Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleCreative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported Licence
Correction: The role of Sox9 in collagen hydrogel-mediated chondrogenic differentiation of adult mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs)
Xianfang
Jiang†
 a,
Xianyuan
Huang†
b,
Tongmeng
Jiang†
a,
Xianyuan
Huang†
b,
Tongmeng
Jiang†
 bc,
Li
Zheng
bc,
Li
Zheng
 *bde,
Jinmin
Zhao
*bde,
Jinmin
Zhao
 bde and
Xingdong
Zhang
f
bde and
Xingdong
Zhang
f
aThe College of Stomatology, Guangxi Medical University, Nanning, 530021, China
bGuangxi Engineering Center in Biomedical Material for Tissue and Organ Regeneration, The First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi Medical University, Nanning, 530021, China. E-mail: zhengli224@163.com; Fax: +86-07715350975; Tel: +86-07715358132
cDepartment of Orthopaedics Trauma and Hand Surgery, The First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi Medical University, Nanning, 530021, China
dGuangxi Collaborative Innovation Center for Biomedicine, The First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi Medical University, Nanning, China
eGuangxi Key Laboratory of Regenerative Medicine, The First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi Medical University, Nanning, China
fNational Engineering Research Center for Biomaterials, Sichuan University, Chengdu, 610064, China
First published on 24th July 2019
Abstract
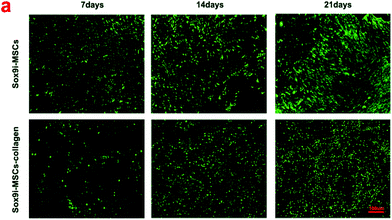
Correction for ‘The role of Sox9 in collagen hydrogel-mediated chondrogenic differentiation of adult mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs)’ by Xianfang Jiang, et al., Biomater. Sci., 2018, 6, 1556–1568.
Fig. 4a in the original manuscript is incorrect. The correct figure is shown below.
The Royal Society of Chemistry apologises for these errors and any consequent inconvenience to authors and readers.
Footnote |
| † These authors are contributed equally to this work. |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2019 |