Facile preparation of self-assembled hydrogels constructed from poly-cyclodextrin and poly-adamantane as highly selective adsorbents for wastewater treatment†
Abstract
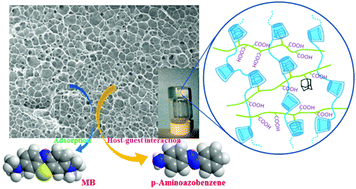
Self-assembled hydrogel materials constructed from cyclodextrin polymer (P-CD)/adamantane-modified poly acrylic acid (PAA-Ad) were designed and prepared via host–guest interactions. It was observed that the prepared supramolecular hydrogels had an interconnected three-dimensional porous network. In addition, the obtained hydrogels showed a recovery performance and it was confirmed that the host–guest interactions between β-cyclodextrin and adamantane were the main driving force for the formation of the hydrogels. The mechanical properties of the hydrogels could be adjusted by varying the concentrations of PAA-Ad. In particular, the prepared supramolecular hydrogels exhibited superior performances in water purification. The results demonstrated that the hydrogels possessed different mechanisms in the adsorption of the four typical poisonous organic dye molecules used, including bisphenol A (BPA), 4-aminoazobenzene (N-Azo), methylene blue (MB), and rhodamine B (RhB). The hydrogels mainly adsorbed N-Azo by host–guest interaction and adsorbed BPA by host–guest interaction and hydrogen bond synergy. They also adsorbed MB and RhB by hydrogen bonding and electrostatic interaction.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...