Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleCreative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported Licence
Correction: Surface phosphonation treatment shows dose-dependent enhancement of the bioactivity of polyetheretherketone
Lvhua Liua,
Yanyan Zheng*a,
Qianyu Zhangb,
Lin Yuc,
Ziliang Hud and
Ying Liu*b
aSchool of Basic Medical Sciences, North Sichuan Medical College, Nanchong, China. E-mail: yanyzheng@163.com
bDepartment of Stomatology, North Sichuan Medical College, Affiliated Hospital of North Sichuan Medical College, Nanchong, China. E-mail: ying_nsmc@hotmail.com
cDepartment of Pharmacology, North Sichuan Medical College, Nanchong, China
dDepartment of Preventive Medicine, North Sichuan Medical College, Nanchong, China
First published on 30th April 2020
Abstract
Correction for ‘Surface phosphonation treatment shows dose-dependent enhancement of the bioactivity of polyetheretherketone’ by Lvhua Liu et al., RSC Adv., 2019, 9, 30076–30086, DOI: 10.1039/C9RA05229A.
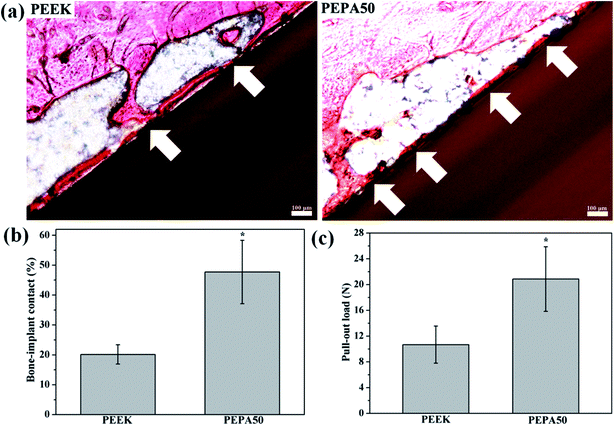
The authors regret that an incorrect version of Fig. 9 was included in the original article. The correct version of Fig. 9 is presented below.
The Royal Society of Chemistry apologises for these errors and any consequent inconvenience to authors and readers.
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2020 |