Nickel reduces calcium dependent dimerization in neural cadherin†
Abstract
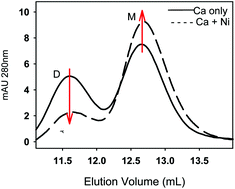
Cadherins are the transmembrane component in adherens junctions, structures that link the actin cytoskeletons in adjacent cells within solid tissues including neurological synapses, epithelium and endothelium. Cell–cell adhesion by cadherins requires the binding of calcium ions to specific sites in the extracellular region. Given the complexity of the cell adhesion microenvironment, we are investigating whether other divalent cations might affect calcium-dependent dimerization of neural (N) cadherin. The studies reported herein characterize the impact of binding physiological magnesium(II) or neurotoxic nickel(II) on calcium-dependent N-cadherin function. Physiological levels of magnesium have only a small effect on the calcium-binding affinity and calcium-induced dimerization of N-cadherin. However, a tenfold lower concentration of nickel decreases the apparent calcium-binding affinity and calcium-induced dimerization of N-cadherin. Competitive binding studies indicate that the apparent dissociation constants for nickel and magnesium are 0.2 mM and 2.5 mM, respectively. These Kd values are consistent with concentrations observed for a range of divalent cations in the extracellular space. Results from these studies indicate that calcium-induced dimerization by N-cadherin is attenuated by natural and non-physiological divalent cations in the extracellular microenvironment.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...