Electrokinetic energy conversion in nanochannels grafted with pH-responsive polyelectrolyte brushes modelled using augmented strong stretching theory
Abstract
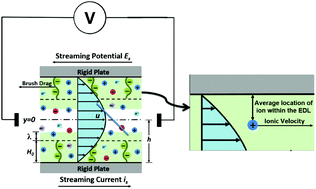
In this paper, we develop a theory to quantify the electrokinetic energy conversion in electrolyte-filled nanochannels grafted with pH-responsive polyelectrolyte (PE) brushes. A pressure-driven flow drives the mobile electrolyte ions of the electric double layer (EDL) supported by the charged PE brushes leading to the generation of a streaming current, a streaming electric field and eventually an electrical energy. The salient feature of this study is that the brushes are described using our recently developed augmented Strong Stretching Theory (SST) model. In all the previous theoretical studies on liquid transport in PE-brush-grafted nanochannels, the brushes have either been assumed to be of constant height (independent of salt concentration or pH) or modelled using the Alexander–de-Gennes model that considers uniform monomer distribution along the brush height. Such simplifications have meant that the salt and the pH dependence of the brush height, the monomer distribution, and the resulting electrostatics have not been appropriately accounted for in the transport calculations. This paper addresses these limitations and provides a much more detailed description of the brushes while capturing the corresponding electrokinetic energy conversion. The results establish that the presence of the PE brushes ensures a localization of the average EDL charge density away from the grafting surface, thereby enabling the migration of the EDL ions with a larger background flow velocity; as a consequence, there is an enhancement of the streaming current, streaming electric field, and the resulting electrical energy generation under certain grafting densities of the PE brushes.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...