Synthesis, ribosomal selectivity, and antibacterial activity of netilmicin 4′-derivatives†
Abstract
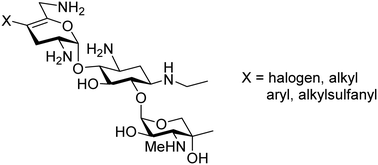
Halogenation of a suitably protected netilmicin derivative enables preparation of 4′-chloro-, bromo-, and iodo derivatives of netilmicin after deprotection. Suzuki coupling of a protected 4′-bromo derivative with phenylboronic acid or butyltrifluoroborate affords the corresponding 4′-phenyl and 4′-butyl derivatives of netilmicin. Sulfenylation of suitably protected netilmicin derivative with ethanesulfenyl chloride followed by deprotection affords 4′-ethylsulfanylnetilmicin. All netilmicin 4′-derivatives displayed reduced levels of inhibition for prokaryotic ribosomes and reduced antibacterial activity against typical Gram-positive and Gram-negative strains. None of the derivatives displayed enhanced target selectivity.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Antimicrobial Resistance


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...