared to 3, accompanied by a small increase of the Al–Al bond length due to further rotation of the NHC planes towards the Al–Al plane, enabling more effective π-interaction of NHC and the AlAl moiety. This also becomes more apparent upon examination of the corresponding frontier orbitals with IMe43. This features enhanced delocalisation of the HOMO onto the NHC moiety, as a consequence of further rotation of the NHC planes towards the Al–Al bond (angle between NHC planes: 49°). In contrast, the HOMO in IMe43Si exhibits contributions from the silyl groups, as conjugation towards the NHC π-system is not possible due to the different orientation. Moreover, the HOMO–LUMO gap decreases for aryl and increases for the silyl case, attributed to the decreased/increased trans-bent geometry.
The smallest possible model systems, by reducing IiPr2Me2 to IH4 as well as Tipp/SitBu2Me to phenyl/TMS, were calculated and yield comparable results: S3 and S3Si both possess trans-bent but no twisted configuration. In S3Si a slightly shorter Al–Al bond length and a decreased trans-bent angle (21.2° vs. 31.8° for S3) are observed; however, in each case the NHC planes are rotated towards the Al![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) Al bond (see Fig. S61†). Hence, trans-bent structures are obtained for the aryl and the silyl substituted dialumenes bearing minimal steric effects. Thus, it is clearly demonstrated that the steric effects of both NHC and the ligands govern the binding motif of dialumenes. The shape of the ligand influences the interaction with the NHC: either only a weak and purely σ-donating type of interaction, as observed in planar 3Si, or more flexible coordination of the NHC, with the p-orbital of the Ccarbene able to form a slipped π-bond with the AlAl core, as observed in 3. The trans-bent and twisted structure obtained for 3 is therefore a result of the difference in steric demand of the Tipp ligand compared to SitBu2Me.
Al bond (see Fig. S61†). Hence, trans-bent structures are obtained for the aryl and the silyl substituted dialumenes bearing minimal steric effects. Thus, it is clearly demonstrated that the steric effects of both NHC and the ligands govern the binding motif of dialumenes. The shape of the ligand influences the interaction with the NHC: either only a weak and purely σ-donating type of interaction, as observed in planar 3Si, or more flexible coordination of the NHC, with the p-orbital of the Ccarbene able to form a slipped π-bond with the AlAl core, as observed in 3. The trans-bent and twisted structure obtained for 3 is therefore a result of the difference in steric demand of the Tipp ligand compared to SitBu2Me.
From the different aspects, steric as well as electronic, discussed above we thus conclude that the structural difference between 3 and 3Si is caused by the different steric demand of the ligands. From the electronic point of view the change of silyl to Tipp ligand in the dialumene changes the orbital situation at the central AlAl core, which is accompanied by a reduced HOMO–LUMO gap. Moreover, the polarisation of the aluminium centres is different, based on differences in electronegativity between C and Si. We thus anticipate differences in reactivity with respect to activation of strong bonds, such as those in small molecules, as well as an increased accessibility towards a bigger range of reagent molecules of 3, based on the increased flexibility of this system.
Reactivity of dialumenes
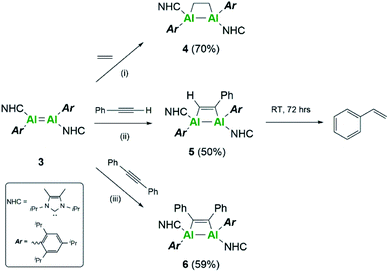
Further differences between these two systems were sought experimentally. Firstly, reactivity towards a series of C–C multiple bonds was examined (Scheme 2). In the case of ethylene, compound 3 underwent formal [2 + 2]-cycloaddition to yield the dialuminacyclobutane compound 4, akin to the reactivity observed with 3Si.15 Upon reaction with 1 equivalent of phenylacetylene, clean formation of a single species by NMR spectroscopy was noted to occur to form compound 5. This is in contrast to the reactivity of 3Si where both [2 + 2]-cycloaddition (5Si) and C–H activation were observed. Varying the number of equivalents of phenyl acetylene (2![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 and 3
1 and 3![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 with respect to 3) did not result in further incorporation of phenyl acetylene into the complex even at elevated temperatures. However, compound 5 was found to decompose in solution to yield styrene (see ESI Fig. S37 and S38†). Monitoring a C6D6 solution of 5 showed that this occurs intramolecularly, with the additional protons required to make styrene likely the result of C–H activation. In further support of an intramolecular C–H activation, addition of a hydrogen source, e.g. dihydrogen, phenyl silane, pinacol borane or amine borane, failed to provide any notable increase in the rate of styrene formation. Unfortunately, attempts to identify the fate of the resulting aluminium containing species were unsuccessful. It is proposed that initially [2 + 2]-cycloaddition occurs to form compound 5, followed by C–H activation of the iso-propyl groups of the Tipp ligand, as this was not observed with the analogous silyl complex. Intramolecular C–H activation of the Mes* ligand (Mes* = 2,4,6-tri-tert-butylphenyl) has been previously observed by thermolysis of (Mes*)2AlH,33 whilst 1-germapropadiene, which contains a Ge
1 with respect to 3) did not result in further incorporation of phenyl acetylene into the complex even at elevated temperatures. However, compound 5 was found to decompose in solution to yield styrene (see ESI Fig. S37 and S38†). Monitoring a C6D6 solution of 5 showed that this occurs intramolecularly, with the additional protons required to make styrene likely the result of C–H activation. In further support of an intramolecular C–H activation, addition of a hydrogen source, e.g. dihydrogen, phenyl silane, pinacol borane or amine borane, failed to provide any notable increase in the rate of styrene formation. Unfortunately, attempts to identify the fate of the resulting aluminium containing species were unsuccessful. It is proposed that initially [2 + 2]-cycloaddition occurs to form compound 5, followed by C–H activation of the iso-propyl groups of the Tipp ligand, as this was not observed with the analogous silyl complex. Intramolecular C–H activation of the Mes* ligand (Mes* = 2,4,6-tri-tert-butylphenyl) has been previously observed by thermolysis of (Mes*)2AlH,33 whilst 1-germapropadiene, which contains a Ge![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C double bond supported by Tipp ligands, also undergoes C–H activation of the Tipp ligand.34
C double bond supported by Tipp ligands, also undergoes C–H activation of the Tipp ligand.34
Further reactivity towards C–C multiple bonds was trialed with diphenylacetylene (PhCCPh). Addition of 1 eq. of PhCCPh to 3Si failed to cause a reaction, and after prolonged heating only decomposition of 3Si was observed. In contrast, PhCCPh was observed to react readily with 3, notably through the instant colour change from the dark black solution of 3 to a yellow solution of compound 6. This difference in reactivity was surprising, considering that both 3 and 3Si reacted cleanly with both non-polar (ethylene to form 4 and 4Si) and polar (phenylacetylene to form 5 and 5Si) C–C multiple bonds. This difference in reactivity is thought to be a direct result of the choice of stabilising ligand. The flexibility of the Tipp ligand, due to the rotational iso-propyl groups, makes the central AlAl core more accessible for reactant molecules, thus enabling reactivity with more sterically demanding reagents. Moreover, the positive NPA charges of 3 make it more electrophilic in comparison to 3Si, thus implying higher reactivity towards nucleophilic C–C multiple bonds.
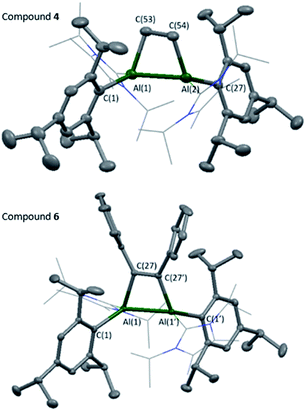
Compounds 4 and 6 were crystallised from concentrated pentane solutions at −30 °C. The XRD structures revealed addition of the C–C multiple bonds to the dialumene, resulting in the formation of 4-membered rings (Fig. 4). Loss of double bond character from the dialumene was confirmed due to elongation of the Al–Al bond (4 2.6035(13), 6 2.5918(6) vs.3 2.4039(8) Å). Also noted to occur is the elongation of the Al–CNHC bond lengths (4 2.079(3), 2.093(3), 6 2.1097(15) vs.3 2.0596(16), 2.0422(17) Å). The 4-membered ring in 6 is almost planar (6.37° between Al–Al–C(27) planes), whilst 4 is puckered due to the presence of the sp3 carbons.
Extension of this work towards C–N triple bonds focused on the use of 2,6-dimethylphenylisocyanide (XylNC). Previously, Tokitoh and co-workers had shown that reaction of their masked dialumene species resulted in homocoupling of isocyanides.35 Reactions of varying equivalents of XylNC to 3Si all resulted in an ill-defined mixture of species; unfortunately, attempts to separate species through fractional crystallisation failed. In contrast, reaction of 2 eq. of XylNC with 3 resulted in a clear colour change from black to red and produced a well-defined but complex 1H NMR spectrum of compound 7 (Scheme 3). This complex contains bridging CNXyl units due to the observed downfield signal in the 13C NMR spectrum at δ 303.4 ppm. This was similar to the previously observed bridging carbonyl fragment observed with 3Si, in the rearrangement of CO2 (δ 276.0 ppm)16 and the bridging isocyanide intermediate reported by Tokitoh (δ 294.7 ppm).35 Single crystals of 7 were grown from a 2![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 (toluene
1 (toluene![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
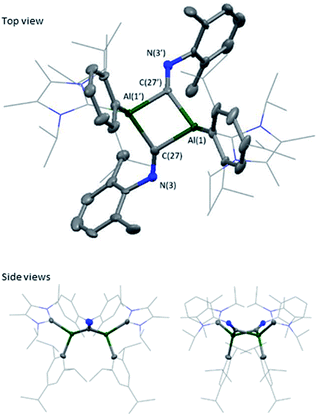
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) hexane) mixture at 5 °C, revealing a butterfly configuration with two μ-CNXyl units (Fig. 5).
hexane) mixture at 5 °C, revealing a butterfly configuration with two μ-CNXyl units (Fig. 5).
The central Al–CXyl–Al–CXyl core in compound 7 is puckered (34.3° between the two CXyl–Al–CXyl planes), with the supporting NHC and Tipp ligands now cis to the ring. This change from trans to cis-conformation has been observed previously for the C–H activated phenylacetylene product on reaction with 3Si. However, the reasons for such a change in conformation are unclear. Again, elongation of the Al–CNHC bond lengths are observed (Al–CNHC 2.109(3) Å), with the change in Al–CTipp negligible (7 2.042(7) vs.3 (2.0292(16) Å). Reduction of the C–N triple bond to a double bond is confirmed on inspection of the bond length (C(27)–N(3) 1.292(4) Å), which is in line with average C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N bond lengths.36–39 Additionally, the change in angle around the nitrogen in XylNC from linear to bent (126.3 (2) °) confirms reduction of the C–N triple bond. This butterfly configuration has been previously observed with transition metal complexes;40–47 however, they all contain a M–M bond, and those without M–M bonds contain a planar central ring.48–52
N bond lengths.36–39 Additionally, the change in angle around the nitrogen in XylNC from linear to bent (126.3 (2) °) confirms reduction of the C–N triple bond. This butterfly configuration has been previously observed with transition metal complexes;40–47 however, they all contain a M–M bond, and those without M–M bonds contain a planar central ring.48–52
To confirm the nature of the bonding within compound 7 DFT studies were performed again, at the B3LYP-D3/6-311G(d) level of theory. The optimised structure is in good agreement with the one obtained experimentally by SC-XRD, including the calculated C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N IR stretching frequencies (experimental: 1545 cm−1vs. calculated: 1568 cm−1). Orbital analysis (Fig. 6) revealed the HOMO as an orbital overlap of aluminium and π*(C–N). The LUMO represents the combination perpendicular to the HOMO, including conjugation across the central ring. NBO calculations confirmed that no C–C or Al–Al bond is present in 7 (WBI (C27C27′):0.06; WBI (Al1Al1′): 0.04).
N IR stretching frequencies (experimental: 1545 cm−1vs. calculated: 1568 cm−1). Orbital analysis (Fig. 6) revealed the HOMO as an orbital overlap of aluminium and π*(C–N). The LUMO represents the combination perpendicular to the HOMO, including conjugation across the central ring. NBO calculations confirmed that no C–C or Al–Al bond is present in 7 (WBI (C27C27′):0.06; WBI (Al1Al1′): 0.04).
Small molecule activation
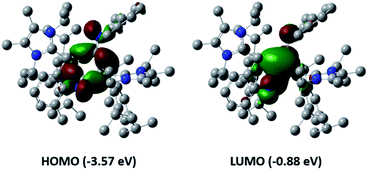
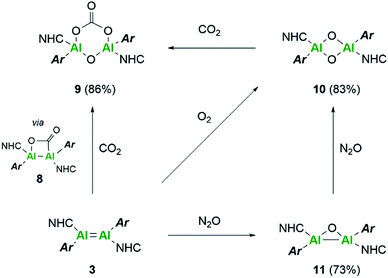
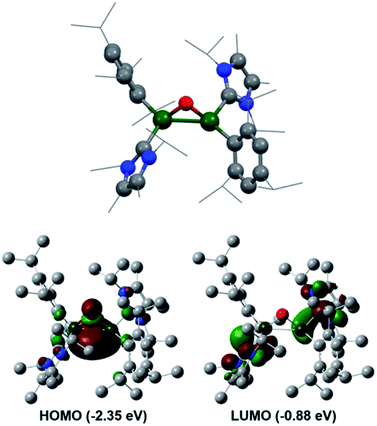
Further reactivity differences were sought through investigation towards small molecules (Scheme 4). Previously, reaction of 3Si towards carbon dioxide (CO2) resulted in an initial CO2 fixation complex.16 This subsequently underwent C–O cleavage reaction, in the absence of additional CO2 through rearrangement to a bridging carbonyl complex, whilst in the presence of CO2, formation of a carbonate species with elimination of CO was observed. On reaction of 3 with CO2 immediate loss of the black colour and formation of a colourless solution was observed. On inspection of the 13C NMR spectrum, the presence of CO (δ 184.4 ppm) and CO3 (δ 159.12 ppm) was observed, indicating the formation of the carbonate complex compound 9. In contrast to 3Si, attempts to isolate the CO2 fixation product were unsuccessful as it rapidly converted to compound 9. Use of the labile IiPr2Me2–CO2 species allowed for the formal [2 + 2]-cycloaddition product (compound 8) to be observed due to its characteristic 13C resonance at δ 207.7 ppm (8Siδ 209.9 ppm). However, this reaction resulted in multiple species as well as compound 9, owing to the higher reactivity of the Tipp dialumene (compound 3), thus indicating that formation of 9 proceeds through the CO2 fixation species in a similar manner to 3Si.Reaction of 3 with O2 resulted in the expected dioxo product, compound 10, same as the previously reported reaction of 3Si. In a similar manner to 10Si, compound 10 can also be reacted with CO2 resulting in carbonate complex 9. In a notable difference to the silyl supported reactivity, addition of N2O to compound 3 resulted in a dark red solution at room temperature (3Si yielded colourless compound 10Si). This red solution was observed to slowly fade to colourless over a few hours and the formation of compound 10 was confirmed by 1H NMR spectroscopy. Use of 1 eq. of an oxygen donor reagent, namely N-methylmorpholine-N-oxide, with 3 allowed for clean isolation of the red species, compound 11. Compound 11 is stable in the solid state for up to two months in a glovebox freezer; however, at room temperature and in solution, further oxidation to compound 10 occurs. Whilst 1H NMR showed similar environments for both 10 and 11 (Fig. S39†), compound 11 is intensely coloured (UV/vis = 512 nm, ε = 1155 L mol−1 cm−1) whilst 10 is colourless. As such compound 11 was tentatively assigned as a bridging aluminium(II) mono-oxide species, rather than a terminal aluminium(III) mono-oxide complex. Unfortunately, SC-XRD analysis did not provide clear structural parameters for the mono-oxide species due to superposition with compound 10 (Fig. S55†). To provide further insight, calculations were also performed on compounds 10 and 11. The optimised structure of 10 is symmetric relating to the Al–O bonds, as previously observed for the analogous silyl compound (10Si).16 TD-DFT calculations revealed the highest transition at 259 nm, in line with the experimental colourless appearance. In contrast, compound 11 bears substantial π-electron density between the two aluminium centres in the HOMO as depicted in Fig. 7, reminiscent of the disilaoxirane reported by our group.53 The LUMO represents the unoccupied π(Al–CNHC) bond. TD-DFT calculations verified the experimentally observed red colour (UV-vis 512 nm) with good accordance (calc. 519 nm), assigned to the HOMO to LUMO transitions of 11.
Extension of this small molecule reactivity towards dihydrogen was investigated. Firstly, a J-Young NMR tube containing a purple solution of 3Si was freeze–pump–thaw degassed and then backfilled with approximately 1 atm of H2. After 24 hours at room temperature no reaction was noted to have occurred; increasing the temperature to 60 °C and regular monitoring only resulted in the observed decomposition of 3Si.
Repetition of this reaction with the aryl stabilised dialumene, compound 3, also resulted in no reaction at room temperature. After 16 h at 50 °C, however, the black colour of 3 had faded to a dark brown/yellow solution (Scheme 5). On inspection of the 1H NMR spectrum, no Al–H signals could be observed owing to the quadrupolar nature of the Al centre. Additionally, three distinct iso-propyl signals similar to that observed for compound 1 were identified. These, however, were not identical and therefore complete hydrogenation and cleavage of the Al–Al bond can be ruled out. Thus, it is likely that compound 12 consists of either terminal or bridging hydrides.
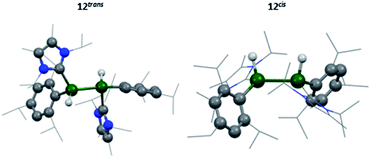
IR spectroscopy was utilised to differentiate between the two likely structures; two broad but distinct peaks at 1593 and 1634 cm−1 were observed. Compounds containing no Al–Al bond but both terminal and bridging hydrides are found at approximately 1880 cm−1 and 1350 cm−1, respectively,20,54 whilst terminal hydrides within complexes containing Al–Al bonds are found within 1680–1835 cm−1,55 thus pointing more in the direction of a terminal hydride with Al–Al bonds. Additionally, for the previous terminal hydride in the related silyl system, from C–H activation of phenyl acetylene, this Al–H was found at 1666 cm−1.15 Unfortunately, attempts to grow crystals suitable for SC-XRD were unsuccessful. Therefore, additional insight for this structure was sought computationally. Different possible isomers of product 12 were calculated, including bridging, terminal, and combinations of both as well as different rotational isomers (H: cis or trans; NHC and Tipp ligands: cis or trans).
The two lowest lying isomers were found to possess terminal hydrides in the cis and trans configurations (Fig. 8). The Al–H stretching frequencies were calculated to be 1634 and 1676 cm−1, respectively, which is in good agreement with the experimentally obtained values (for detailed information see the ESI†). It is, therefore, suggested that the activation of hydrogen by 3 results in both the cis and trans isomers of compound 12.
Catalysis
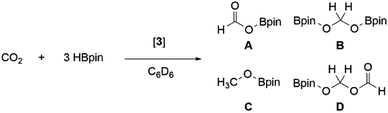
Further comparisons between the two dialumenes examined their use in catalytic applications. Two archetypal catalytic reactions (hydroboration and dehydrocoupling) were studied due to their prevalence in main group catalysis, as well as the implication of metal-hydrides in facilitating turnover.56,57 With the ability to form dialuminium-hydrides in the case of 3 and not for 3Si, differences in activity and mechanistic pathways are anticipated.CO2 hydroboration
Previously, 3Si was found to selectively catalyse the reduction of CO2 to a formic acid equivalent (product A, Scheme 6) with pinacol borane (HBpin).16 Whilst this reaction does proceed at room temperature, it required up to 1 week and 10 mol% of 3Si (Table 1, entry 1); use of higher temperatures allowed for reduced catalyst loadings and decreased reaction times (Table 1, entry 2). As 3 has so far shown increased reactivity, a trial reaction with 5 mol% of 3 towards hydroboration of CO2 at room temperature was carried out (Table 1, entry 3). On regular monitoring through 1H and 11B NMR spectroscopy the consumption of HBpin was noted to occur along with the formation of new B–O containing species. The corresponding 1H NMR spectrum showed the presence of further reduced species (A–D, Scheme 6), indicating that 3 is not only more catalytically active, but also proceeds through an alternate mechanism due to the presence of B–C.| Entry | Catalyst | Loading/mol% | Time/h | Temp/°C | Conversiona/% | Product distributionb/% | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | C | D | ||||||
| a Conversion of HBpin based on 11B NMR integrals. b Ratio of products based on 1H NMR integrals. | |||||||||
| 1 | 3Si | 10 | 110 | 20 | 86 | 86 | 7 | 7 | 0 |
| 2 | 3Si | 5 | 4 | 60 | 68 | 94 | 2 | 4 | 0 |
| 3 | 3 | 5 | 58 | 20 | 81 | 39 | 27 | 34 | 0 |
| 4 | 3 | 5 | 24 | 20 | 66 | 65 | 15 | 17 | 3 |
| 5 | 3 | 1 | 24 | 60 | 62 | 49 | 7 | 41 | 3 |
Again, through use of a higher temperature (60 °C), the catalyst loading could be decreased down to 1 mol% (Table 1, entry 5). This resulted in the same consumption of HBpin after 24 h (at RT) as with 5 mol% (Table 1, entry 4); however, the resulting product distribution differs, with higher temperatures favouring the formation of the triply reduced methanol equivalent (product C, Scheme 6).
The formation of more highly reduced species indicates a likely change in the mechanism. Previously, 3Si showed no reactivity towards HBpin and as such a non-hydridic mechanism based on the initial formation of 9Si was proposed. From computational analysis, coordination of HBpin and subsequent reduction of the exocyclic carbonyl of 9Si was found to be rate determining. Turnover was achieved through coordination/insertion of an additional CO2 on the opposite side of the Al⋯Al plane resulting in formation of an 8-membered ring which collapses to reform 9Si with release of the formic acid equivalent. This mechanism also further supports the observed selectivity towards product A.16
In this instance, use of 3 results in the formation of products B–D in notable amounts; therefore, an alternative mechanism for the hydroboration of CO2 is highly likely. As such, 3 was reacted with 1 eq. of HBpin; the 11B NMR spectrum showed complete consumption of HBpin and formation of a new upfield doublet at δ 2.57 ppm (JHB = 112.18 Hz). The same signal and coupling were observed from the reaction of HBpin and IiPr2Me2; therefore it is proposed that the stoichiometric reaction of 3 and HBpin results in NHC abstraction. Notably, this does not result in H–B bond cleavage and formation of an Al(H)–Al(Bpin) type species, which was observed with diborene58 and disilyne59 chemistry. Addition of CO2 to this IiPr2Me2–HBpin adduct did not result in formation of any reduced CO2 species, or any reaction after 24 h at room temperature; therefore it is unlikely that this is the catalytically active species. It is of note that NHCs have been shown to catalyse hydroboration (with HBpin) of carbonyl compounds, in acetonitrile.60
Whilst these experimental observations preclude definitive mechanistic analysis, it is proposed that the aryl stabilised dialumene (3) acts as a pre-catalyst, with CO2 hydroboration occurring through an initial hydroalumination of CO2 and subsequent Al–O/B–H σ-bond metathesis, in line with other previously reported main group hydroelementation of CO2 mechanisms.61–70
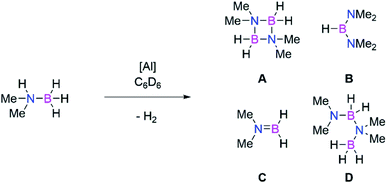
Amine borane dehydrogenation
Main group catalysts (largely group 1, 2, and 13) have also been shown to be viable dehydrocoupling catalysts.56,57,71,72 These reactions largely proceed through formation of M–H and M–E bonds, via σ-bond metathesis reactions due to the differing protic and hydridic substrates. Therefore, to probe the intermediacy of aluminium hydrides we examined the use of both dialumenes in amine-borane dehydrocoupling catalysis. Use of 5 mol% of 3 and 3Si with Me2NHBH3 in C6D6 showed rapid evolution of gas at room temperature in the case of the aryl substituted dialumene (3). Regular monitoring of both reaction mixtures at room temperature by 1H and 11B NMR spectroscopy confirmed the formation of H2 and showed several boron containing species by 11B NMR (Scheme 7, products A–D). After 5 h approximately 70% of the Me2NHBH3 had been consumed in the case of 3 (Table 2, entry 1); in contrast, the silyl dialumene 3Si after three times as long resulted in 17% consumption of Me2NHBH3 (Table 2, entry 3). Notably, prolonged reaction times in the case of the 3 did not lead to significant or complete consumption of Me2NHBH3 (Table 2, entry 2), and only a small change in the product distribution was observed with increased reaction times.| Entry | Catalyst | Loading/mol% | Time/hr | Temp/°C | Conversiona/% | Product distributionb/% | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | C | D | ||||||
| a Conversion of Me2NHBH3 based on 11B NMR integrals. b Ratio of products based on 11B NMR integrals. | |||||||||
| 1 | 3 | 5 | 5 | 20 | 72 | 25 | 5 | — | 27 |
| 2 | 3 | 5 | 44 | 20 | 78 | 35 | 5 | — | 23 |
| 3 | 3Si | 5 | 16.5 | 20 | 17 | 5 | 1 | — | 11 |
| 4 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 20 | 28 | 8 | 1 | <1 | 13 |
| 5 | 3 | 1 | 16.5 | 20 | 60 | 45 | 1 | <1 | 14 |
| 6 | 1 | 5 | 24 | 20 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 7 | 1 | 5 | 24 | 60 | 31 | 11 | — | — | 15 |
It was also possible to use 1 mol% of 3; again, fast consumption of Me2NHBH3 was observed within the first few hours (Table 2, entry 4) with the reaction rate slowing with increased Me2NHBH3 consumption (Table 2, entry 5). As aluminium-hydrides have been used in amine borane catalysis previously,73 and to rule out complete hydrogenation and Al–Al bond cleavage during the reaction, compound 1 was tested for dehydrocoupling activity. After 24 h at room temperature (Table 2, entry 6) no conversion of Me2NHBH3 was observed; on increasing the temperature to 60 °C (Table 2, entry 7), some formation of H2 and products A–D was observed. Due to the increased temperature and prolonged reaction times required for compound 1, it is proposed that the retention of an Al–Al bond accounts for the increased catalytic activity.
Comparable to hydroboration reactions, the aryl stabilised dialumene (3) was found to be more catalytically active than the silyl-stabilised counterpart (3Si). Mechanistically speaking, amine-borane dehydrocoupling reactions generally occur through formation of M–H and M–E bonds.57 As such, it has been shown that formation of Al–H bonds is more accessible from 3 compared to 3Si, therefore accounting for the difference in catalytic activity. Both reactions show initial formation of a catalytic equivalent of HB(NMe2)2 (product B, Scheme 7) which then remains constant throughout the catalysis. It has previously been shown by Wright and co-workers that formation of B is the result of the formation of the catalytically active Al–H containing species from Al(NR3)3 (R = Me, iPr).74 Furthermore, Braunschweig and co-workers recently showed that Me2NHBH3 can be used to isolate hydrogenated diborenes; thus, analogous reactivity is anticipated.75 However, in our hands, stoichiometric reactions of 3 and Me2NHBH3 resulted in a mixture of species, whilst reaction with a higher number of equivalents of Me2NHBH3 resulted in the dehydrocoupling products. We therefore conclude that the dialumene acts as a pre-catalyst in this reaction and the active catalyst is generated in situ.
Conclusions
In conclusion, we have shown the fundamental differences between aryl and silyl supporting ligands for the stabilisation of dialumenes and their subsequent influence on reactivity. The increased flexibility of the trans-bent and twisted structure for the aryl dialumene (3) enables reactivity with more sterically demanding substrates, and in addition is now able to activate dihydrogen. Further differences are observed in the catalytic ability of the two dialumenes, with the latter exhibiting higher activity. This is likely due to different mechanisms in the catalytic cycle and the ability of the aryl dialumene to stabilise a metal-hydride intermediate in contrast to the silyl ligand.Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.Acknowledgements
We thank Prof. Dr M. C. Holthausen and Dr J. I. Schweizer (Goethe-Universität Frankfurt am Main) for fruitful discussions, computational resources, and advice. Quantum chemical calculations were performed in parts at the Leibniz Supercomputing Center of the Bavarian Academy of Science and Humanities. We are also grateful to Dr A. Pöthig and Dr C. Jandl for crystallographic advice, and M. Muhr (Prof. R. A. Fischer, TUM) for the LIFDI-MS measurements. This project has received funding from the European Union's Horizon 2020 research and innovation program under the Marie Skłodowska-Curie grant agreement No 754462 (Fellowship CW), as well as the European Research Council (SILION 637394) and WACKER Chemie AG.Notes and references
- F. A. Cotton, C. A. Murillo and R. A. Walton, Multiple Bonds Between Metal Atoms, Springer, New York, 3rd edn, 2005 Search PubMed.
- R. West, M. J. Fink and J. Michl, Science, 1981, 214, 1343 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. J. Davidson and M. F. Lappert, J. Chem. Soc., Chem. Commun., 1973, 317a RSC.
- A. G. Brook, F. Abdesaken, B. Gutekunst, G. Gutekunst and R. K. Kallury, J. Chem. Soc., Chem. Commun., 1981, 191–192 RSC.
- M. Yoshifuji, I. Shima, N. Inamoto, K. Hirotsu and T. J. Higuchi, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1981, 103, 4587–4589 CrossRef CAS.
- P. P. Power, Chem. Rev., 1999, 99, 3463–3504 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. C. Fischer and P. P. Power, Chem. Rev., 2010, 110, 3877–3923 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. P. Power, Nature, 2010, 463, 171–177 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Weetman and S. Inoue, ChemCatChem, 2018, 10, 4213–4228 CrossRef CAS.
- R. L. Melen, Science, 2019, 363, 479–484 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- G. H. Spikes, J. C. Fettinger and P. P. Power, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2005, 127, 12232–12233 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Kira, S. Ohya, T. Iwamoto, M. Ichinohe and C. Kabuto, Organometallics, 2000, 19, 1817–1819 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Kira, Proc. Jpn. Acad., Ser. B, 2012, 88, 167–191 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. Wendel, T. Szilvási, C. Jandl, S. Inoue and B. Rieger, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2017, 139, 9156–9159 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. Bag, A. Porzelt, P. J. Altmann and S. Inoue, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2017, 139, 14384–14387 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Weetman, P. Bag, T. Silvási, C. Jandl and S. Inoue, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2019, 58, 10961–10965 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. Bag, C. Weetman and S. Inoue, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2018, 57, 14394–14413 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. J. Wright, A. D. Phillips and P. P. Power, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2003, 125, 10784–10785 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. Agou, K. Nagata and N. Tokitoh, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2013, 52, 10818–10821 CrossRef CAS.
- K. Nagata, T. Murosaki, T. Agou, T. Sasamori, T. Matsuo and N. Tokitoh, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2016, 55, 12877–12880 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- N. J. Hardman, R. J. Wright, A. D. Phillips and P. P. Power, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2003, 125, 2667–2679 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Z. Zhu, R. C. Fischer, B. D. Ellis, E. Rivard, W. A. Merrill, M. M. Olmstead, P. P. Power, J. D. Guo, S. Nagase and L. Pu, Chem.–Eur. J., 2009, 15, 5263–5272 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. J. Wright, A. D. Phillips, S. Hino and P. P. Power, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2005, 127, 4794–4799 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- E. Rivard and P. P. Power, Inorg. Chem., 2007, 46, 10047–10064 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Moilanen, P. P. Power and H. M. Tuononen, Inorg. Chem., 2010, 49, 10992–11000 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. A. Caputo, J.-D. Guo, S. Nagase, J. C. Fettinger and P. P. Power, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2012, 134, 7155–7164 CrossRef CAS.
- C. A. Caputo, J. Koivistoinen, J. Moilanen, J. N. Boynton, H. M. Tuononen and P. P. Power, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2013, 135, 1952–1960 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. A. Caputo and P. P. Power, Organometallics, 2013, 32, 2278–2286 CrossRef CAS.
- Attempts to follow a similar synthetic strategy to the previous dihalide precursor, i.e. halogenation followed by salt metathesis with LiTipp, resulted in a largely unreacted mixture after 36 hrs at room temperature with 10% conversion to a mixture of compounds which could not be separated.
- P. Pyykkö and M. Atsumi, Chem.–Eur. J., 2009, 15, 186–197 CrossRef PubMed.
- Compared to 3Si, mixing of the π(Al–Al) and π*(CNHC–N) raises the HOMO energy, with the HOMO to LUMO transition shifted to higher wavelength in the UV-vis spectrum. Several smaller absorptions, only observable as a broad band around 600 nm (see Table S4†), are attributed to HOMO to LUMO+1/+3 transitions.
- Experimental attempts to isolate an IMe4 stabilised dialumene failed in both silyl and Tipp based systems. This was trialed both through analogous synthetic procedures and ligand exchange reactions on the isolated complexes 3 and 3Si.
- R. J. Wehmschulte and P. P. Power, Inorg. Chem., 1998, 37, 2106–2109 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- B. E. Eichler, D. R. Powell and R. West, Organometallics, 1999, 18, 540–545 CrossRef CAS.
- K. Nagata, T. Agou, T. Sasamori and N. Tokitoh, Chem. Lett., 2015, 44, 1610–1612 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Weetman, M. S. Hill and M. F. Mahon, Chem. Commun., 2015, 51, 14477–14480 RSC.
- W. Uhl and M. Matar, Z. Naturforsch., B: Chem. Sci., 2004, 59, 1214–1222 CAS.
- R. Lalrempuia, C. E. Kefalidis, S. J. Bonyhady, B. Schwarze, L. Maron, A. Stasch and C. Jones, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2015, 137, 8944–8947 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Spielmann and S. Harder, Chem.–Eur. J., 2007, 13, 8928–8938 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. C. Pettersen and G. G. Cash, Acta Crystallogr., Sect. B: Struct. Crystallogr. Cryst. Chem., 1977, 33, 2331–2334 CrossRef.
- F. A. Cotton and B. A. Frenz, Inorg. Chem., 1974, 13, 253–256 CrossRef CAS.
- R. D. Adams, F. A. Cotton and G. A. Rusholme, J. Coord. Chem., 1972, 1, 275–283 CrossRef CAS.
- W. E. Carroll, M. Green, A. M. R. Galas, M. Murray, T. W. Turney, A. J. Welch and P. Woodward, J. Chem. Soc., Dalton Trans., 1980, 80–86 RSC.
- T. Takao, N. Obayashi, B. Zhao, K. Akiyoshi, H. Omori and H. Suzuki, Organometallics, 2011, 30, 5057–5067 CrossRef CAS.
- G. Cox, C. Dowling, A. R. Manning, P. McArdle and D. Cunningham, J. Organomet. Chem., 1992, 438, 143–158 CrossRef CAS.
- K. Boss, C. Dowling, A. R. Manning, D. Cunningham and P. McArdle, J. Organomet. Chem., 1999, 579, 252–268 CrossRef CAS.
- A. R. Manning, K. Boss, M. G. Cox, A. McCabe, P. Soye, S. C. Wade, P. A. McArdle and D. Cunningham, J. Organomet. Chem., 1995, 487, 151–162 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Weidenbruch, B. Brand-Roth, S. Pohl and W. Saak, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 1990, 29, 90–92 CrossRef.
- M. Weidenbruch, J. Hamann, H. Piel, D. Lentz, K. Peters and H. G. von Schnering, J. Organomet. Chem., 1992, 426, 35–40 CAS.
- D. Lentz, I. Brüdgam and H. Hartl, J. Organomet. Chem., 1986, 299, C38–C42 CAS.
- D. Lentz and S. Willemsen, J. Organomet. Chem., 2000, 612, 96–105 CrossRef CAS.
- A. K. Adhikari, M. B. Sárosi, T. Grell, P. Lönnecke and E. Hey-Hawkins, Chem.–Eur. J., 2016, 22, 15664–15668 CrossRef PubMed.
- D. Wendel, T. Szilvási, D. Henschel, P. J. Altmann, C. Jandl, S. Inoue and B. Rieger, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2018, 57, 14575–14579 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. J. Wehmschulte and P. P. Power, Inorg. Chem., 1994, 33, 5611–5612 CrossRef CAS.
- S. J. Bonyhady, D. Collis, G. Frenking, N. Holzmann, C. Jones and A. Stasch, Nat. Chem., 2010, 2(10), 865–869 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. S. Hill, D. J. Liptrot and C. Weetman, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2016, 45, 972–988 RSC.
- R. L. Melen, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2016, 45, 775–788 RSC.
- H. Braunschweig, R. D. Dewhurst, C. Hörl, A. K. Phukan, F. Pinzner and S. Ullrich, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2014, 53, 3241–3244 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. Takeuchi, M. Ikoshi, M. Ichinohe and A. Sekiguchi, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2010, 132, 930–931 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. Li, J. Zhang and C. Cui, Chin. J. Chem., 2019, 37, 679–683 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Caise, D. Jones, E. L. Kolychev, J. Hicks, J. M. Goicoechea and S. Aldridge, Chem.–Eur. J., 2018, 24, 13624–13635 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. Franz, C. Jandl, C. Stark and S. Inoue, ChemCatChem, 2019, 11, 5275–5281 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. D. Anker, M. Arrowsmith, P. Bellham, M. S. Hill, G. Kociok-Köhn, D. J. Liptrot, M. F. Mahon and C. Weetman, Chem. Sci., 2014, 5, 2826–2830 RSC.
- G. Tan, W. Wang, B. Blom and M. Driess, Dalton Trans., 2014, 43, 6006–6011 RSC.
- D. Mukherjee, S. Shirase, T. P. Spaniol, K. Mashima and J. Okuda, Chem. Commun., 2016, 52, 13155–13158 RSC.
- D. Mukherjee, H. Osseili, T. P. Spaniol and J. Okuda, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2016, 138, 10790–10793 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Jana, D. Ghoshal, H. W. Roesky, I. Objartel, G. Schwab and D. Stalke, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2009, 131, 1288–1293 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. J. Hadlington, C. E. Kefalidis, L. Maron and C. Jones, ACS Catal., 2017, 7, 1853–1859 CrossRef CAS.
- J. A. Abdalla, I. M. Riddlestone, R. Tirfoin and S. Aldridge, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2015, 54, 5098–5102 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Jana, G. Tavčar, H. W. Roesky and M. John, Dalton Trans., 2010, 39, 9487–9489 RSC.
- R. J. Less, R. L. Melen and D. S. Wright, RSC Adv., 2012, 2, 2191–2199 RSC.
- J. D. Erickson, T. Yi Lai, D. J. Liptrot, M. M. Olmstead and P. P. Power, Chem. Commun., 2016, 52, 13656–13659 RSC.
- C. Weetman, N. Ito, M. Unno, F. Hanusch and S. Inoue, Inorganics, 2019, 7, 92–103 CrossRef CAS.
- H. J. Cowley, M. S. Holt, R. L. Melen, J. M. Rawson and D. S. Wright, Chem. Commun., 2011, 47, 2682–2684 RSC.
- M. Dömling, M. Arrowsmith, U. Schmidt, L. Werner, A. C. Castro, J. O. C. Jiménez-Halla, R. Bertermann, J. Müssig, D. Prieschl and H. Braunschweig, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2019, 58, 9782–9786 CrossRef PubMed.
Footnote |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available. CCDC 1989167–1989172. For ESI and crystallographic data in CIF or other electronic format see DOI: 10.1039/d0sc01561j |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2020 |