Near-infrared-triggered antibacterial and antifungal photodynamic therapy based on lanthanide-doped upconversion nanoparticles†
Abstract
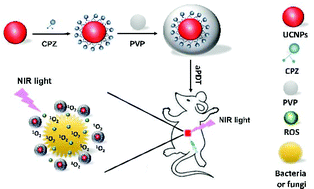
An alarming worldwide increase in microbial resistance to traditional drugs and classical pharmacophores has spurred the search for new antimicrobial compounds. Antimicrobial photodynamic therapy (aPDT) has recently emerged as an effective modality for the selective destruction of bacteria and other pathogenic microorganisms. However, some of the factors, including the aggregation of the hydrophobic photosensitizer (PS) in aqueous media and the inefficient biodistribution of PS limit its expansion to clinical conditions. In addition, the photoactivation under visible-light irradiation limits the therapeutic effect of aPDT for deep-tissue infection. To overcome these limitations, a PS (β-carboxyphthalocyanine zinc, CPZ) delivery system with lanthanide-doped upconversion nanoparticles (UCNPs, LiYF4:Yb/Er) and polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) was prepared and its antimicrobial (antibacterial and antifungal) activities were investigated. Such a near-infrared (NIR) triggered UCNPs-CPZ-PVP system significantly reduced the aggregation of CPZ and presented a high anti-infectious activity against multi-drug resistant (MDR) bacteria (methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus by 4.7 log10 and MDR Escherichia coli by 2.1 log10) post aPDT (at 50 μg mL−1 UCNPs-CPZ-PVP with 0.5 W cm−2 980 nm light). In particular, UCNPs-CPZ-PVP showed high antifungal efficacy against Candida albicans. In vivo aPDT experiments were further carried out using an MDR bacterial infection murine model in the presence of 5 mm thick tissue specimens, demonstrating the great potential of UCNPs-CPZ-PVP against infections in deep tissue. Altogether, we reveal an efficient NIR-triggered nano-photosensitizer with promising antifungal and antibacterial efficacy for clinical antimicrobial therapy.
- This article is part of the themed collection: International Year of the Periodic Table : Lanthanides for Precision Therapy and Beyond


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...