Electrostatic interactions between charged dielectric particles in an electrolyte solution: constant potential boundary conditions
Abstract
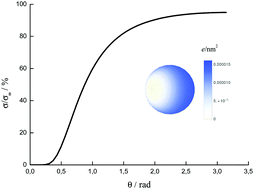
The problem of electrostatic interactions between colloidal particles in an electrolyte solution has been solved within the Debye–Hückel approximation using the boundary condition of constant potential. The model has been validated in two independent ways – by considering the limiting cases obtained from DLVO theory and comparison with the available experimental data. The presented methodology provides the final part of a complete theory of pairwise electrostatic interactions between spherical colloidal particles; one that embraces all possible chemical scenarios within the boundary conditions of constant potential and constant charge.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Electrostatics and Soft Matter


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...