Novel MAB phases and insights into their exfoliation into 2D MBenes†
Abstract
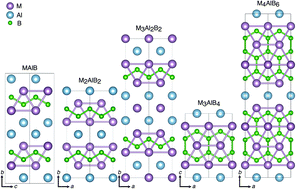
Considering the recent breakthroughs in the synthesis of novel two-dimensional (2D) materials from layered bulk structures, ternary layered transition metal borides, known as MAB phases, have come under scrutiny as a means of obtaining novel 2D transition metal borides, the so-called MBenes. Here, based on a set of phonon calculations, we show the dynamic stability of many Al-containing MAB phases, MAlB (M = Ti, Hf, V, Nb, Ta, Cr, Mo, W, Mn, Tc), M2AlB2 (Sc, Ti, Zr, Hf, V, Cr, Mo, W, Mn, Tc, Fe, Rh, Ni), M3Al2B2 (M = Sc, T, Zr, Hf, Cr, Mn, Tc, Fe, Ru, Ni), M3AlB4 (M = Sc, Ti, Zr, Hf, V, Nb, Ta, Cr, Mo, W, Mn, Fe), and M4AlB6 (M = Sc, Ti, Zr, Hf, V, Nb, Ta, Cr, Mo). By comparing the formation energies of these MAB phases with those of their available competing binary M–B and M–Al, and ternary M–Al–B phases, we find that some of the Sc-, Ti-, V-, Cr-, Mo-, W-, Mn-, Tc-, and Fe-based MAB phases could be favorably synthesized under appropriate experimental conditions. In addition, by examining the strengths of various bonds in MAB phases via crystal orbital Hamilton population and spring constant calculations, we find that the B–B and then M–B bonds are stiffer than the M–Al and Al–B bonds. The different strengths between these bonds imply the etching possibility of Al atoms from MAB phases, consequently forming various 2D MB, M2B3, and M3B4 MBenes. Furthermore, we employ the nudged elastic band method to investigate the possibility of the structural phase transformation of the 2D MB MBenes into graphene-like boron sheets sandwiched between transition metals and find that the energy barrier of the transformation is less than 0.4 eV per atom.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...