Simultaneous enhancement of photoluminescence and afterglow luminescence through Bi3+ co-doping in the Sr3Al2O5Cl2:Eu2+ phosphor
Abstract
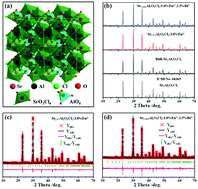
In this work, the Sr3Al2O5Cl2:Eu2+ and Sr3Al2O5Cl2:Eu2+,Bi3+ phosphors are synthesized by high temperature solid state reactions. Various characterization techniques, such as X-ray diffraction (XRD), Rietveld refinement, photoluminescence (PL) spectroscopy, afterglow spectroscopy, decay curves and thermoluminescence (TL) spectroscopy, are used to examine the phase purity and PL properties of all samples. The XRD results show that all samples belong to the targeted orthorhombic Sr3Al2O5Cl2 phase with the space group of P212121. Upon excitation with UV light, Eu2+-related reddish photoemission and afterglow luminescence are observed in the Sr3Al2O5Cl2:Eu2+ samples. More remarkably, we find that co-doping with Bi3+ ions can enhance the Eu2+-related photoemission and afterglow intensity as well the afterglow duration. For the optimal Sr3Al2O5Cl2:Eu2+,Bi3+ sample, the afterglow luminescence can continue for nearly 550 min in the dark, which is almost 3-fold the duration of the afterglow luminescence of the optimal Sr3Al2O5Cl2:Eu2+ sample. The TL spectra reveal that co-doping with Bi3+ ions can enhance the defect population that corresponds to trap depths at 63 °C, 75 °C and 150 °C, of which the former two trap depths may help to improve the Eu2+-related luminescence in addition to the afterglow property. Due to an increase in the trap concentration, there is an increase in the re-trapping possibility for the released carriers. This work not only achieves enhanced afterglow luminescence of the Sr3Al2O5Cl2:Eu2+ phosphor by co-doping with the non-rare earth (RE) Bi3+ ions, but also provides new insights into the design of RE and non-RE related enhanced afterglow photonic materials for the future.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...