Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleCreative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported Licence
Photoacoustic probes for real-time tracking of endogenous H2S in living mice†
Ben
Shi
a,
Xianfeng
Gu
b,
Qiang
Fei
a and
Chunchang
Zhao
*a
aKey Laboratory for Advanced Materials, Institute of Fine Chemicals, School of Chemistry and Molecular Engineering, East China University of Science & Technology, Shanghai 200237, P. R. China. E-mail: zhaocchang@ecust.edu.cn
bDepartment of Medicinal Chemistry, School of Pharmacy, Fudan University, Shanghai, 201203 China
First published on 30th November 2016
Abstract
H2S is a key chemical mediator that exerts a vital role in diverse physiological and pathological processes. However, in vivo tracking of endogenous H2S generation still remains difficult due to the lack of reliable analytical methods. Herein, we present the first example of activatable photoacoustic probes for real-time imaging of H2S in living mice through the full utilization of the superiority of photoacoustic imaging modality at fine spatial resolution during deep tissue penetration. The designed probe can generate high NIR absorption at 780 nm in the presence of H2S, thus producing a strong photoacoustic signal output in the NIR region. Furthermore, this probe exhibits extremely fast and highly selective responsiveness, good water-solubility and excellent biocompatibility. In light of these outstanding features, this probe realizes the direct photoacoustic trapping of endogenous H2S generation in a HCT116 tumor-bearing mouse model. These preliminary imaging studies show that HCT116 colon tumors exhibit CBS upregulation activity, resulting in an increased rate of H2S generation.
Introduction
Mounting studies have shown that H2S plays a vital role in diverse physiological and pathological processes. It has been identified as a physiological gasotransmitter with robust cytoprotective actions in multiple organ systems, including regulatory roles in the cardiovascular system and modulation of the central nervous, respiratory, and gastrointestinal systems.1,2 Nevertheless, abnormal production of H2S can contribute to a variety of diseases ranging from Down's syndrome and Alzheimer's disease to diabetes and hypertension.3 As such, it is of great scientific interest to develop selective methods for the real-time tracking of this small molecule in living systems. To data, a number of reaction-based fluorescent probes have been designed as attractive molecular imaging techniques for monitoring H2S in living cells.4–7 However, few probes have been employed for in vivo H2S imaging due to the fact that fluorescence imaging suffers from limitations such as shallow tissue penetration and poor spatial resolution inside deep biological tissue. Therefore, development of reaction-based probes with new imaging modality is highly demanded in order to address these challenges.Photoacoustic (PA) imaging is a state-of-the-art imaging modality which relies on the translation of excitation light into ultrasonic waves based on the PA effect, and provides deeper tissue imaging penetration and higher in vivo spatial resolution when compared with traditional optical imaging techniques.8 As a result of these significant advantages, PA imaging has found broad applications in biology and medicine as a noninvasive imaging tool.9,10 However, it is still a big challenge to devise activatable probes for the photoacoustic imaging of molecular targets of interest. Given that H2S is a key chemical mediator, the full utilization of the superiority of PA imaging modality for the construction of H2S-activatable photoacoustic probes should be imperative to fully explore the biological roles of H2S in vivo. To our knowledge, there are no probes available for the PA imaging of this important small molecule. Herein, we present the first example of reaction-based PA probes that show a fast response to H2S accompanied with “turn-on” PA signals.
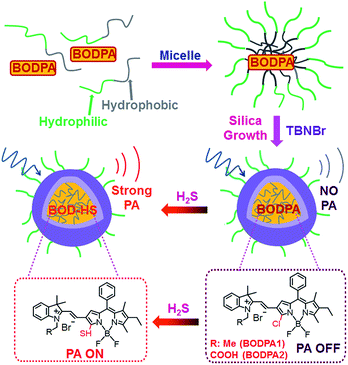
In this contribution, a H2S-activatable probe was fabricated by encapsulating semi-cyanine-BODIPY hybrid dyes (BODPA) into the hydrophobic interior of core–shell silica nanocomposites for in vivo photoacoustic imaging (Scheme 1). Our design strategy is based on modulating the electronic nature of the substituents to generate a near-infrared absorbing dye to produce PA signals, employing the feasible thiol–halogen nucleophilic substitution of a monochlorinated hybrid dye with H2S. Indeed, the presence of H2S transformed BODPA into BOD-HS inside nanoparticles through aromatic nucleophilic substitution, which resulted in high NIR absorption around 780 nm. Thus, the Si@BODPA probe generated a strong photoacoustic signal output in the NIR region. As shells of these nanoparticles were composed of poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) and positively charged silica units, Si@BODPA possessed good water-solubility and excellent biocompatibility as well as extremely fast responsiveness, enabling real-time imaging of H2S-related biological processes. In light of these outstanding features, Si@BODPA allowed the direct photoacoustic tracking of endogenous H2S generation in a HCT116 (human colon cancer cells) tumor-bearing mouse model.
Results and discussion
Two monochlorinated BODIPY-based hybrid dyes (BODPA1 and BODPA2) were chosen to prepare core–shell silica nanocomposites. Both dyes responded to H2S readily and were efficiently converted to BOD-HS within 50 minutes in CH3CN/PBS buffer mixtures (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1, v/v, 20 mM, pH 7.4, room temperature), which was demonstrated by HPLC and HRMS (Fig. S1†). Specifically, a strong NIR absorption band around 735 nm was activated, accompanied by a decrease of absorption at 540 nm (Fig. S2†), indicative of BODPAs as building blocks for the construction of activatable photoacoustic probes. Notably, BOD-HS is non-fluorescent which facilitates thermal deactivation to generate much stronger PA signals.10b Considering the limited solubility of BODPAs as well as their slow reaction with H2S in aqueous solution, we here intended to apply hydrophilic nanoparticles for the encapsulation of BODPAs to overcome this issue. Firstly, BODPAs and mPEG-DSPE were mixed in a 0.85 N hydrochloride solution under rigorous stirring, leading to the formation of self-assembled micelles with hydrophobic inner cores and hydrophilic PEG chains as outer arms.11 The hydrophobicity of BODIPY dyes trap them in the interior core. Following the in situ growth of silica shells under acidic conditions with N-trimethoxysilylpropyl-N,N,N-tri-n-butylammonium bromide (TBNBr) as silica agents for cross-linking, water-dispersible nanoparticles (Si@BODPA) were afforded, which were dialyzed for 48 h to remove unreacted chemicals. Additional characterization using TEM and DLS were carried out, which were identified in Fig. S3.†
1, v/v, 20 mM, pH 7.4, room temperature), which was demonstrated by HPLC and HRMS (Fig. S1†). Specifically, a strong NIR absorption band around 735 nm was activated, accompanied by a decrease of absorption at 540 nm (Fig. S2†), indicative of BODPAs as building blocks for the construction of activatable photoacoustic probes. Notably, BOD-HS is non-fluorescent which facilitates thermal deactivation to generate much stronger PA signals.10b Considering the limited solubility of BODPAs as well as their slow reaction with H2S in aqueous solution, we here intended to apply hydrophilic nanoparticles for the encapsulation of BODPAs to overcome this issue. Firstly, BODPAs and mPEG-DSPE were mixed in a 0.85 N hydrochloride solution under rigorous stirring, leading to the formation of self-assembled micelles with hydrophobic inner cores and hydrophilic PEG chains as outer arms.11 The hydrophobicity of BODIPY dyes trap them in the interior core. Following the in situ growth of silica shells under acidic conditions with N-trimethoxysilylpropyl-N,N,N-tri-n-butylammonium bromide (TBNBr) as silica agents for cross-linking, water-dispersible nanoparticles (Si@BODPA) were afforded, which were dialyzed for 48 h to remove unreacted chemicals. Additional characterization using TEM and DLS were carried out, which were identified in Fig. S3.†
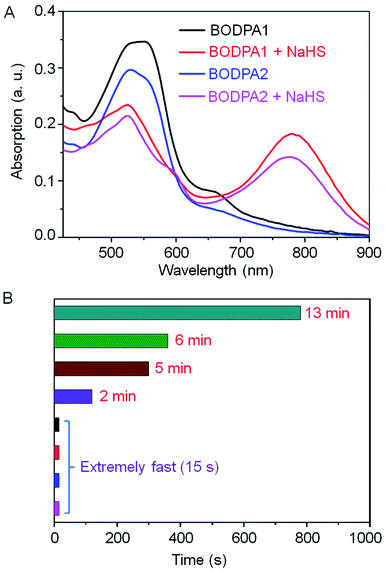
The response of Si@BODPA toward H2S was then evaluated in PBS buffer solutions (pH 7.4) using UV-vis spectroscopy. The addition of NaHS induced the generation of the NIR absorption at 780 nm and 777 nm for BODPA1 and BODPA2, respectively. The reduction of the original peak at around 540 nm was also noted (Fig. 1A). This observation was in good agreement with that of BODPAs when interacted with NaHS in CH3CN/PBS, which demonstrated the occurrence of a reaction between BODPAs and H2S within the water-dispersible silica core–shell nanoparticles. Notably, BOD-HS in the hydrophobic interior of the nanocomposites showed an obvious red-shift of 45 nm in its absorption compared to that in CH3CN/PBS buffer mixtures (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1, v/v). This variation could be rationalized as the effect of H-bonding interactions between the sulfur atom and H atom of H2O. Such interactions existing in aqueous solutions rather than in nanocomposites reduced the electron-donating ability of sulfur which ultimately led to the shift of the absorption to shorter wavelengths. Impressively, the dynamics of the reaction between BODPAs and H2S in Si@BODPA was Si dose-dependent (Fig. 1B and S4†). In general, increasing the amount of Si in the shell, as determined by energy dispersive X-ray (EDX) spectroscopy (Fig. S5†), caused a much faster reaction. The process of absorption change in Si@BODPA30 could reach completion in about 5 and 13 minutes for BODPA1 and BODPA2, respectively. In the case of Si@BODPA90, such change was promoted to be about 2 min and 6 min for BODPA1 and BODPA2, respectively. Gratifyingly, the responsive reaction was dramatically accelerated when further increasing the Si content, resulting in ideal probes, Si@BODPA180 and Si@BODPA270, which could rapidly detect H2S within 15 s. Given the transient nature of H2S which is catabolized rapidly in biological systems, one of the most important prerequisites for a probe is the extremely fast reactivity toward H2S. Thus, the nanoprobes established here possess the superiority and capability of trapping transient H2S and monitoring of H2S-related biological processes in real-time. As an example, Si@BODPA180 was chosen as a model probe for studying its potential applications. Undoubtedly, the entrapment of BODPAs into the interior of silica nanocomposites enables the advantage of rapid reaction, which can be attributed to the transfer of H2S via the hydrophilic assembly from water into its polar interior, which facilitates nucleophilic substitution.12 Such a polar microenvironment within the core is due to the positively charged ammonium functionality in TBNBr. More importantly, these nanoparticles are smaller than 100 nm and therefore are feasibly endocytosed by cells.
1, v/v). This variation could be rationalized as the effect of H-bonding interactions between the sulfur atom and H atom of H2O. Such interactions existing in aqueous solutions rather than in nanocomposites reduced the electron-donating ability of sulfur which ultimately led to the shift of the absorption to shorter wavelengths. Impressively, the dynamics of the reaction between BODPAs and H2S in Si@BODPA was Si dose-dependent (Fig. 1B and S4†). In general, increasing the amount of Si in the shell, as determined by energy dispersive X-ray (EDX) spectroscopy (Fig. S5†), caused a much faster reaction. The process of absorption change in Si@BODPA30 could reach completion in about 5 and 13 minutes for BODPA1 and BODPA2, respectively. In the case of Si@BODPA90, such change was promoted to be about 2 min and 6 min for BODPA1 and BODPA2, respectively. Gratifyingly, the responsive reaction was dramatically accelerated when further increasing the Si content, resulting in ideal probes, Si@BODPA180 and Si@BODPA270, which could rapidly detect H2S within 15 s. Given the transient nature of H2S which is catabolized rapidly in biological systems, one of the most important prerequisites for a probe is the extremely fast reactivity toward H2S. Thus, the nanoprobes established here possess the superiority and capability of trapping transient H2S and monitoring of H2S-related biological processes in real-time. As an example, Si@BODPA180 was chosen as a model probe for studying its potential applications. Undoubtedly, the entrapment of BODPAs into the interior of silica nanocomposites enables the advantage of rapid reaction, which can be attributed to the transfer of H2S via the hydrophilic assembly from water into its polar interior, which facilitates nucleophilic substitution.12 Such a polar microenvironment within the core is due to the positively charged ammonium functionality in TBNBr. More importantly, these nanoparticles are smaller than 100 nm and therefore are feasibly endocytosed by cells.
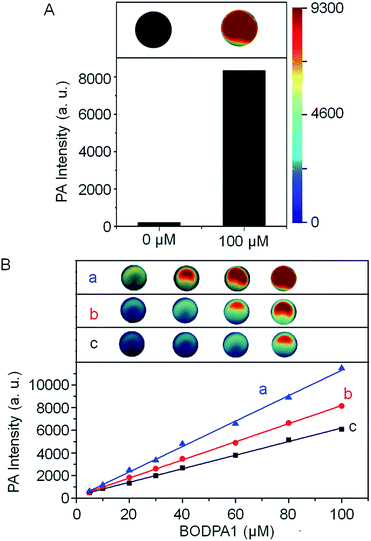
The photoacoustic responsiveness to H2S was then established. In the absence of H2S, Si@BODPA180 showed no detectable photoacoustic signals in PBS buffer solutions (pH 7.4). When H2S was introduced to the solution, Si@BODPA180 efficiently produced bright photoacoustic signals following excitation at 780 nm and ultimately led to a 44-fold turn-on response (Fig. 2A), which was in agreement with H2S-triggered formation of BOD-HS within nanoparticles. These results infer that this nanoprobe could serve as an activatable photoacoustic probe.
H2S triggered photoacoustic amplitudes of the nanocomposites upon excitation at 780 nm were examined at various concentrations. A linear correlation could be obtained between the PA signal and concentration (Fig. 2B). To explore the effect of local concentrations of BODPA within the interior of the nanoparticles on the activated PA properties, we also prepared Si@BODPA with different ratios of BODPA/mPEG-DSPE in weight. It was found that, at the same concentration of BODPA, nanoparticles Si@BODPA180(7) with the ratio of 7/100 exhibited higher PA signals than those of Si@BODPA180(1) and Si@BODPA180(4) obtained from the ratio of 1/100 and 4/100, inferring that Si@BODPA180(7) is a superior system for the establishment of photoacoustic imaging probes. These results reflect that elevated local concentrations of BODPA benefit the thermal deactivation of the excited chromophores, thereby affording stronger PA signals.
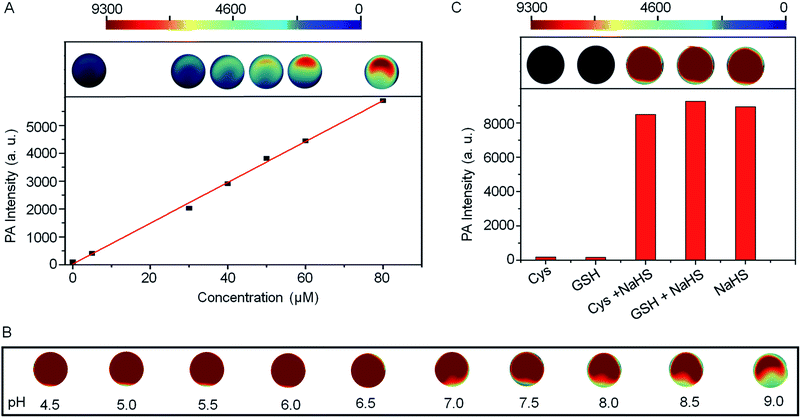
The PA intensities of Si@BODPA180(7) showed a linear and dose-dependent correlation with the concentrations of NaHS in the range of 0–80 μM (Fig. 3A). The detection limit was determined to be as low as 53 nM, suggesting sufficient sensitivity to detect endogenous H2S in living systems. Furthermore, Si@BODPA180(7) was found to give excellent PA responsiveness to H2S within a physiological range from pH 9 to approximately 4.5 (Fig. 3B).
Si@BODPA180(7) also showed a highly selective PA response to H2S over various potentially interfering species (Fig. 3C and S6†). It was noticeable that only H2S induced a bright PA signal upon excitation at 780 nm, while other analytes, including reactive sulfur (RSS), oxygen (ROS), and nitrogen (RNS) species triggered no obvious PA response. Of note, the strong PA signal elicited by H2S was not affected by the presence of 1 mM GSH and 1 mM Cys in competition assays, highlighting the potential applications in a complex biological system.
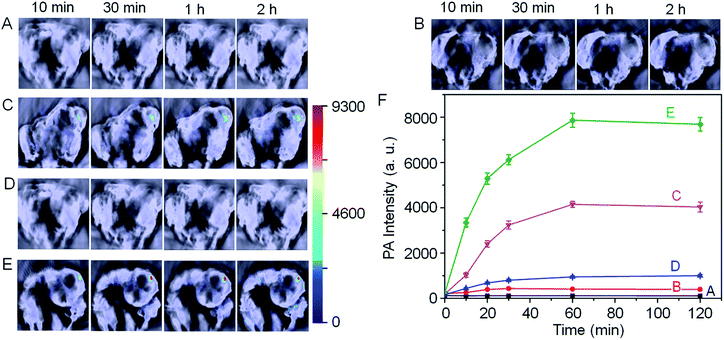
With these promising results in hand, we next employed Si@BODPA180(7) for the in vivo photoacoustic imaging of endogenous H2S generation in a HCT116 tumor-bearing mouse model. It has been suggested that the H2S-producing enzyme cystathionine-β-synthase (CBS) is overexpressed in colon cancer, resulting in increased H2S production.13 In this study, we employed Si@BODPA180(7) as an imaging tool to provide direct evidence for supporting such a functional relationship. In these experiments, saline or Si@BODPA180(7) were injected subcutaneously into tumor regions and normal regions, and images were recorded at various times after probes injection (Fig. 4). To our delight, robust activation of PA signals could be observed specifically in the tumor region in the probe-treated mice within 10 min post-injection (Fig. 4C), indicative of a rapid activation of the probe in vivo. Notably, minimal PA signals were observed in the normal site injected with the probe within 2 h (Fig. 4B). Furthermore, no detectable PA signals in the tumor and normal sites could be observed in the saline-treated mice (Fig. 4A). These results indicated that Si@BODPA180(7) can serve as a promising probe for imaging markedly enhanced H2S production in colon tumors.
In our study, we also found that the PA signals were greatly attenuated by the CBS inhibitor aminooxyacetic acid (AOAA) (Fig. 4D). In sharp contrast, addition of an allosteric CBS activator S-adenosyl-L-methionine (SAM) afforded dramatic elevation of PA signals (Fig. 4E). These preliminary imaging studies suggested that HCT116 colon tumors exhibited CBS upregulation activity which resulted in an increased rate of H2S generation. Undoubtedly, this activatable probe can be explored for trapping transient H2S and for the real-time monitoring of H2S-related biological processes in vivo.
Experimental
Live subject statement
All animal experiments were performed in compliance with the relevant laws and institutional guidelines for the Care and Use of Research Animals established by Fudan University Animal Studies Committee, and the experiments were approved by the committee.General procedure for preparation of Si@BODPAs
BODPAs (0.3 μmol) were rapidly poured into a solution of mPEG-DSPE (19.1 mg) in 3 mL 0.85 N hydrochloride solution under rigorous stirring, resulting in the formation of nanosized micelles. The in situ shell cross-linking under acidic conditions with desired amount of silylation agent was carried out at room temperature while kept stirring for 24 h. Then the aqueous solution was dialyzed for 2 days, and the stock solution was thus obtained, which can be diluted to the desired concentration for further studies. The concentration of BODPA1 or BODPA2 in Si@BODPAs was determined according to their standard UV-vis absorption.The in situ shell cross-linking under acidic conditions with TBNBr of 5.73 mg (TBNBr/mPEG-DSPE = 30/100, w/w), 17.19 mg (TBNBr/mPEG-DSPE = 90/100, w/w), 34.38 mg (TBNBr/mPEG-DSPE = 180/100, w/w) and 51.57 mg (TBNBr/mPEG-DSPE = 270/100, w/w), afforded water dispersible nanocomposites Si@BODPA30, Si@BODPA90, Si@BODPA180 and Si@BODPA270, respectively.
BODPA1 (0.3 μmol), mPEG-DSPE (19.1 mg) and TBNBr (34.38 mg) afforded Si@BODPA180(1); BODPA1 (1.2 μmol), mPEG-DSPE (19.1 mg) and TBNBr (34.38 mg) afforded Si@BODPA180(4); BODPA1 (2.1 μmol), mPEG-DSPE (19.1 mg) and TBNBr (34.38 mg) afforded Si@BODPA180(7).
Conclusions
In summary, we have successfully presented an activatable photoacoustic probe for imaging endogenous H2S in living mice. The probe was fabricated by encapsulating semi-cyanine-BODIPY hybrid dyes into the hydrophobic interior of core–shell silica nanocomposites, thus endowing the probe with good water-solubility and excellent biocompatibility. In the presence of H2S, a high NIR absorption around 780 nm was triggered, ultimately leading to a strong photoacoustic signal output in the NIR region. Furthermore, the designed probe showed a highly selective PA response to H2S with a favourable detection limit of 53 nM. In particular, this probe displayed an extremely fast response, permitting the trapping of transient H2S and real-time monitoring of H2S-related biological processes. More importantly, this probe could serve as a promising tool for the direct photoacoustic imaging of endogenous H2S generation in a HCT116 tumor-bearing mouse model, verifying the activating effect of CBS upregulation on the elevated level of H2S. To the best of our knowledge, this work represents the first example of NIR-activatable photoacoustic probes capable of reporting the endogenous production of H2S in real time, which may facilitate further exploration of the complex roles of H2S in living systems.Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge the financial support from the National Science Foundation of China (grant numbers 21172071, 21190033, 21372083, 21572039), NSFC for Creative Research Groups (21421004), National 973 Program (2013CB733700) and the Programme of Introducing Talents of Discipline to Universities (B16017). We thank Prof. Ping Shi and Yajing Liu for assistance with in vivo imaging.Notes and references
- (a) H. Kimura, Antioxid. Redox Signaling, 2010, 12, 1111 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) N. Skovgaard, A. Gouliaev, M. Aalling and U. Simonsen, Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol., 2011, 12, 1385 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) R. Wang, Physiol. Rev., 2012, 92, 791 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) G. Tang, G. Yang, B. Jiang, Y. Ju, L. Wu and R. Wang, Antioxid. Redox Signaling, 2013, 19, 1634 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) K. Kondo, S. Bhushan, A. L. King, S. D. Prabhu, T. Hamid, S. Koenig, T. Murohara, B. L. Predmore, G. Gojon Sr, G. Gojon Jr, R. Wang, N. Karusula, C. K. Nicholson, J. W. Calvert and D. J. Lefer, Circulation, 2013, 127, 1116 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) P. Kamoun, M.-C. Belardinelli, A. Chabli, K. Lallouchi and B. Chadefaux-Vekemans, Am. J. Med. Genet., 2003, 116A, 310 CrossRef PubMed; (b) M. Lee, C. Schwab, S. Yu, E. McGeer and P. L. McGeer, Neurobiol. Aging, 2009, 30, 1523 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) W. Yang, G. Yang, X. Jia, L. Wu and R. Wang, J. Physiol., 2005, 569, 519 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (d) B. D. Paul, J. I. Sbodio, R. Xu, M. S. Vandiver, J. Y. Cha, A. M. Snowman and S. H. Snyder, Nature, 2014, 509, 96 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) V. S. Lin, W. Chen, M. Xian and C. J. Chang, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2015, 44, 4596 RSC; (b) X. Zhou, S. Lee, Z. Xu and J. Yoon, Chem. Rev., 2015, 115, 7944 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) J. Chan, S. C. Dodani and C. J. Chang, Nat. Chem., 2012, 4, 973 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) A. R. Lippert, E. J. New and C. J. Chang, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2011, 133, 10078 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) H. Peng, Y. Cheng, C. Dai, A. L. King, B. L. Predmore, D. J. Lefer and B. Wang, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2011, 50, 9672 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) W. Xuan, C. Sheng, Y. Cao, W. He and W. Wang, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2012, 51, 2282 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (d) S. K. Bae, C. H. Heo, D. J. Choi, D. Sen, E.-H. Joe, B. R. Cho and H. M. Kim, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2013, 135, 9915 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (e) V. S. Lin, A. R. Lippert and C. J. Chang, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2013, 110, 7131 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (f) M. D. Hammers, M. J. Taormina, M. M. Cerda, L. A. Montoya, D. T. Seidenkranz, R. Parthasarathy and M. D. Pluth, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2015, 137, 10216 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (g) D.-W. Li, L.-L. Qu, K. Hu, Y.-T. Long and H. Tian, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2015, 54, 12758 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (h) H. A. Henthorn and M. D. Pluth, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2015, 137, 15330 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (i) W. Chen, A. Pacheco, Y. Takano, J. J. Day, K. Hanaoka and M. Xian, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2016, 55, 9993 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) C. Liu, J. Pan, S. Li, Y. Zhao, L. Y. Wu, C. E. Berkman, A. R. Whorton and M. Xian, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2011, 50, 10327 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) Y. Qian, J. Karpus, O. Kabil, S. Y. Zhang, H. L. Zhu, R. Banerjee, J. Zhao and C. He, Nat. Commun., 2011, 2, 495 CrossRef PubMed; (c) Y. Qian, L. Zhang, S. T. Ding, X. Deng, C. He, X. E. Zheng, H.-L. Zhu and J. Zhao, Chem. Sci., 2012, 3, 2920 RSC; (d) F. Yu, P. Li, P. Song, B. Wang, J. Zhao and K. Han, Chem. Commun., 2012, 48, 2852 RSC; (e) X. Wang, J. Sun, W. Zhang, X. Ma, J. Lv and B. Tang, Chem. Sci., 2013, 4, 2551 RSC; (f) Y. Chen, C. Zhu, Z. Yang, J. Chen, Y. He, Y. Jiao, W. He, L. Qiu, J. Cen and Z. Guo, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2013, 52, 1688 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (g) L. Zhang, H. Zhu, M. Li and X. Gu, Chem. Commun., 2015, 51, 13135 RSC; (h) C. Liu, W. Chen, W. Shi, B. Peng, Y. Zhao, H. Ma and M. Xian, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2014, 136, 7257 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (i) W. Chen, E. W. Rosser, T. Matsunaga, A. Pacheco, T. Akaike and M. Xian, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2015, 54, 13961 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (j) S. Wang, S. Xu, G. Hu, X. Bai, T. D. James and L. Wang, Anal. Chem., 2016, 88, 1434 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (k) C. Zhao, X. Zhang, K. Li, S. Zhu, Z. Guo, L. Zhang, F. Wang, Q. Fei, S. Luo, P. Shi, H. Tian and W.-H. Zhu, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2015, 137, 8490 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) K. Sasakura, K. Hanaoka, N. Shibuya, Y. Mikami, Y. Kimura, T. Komatsu, T. Ueno, T. Terai, H. Kimura and T. Nagano, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2011, 133, 18003 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) X. Gu, C. Liu, Y.-C. Zhu and Y.-Z. Zhu, Tetrahedron Lett., 2011, 52, 5000 CrossRef CAS; (c) S. Sarkar, Y. S. Ha, N. Soni, G. Il An, W. Lee, M. H. Kim, P. T. Huynh, H. Ahn, N. Bhatt, Y. J. Lee, J. Y. Kim, K. M. Park, I. Ishii, S.-G. Kang and J. Yoo, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2016, 55, 9365 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. V. Wang and S. Hu, Science, 2012, 335, 1458 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) K. Pu, A. J. Shuhendler, J. V. Jokerst, J. Mei, S. S. Gambhir, Z. Bao and J. Rao, Nat. Nanotechnol., 2014, 9, 233 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) J. Levi, S. R. Kothapalli, T.-J. Ma, K. Hartman, B. T. Khuri-Yakub and S. S. Gambhir, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2010, 132, 11264 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) A. Dragulescu-Andrasi, S.-R. Kothapalli, G. A. Tikhomirov, J. Rao and S. S. Gambhir, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2013, 135, 11015 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (d) H. Li, P. Zhang, L. P. Smaga, R. A. Hoffman and J. Chan, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2015, 137, 15628 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (e) Q. Chen, X. Liu, J. Chen, J. Zeng, Z. Cheng and Z. Liu, Adv. Mater., 2015, 27, 6820 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (f) Q. Miao, Y. Lyu, D. Ding and K. Pu, Adv. Mater., 2016, 28, 3662 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) J. F. Lovell, C. S. Jin, E. Huynh, H. Jin, C. Kim, J. L. Rubinstein, W. C. W. Chan, W. Cao, L. V. Wang and G. Zheng, Nat. Mater., 2011, 10, 324 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) K. Pu, J. Mei, J. V. Jokerst, G. Hong, A. L. Antaris, N. Chattopadhyay, A. J. Shuhendler, T. Kurosawa, Y. Zhou, S. S. Gambhir, Z. Bao and J. Rao, Adv. Mater., 2015, 27, 5184 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) C. Zhu, Y. Yang, M. Luo, C. Yang, J. Wu, L. Chen, G. Liu, T. Wen, J. Zhu and H. Xia, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2015, 54, 6181 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (d) L. Wang, P.-P. Yang, X.-X. Zhao and H. Wang, Nanoscale, 2016, 8, 2488 RSC.
- (a) X. Wu, S. Chang, X. Sun, Z. Guo, Y. Li, J. Tang, Y. Shen, J. Shi, H. Tian and W. Zhu, Chem. Sci., 2013, 4, 1221 RSC; (b) X.-D. Wang, J. A. Stolwijk, T. Lang, M. Sperber, R. J. Meier, J. Wegener and O. S. Wolfbeis, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2012, 134, 17011 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) Y. Li, A. Shao, Y. Wang, J. Mei, D. Niu, J. Gu, P. Shi, W. Zhu, H. Tian and J. Shi, Adv. Mater., 2016, 28, 3187 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (d) B. M. Weckhuysen and J. Yu, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2015, 44, 7022 RSC.
- S. Bai, H. Yang, P. Wang, J. Gao, B. Li, Q. Yang and C. Li, Chem. Commun., 2010, 46, 8145 RSC.
- (a) C. Szabo, C. Coletta, C. Chao, K. Módis, B. Szczesny, A. Papapetropoulos and M. R. Hellmich, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2013, 110, 12474 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) K. Módis, C. Coletta, A. Asimakopoulou, B. Szczesny, C. Chao, A. Papapetropoulos, M. R. Hellmich and C. Szabo, Nitric Oxide, 2014, 41, 146 CrossRef PubMed.
Footnote |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available: Procedures for the synthesis of BODPA, living mice imaging, characterization data, and supplementary figures. See DOI: 10.1039/c6sc04703c |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 |