Hydrogen-atom tunneling through a very high barrier; spontaneous thiol → thione conversion in thiourea isolated in low-temperature Ar, Ne, H2 and D2 matrices†
Abstract
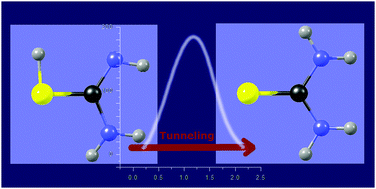
Spontaneous thiol → thione hydrogen-atom transfer has been investigated for molecules of thiourea trapped in Ar, Ne, normal-H2 (n-H2) and normal-D2 (n-D2) low-temperature matrices. The most stable thione isomer was the only form of the compound present in the matrices after their deposition. According to MP2/6-311++G(2d,p) calculations, the thiol tautomer should be higher in energy by 62.5 kJ mol−1. This less stable thiol form of the compound was photochemically generated in a thione → thiol process, occurring upon UV irradiation of the matrix. Subsequently, a very slow spontaneous conversion of the thiol tautomer into the thione form was observed for the molecules isolated in Ar, Ne, n-H2 and n-D2 matrices kept at 3.5 K and in the dark. Since the thiol → thione transformation in thiourea is a process involving the dissociation of a chemical bond, the barrier for this hydrogen-atom transfer is very high (104–181 kJ mol−1). Crossing such a high potential-energy barrier at a temperature as low as 3.5 K, is possible only by hydrogen-atom tunneling. The experimentally measured time constants of this tunneling process: 52 h (Ar), 76 h (Ne), 94 h (n-H2) and 94 h (n-D2), do not differ much from one another. Hence, the dependence of the tunneling rate on the matrix environment is not drastic. The progress of the thiol → thione conversion was also monitored for Ar matrices at different temperature: 3.5 K, 9 K and 15 K. For this temperature range, the experiments revealed no detectable temperature dependence of the rate of the tunneling process.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...