Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleWS2/g-C3N4 composite as an efficient heterojunction photocatalyst for biocatalyzed artificial photosynthesis†
Peng Zengab,
Xiaoyuan Jiac,
Zhiguo Sua and
Songping Zhang *a
*a
aState Key Laboratory of Biochemical Engineering, Institute of Process Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100190, P. R. China. E-mail: spzhang@ipe.ac.cn; Fax: +86 10 82544958; Tel: +86 10 82544958
bUniversity of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049, P. R. China
cSchool of Pharmaceutical Sciences (Shenzhen), Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510275, P. R. China
First published on 5th June 2018
Abstract
A heterogeneous WS2/g-C3N4 composite photocatalyst was prepared by a facile ultrasound-assisted hydrothermal method. The WS2/g-C3N4 composite was used for photocatalytic regeneration of NAD+ to NADH, which were coupled with dehydrogenases for sustainable bioconversion of CO2 to methanol under visible light irradiation. Compared with pristine g-C3N4 and the physical mixture of WS2 and g-C3N4, the fabricated WS2/g-C3N4 composite catalyst with 5 wt% of WS2 showed the highest activity for methanol synthesis. The methanol productivity reached 372.1 μmol h−1 gcat−1, which is approximately 7.5 times higher than that obtained using pure g-C3N4. For further application demonstration, the activity of the WS2/g-C3N4 composite catalyst toward photodegradation of Rhodamine B (RhB) was evaluated. RhB removal ratio approaching 100% was achieved in 1 hour by using the WS2/g-C3N4 composite catalyst with 5 wt% of WS2, at an apparent degradation rate approximately 2.6 times higher than that of pure g-C3N4. Based on detailed investigations on physiochemical properties of the photocatalysts, the significantly enhanced reaction efficiency of the WS2/g-C3N4 composite was considered to be mainly benefiting from the formation of a heterojunction interface between WS2 and g-C3N4. Upon visible-light irradiation, the photo-induced electrons can transfer from the conduction band of g-C3N4 to WS2, thus recombination of electrons and holes was decreased and the photo-harvesting efficiency was enhanced.
1. Introduction
With the increasing concerns regarding the energy crisis and greenhouse gas emissions, it has become urgent to develop a new channel to achieve the conversion of CO2 to low-carbon fuel.1–5 Among the energy conversion systems, methanol conversion from CO2 by a cascade catalyzed by formate dehydrogenase (FateDH), formaldehyde dehydrogenase (FaldDH) and alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) is considered to be one of the most promising ways.6,7 However, the regeneration of coenzyme NADH in this multi-enzyme system is the key to the reaction process, since 3 moles of NADH are consumed for every mole of methanol produced.8,9 In the past decade, inspired by natural photosynthesis, photocatalytic regeneration of coenzyme with the process of reducing CO2 by multiple enzymes has brought new hope for solving this problem. For the success of such artificial photosynthesis systems, however, the major challenge is the development of efficient visible-light active photocatalysts.10–12Graphitic carbon nitride (g-C3N4), a polymeric semiconductor with a band gap of about 2.7 eV, has attracted significant attention in recent years because of its excellent visible light response,1,13,14 non-toxicity, low cost, and abundant raw materials. As a visible-light active photocatalyst, g-C3N4 has been widely applied for photocatalytic degradation of pollutants, water splitting, and regeneration of NADH since 2009.15,16 Nevertheless, fast recombination of photogenerated electron–hole pairs and low quantum efficiency limits its further applications. In general, there are three routes to improve the photocatalytic efficiency of g-C3N4, which include construction of nanostructure, elemental doping, and hybridization. By fabricating nanosheets,17 diatom frustule structure,18 multishell nanocapsules,19 and some other novel nanostructures,20 more active sites were exposed on g-C3N4 for enhanced light harvesting due to significantly increased specific surface area, and the migration rate of photo-generated electrons was promoted and the recombination of electrons and holes reduced.18–20 Elemental doping was another widely adopted method for reducing the recombination of electron–hole pairs by replacing the lattice defects of g-C3N4.21,22 Nevertheless, fabrication of new nanostructures and elemental doping often involve complicated preparation process and uncontrollable results. Compared with these above two methods, hybridization of g-C3N4 with some other semiconductors was is relative simple but efficient. The hybrid materials, which usually have an unsaturated outer layer electron, can act as a new electron carrier to trap the electrons in the conduction band (CB) of g-C3N4 through formation heterojunction or “Z” scheme electron transfer chain.4,23,24 Nevertheless, either construction of heterojunction or “Z” scheme transfer chain, there are certain requirements for the band structure of hybrid materials, which need a good coordinated relationship with that of g-C3N4.
In recent years, transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDCs) have emerged and received tremendous attentions. TMDCs such as WS2, MoS2, WSe2, and MoSe2, have various unique electronic, optical, mechanical and chemical properties, promising their potential applications in electronic devices, transistors, energy storage devices and catalysis.25–27 Among TMDCs, the 2H-WS2 has a band gap of about 2.64 V, with conduction band (CB) and valence band (VB) positions at ≈−1.03 V and 1.61 V versus normal hydrogen electrode,26,28 respectively; which means the WS2 possesses energy level of CB and VB both lower than that of g-C3N4, but the CB offset between g-C3N4 and WS2 is much shorter than the band gap of g-C3N4. Therefore, there would be a perfect band structure coordination between WS2 and g-C3N4 to construct a heterojunction structure. The good match for the energy level would possibly enable fast transfer of the photo-induced electrons in the CB of g-C3N4 to the CB of WS2 before recombination with holes in VB of itself, so that the light harvesting efficiency and utilization of photo-induced electrons would be improved largely.29–32
In this present work, a heterogeneous WS2/g-C3N4 composite photocatalyst was prepared via ultrasound assisted hydrothermal method. The photocatalytic performance was evaluated through the regeneration of NADH and degradation of RhB under visible light. Detailed investigations of the physiochemical and photochemical properties of the photocatalysts were performed to elucidate the photoinduced electron-transfer mechanism involved in the heterogeneous WS2/g-C3N4 composite photocatalyst. Therefore, our work highlights the promise of constructing heterojunction based on g-C3N4 for photocatalyzed NADH regeneration and pollutant degradation, and encourages further in-depth investigations of this novel type of heterojunction for artificial photocatalysis.
2. Experimental section
2.1. Material
Formate dehydrogenase (FateDH), formaldehyde dehydrogenase (FaldDH), yeast alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH), β-nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (β-NAD+), reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH), dicyandiamide, triethanolamine (TEOA), dichloro (pentamethylcyclopentadienyl) rhodium(III) dimer, 1,10-phenanthroline were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich. Tungsten disulfide (WS2) was purchased from Shanghai Macklin Biochemical Co., Ltd (Shanghai, China).The organometallic electron mediator (M), [Cp*Rh(phen)H2O]2+, (Cp* = 5-C5Me5, phen = 1,10-phenanthroline) was synthesized as follows. Briefly, 103.01 mg of dichloro (pentamethylcyclopentadienyl) rhodium(III) dimer was added to 10 mL of methylene chloride, where the solid was insoluble. Then, 60.07 mg of 1,10-phenanthroline was added to the mixture. After stirring at room temperature for 3 h, the color of the solution changed from dark orange to orange. After removing the solvent by evaporation under reduced pressure, M was obtained.
2.2. Preparation of g-C3N4 and WS2/g-C3N4 composites catalysts
To prepare graphite phase carbon nitride (g-C3N4), 10 g of dicyandiamide was ground into a powder and placed in a capped alumina crucible covered with aluminum foil and then calcined at 550 °C for 4 hours in a muffle furnace at a rate of 3 °C min−1. The g-C3N4 was obtained as yellow solid.WS2/g-C3N4 composites were synthesized via a two-step self-assembly procedure. Herein, 100 mg of g-C3N4 was added into 100 mL deionized water and sonicated for one hour. Into the above suspension, definite amount of WS2 powder was added to obtain a WS2 mass fraction of 1, 5, 10%. The suspension mixture was sonicated for 30 min followed by 36 h mechanical stirring. To consolidate the heterojunction interface in the WS2/g-C3N4 composites, the mixture was sealed into a 100 mL Teflon-lined stainless steel autoclave and heated to 140 °C for 6 h. After cooling down to room temperature and evaporating the solvent, WS2/g-C3N4 composites with different composition proportions were obtained.
2.3. Catalyst characterization
Scanning electron microscope (SEM) analysis was performed on a JSM 6700F cold field emission scanning electron microscope at beam energy of 10.0 kV. Transmission electron microscope (TEM) images were taken on JEM 2100F instrument at an acceleration voltage of 200 kV. Atomic force microscopy was performed using Bruker FASTSCANIO microscope. Thermo gravimetric analysis (TGA), was carried out in a flow of nitrogen gas (10 mL min−1) at a heating rate of 10 °C min−1 using Synchronous DSC-TGA Thermal Analysis (SDT Q600). The specific surface areas were measured on ASAP 2020HD88 by the BET method. The crystal structures of WS2/g-C3N4 composites were identified by X-ray diffraction (XRD) with Empyrean X-ray diffractometer from PANalytical B.V. of the Netherlands. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) analysis was performed on ESCALAB 250Xi instrument. The Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) spectra were collected from 400 to 4000 cm−1 at the spectral resolution of 0.482 cm−1 on NICOLET iS 50 infrared spectrometer. UV-vis diffuse reflectance spectroscopy (UV-vis DRS) were recorded in the range of 200–900 nm by a TU-1901 spectrophotometer with the reference of BaSO4. Photoluminescence (PL) spectra were determined on a NanoLOG-TCSPC steady state/transient fluorescence spectrometer. The wavelength of the excitation light was 340 nm.2.4. Photocatalytic regeneration of NADH
The photocatalytic regeneration of NADH reaction was carried out in a side-irradiation vial under an irradiation of 300 W Xe lamp with a 400 nm cut-off filter. In the regeneration procedure, the reaction medium (3 mL) was composed of NAD+ (1 mM), TEOA (15 w/v%), M (0.25 mM), phosphate buffer (100 mM, pH 7.0) and catalyst (3 mg). The distance between reactor and Xe lamp was fixed at 20 cm. Before irradiation, the reaction solution was placed in a dark environment for 1 h to achieve adsorption–desorption equilibrium. The concentration of NADH regenerated from NAD+ was monitored by measuring the absorbance at 340 nm (εNADH = 6.22 mM−1 cm−1) using a UV-vis spectrophotometer (UV-2800, Unico).2.5. Conversion CO2 to methanol
The conversion of CO2 to methanol was performed in quartz reactor. The reaction solution was composed of 3 mg catalyst, NADH (1 mM), KHCO3 (0.1 M), 15 w/v% triethanolamine (TEOA), M (0.125 mM), FateDH (0.2 mg), FaldDH (0.3 mg), and ADH (1.5 mg) in 2 mL 0.1 M PBS buffer (pH 7.0). Prior to the addition of enzyme, the PBS buffer was firstly saturated with gaseous CO2. The amount of methanol was detected by gas chromatograph as described in our previous reports.112.6. Degradation of RhB
The degradation of RhB was performed in quartz reactor. The photocatalytic reaction system consisted of 300 W Xe lamp with a 400 nm cut-off filter. All experiments were conducted at room temperature. In a typical run, 5 mg of catalysts was added into 5 mL of 10 mg L−1 RhB solution. Prior to irradiation, the suspension was magnetically stirred in the dark for 1 h to ensure the adsorption–desorption equilibrium. The concentration of RhB was monitored by measuring the absorbance at 554 nm using a UV-vis spectrophotometer (UV-2800, Unico). The procedures of the scavenging experiments of reactive oxygen species were similar to that of the photo degradation experiment. Various scavengers, including isopropyl alcohol (IPA, 1 mM), TEOA (1 mM), KI (1 mM), and 0.5 h nitrogen purging (N2) were subjected into the RhB solution prior to irradiation.3. Results and discussions
3.1. Fabrication and characterization of WS2/g-C3N4 composites
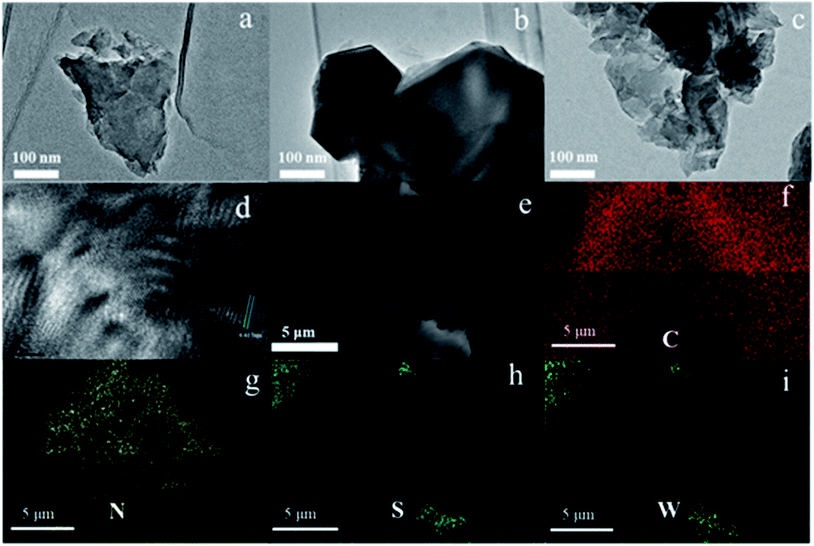
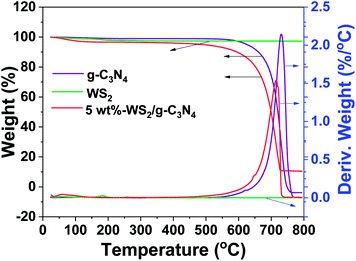
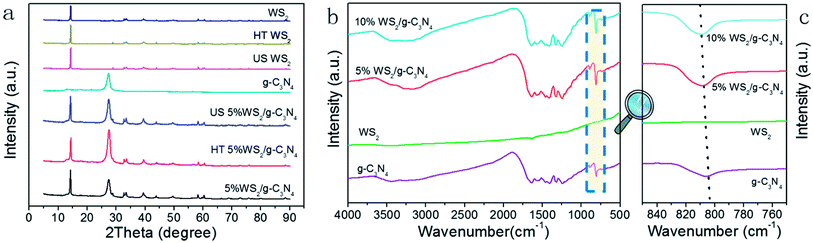
The WS2/g-C3N4 composites were fabricated by a two-step self-assembly procedure, the morphologies of g-C3N4, WS2 and the 5 wt% WS2/g-C3N4 composites were observed by TEM. As shown in Fig. 1a, a stacked layer structure is clearly observed in the g-C3N4 sample, which is consistent with existing reports.33 The WS2 sample displays a structure of hexagonal lamellar stacking (Fig. 1b).34 For WS2/g-C3N4 composites, g-C3N4 is found to be covered by WS2. The darker part with hexagonal shape in Fig. 1c should be WS2 and the lighter part is g-C3N4, which demonstrates the well distribution of WS2 on g-C3N4. The high-resolution TEM image shows the microstructure of the WS2/g-C3N4 composite, in which the interplanar spacing is very close to the 001 plane of WS2 (Fig. 1d). SEM images (Fig. 1e) of the 5 wt% WS2/g-C3N4 composite and the corresponding energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS) elemental mapping of C, N, S and W, which are characteristic elements of g-C3N4 and WS2, respectively, clearly confirmed the uniform coupling of g-C3N4 with WS2 (Fig. 1f–i). This coupling would be favorable for the charge transfer between WS2 and g-C3N4 and then promotes the separation of photo-generated electron–hole pairs. Moreover, the TGA measurement shows that the decomposition temperature of WS2/g-C3N4 composites is lower than the pristine g-C3N4. Similar phenomena were also observed in some other g-C3N4-based heterojunction, such as g-C3N4/AgBr/Fe3O4, SnO2−x/g-C3N4, TiO2/g-C3N4, DyVO4/g-C3N4, g-C3N4/SmVO4.24,35–37 The shift of weight loss towards lower temperature was considered due to some changes in surface chemistry of the g-C3N4 during forming of heterojunction structure with other materials (Fig. 2).38,39XRD were adopted to analyze the composition and structure of as-prepared WS2/g-C3N4 composites. To understand the crystallization of the composite and also mutual interface of each semiconductor over the other during composite formation, the XRD patterns of the following materials were presented in Fig. 3a, which include the obtained WS2, hydrothermally treated WS2 (referred as HT WS2) and ultrasonicated WS2 (referred as US WS2) in absence of g-C3N4; as formed g-C3N4; ultrasonicated 5% WS2/g-C3N4 composite (US 5% WS2/g-C3N4), hydrothermally treated (HT 5% WS2/g-C3N4), as well as the 5% WS2/g-C3N4 composites fabricated through combined ultrasonication-hydrothermal treatments. As shown in Fig. 3a, the XRD pattern of obtained g-C3N4 showed the typical diffraction peaks at 13.1° and 27.3°, perfectly indexed as the (100) and (002) planes, respectively, which were ascribed to in-planar tri-s-triazine unit and the interplanar stacking of aromatic systems.17,40–44 The XRD patterns of the obtained WS2 exhibit many distinct diffraction peaks, indicating its hexagonal structure,28,34 which is consistent with the 2H configuration in the standard card library. The HT WS2 and US WS2 presents the same XRD as that of the obtained WS2, indicating the crystallization of WS2 was not affected by ultrasonication and hydrothermal treatments. For the 5% WS2/g-C3N4 composites, the XRD patterns of all the three composites display the combination of the two sets of diffraction data for both g-C3N4 and WS2 and no other phase is detected, implying that WS2 was not incorporated into the lattice of g-C3N4.
 | ||
| Fig. 3 (a) XRD patterns and (b) FT-IR spectra of obtained g-C3N4, WS2, WS2/g-C3N4 composites; (c) local magnification of the FT-IR spectra at around 810 cm−1 of spectra in (b). | ||
The FT-IR was also adopted to test the obtained g-C3N4, WS2, and WS2/g-C3N4 composite. As shown in Fig. 3b, pure g-C3N4 has a much stronger IR response than WS2, and the addition of WS2 shows no obvious effect on the IR spectrum of g-C3N4. For the g-C3N4, the strong bands in the region of 1200–1700 cm−1 are assigned to the typical stretching vibration modes of C–N heterocycles. The peaks at 3000–3700 cm−1 represent the N–H and O–H stretching vibration. The sharp peak at 810 cm−1 originates from the characteristic breathing mode of tri-s-triazine units.45–49 For the WS2/g-C3N4 composites, the overall patterns of the spectra are the same as the g-C3N4, confirming the existence of heptazine heterocyclic rings in WS2/g-C3N4 composites. In generally, there is no obvious difference from the FTIR spectrogram before and after doping, but it's not difficult for us to see that the position of the characteristic peak from the tri-s-triazine vibration of g-C3N4 has a certain degree of shift (Fig. 3c), indicating that there might be some interactions between the “nitrogen pots” of g-C3N4 and W species of WS2.24 As a complement to FT-IR, the Raman spectra of the g-C3N4 and the 5% WS2/g-C3N4 were also recorded. As shown in Fig. S1,† the catalysts show several very weak distinctive peaks at 458, 679 and 1220 cm−1, which is basically consistent with the situation of g-C3N4 reported in the literatures.50,51 The formation of 5% WS2/g-C3N4 composite did not lead to apparent new peak, which may be due to the strong photoluminescence effect of g-C3N4 and the small faction of WS2 in the composite.
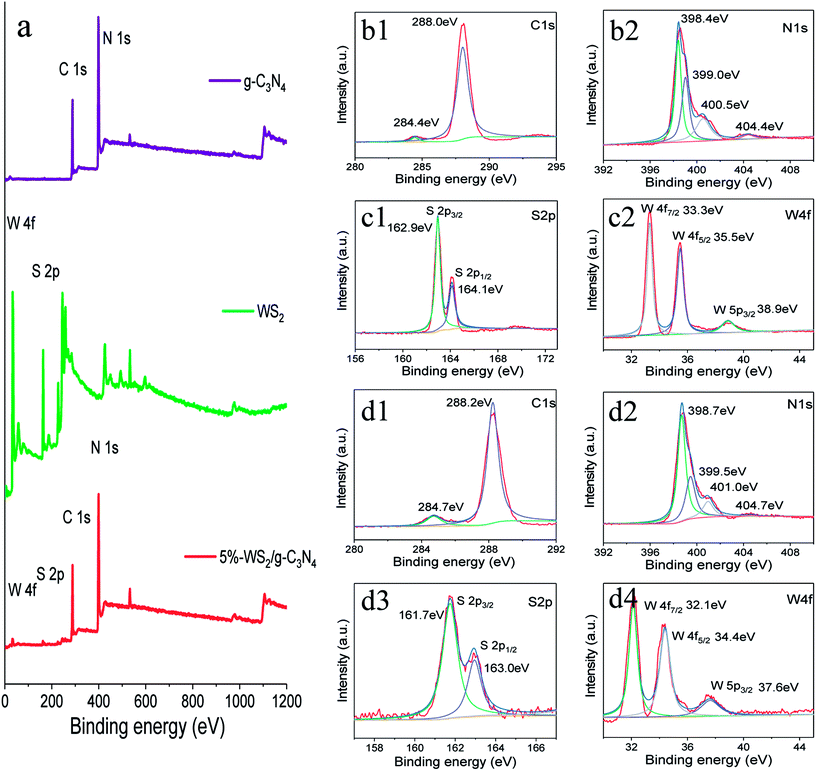
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) analysis was employed to determine the chemical composition and bonding configuration of the g-C3N4, WS2 and the WS2/g-C3N4 composites (Fig. 4a), with the high-resolution spectrum of each sample were illustrated in Fig. 4b–d. The survey XPS spectra shown in Fig. 4a indicate that the prepared WS2/g-C3N4 samples are composed of C, N, W and S. Specifically, the C1s spectrum (Fig. 4d1) of WS2/g-C3N4 composites show there are two C1s peaks located at 284.7 and 288.2 eV, the former is ascribed to the adventitious hydrocarbon from the XPS instrument, while the latter is assigned to sp2-bonded carbon atom (N–C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N) of g-C3N4 in aromatic rings. The high-resolution N1s spectrum of the WS2/g-C3N4 composites could be fitted into four peaks (Fig. 4d2). The peaks centered at 398.7 and 399.5 eV were attributed to sp2-hybridized nitrogen atom (C
N) of g-C3N4 in aromatic rings. The high-resolution N1s spectrum of the WS2/g-C3N4 composites could be fitted into four peaks (Fig. 4d2). The peaks centered at 398.7 and 399.5 eV were attributed to sp2-hybridized nitrogen atom (C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N–C group) and tertiary nitrogen (N–C3 group or H–N–C2), respectively; the peaks at 401.0 and 404.7 eV derived from amino function groups and charging effect localization in heterocycles, respectively.4,24,52 As compared with the C1s and N1s spectrum (Fig. 4b1 and b2) of pure g-C3N4, all those peaks of the WS2/g-C3N4 composites shifted to a position with a higher binding energy.
N–C group) and tertiary nitrogen (N–C3 group or H–N–C2), respectively; the peaks at 401.0 and 404.7 eV derived from amino function groups and charging effect localization in heterocycles, respectively.4,24,52 As compared with the C1s and N1s spectrum (Fig. 4b1 and b2) of pure g-C3N4, all those peaks of the WS2/g-C3N4 composites shifted to a position with a higher binding energy.
Fig. 4d3 and d4 display the S2p spectra and the W4f spectra of the WS2/g-C3N4 composites. The peaks at 161.7 and 163 eV can be ascribed to the S2− species, donated as S2p3/2 and S2p1/2, respectively;34 the W4f peaks at 32.1, 34.4, and 37.6 eV can be ascribed to the W4+ species, donated as W4f7/2, W4f5/2 and W5p3/2.28,53 In contrast to the W4f and S2p spectrum (Fig. 4c1 and c2) of WS2, all these above peaks of the WS2 shifted to a position with a lower binding energy after coupling with g-C3N4. Thus, the C1s and N1s peaks of g-C3N4 shifted toward the higher binding energy, while the W4f and S2p peaks of WS2 shifts towards the lower binding energy. It was suggested that there might be some S–C chemical bonds formed between the heterojunction interfaces of WS2/g-C3N4 composites, thus electron transfer could occur from g-C3N4 to WS2 at this interfaces due to their different electron concentration.24,54
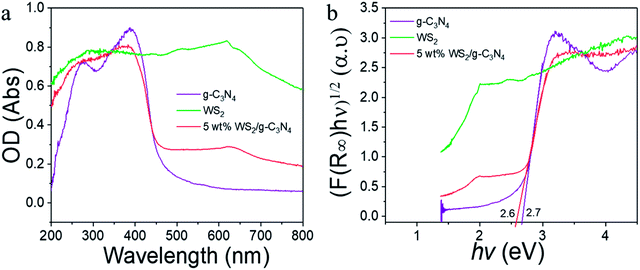
The optical properties of WS2, g-C3N4 and the WS2/g-C3N4 composites were revealed by the UV-vis diffuse reflectance spectra (DRS). As shown in Fig. 5a, pure g-C3N4 had absorption from UV to visible region, with an absorption edge at 460 nm, which corresponding to a band gap about 2.7 eV according to the Kubelka–Munk conversion (Fig. 5b).55,56 However, with the coupling of WS2, the absorption range of the composite became wider than that of pure g-C3N4, a remarkable enhanced light-harvesting ability is observed for the WS2/g-C3N4, and the band gap width estimated from the K–M equation became narrower accordingly, which implied that the light absorption ability of the WS2/g-C3N4 composites became stronger. The coupling of WS2 on g-C3N4 may generate an impurity energy level in the valence band (VB) and narrow the band gap. The defect energy levels increased the light absorption efficiency of the materials and thus may exhibit photocatalytic performance superior to that of the individual material. In addition, the DRS spectra of US 5% WS2/g-C3N4 and HT 5% WS2/g-C3N4 composites were also measured and compared with that of the 5% WS2/g-C3N4, it is indicated that the omitting the ultrasonication or hydrothermal treatments during composite formation lead to negligible changes in the band structure (Fig. S2†).
Fig. 6 presents the BET surface areas measurement of 5 wt% WS2/g-C3N4 composites. For comparison, the surface areas of g-C3N4 and the physical mixture of g-C3N4 with 5 wt% WS2 (referred as PM-WS2/g-C3N4 in the following text) were also determined, the results were listed in Table S2.† The specific surface area of g-C3N4 was 7.34 m2 g−1, which is similar to the value reported by He et al.,24 but lower than those reported for most g-C3N4 nanosheets,54,57 which indicates that the g-C3N4 has multi-layered structure. Slight decrease in surface area was observed for the PM-WS2/g-C3N4 (6.87 m2 g−1); while the 5 wt% WS2/g-C3N4 composites exhibited much higher BET values (12.22 m2 g−1), which indicated that some reactions might have occurred between g-C3N4 and WS2 during recombination. This larger specific surface area of WS2/g-C3N4 composites also could supply more reactive sites for light and substrates, improve the whole efficiency of the reaction. It should be noted that the specific surface area of the 5 wt% WS2/g-C3N4 composites are still far lower than the g-C3N4 nanosheets, indicating the ultrasonication and hydrothermal treatments during composite formation still could not result in effective exfoliation of the g-C3N4. After BJH (Barrett–Joyner–Halenda) plotting, the pore size distribution of each samples were analyzed (Fig. 6b). Compared with the pure g-C3N4, coupling of WS2 lead to slight decrease in pore diameter.
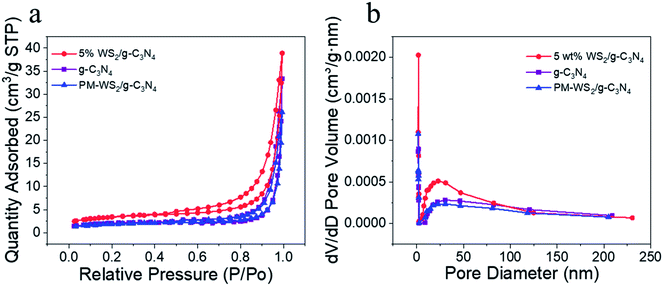 | ||
| Fig. 6 (a) The N2 adsorption/desorption isotherms, (b) the corresponding pore-size distribution. BET surface area was measured by nitrogen sorption isotherms at 77.5 K and up to 1.03 bar. | ||
3.2. Photocatalytic performance for NADH regeneration and CO2 reduction
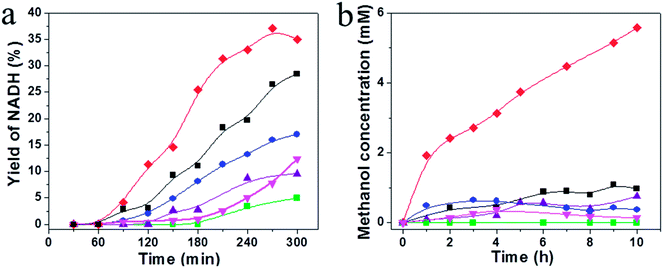
Conversion of CO2 to methanol through redox multienzymatic cascade reaction has been widely explored.7,10,12 However, consumption of the expensive NADH cofactor at stoichiometric ratios imposes great hurdles to the practice of these processes. Here in the present work, we intended to develop a biocatalyzed artificial photosynthesis system by coupling the reduction of CO2 catalyzed by FateDH, FaldDH, and ADH with the newly developed WS2/g-C3N4 composite as the photocatalyst to regenerate NADH using solar energy.Based on the above photochemical investigations of the g-C3N4 and the WS2/g-C3N4 composites, their performance for visible light-driven photocatalytic NADH regeneration were examined. The reactant solution consisted of 15 wt% TEOA, 0.25 mM electron mediator M, and NAD+ with an initial concentration of 1 mM and an active g-C3N4 content of 1 mg mL−1 was maintained in all the experiments. The photocatalytic activity comparison among pure g-C3N4, WS2, PM-WS2/g-C3N4 and WS2/g-C3N4 composite with WS2 content of 1%, 5% and 10% are presented in Fig. 7a. The monolithic g-C3N4 and WS2 had rather low catalytic efficiency, NADH regeneration yield at 6 h was below 10%. By physically mixing 5 wt% WS2 with g-C3N4, the NADH photo-regeneration yield enhanced to 15%. While the 5 wt% WS2/g-C3N4 composite presents the best performance, a NADH yield of 37.1% was achieved, which were about four times of those obtained by using monolithic g-C3N4 and WS2. With further increasing the WS2 content in the composite to 10 wt%, however, leading to decrement in activity for the photo-regeneration of NADH. Presumably, coupling of high amount WS2 may lead to shielding of active site of g-C3N4 by WS2 or loss of favorable interfaces between g-C3N4 and WS2. Similar phenomenon was also observed on the activity of mesoporous graphitic carbon nitride (mpg-CN) loaded with WS2 towards H2 generation. About 0.3 at% WS2 loading amount was found optimal to reach highest rate of hydrogen evolution, and heavy loading of WS2 led to decrease in activity of the heterojunctions photocatalyst.29
To justify the necessity of multiplicative steps involving ultrasonication, mechanical stirring and hydrothermal treatment for the preparation of WS2/g-C3N4, a series of WS2/g-C3N4 composites were prepared by simpler steps and evaluated for its activity towards NADH photoregeneration. Results presented in Fig. S3 and Table S3† clearly indicated that either omitting of the ultrasonication or hydrothermal treatments, or even the mechanical stirring between these two operations during composite formation, led to significantly lower activity of the fabricated WS2/g-C3N4. The hydrothermal time and temperature did not show remarkable influence on the activity of the composite photocatalyst. Therefore, the two-step sonication and subsequent hydrothermal treatments are necessary, though somewhat tedious, to ensure the photocatalyst a high activity of the 5 wt% WS2/g-C3N4 composite, which presents the highest NADH photo regeneration yield of 37.1%. It was believed that the first step of sonication was to ensure a good dispersion of g-C3N4 particles, the second step of sonication of g-C3N4 and WS2 mixture was for a full contact between these two materials, which was crucial for the subsequent hydrothermal reaction.
In another set of experiment, we tried to address the more challenging question of a potential mediator-free regeneration of NADH. To our surprise, the mediator-free with system with 5 wt% WS2/g-C3N4 composite as photocatalyst was also possible, though the regeneration yield at 6 h was only about half of that obtained in presence of M (Fig. S3, Table S3†). This can be explained from the following two points. Firstly, a mixture of 1,4-NADH and 1,6-NADH would possibly formed, while in presence of M, 1,4-NADH will be unique production; secondly, without a strong redox agent, i.e., mediator, g-C3N4 also catalyzes the back reaction, meaning an equilibrium between NAD+ and NADH.18
We then evaluated the WS2/g-C3N4 composite as a photocatalyst of the artificial photosynthesis system for bioconversion of CO2 to methanol. As expected, the photocatalysts showed higher activity for NADH regeneration also exhibited higher efficiency for methanol synthesis from CO2, when the NADH photoregeneration process was coupled with the biocatalytic process. The highest methanol concentration up to 5.58 mM were obtained by using 5 wt% WS2/g-C3N4 composite as photocatalysts, corresponding to a methanol productivity of 372.1 μmol h−1 gcat−1, which was about 7.5 times higher than that obtained by using g-C3N4 (50.31 μmol h−1 gcat−1). This result clearly indicated that the formation of WS2/g-C3N4 heterojunction generated significant photo-synergistic effect and played key roles in the enhancement in the photocatalytic activity.
3.3. Photocatalytic performance for RhB degradation
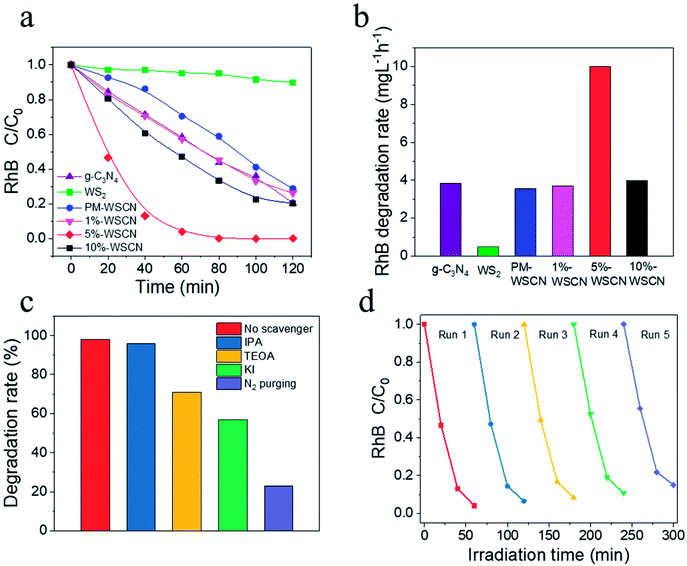
To further demonstrate the effectiveness of formation of heterojunction structures between the components of the WS2/g-C3N4 composites, the photocatalytic activity of the composites for the degradation of RhB was also evaluated, and results were compared with pure g-C3N4 and WS2. As shown in Fig. 8a, the degradation ratio of RhB reached to about 100% by using the 5 wt% WS2/g-C3N4 composites under visible light irradiation for 60 min, which was much higher than the corresponding degradation ratios obtained by using pristine g-C3N4 (∼70% at 120 min) and WS2 (∼10% at 120 min), as well as the PM-WS2/g-C3N4 (∼70% at 120 min). Fig. 8b presents the apparent degradation rate derived by simple linearly plotting of RhB concentration decrease against irradiation time. The results indicate that the degradation rate using composite photocatalyst containing 5 wt% WS2 was about 2.6 and 19.7 times higher than that of g-C3N4 and WS2, respectively.In general, some reactive oxygen species including hydroxyl radicals (˙OH) and superoxide radicals (˙O2−), as well as holes (h+) are expected to be involved in the photocatalytic process of RhB degradation.55,58 To investigate the role of these reactive species, the effects of some radical scavengers and N2 purging on the photodegradation of RhB were studied to propose the possible photocatalytic mechanism. Results in Fig. 8c indicate that the addition of IPA (˙OH scavengers) had almost no effect on RhB degradation. While addition of TEOA (h+ scavengers) and KI (scavenger of both ˙OH and h+) led the degradation rate after 1 h's irradiation decreased to about 70% and 58%, respectively. When N2 purging was conducted which acts as ˙O2− scavenger, the degradation rate decreased dramatically to about only 22%. These results suggested that the ˙O2− plays major roles in the photodegradation of RhB catalyzed by the WS2/g-C3N4 heterojunction photocatalyst, which is consistent with results in other reports.55,58
Reusability of photocatalyst is a very important parameter from an economical viewpoint. The reusability and stability of the 5 wt% WS2/g-C3N4 composites was examined by measuring the RhB degradation during repeated usages. As shown in Fig. 8d, after five successive runs, there is no remarkable decrease in its activity. Hence, the photocatalyst has a good stability during the photocatalytic reactions.
3.4. Proposed mechanism
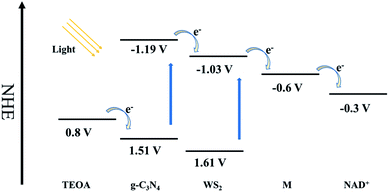
High efficient charge separation was the crucial fact for the improvement of photocatalytic activity. Construction of heterojunction structure is one of the most effective means to improve photocatalytic activity via fast and efficient transfer photo-excited electron in the CBs in the heterojunction. In this study, WS2 was hybridized with g-C3N4 to generate an efficient heterojunction structure. Based on the energy band structure of g-C3N4 and WS2, as shown in Fig. 9, the CB and VB of g-C3N4 are all higher than that of WS2.24,28 Because of the unstable state of photo-generated electrons and holes, they will tend to recombine quickly to achieve steady state. However, due to the distance between CB of g-C3N4 and CB of WS2 is much shorter than the band gap of g-C3N4, the CB offset of 0.16 eV will possibly drive the photo-excited electrons on the CB of g-C3N4 transfer to the CB of WS2 before recombination with holes in the VB of g-C3N4. Based on the similar mechanism, the holes in the VB of WS2 tend to transfer to the VB of g-C3N4, driven by the VB offset of 0.10 eV. Therefore, an orientated transfer of the charge carrier across the heterojunction interface was realized.To further demonstrate the photoinduced electron-transfer mechanism, as well as elucidate the effect of amount of WS2 in WS2/g-C3N4 heterojunction on the overall reaction efficiency, detailed investigations of the photochemical properties were performed on WS2/g-C3N4 heterojunction hybridized with different amount of WS2 ranging from 1 wt% to 10 wt%. For most semiconductors, photogenerated electrons and holes can bind after the excitation by incident light, leading to the transfer of partial energy to fluorescence. In general, the binding efficiency and photoelectron lifetime can be measured by monitoring fluorescence intensity and lifetime.17,57,59,60 Fig. 10a presents the fluorescence spectrum of pure g-C3N4, which shows strong fluorescence intensity at 437 nm. However, the physical mixing WS2 and g-C3N4 (PM-WS2/g-C3N4) and the WS2/g-C3N4 heterojunction all show a decremental effect on the fluorescence spectra. More interesting, the WS2/g-C3N4 heterojunction with 5 wt% WS2 presents the lowest fluorescence intensity, which means more electrons on the CB of g-C3N4 transfer to WS2 instead of recombining with the holes in the VB of g-C3N4. The suppressed recombination of electron–hole pairs of g-C3N4 may attribute to the fast electron transfer from CB of g-C3N4 to the CB of WS2, which also demonstrate the electron transfer mechanism and explain the highest activity of 5 wt% WS2/g-C3N4 heterojunction.
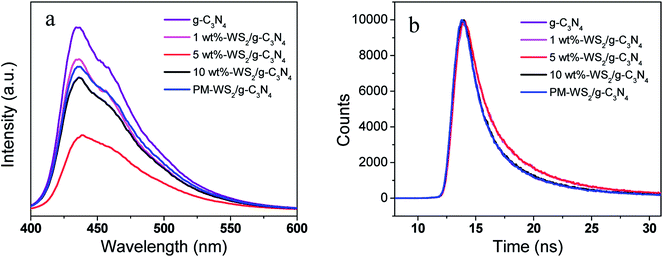 | ||
| Fig. 10 (a) PL spectra of g-C3N4, WS2 and WS2/g-C3N4 composite photocatalysts. (b) Excited state electron radioactive decay of g-C3N4, WS2 and WS2/g-C3N4 composite. | ||
In order to confirm the suppressed recombination of electron–hole pairs in 5 wt% WS2/g-C3N4 heterojunction, time-resolved fluorescence decay analysis was carried out. The excited state electron radioactive decay lifetime (Fig. 10b) show that the 5 wt% WS2/g-C3N4 heterojunction owns the longest fluorescence lifetime (11.080 ns) compared with that of 10 wt% WS2/g-C3N4 (10.549 ns), 1 wt% WS2/g-C3N4 (10.368 ns), PM-WS2/g-C3N4 (10.554 ns), and g-C3N4 (10.487 ns), indicating that the incorporation of WS2 increased the photoelectron lifetime of WS2/g-C3N4. This result further certified that 5 wt% WS2/g-C3N4 heterojunction has the best coordination between g-C3N4 and WS2 for the most efficient and fastest photo-excited electrons transfer.
4. Conclusions
In summary, we successfully fabricated and applied a heterogeneous WS2/g-C3N4 composite photocatalyst for methanol conversion from CO2 and pollutant degradation under irradiation of visible light. A methanol generation rate of 372.1 μmol h−1 gcat−1, and 100% RhB removing efficiency within 1 h were achieved by using 5wt% WS2/g-C3N4 heterojunction, which were improved greatly compared with pure g-C3N4. Based on detailed investigations of the photochemical properties, the heterojunction structure of WS2/g-C3N4 composite was correlated with their electron-transfer efficacy and the overall reaction efficiency. The results show that the band structure coordination between WS2 and g-C3N4 made it possible to construct a structure of heterojunction. The photo-induced electrons in the CB of g-C3N4 would transfer to the CB of WS2 before recombination with holes in VB of g-C3N4, so that the recombination of electron–hole pairs was eliminated and coefficient of utilization of photo-induced electrons was improved greatly. This work provides a novel platform for the efficient and sustained production of a broad range of chemicals and fuels from sunlight.Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.Acknowledgements
The authors thank the support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 91534126 and 21676276).Notes and references
- S. Ye, R. Wang, M.-Z. Wu and Y.-P. Yuan, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2015, 358, 15–27 CrossRef.
- K. Sekizawa, K. Maeda, K. Domen, K. Koike and O. Ishitani, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2013, 135, 4596–4599 CrossRef PubMed.
- W. Wang, S. Wang, X. Ma and J. Gong, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2011, 40, 3703–3727 RSC.
- Y. He, Y. Wang, L. Zhang, B. Teng and M. Fan, Appl. Catal., B, 2015, 168, 1–8 Search PubMed.
- Y. Amao, ChemCatChem, 2011, 3, 458–474 CrossRef.
- F. S. Baskaya, X. Zhao, M. C. Flickinger and P. Wang, Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol., 2010, 162, 391–398 CrossRef PubMed.
- B. C. D. Obert and R. Obert, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1999, 121, 12192–12193 CrossRef.
- X. Tong, B. El-Zahab, X. Zhao, Y. Liu and P. Wang, Biotechnol. Bioeng., 2011, 108, 465–469 CrossRef PubMed.
- H. Wu, C. Tian, X. Song, C. Liu, D. Yang and Z. Jiang, Green Chem., 2013, 15, 1773–1789 RSC.
- Y. Jiang, Q. Sun, L. Zhang and Z. Jiang, J. Mater. Chem., 2009, 19, 9068–9074 RSC.
- X. Ji, Z. Su, P. Wang, G. Ma and S. Zhang, Small, 2016, 12, 4753–4762 CrossRef PubMed.
- X. Ji, Z. Su, P. Wang, G. Ma and S. Zhang, ACS Nano, 2015, 9, 4600–4610 CrossRef PubMed.
- F. L. Yang, F. F. Xia, J. Hu, C. Z. Zheng, J. H. Sun and H. B. Yi, RSC Adv., 2018, 8, 1899–1904 RSC.
- K. Xu and J. Feng, RSC Adv., 2017, 7, 45369–45376 RSC.
- P. Wang, I. Sinev, F. Sun, H. Li, D. Wang, Q. Li, X. Wang, R. Marschall and M. Wark, RSC Adv., 2017, 7, 42774–42782 RSC.
- X. Wang, K. Maeda, A. Thomas, K. Takanabe, G. Xin, J. M. Carlsson, K. Domen and M. Antonietti, Nat. Mater., 2009, 8, 76–80 CrossRef PubMed.
- P. Niu, L. Zhang, G. Liu and H.-M. Cheng, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2012, 22, 4763–4770 CrossRef.
- J. Liu and M. Antonietti, Energy Environ. Sci., 2013, 6, 1486–1493 Search PubMed.
- Z. Tong, D. Yang, Z. Li, Y. Nan, F. Ding, Y. Shen and Z. Jiang, ACS Nano, 2017, 11, 1103–1112 CrossRef PubMed.
- Z. Tong, D. Yang, Y. Sun, Y. Nan and Z. Jiang, Small, 2016, 12, 4093–4101 CrossRef PubMed.
- G. Liu, P. Niu, C. H. Sun, S. C. Smith, Z. G. Chen, G. Q. Lu and H. M. Cheng, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2010, 132, 11642–11648 CrossRef PubMed.
- X. C. Wang, X. F. Chen, A. Thomas, X. Z. Fu and M. Antonietti, Adv. Mater., 2009, 21, 1609–1612 CrossRef.
- X. Lu, Q. Wang and D. Cui, J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 2010, 26, 925–930 Search PubMed.
- Y. He, L. Zhang, M. Fan, X. Wang, M. L. Walbridge, Q. Nong, Y. Wu and L. Zhao, Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells, 2015, 137, 175–184 CrossRef.
- Y. Liu, X. She, X. Zhang, C. Liang, J. Wu, P. Yu, Y. Nakanishi, B. Xie, H. Xu, P. M. Ajayan and W. Yang, RSC Adv., 2017, 7, 55269–55275 RSC.
- B. Peng, P. K. Ang and K. P. Loh, Nano Today, 2015, 10, 128–137 CrossRef.
- Q. Lu, Y. Yu, Q. Ma, B. Chen and H. Zhang, Adv. Mater., 2016, 28, 1917–1933 CrossRef PubMed.
- B. Mahler, V. Hoepfner, K. Liao and G. A. Ozin, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2014, 136, 14121–14127 CrossRef PubMed.
- Y. Hou, Y. Zhu, Y. Xu and X. Wang, Appl. Catal., B, 2014, 156–157, 122–127 CrossRef.
- M. S. Akple, J. Low, S. Wageh, A. A. Al-Ghamdi, J. Yu and J. Zhang, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2015, 358, 196–203 CrossRef.
- Y. Ma, J. Li, E. Liu, J. Wan, X. Hu and J. Fan, Appl. Catal., B, 2017, 219, 467–478 CrossRef.
- X. Xu, Y. Liu, Y. Zhu, X. Fan, Y. Li, F. Zhang, G. Zhang and W. Peng, ChemElectroChem, 2017, 4, 1498–1502 CrossRef.
- T. Zhou, Y. Xu, H. Xu, H. Wang, Z. Da, S. Huang, H. Ji and H. Li, Ceram. Int., 2014, 40, 9293–9301 CrossRef.
- G. Pagona, C. Bittencourt, R. Arenal and N. Tagmatarchis, Chem. Commun., 2015, 51, 12950–12953 RSC.
- A. Akhundi and A. Habibi-Yangjeh, Ceram. Int., 2015, 41, 5634–5643 CrossRef.
- J. Lei, Y. Chen, F. Shen, L. Wang, Y. Liu and J. Zhang, J. Alloys Compd., 2015, 631, 328–334 CrossRef.
- H. Xiao, W. Wang, G. Liu, Z. Chen, K. Lv and J. Zhu, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2015, 358, 313–318 CrossRef.
- Y. He, J. Cai, T. Li, Y. Wu, Y. Yi, M. Luo and L. Zhao, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2012, 51, 14729–14737 CrossRef.
- T. Li, L. Zhao, Y. He, J. Cai, M. Luo and J. Lin, Appl. Catal., B, 2013, 129, 255–263 CrossRef.
- X. Wang, K. Maeda, A. Thomas, K. Takanabe, G. Xin, J. M. Carlsson, K. Domen and M. Antonietti, Nat. Mater., 2009, 8, 76–80 CrossRef PubMed.
- X. Wang, X. Chen, A. Thomas, X. Fu and M. Antonietti, Adv. Mater., 2009, 21, 1609–1612 CrossRef.
- Y. Wang, J. S. Zhang, X. C. Wang, M. Antonietti and H. R. Li, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2010, 49, 3356–3359 CrossRef PubMed.
- D. Portehault, C. Giordano, C. Gervais, I. Senkovska, S. Kaskel, C. Sanchez and M. Antonietti, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2010, 20, 1827–1833 CrossRef.
- L. Lin, H. Ou, Y. Zhang and X. Wang, ACS Catal., 2016, 6, 3921–3931 CrossRef.
- S. Thaweesak, S. Wang, M. Lyu, M. Xiao, P. Peerakiatkhajohn and L. Wang, Dalton Trans., 2017, 46, 10714–10720 RSC.
- S. Zhang, L. Gao, D. Fan, X. Lv, Y. Li and Z. Yan, Chem. Phys. Lett., 2017, 672, 26–30 CrossRef.
- Z. A. Lan, Y. Fang, Y. Zhang and X. Wang, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2018, 57, 470–474 CrossRef PubMed.
- H. Ou, L. Lin, Y. Zheng, P. Yang, Y. Fang and X. Wang, Adv. Mater., 2017, 29, 1700008 CrossRef PubMed.
- H. Ou, P. Yang, L. Lin, M. Anpo and X. Wang, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2017, 56, 10905–10910 CrossRef PubMed.
- S. Kang, Y. Fang, Y. Huang, L.-F. Cui, Y. Wang, H. Qin, Y. Zhang, X. Li and Y. Wang, Appl. Catal., B, 2015, 168, 472–482 CrossRef.
- Y. Hou, Z. Wen, S. Cui, X. Guo and J. Chen, Adv. Mater., 2013, 25, 6291–6297 CrossRef PubMed.
- H. Katsumata, Y. Tachi, T. Suzuki and S. Kaneco, RSC Adv., 2014, 4, 21405–21409 RSC.
- D. Voiry, H. Yamaguchi, J. Li, R. Silva, D. C. Alves, T. Fujita, M. Chen, T. Asefa, V. B. Shenoy, G. Eda and M. Chhowalla, Nat. Mater., 2013, 12, 850–855 CrossRef PubMed.
- Z. Zhang, J. Huang, M. Zhang, Q. Yuan and B. Dong, Appl. Catal., B, 2015, 163, 298–305 CrossRef.
- S. C. Yan, Z. S. Li and Z. G. Zou, Langmuir, 2010, 26, 3894–3901 CrossRef PubMed.
- Y. Imanaka, T. Anazawa, T. Manabe, H. Amada, S. Ido, F. Kumasaka, N. Awaji, G. Sanchez-Santolino, R. Ishikawa and Y. Ikuhara, Sci. Rep., 2016, 6, 35593 CrossRef PubMed.
- L. Ma, H. Fan, J. Wang, Y. Zhao, H. Tian and G. Dong, Appl. Catal., B, 2016, 190, 93–102 CrossRef.
- S. Kumar, T. Surendar, B. Kumar, A. Baruah and V. Shanker, RSC Adv., 2014, 4, 8132–8137 RSC.
- W. Li, C. Feng, S. Dai, J. Yue, F. Hua and H. Hou, Appl. Catal., B, 2015, 168–169, 465–471 CrossRef.
- S. G. Kumar and K. S. R. K. Rao, RSC Adv., 2015, 5, 3306–3351 RSC.
Footnote |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available. See DOI: 10.1039/c8ra02807a |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 |