High stability SrTi1−xFexO3−δ electrodes for oxygen reduction and oxygen evolution reactions†
Abstract
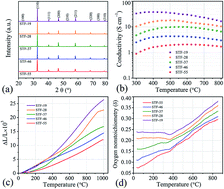
Sr(Ti1−xFex)O3−δ (STF) has recently been explored as an oxygen electrode for solid oxide electrochemical cells (SOCs). Model thin film electrode studies show oxygen surface exchange rates that generally improve with increasing Fe content when x < 0.5, and are comparable to the best Co-containing perovskite electrode materials. Recent results on porous electrodes with the specific composition Sr(Ti0.3Fe0.7)O3−δ show excellent electrode performance and stability, but other compositions have not been tested. Here we report results for porous electrodes with a range of compositions from x = 0.5 to 0.9. The polarization resistance decreases with increasing Fe content up to x = 0.7, but increases for further increases in x. This results from the interaction of two effects – the oxygen solid state diffusion coefficient increases with increasing x, but the electrode surface area and surface oxygen exchange rate decrease due to increased sinterability and Sr surface segregation for the Fe-rich compositions. Symmetric cells showed no degradation during 1000 h life tests at 700 °C even at a current density of 1.5 A cm−2, showing that all the STF electrode compositions worked stably in both fuel cell mode and electrolysis modes. The excellent stability may be explained by X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS) results showing that the amount of surface segregated Sr did not change during the long-term testing, and by relatively low polarization resistances that help avoid electrode delamination.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...
