Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleArylnaphthalene lactone analogues: synthesis and development as excellent biological candidates for future drug discovery
Chuang Zhaoa,
K. P. Rakesh *ab,
Saira Mumtaza,
Balakrishna Mokua,
Abdullah M. Asiri
*ab,
Saira Mumtaza,
Balakrishna Mokua,
Abdullah M. Asiri c,
Hadi M. Marwanic,
H. M. Manukumar
c,
Hadi M. Marwanic,
H. M. Manukumar d and
Hua-Li Qin
d and
Hua-Li Qin *a
*a
aDepartment of Pharmaceutical Engineering, School of Chemistry, Chemical Engineering and Life Science, Wuhan University of Technology, 205 Luoshi Road, Wuhan, 430073, PR China. E-mail: rakeshasg@gmail.com; qinhuali@whut.edu.cn; Fax: +86 13007173116; Fax: +86 27 87749300
bSri Ram Chem, R & D Centre, Plot No. 31, JCK Industrial Park, Belagola Industrial Area, Mysore 570016, Karnataka, India
cDepartment of Chemistry, Faculty of Science, King Abdulaziz University, Jeddah 21589, Saudi Arabia
dDepartment of Studies in Biotechnology, University of Mysore, Manasagangotri, Mysuru-570006, Karnataka, India
First published on 6th March 2018
Abstract
Arylnaphthalene lactones are natural products extracted from a wide range of different parts of plants. The progressing interest in the synthesis of these compounds is due to their significant biological activities, which have made them potential candidates in drug discovery and development. This review mainly covers recent developments in the synthesis and biological applications of arylnaphthalene lactone analogs.
Introduction
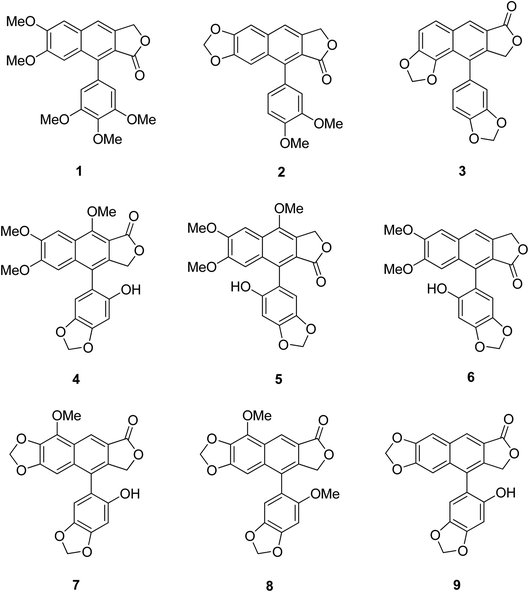
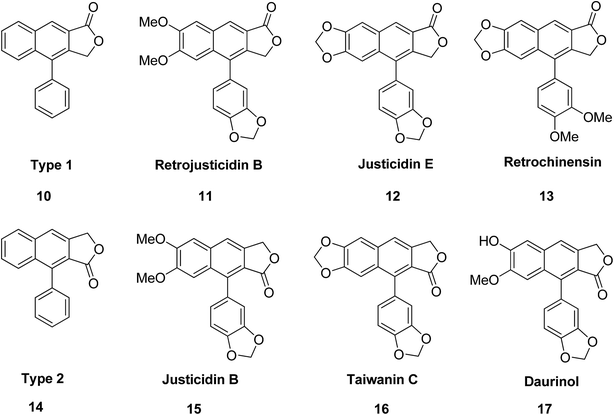
Certain structural features of natural products are responsible for their biological activities. Identifying such special scaffolds is of great interest to researchers.1,2 Laboratory synthesis of molecules containing similar scaffolds has served as an effective strategy for new drug synthesis.3 Naturally occurring arylnaphthalene lactones are a subclass of lignans present in many dietary or medicinal plants.4 As a representative example, 1-arylnaphthalene lactone lignans (Fig. 1, 1–9)5 are reported to exhibit a lot of biological activities6 such as antibacterial,7 antiviral,8–11 antitumor,12–14 antiplatelet,15,16 phosphodiesterase inhibition,17,18 5-lipoxygenase inhibition,19–21 HIV reverse transcriptase inhibition22–24 and cytotoxic activities.25Arylnaphthalene lactone lignans contain two arylpropanoid units, in which the aromatic rings are polyoxygenated (i.e., coniferyl alcohol). In biosynthetic pathways the two units are assembled using enzymes.26,27 The arylnaphthalene lactones in Fig. 2 (10–17) are structurally classified into two types, denoted type I and type II. Daurinol is a type II arylnaphthalene lactone. It is a potent anticancer agent isolated from Haplophyllum dauricum and traditionally it has been used for the treatment of cancer in Mongolia, Russia, and China.
Lignans are distributed widely in higher classes of plants and as secondary metabolites are also known to protect plants from herbivores. This forms a basis for the growing interest in exploiting lignans and their synthetic analogs as potential anticancer agents.28,29 Some cytotoxic lignan derivatives have already reached phase I and II clinical trials as antitumor agents including GP-11,30 NK-611,31,32 TOP-53,33 NPF,34 and GL-331.35–39 Moreover, recently lignan F11782 has been reported as a novel catalytic inhibitor of topoisomerases I and II (key promoters of DNA replication).40
Many routes are available for the synthesis of arylnaphthalene lactones. 1-Phenyl naphthalene anhydride can be obtained through dimerization followed by reduction (in Zn/AcOH) of phenylpropionic acid. Alternatively, 1-phenyldihydronaphthofuran can be oxidized using Jones reagent into type 1 and type 2 lactones. The synthesis of arylnaphthalene lactones bearing aryl ethers or phenolic OHs on a benzene ring was carried out by the Stevenson group using an intramolecular Diels–Alder reaction of 3-arylprop-2-yn-1-yl-3-arylpropiolate or 3-arylprop-2-en-1-yl-3-arylpropiolate.41–43 The Mori group44 and Anastas group45,46 have reported the synthesis of arylnaphthalene lactone analogs using Pd and Ag-catalyzed [2 + 2 + 2] cyclization, respectively. The Tanabe group also synthesized arylnaphthalene lactone analogs using the regiocontrolled benzannulation of diaryl(gem-dichlorocyclopropyl)methanols,47 see Table 1.
| Ref. | Starting material(s) | Reagent(s) | Solvent | Type 1 and type II ANL yields (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 41 | Arylpropargyl, arylpropiolate esters | 4-Vinylpyridin, (P4-VP) | Xylene | 50–60 |
| 42 | Phenylpropiolic acid, phenylpropargyl alcohol | P4-VP, acid catalyst | Xylene | 45–50 |
| 43 | Isovanillin | Benzyl chloride | Xylene | 70–75 |
| 44 | Diynes and arynes | Pd catalyzed | CH3CN | 40–70 |
| 45 | 1-Phenyldihydronaphthofuran | Jones reagent | DMAc | 20–30 |
| 46 | Phenylpropargyl chloride, phenylacetylene | Ag catalyzed | DMA | 16–30 |
| 47 | AACMs | Lewis acid | CF3COOH | 50–65 |
The present review will summarize recent advances in the synthesis of arylnaphthalene lactone lignan containing analogs, and their diverse biological activities and structure–activity relationships (SARs). In particular, the review will focus on the synthesis and biological activities (in vitro and in vivo) of arylnaphthalene lactone containing analogs, particularly for drug discovery and development.
Synthesis of arylnaphthalene lactones
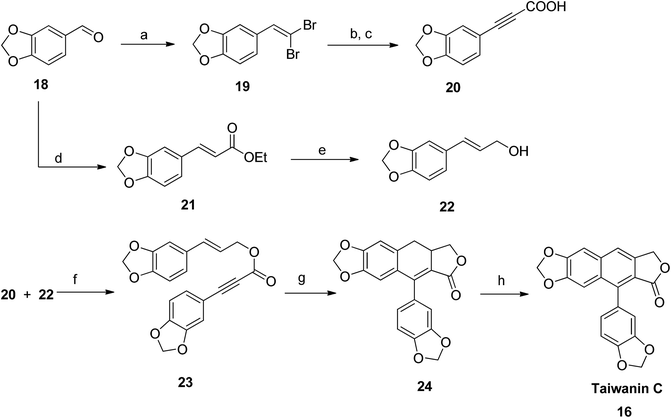
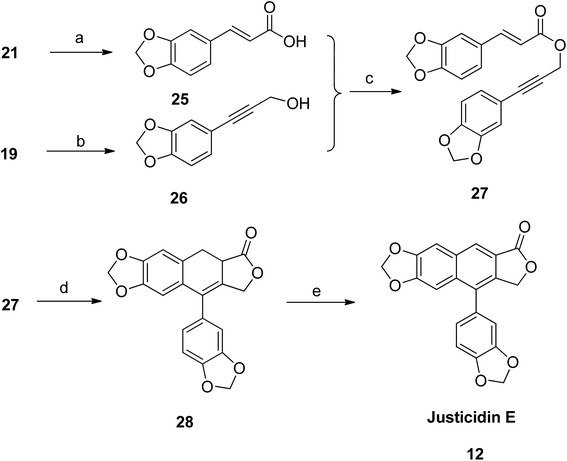
Park et al.,48 synthesized taiwanin C using an intramolecular Diels–Alder method. The starting material piperonal 18 was converted to gem-dibromoalkene 19 (route a: via reaction with triphenylphosphine and carbontetrabromide at room temperature) and to piperonal ester 21 (route d: via reaction with sodium hydride and triethyl phosphonoacetate at 0 °C). The dibromocompound 19 reacted with n-BuLi in THF (at −78 °C) to generate an alkyne anion, which, upon addition of methyl chloroformate and subsequent hydrolysis with K2CO3, resulted in formation of acid intermediate 20. 3-Arylallyl alcohol 22 was then prepared via reduction of piperonal ester 21 with DIBAL-H. Compounds 20 and 22 were coupled with coupling reagents DCC and DMAP in CH2Cl2 to yield compound 23. Finally, an intramolecular Diels–Alder precursor dihydronaphthalene 24 was readily converted to taiwanin C 16 in the presence of a catalyst, DDQ (Scheme 1).Justicidin E (12) was also prepared following the same strategy. The ester group in compound 21 was hydrolyzed using alkaline solution to get the respective acid 25. The gem-dibromoalkene 19 was converted to arylpropargyl alcohol 26. Both 25 and 26 were coupled using coupling reagents DCC and DMAP to get the precursor compound 27. Under intramolecular Diels–Alder conditions, the compound 27 was cyclised to dihydronaphthalene (28). Subsequently, compound 28 was aromatized to give the desired analog justicidin E (12) using DDQ as a catalyst (Scheme 2).
Synthesis of type I arylnaphthalene lactone daurinol (17)
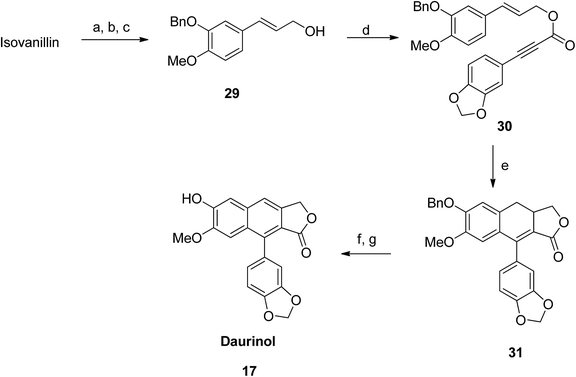
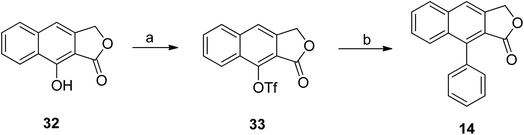
Initially, benzylation of isovanillin was performed to obtain compound 29. Afterwards, coupling of compound 21 with 29 was carried out using DCC and DMAP in CH2Cl2 to form compound 30. Dihydronaphthalene 31 was thus obtained from an intramolecular Diels–Alder reaction of 30. Further aromatization (using an oxidant) followed by hydrogenolysis (of benzyl ether) converted 30 to the desired daurinol 17 (Scheme 3).Hayet et al.49 reported the synthesis of arylnaphthalene lactone from naphthol (32). Compound 32 was converted to triflate 33 using N-phenylbis(trifluoromethanesulfonimide) and NaH.50 A Suzuki reaction was further performed to introduce an aryl group to compound 33 using palladium, phenyl boronic acids and additives (depending on the substrates) to get compound 14 (Scheme 4).51,52
 | ||
| Scheme 4 Synthesis of arylnaphthalene lactone. Reagents and conditions: (a) PhN(Tf)2, Et3N, DMAP, THF; (b) Pd(PPh3)4, PhB(OH)2, K3PO4, DMF. | ||
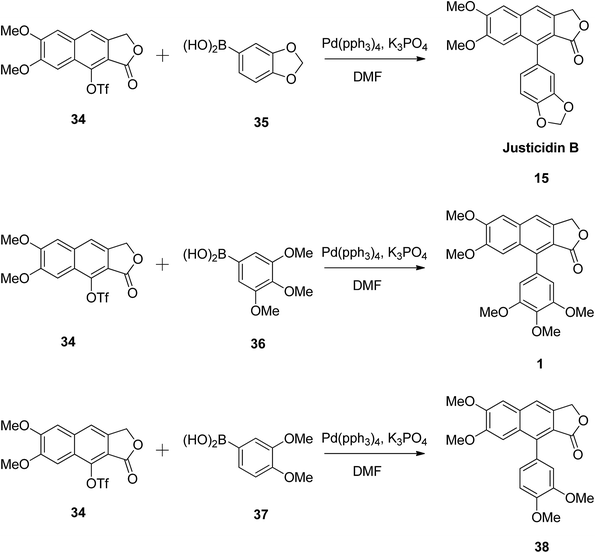
The versatility of the reaction was established by synthesising justicidin B (15), 3,4,5-trimethoxyphenylnaphthalene lactone (1), and 3,4-dimethoxyphenylnaphthalene lactone (38) using the same methodology.49 Compound 34 reacted with different boronic acids (35, 36 and 37) in the presence of Pd and a base (Scheme 5). The authors believe that this approach can be widely utilised in the synthesis of arylnaphthalene lactone derivatives to elucidate the structure–activity relationships of these compounds for biological studies.
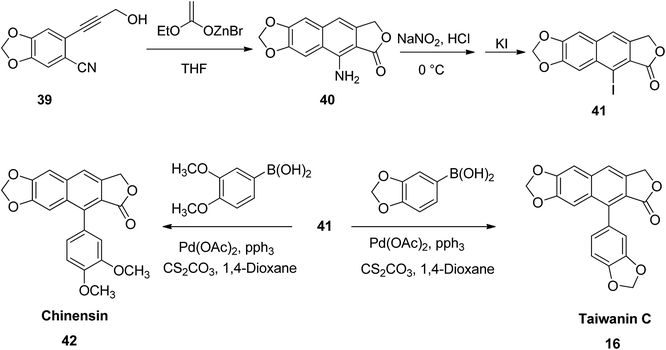
He et al.53 reported a simple protocol for the total synthesis of arylnaphthalene lactones. Briefly, compound 39 reacted with a zinc analog to yield 9-amino-6,7-methylenedioxynaphtho[2,3-c]furan-1(3H)-one (40). This, upon reaction with sodium nitrite in an aqueous hydrochloric acid, followed by addition of potassium iodide, furnished 9-iodo-6,7-methylenedioxynaphtho[2,3-c]furan-1(3H)-one (41). The Suzuki coupling of compound 41 with benzo[d][1,3]dioxol-5-yl boronic acid leads to the principle compound taiwanin C (16) (Scheme 6).
Similarly, the coupling of compound 41 with 3,4-dimethoxyphenyl boronic acid leads to the formation of chinensin (42). The broad scope of compounds 16 and 42 established the versatility of the new strategy. Thus, a number of arylnaphthalene lactone lignans with diverse substitution patterns or functional moieties can be obtained. This can significantly enhance their biological properties for future drug discovery programs.
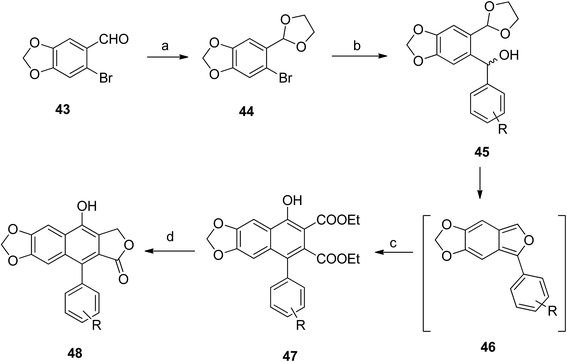
Hui et al.54 synthesized a large number of arylnaphthalene lactone derivatives from 43 in multi-step reactions. Compound 43 reacted with p-TsOH in glycol and benzene to form compound 44, which reacted with different aldehydes to give compound 45. Intramolecular cyclization of 45 formed compound 46. Reaction of 46 with DEADC in DCM and acetic acid formed compound 47. The final product (48) was obtained from the reaction of 47 with sodium borohydride and methanol (Scheme 7).
Patrick Foley et al.55 demonstrated the silver-catalyzed one-pot synthesis of arylnaphthalene lactone cores (53–57) using carbon dioxide, arylphenylpropargyl chloride (49 and 50), and arylphenylacetylenes (51 and 52). This new approach was employed in the synthesis of retrochinensin, justicidin B, retrojusticidin B, chinensin, justicidin E and taiwanin C (Scheme 8).
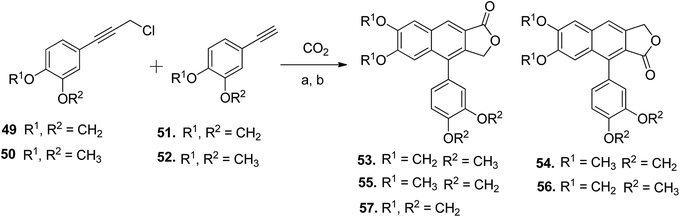 | ||
| Scheme 8 Synthesis of novel arylnaphthalene lactone lignans. Reagents and conditions: (a) SOCl2 and DMA; (b) K2CO3, 18-crown-6, 4 Å molecular sieves and DMA, 100 °C. | ||
Kocsis et al.56 devised a new route for the synthesis of a series of novel arylnaphthalene lactone lignans along with their regioisomers. Compounds 59 and 60 reacted with sulphuric acid, methanol and DIBALH to give compounds 60 and 61, which, upon reaction with compounds 62 and 63 under optimized DDA, formed styrenyl precursors (64–66). Compound 64 reacted with PhNO2 to yield a 2![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 mixture of arylnaphthalene lactone 67 and its regioisomer (70). Likewise, compound 65 under the same reaction conditions furnished a 2
1 mixture of arylnaphthalene lactone 67 and its regioisomer (70). Likewise, compound 65 under the same reaction conditions furnished a 2![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 mixture of arylnaphthalene lignan 68 and its regioisomer (71). The reaction of compound 66 gave a 3
1 mixture of arylnaphthalene lignan 68 and its regioisomer (71). The reaction of compound 66 gave a 3![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 mixture of arylnaphthalene lignans 69 and 72 (Scheme 9).
1 mixture of arylnaphthalene lignans 69 and 72 (Scheme 9).
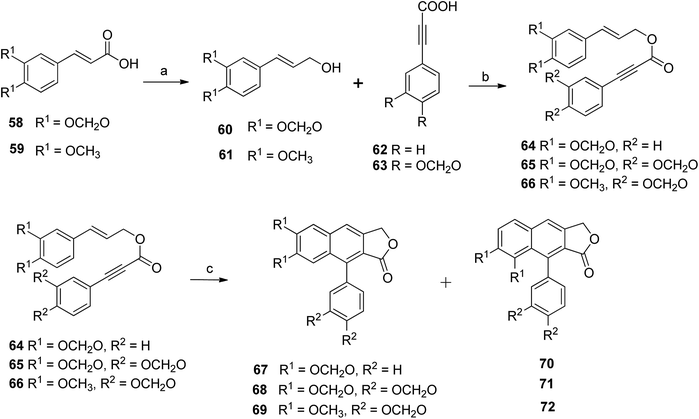 | ||
| Scheme 9 Synthesis of arylnaphthalene lactone lignan natural products. Reagents and conditions: (a) H2SO4, MeOH, DIBALH and DCM; (b) DCC, DMAP and DCM; (c) PhNO2 and MWI, 180 °C, 5 min. | ||
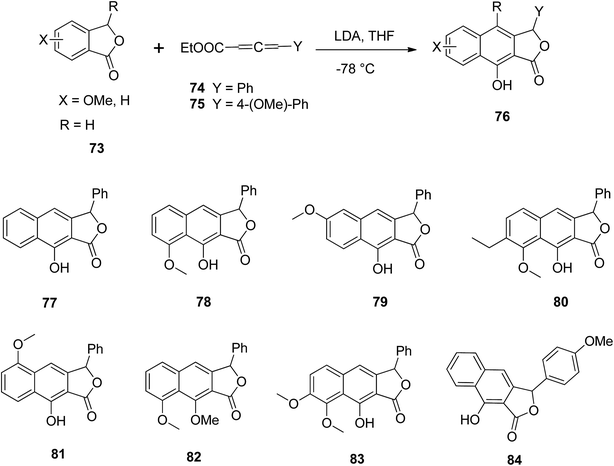
Mal and Jana57 described a single step synthesis of naphthalene lactone analogs. Various phthalides 73 reacted with allene carboxylates 74 and LDA in THF to yield the respective arylnaphthalene lactone 76. Various functional groups (77–84) were tolerated well under the reaction conditions (Scheme 10).
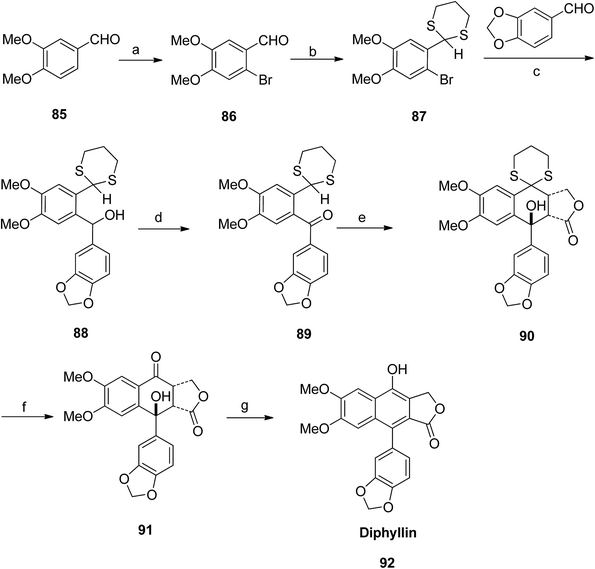
Patrick Foley et al.58 isolated derivatives of diphyllin (92) and patentiflorin A (97) from the medicinal plant Justicia gendarussa. The synthetic pathway adopted by the group included bromination of 85 to give compound 86, which further reacted with p-TsOH to form compound 87. Reaction of 87 with benzo[d][1,3]dioxole-5-carbaldehyde and n-BuLi furnished compound 88. Compound 88 was treated with MnO2 to form compound 89. Compound 90 was obtained upon reaction of 89 with LDA. Compound 90 was converted to 91 when reacted with HgO and HgCl2. Finally, compound 91 was treated with p-TsOH to give diphyllin (92) (Scheme 11).
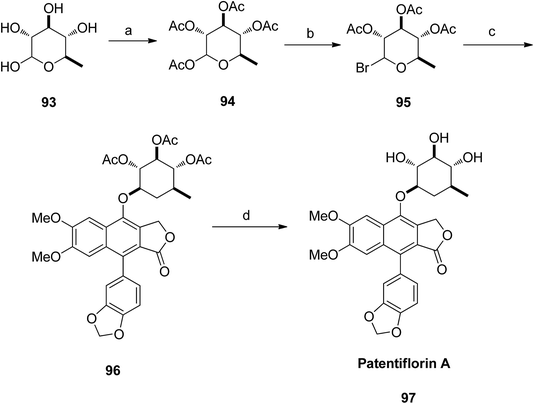
The aglycone diphyllin (92) served as a key intermediate for the synthesis of patentiflorin A (97), which was obtained via glycosylation of diphyllin 92 at C-7 with D-quinovose 93 (Scheme 12).
The previously described silver-catalysed one-pot synthetic protocol55 was first optimised for the synthesis of unsubstituted arylnaphthalene lactones. Afterwards, the methodology was extended towards the synthesis of a tetramethoxy-substituted arylnaphthalene lactone natural product analog58 (Scheme 13). The chloride precursor 99 was obtained from the 3,4 dimethoxyphenylpropargyl alcohol 98. Reaction of 99 and 100 with CO2 in the presence of a Ag catalyst formed two major isomers (101 and 102) in a 2![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 ratio.
1 ratio.
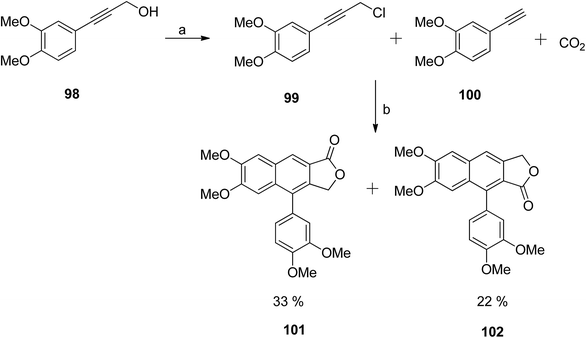 | ||
| Scheme 13 Synthesis of arylnaphthalene lactones. Reagents and conditions: (a) SOCl2 and DMA; (b) AgI, K2CO3, 18-crown-6, DMAc and molecular sieves. | ||
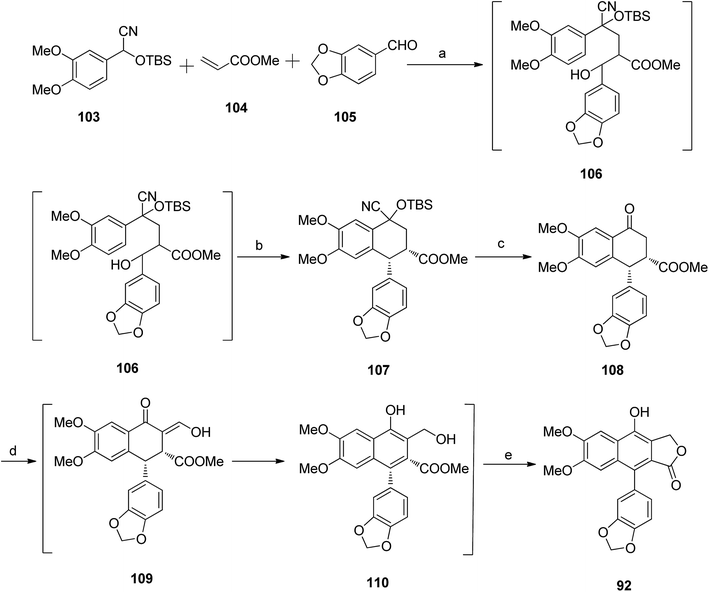
Ogiku et al.59 reported the synthesis of diphyllin 92 following the synthesis route in Scheme 14. The conjugate addition of the anion generated from compound 103 with LDA to methyl acrylate, followed by trapping of the resultant enolate with piperonal in situ, furnished a mixture of diastereomers 106. The crude product was further treated with TFA to give compound 107, which reacted with tetra-n-butyl ammonium fluoride to yield stereoisomers of compound 108. Compound 108 reacted with HCOOMe and NaOMe to form a mixture of intermediate 109 and compound 110. The reaction mixture was treated with conc. HCl to afford diphyllin 92.
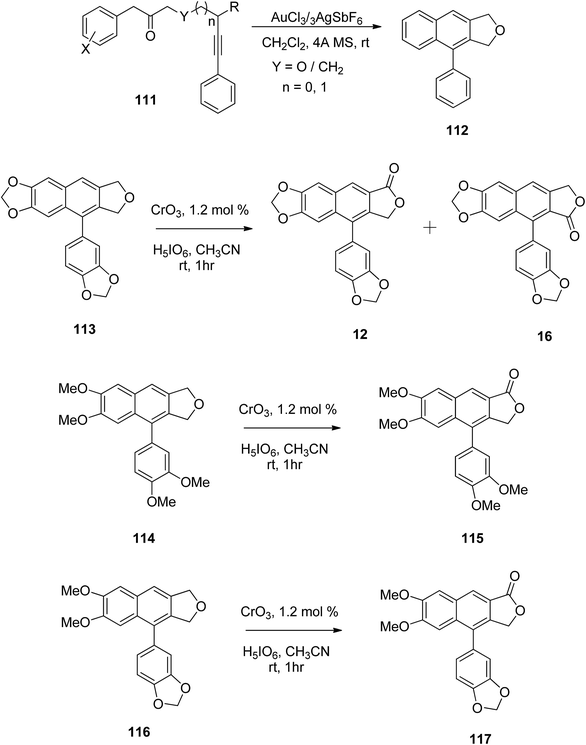
Gudla and Balamurugan60 used oxidation methods for the synthesis of different arylnaphthalene lactones. Arylnaphthalenes fused with furan served as precursors in the preparation of arylnaphthalene lactone lignan and its analogs. The benzylic oxidation of compound 112 has already been reported using Jones reagent, which resulted in both possible arylnaphthalene lactones.61 However, the CrO3/H5IO6/CH3CN system offers smooth benzylic oxidation at room temperature.62 Under these conditions benzylic oxidation was carried out for compounds 113, 114 and 116 to yield arylnaphthalene lactones 12, 16, 115 and 117 (Scheme 15). Substrate 113, which contains fused dioxlane in the naphthalene ring resulted in a mixture of lactones, justicidin E (12) and taiwani C (16).
Biological studies
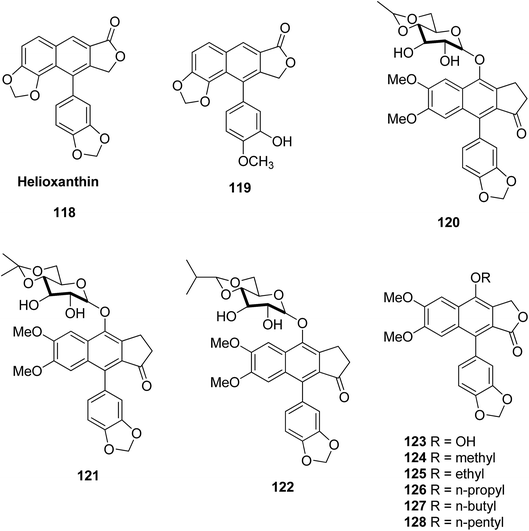
Janmanchi et al.63 reported helioxanthin 118 analogs as potential anti-hepatitis B virus agents. Modification of the lactone ring and methylenedioxy unit of helioxanthin resulted in different antiviral activities. Compound 119 was found to be the most effective anti-HBV agent, inhibiting secretion of viral surface antigens and e antigens in HepA2 cells. The EC50 values for each were 0.06 and 0.14 μM, respectively. Compound 119 not only inhibited wild-type HBV and lamivudine-resistant strains but also suppressed the HBV mRNA, core proteins, and viral promoters successfully. This type of analog exhibits unique actions that are different to those of existing therapeutic drugs currently in use as novel anti-HBV agents.Da-Kuo Shi et al.64 reported a series of novel compounds containing glycosylated diphyllin with different sugar derivatives. They tested them against many human tumor cell lines. Some of the synthesized compounds showed promising cytotoxicity with IC50 values in the μM–nM range. Compounds 120, 121 and 122 are potent against HCT-116, MCF-7, and KD tumor cell lines. Sugar moieties with cyclic lipophilic groups at C4′ and C6′ showed a further increase in bioactivity. All the synthesized compounds were tested using a Topo II-induced kDNA decatenation assay and the results were consistent with their in vitro cytotoxicity. This signifies that Topo II is one of the targets for such compounds, and also showed G0/G1 arrest and DNA fragmentation, which leads to the death of the cell by apoptosis in human leukemia HL-60 cell lines. These results suggest that the sugar moiety on C4 of diphyllin is key for its antitumor activity. The SAR analysis revealed that (i) the sugar moiety on the diphyllin is essential, (ii) equatorial C′4-OH on the sugar is superior to an axial one, and (iii) a proper cyclic lipophilic group at the C′4 and C′6 of sugar might enhance the anticancer activity.
Yu et al.65 isolated nine natural lignan justicidin A analogs and tested their cytotoxic activities against hepatocellular carcinoma (HepG2) cell lines. Compounds 123–128 showed potent antitumor activity, better than that of the standard drug etoposide. These compounds showed good antitumor activity. In their reported investigations modifications of justicidin A analogs further increased the antitumor activity.
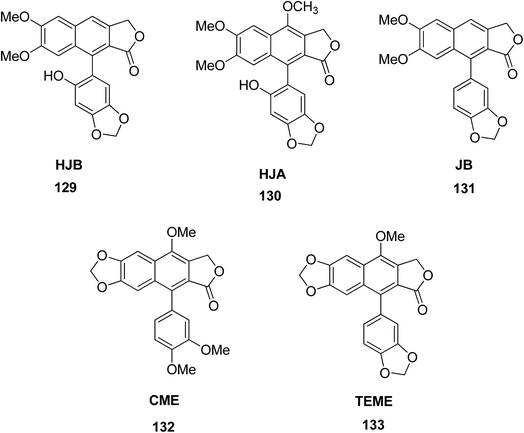
Luo et al.66 isolated five arylnaphthalene lignans including 6′-hydroxy justicidin A (HJA) 129, 6′-hydroxy justicidin B (HJB) 130, justicidin B (JB) 131, chinensinaphthol methyl ether (CME) 132, and taiwanin E methyl ether (TEME) 133 from Justicia procumbens. The effects of these lignans on the proliferation and apoptosis of human leukemia K562 cell lines were investigated along with their structure–activity relationships. The results showed that HJB, HJA and JB significantly repressed the growth of K562 cells by reducing proliferation and SOD activity led by apoptosis. The decreasing order of anti-proliferative activity of the five tested arylnaphthalenes was HJB > HJA > JB > CME, TEME. SAR studies suggested that hydroxyl substitution at C-1′ and C-6′ significantly increases the anti-proliferative activity of arylnaphthalene lignans, while a methoxyl at C-1′ significantly decreases this effect consistently.
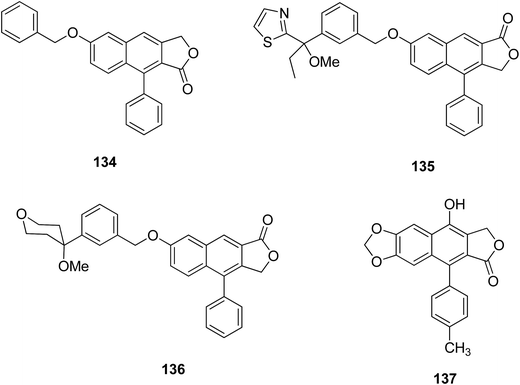
The naphthalenic lignan lactones with an oxymethylene or methyleneoxy linker are non-redox 5-lipoxygenase inhibitors. 5-Lipoxygenase is involved in the biosynthesis of leukotrienes from arachidonic acid. Compound 134 showed potent non-redox inhibition activity against the enzyme. The design of a 5-lipoxygenase inhibitor helped alleviate asthmatic, inflammatory, and rheumatoid arthritis diseases. Further modification of 134 led to the synthesis of 135 and 136.67 Compound 136 is more active than 135, and is involved in the production of leukotriene B4 in human polymorphonuclear leukocytes (IC50 1.5 nM) and in human blood (IC50 50 nM); no significant inhibition was observed in the case of 135.68
Hui et al.69 reported a series of novel arylnaphthalene lignan analogs as anticancer candidates against A549, SW480 and KB cell lines, and one normal cell line, HEK293. Compound 137 contains a para-methyl on the D-ring and showed potent antitumor activity, having an IC50 value of 18.9 μM against KB cells and cytotoxicity to HEK293. Fluorescent staining has confirmed that compound 137 induced apoptosis of KB cells. Western blot analysis has shown that compound 137 increased the expression of cleaved-caspase-3 and bax while reducing the expression of bcl-2.
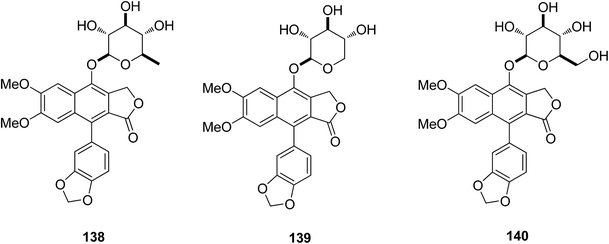
Zhang et al.70 isolated compound 138 from Justicia gendarussa plants in Vietnam and reported it as a potent anti-HIV-1 agent. Compound 138 was tested against M- and T-tropic HIV-1 isolates and showed significantly higher activity than the standard anti-HIV drug, zidovudine (AZT). Patentiflorin A (138) and two congeners (139–140) were synthesized via structural modifications and tested as anti-HIV arylnaphthalene lignin (ANL) glycosides in the search for new drugs. The quinovopyranosyloxy group in the structure (138) was found to be essential for the high level of anti-HIV activity. Patentiflorin A (138) was further tested for HIV-1 gene expression of the R/U5 and U5/gag transcripts. The results confirmed that the compound potentially inhibited HIV-1 reverse transcription. In the SAR study, patentiflorin A (138) showed potential as an anti-HIV-1 drug, and showed a broad activity spectrum against M- and T-tropic HIV-1 isolates. The compound (138) was found to be more effective than AZT in inhibiting four different HIV-1 isolates, either M- or T-tropic, in human PBMCs with IC50 values in the range 14–32 nM. Hence, ANL glycosides have the potential to be developed as novel anti-HIV drugs in the future.
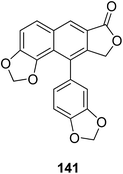
Hajdu et al.71 isolated helioxanthin (141) from fresh roots of Heliopsis helianthoides var. scabra and evaluated its in vitro brain tumor activity. Compound 141 inhibited the migration of melanoma and brain endothelial cells, and also reduced the adhesion of melanoma cells to the brain endothelium. Furthermore, compound 141 enhanced the blood–brain barrier function and the expression of the tight junction protein ZO-1 at the junctions of the endothelial cells. These findings confirmed that 141 potentially interferes with different steps of brain metastasis formation and enhances the barrier function of cerebral endothelial cells.
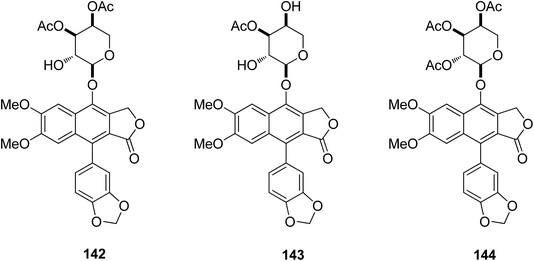
Ren et al.72 isolated two new (142 and 143) and four known (3–6) arylnaphthalene lignan lactones from Phyllanthus poilanei collected in Vietnam, with one further known analog (144) being prepared from phyllanthusmin C (4). Some of these arylnaphthalene lignin lactones were cytotoxic toward HT-29 human colon cancer cells. Compounds 142 and 144 were found to be the more potent inhibitors, with IC50 values of 170 and 110 nM, respectively. Compound 142 showed better activity in in vivo hollow fiber assays using HT-29 cells implanted in immunodeficient NCr nu/nu mice. The mechanistic studies also showed that the compound mediates its cytotoxic effects by inducing tumor cell apoptosis.
Conclusion
Arylnaphthalene lactone lignan analogs display multiple biological and pharmacological activities. In recent years, large numbers of arylnaphthalene lactone compounds have been extracted from different families of plants. They have been synthesized and evaluated for their anticancer, antibacterial, antiviral, antitumor, antiplatelet, phosphodiesterase inhibition, 5-lipoxygenase inhibition, HIV reverse transcriptase inhibition and cytotoxic activities. In the present review, we have mainly focused on the synthesis and in vitro and in vivo biological activities of arylnaphthalene lactone lignan containing analogs, and the possible interest in them for future drug discovery research programs.Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.Abbreviations
| AACMs | Aryl(aryl’)-2,2-dichlorocyclopropylmethanols |
| DIBAL-H | Diisobutylaluminium hydride |
| DDQ | 2,3-Dichloro-5,6-dicyano-1,4-benzoquinone |
| DCC | N,N′-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide |
| DMAP | 4-Dimethylaminopyridine |
| DEADC | Diethyl azodicarboxylate |
| DMAc | Dimethylacetamide |
| LDA | Lithium diisopropylamide |
| p-TsOH | p-Toluenesulfonic acid |
| TFA | Trifluoroacetic acid |
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 21772150) and Wuhan University of Technology for financial support.References
- D. J. Newmann and G. M. Cragg, J. Nat. Prod., 2007, 70, 461–477 CrossRef PubMed.
- K. Kumar and H. Waldmann, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2009, 48, 3224–3242 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. P. Nandy, M. Prakesch, S. Khadem, T. Reddy, U. Sharma and P. Arya, Chem. Rev., 2009, 109, 1999–2060 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. E. Park, J. Lee, S. Y. Seo and D. Shin, Tetrahedron Lett., 2014, 55, 818–820 CrossRef CAS.
- R. S. Ward, Nat. Prod. Rep., 1999, 16, 75–96 RSC.
- S. Apers, A. Vlietinck and L. Pieters, Phytochem. Rev., 2003, 2, 201–217 CrossRef CAS.
- K. Kawazoe, A. Yutani, K. Tamemoto, S. Yuasa, H. Shibata, T. Higuti and Y. Takaishi, J. Nat. Prod., 2001, 64, 588–591 CrossRef CAS.
- K. S. Sagar, C. C. Chang, W. K. Wang, J. Y. Lin and S. S. Lee, Bioorg. Med. Chem., 2004, 12, 4045–4054 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Yeo, Y. Li, L. Fu, J. L. Zhu, E. A. Gullen, G. E. Dutschman, Y. Lee, R. Chung, E. S. Huang, D. J. Austin and Y. C. Cheng, J. Med. Chem., 2005, 48, 534–546 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Li, L. Fu, H. Yeo, J. L. Zhu, C. K. Chou, Y. H. Kou, S. F. Yeh, E. Gullen, D. Austin and Y. C. Cheng, Antiviral Chem. Chemother., 2005, 16, 193–201 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. Janmanchi, Y. P. Tseng, K. C. Wang, R. L. Huang, C. H. Lin and S. F. Yeh, Bioorg. Med. Chem., 2010, 18, 1213–1226 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. B. McDoniel and J. R. Cole, J. Pharm. Sci., 1972, 61, 1992–1994 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Pelter, R. S. Ward, P. Satyanarayana and P. Collins, J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. 1, 1983, 643–647 RSC.
- A. S. Capilla, I. Sánchez, D. H. Caignard, P. Renard and M. D. Pujola, Eur. J. Med. Chem., 2001, 36, 389–393 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. C. Chen, W. C. Hsin, F. N. Ko, Y. L. Huang, J. C. Ou and C. M. Teng, J. Nat. Prod., 1996, 59, 1149–1150 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. R. Weng, H. H. Ko, T. L. Yeh, H. C. Lin and C. N. Lin, Arch. Pharm., 2004, 337, 207–212 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. Ukita, Y. Nakamura, A. Kubo, Y. Yamomoto, M. Takahashi, J. Kotera and T. Ikeo, J. Med. Chem., 1999, 42, 1293 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. Iwasaki, K. Kondo, T. Kuroda, Y. Moritani, S. Yamagata, M. Sugiura, H. Kikkawa, O. Kaminuma and K. Ikezawa, J. Med. Chem., 1996, 39, 2696–2704 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Thérien, B. J. Fitzsimmons, J. Scheigets, D. Macdonald, L. Y. Choo, J. Guay, J. P. Falgueyret and D. Riendeau, Bioorg. Med. Chem., 1993, 3, 2063–2066 CrossRef.
- D. Delorme, Y. Ducharme, C. Brideau, C. C. Chan, N. Chauret, S. Desmarais, D. Dubé, J. P. Falgueyret, R. Fortin and J. Guay, et al., J. Med. Chem., 1996, 39, 3951–3970 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Ducharme, C. Brideau, D. Dubé, C. C. Chan, J. P. Falgueyret, J. W. Gillard and J. Guay, et al., J. Med. Chem., 1994, 37, 512–518 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. W. Chang, M. T. Lin, S. S. Lee, C. S. Karin, K. C. S. Chen Liu, F. L. Hsu and J. Y. Lin, Antiviral Res., 1995, 27, 367–374 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. S. Lee, M. T. Lin, C. L. Liu, Y. Y. Lin and K. C. S. Chen Liu, J. Nat. Prod., 1996, 59, 1061–1065 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Cow, C. Leung and J. L. Charlton, Can. J. Chem., 2000, 78, 553–561 CrossRef CAS.
- S. J. Wu and T. S. Wu, Chem. Pharm. Bull., 2006, 54, 1223–1225 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Hemmatia, T. J. Schmidtb and E. Fuss, FEBS Lett., 2007, 581, 603–610 CrossRef PubMed.
- T. J. Schmidt, S. Hemmati, M. Klaes, B. Konuklugil, A. Mohagheghzadeh, I. Ionkova, E. Fuss and A. W. Alfermann, Phytochemistry, 2010, 71, 1714–1728 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Ramesh, N. Ravindranath, T. S. Ram and B. Das, Chem. Pharm. Bull., 2003, 51, 1299–1300 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. J. Wu and T. S. Wu, Chem. Pharm. Bull., 2006, 54, 1223–1225 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Z. Wang, X. Tian, H. Tsumura, K. Shimura and H. Ito, Anticancer. Drug. Des., 1993, 8, 193–202 CAS.
- L. Daley, Y. Guminski, P. Demerseman, A. Kruczynski and C. Etievant, et al., J. Med. Chem., 1998, 41, 4475–4485 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- I. Rassmann, R. Thodtmann, M. Mross, A. Huttmann and W. E. Berdel, et al., Invest. New Drugs, 1998, 16, 319–324 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. Utsugi, J. Shibata, Y. Sugimoto, K. Aoyagi and K. Wierzba, et al., Cancer Res., 1996, 56, 2809–2814 CAS.
- L. Daley, P. Meresse, E. Bertounesque and C. Monneret, Tetrahedron Lett., 1997, 38, 2673–2676 CrossRef CAS.
- D. S. Van Vliet and K. H. Lee, Tetrahedron Lett., 1990, 40, 2259–2262 CrossRef.
- T. S. Huang, C. C. Lee, Y. Chao, C. H. Shu and L. T. Chen, et al., Pharm. Res., 1999, 16, 997–1002 CrossRef CAS.
- T. S. Huang, C. H. Shu, C. C. Lee, L. T. Chen and J. Whang-Peng, Apoptosis, 2000, 5, 79–85 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. C. Lee and T. S. Huang, Pharm. Res., 2001, 18, 846–851 CrossRef CAS.
- S. K. Lin, H. C. Huang, L. L. Chen, C. C. Lee and T. S. Huang, Mol. Pharmacol., 2001, 60, 768–775 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. M. Barret, C. Etievant, C. Baudouin, K. Skov and M. Charveron, et al., Anticancer Res., 2002, 22, 187–192 CAS.
- R. Stevenson and J. V. Weber, J. Nat. Prod., 1989, 52, 367–375 CrossRef CAS.
- R. Stevenson and J. V. Weber, J. Nat. Prod., 1991, 54, 310–314 CrossRef CAS.
- P. T. Anastas and R. Stevenson, J. Nat. Prod., 1991, 54, 1687–1691 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Sato, T. Tamura and M. Mori, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. Engl., 2004, 43, 2436–2440 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- N. Eghbali, J. Eddy and P. T. Anastas, J. Org. Chem., 2008, 73, 6932–6935 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. Foley, N. Eghbali and P. T. Anastas, J. Nat. Prod., 2010, 73, 811–813 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Nishii, T. Yoshida, H. Asano, K. Wakasugi, J. Morita, Y. Aso, E. Yoshida, J. Motoyoshiya, H. Aoyama and Y. Tanabe, J. Org. Chem., 2005, 70, 2667–2678 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. E. Park, J. Lee, S. Y. Seo and D. Shin, Tetrahedron Lett., 2014, 55, 818–820 CrossRef CAS.
- F. Hayat, L. Kang, C. Y. Lee and D. Shin, Tetrahedron, 2015, 71, 2945–2950 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Xia, P. Qu, Z. Liu, R. Ge, Q. Xiao, Y. Zhang and J. Wang, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2013, 52, 2543–2546 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- F. Alonso, I. P. Beletskaya and M. Yus, Tetrahedron, 2008, 64, 3047–3101 CrossRef CAS.
- M. M. Heravi and E. Hashemi, Tetrahedron, 2012, 68, 9145–9178 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. He, X. Zhang and X. Fan, Chem. Commun., 2014, 50, 5641–5643 RSC.
- J. Hui, Y. Zhao and L. Zhu, Med. Chem. Res., 2012, 21, 3994–4001 CrossRef CAS.
- P. Foley, N. Eghbali and P. T. Anastas, J. Nat. Prod., 2010, 73, 811–813 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- I. S. Kocsis and K. M. Brummond, Org. Lett., 2014, 16, 4158–4161 CrossRef PubMed.
- M. Dipakranjan and S. Jana, J. Org. Chem., 2016, 81, 11857–11865 CrossRef PubMed.
- P. Foley, N. Eghbali and P. T. Anastas, Green Chem., 2010, 12, 888–892 RSC.
- T. Ogiku, S. Yochida, T. Kuroda, H. Ohmizu and T. Iwasaki, Synlett, 1992, 651–652 CrossRef CAS.
- V. Gudla and R. Balamurugan, J. Org. Chem., 2011, 76, 9919–9933 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. Ahmed, T. L. Holmes and R. J. Stevenson, Heterocycl. Chem., 1974, 11, 687–690 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Yamazaki, Org. Lett., 1999, 1, 2129–2132 CrossRef CAS.
- D. Janmanchi, Y. P. Tseng, K. C. Wang, R. L. Huang, C. H. Lin and S. F. Yeh, Bioorg. Med. Chem., 2010, 18, 1213–1226 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. K. Shi, W. Zhang, N. Ding, M. Li and Y. X. Li, Eur. J. Med. Chem., 2012, 47, 424–431 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Zhao, W. Dan, H. Jie and Z. Li, Med. Chem. Res., 2010, 19, 71–76 CrossRef.
- J. Luo, Y. Hu, W. Kong and M. Yang, Plos One., 2014, 3, e93516 Search PubMed.
- Y. Ducharme, C. Brideau, D. Dubé, C. C. Chan, J. P. Falgueyret, J. W. Gillard, J. Guay, J.H. Hutchinson, C. S. McFarlane, D. Riendeau, J. Scheigetz and Y. Girard, J. Med. Chem., 1994, 37, 512–518 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Apers, A. Vlietinck and L. Pieters, Phytochem. Rev., 2003, 2, 201–217 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Hui, Y. Zhao and L. Zhu, Med. Chem. Res., 2012, 21, 3994–4001 CrossRef CAS.
- A. J. Zhang, E. R. Booms, Y. F. Guan, D. Y. Wang, K. L. Liu, W. F. Li, V. H. Nguyen, N. M. Cuong, D. D. Soejarto, H. H. S. Fong and L. Rong, J. Nat. Prod., 2017, 80, 1798–1807 CrossRef PubMed.
- Z. Hajdu, J. Hasko, I. A. Krizbai, I. Wilhelm, N. Jedlinszki, C. Fazakas, J. Molna, P. Forgo and J. Hohmann, J. Nat. Prod., 2014, 77, 2641–2650 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Ren, D. D. Lantvit, Y. Deng, R. Kanagasabai, J. C. Gallucci, T. N. Ninh, H. Chai, D. D. Soejarto and J. R. Fuchs, et al., J. Nat. Prod., 2014, 77, 1494–1504 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 |