Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleBaCu2MIVQ4 (MIV = Si, Ge, and Sn; Q = S, Se): synthesis, crystal structures, optical performances and theoretical calculations†
Leyan Nianab,
Junben Huangb,
Kui Wu*b,
Zhi Su*a,
Zhihua Yang b and
Shilie Pan
b and
Shilie Pan *ab
*ab
aCollege of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Xinjiang Normal University, Urumqi, Xinjiang 830054, China
bKey Laboratory of Functional Materials and Devices for Special Environments of CAS, Xinjiang Key Laboratory of Electronic Information Materials and Devices, Xinjiang Technical Institute of Physics & Chemistry of CAS, 40-1 South Beijing Road, Urumqi 830011, China. E-mail: slpan@ms.xjb.ac.cn
First published on 6th June 2017
Abstract
Five non-centrosymmetric (NCS) quaternary metal chalcogenides, BaCu2SiSe4, BaCu2GeS4, BaCu2GeSe4, BaCu2SnS4, and BaCu2SnSe4, were successfully synthesized by solid-state reaction in vacuum-sealed silica tubes. They crystallized in the three different space groups: Ama2 for BaCu2SnSe4, P3121 for BaCu2GeS4 and BaCu2GeSe4, and P3221 for BaCu2SiSe4 and BaCu2SnS4. Note that BaCu2GeS4 and BaCu2GeSe4 show the mirror symmetrical structures to those of BaCu2SiSe4 and BaCu2SnS4. In comparison with their structures, it can be found that the [CuSe4] units are connected together to form a two-dimensional (2D) layer structure in BaCu2SnSe4, which is different from the 3D framework structure formed by the interlinked [CuQ4] (Q = S and Se) units in other four title compounds. In addition, BaCu2SnSe4 exhibits only one type of tunnel structure with the isolated [BaSe8] units existing in each tunnel, which is also different from the other title compounds (two types of tunnels with the isolated [BaSe8] units and [BaSe6]n chains located). The interesting structural changes also indicate that slight change of cation size would result in different structure features, and future structure prediction should devote considerable attention to the different chalcogen atoms. Moreover, important optical properties (optical bandgap, infrared (IR) absorption edge, second harmonic generation (SHG) response) of the title compounds were systematically investigated. Among them, IR and Raman spectra indicate that all of them exhibit the wide IR absorption edges (∼22 μm). Powder SHG measurement shows that BaCu2SnS4 possesses good SHG response about 1.6 times that of benchmark AgGaS2 (AGS) at the particle size 55–88 μm. All results indicate that BaCu2SnS4 can be expected as a potential IR nonlinear optical (NLO) candidate. Theoretical calculation was also used to analyze the structure–property relationship and their electronic structures and origin of NLO effect were studied in detail.
Introduction
Frequency-conversion technology on nonlinear optical (NLO) materials was invented to extend the laser wavelength ranges and has been further developed for decades.1–4 Recently, a series of excellent nonlinear optical (NLO) materials have been discovered and have basically satisfied the demand for the ultraviolet (UV < 400 nm) region.5–14 However, commercially available IR NLO materials are limited in the IR region because of their inherent performance defects.15–19 Exploration of new IR NLO materials with outstanding performances is still a challenge to be resolved. During the last few decades, metal chalcogenides have become the preferred investigation system owing to their structural diversities and fascinating physicochemical properties.20–33 Most of them contain the tetrahedral units, which have been verified as the “active units” to produce the main contribution for the NLO effect. Note that group 14 elements, such as Si, Ge, and Sn, are generally linked with chalcogens to form the distorted [MIVQ4] tetrahedra.34–41 Up to now, a number of new metal chalcogenides with the [MIVQ4] tetrahedra and attractive NLO performances have been discovered, such as β-K2Hg3Ge2S8,36 Li2CdGeS4,42 Na2BaSnS4,43 Na2Hg3Ge2S8.44 The investigation results also indicate that the coordination environments of the cations play a critical role in determining the structures of group 14 elements-containing compounds. Alkaline-earth metals (such as Ba), as high electropositive elements, have the variable coordination environments with large cation size, so it can affect the structural features and optical properties. In addition, combination of distorted MIVQ4 tetrahedral units and heavy metals into crystal structures may stand a chance to increase the odds of forming acentric structures. Guided by the above-mentioned ideas, we focused our research on the quaternary Ba/Cu/MIV/Q (MIV = Si, Ge, and Sn; Q = S, Se) systems and successfully synthesized five metal chalcogenides, including BaCu2SiSe4, BaCu2GeS4, BaCu2GeSe4, BaCu2SnS4 and BaCu2SnSe4. Among them, although the crystal structures of latter four compounds have been previously reported,45–48 their interesting structural changes and application potential as the IR NLO candidates have not been systematically investigated. Herein, we have studied the structural features and transformation of title compounds and their optical performances (such as optical bandgap, infrared (IR) absorption edge, second harmonic generation (SHG) response) have been reported for the first time. Moreover, theoretical calculation was also used to analyze the structure–property relationship and the origin of NLO effect for title compounds.Experimental
Reagents and synthesis
All the raw reagents with high purity (4 N) were commercially purchased by Shanghai Aladdin Biochemistry Technology Co., Ltd and used without any further purification. Since the Ba metal is easily oxidized in the air, an Ar-filled glove box was used to avoid the effects of oxygen and moisture in the preparation processes. Conventional high temperature solid-state method was used to synthesize the title compounds.BaCu2GeS4 and BaCu2SnS4
The crystals of BaCu2GeS4 and BaCu2SnS4 were synthesized by ratio of the reactants BaS, Cu, Ge/Sn and S in the ratio 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 2
2![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1
1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 3.5. First, the reaction mixture was loaded into the silica tubes (length 20 cm, diameter 10 mm) and sealed with a mixture of methane and oxygen flame under a high vacuum of 10−3 Pa. Second, the furnace was programmed by the following steps: heated from room temperature to 600 °C in 30 h and kept at this temperature for 40 h; then, heated to 1050 °C in 20 h and left at this temperature for 100 h; finally, cooled to 400 °C at a rate of 5 °C h−1 and then the furnace was shut down to room temperature. Third, the obtained products of title compounds were washed with N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF) to remove the unreacted sulfur and other byproducts. Finally, yellow crystals of BaCu2GeS4 and red crystals of BaCu2SnS4 were obtained after drying in air. They are stable in air for several months.
3.5. First, the reaction mixture was loaded into the silica tubes (length 20 cm, diameter 10 mm) and sealed with a mixture of methane and oxygen flame under a high vacuum of 10−3 Pa. Second, the furnace was programmed by the following steps: heated from room temperature to 600 °C in 30 h and kept at this temperature for 40 h; then, heated to 1050 °C in 20 h and left at this temperature for 100 h; finally, cooled to 400 °C at a rate of 5 °C h−1 and then the furnace was shut down to room temperature. Third, the obtained products of title compounds were washed with N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF) to remove the unreacted sulfur and other byproducts. Finally, yellow crystals of BaCu2GeS4 and red crystals of BaCu2SnS4 were obtained after drying in air. They are stable in air for several months.
BaCu2SiSe4, BaCu2GeSe4, and BaCu2SnSe4
A stoichiometric mixture of Ba, Cu, M (M = Si, Ge and Sn), and Se in the molar ratio of 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 2
2![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1
1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 4 was loaded into the silica tubes. The increasing temperature-rise program of the three selenides were similar to that of the above two sulfides. The reaction temperature was set to be 1000 °C, which is different from that for sulfides. After the reaction, the products were also washed by DMF, and many red crystals of BaCu2SiSe4, BaCu2GeSe4, and BaCu2SnSe4 were gained that can be stable in air for several months.
4 was loaded into the silica tubes. The increasing temperature-rise program of the three selenides were similar to that of the above two sulfides. The reaction temperature was set to be 1000 °C, which is different from that for sulfides. After the reaction, the products were also washed by DMF, and many red crystals of BaCu2SiSe4, BaCu2GeSe4, and BaCu2SnSe4 were gained that can be stable in air for several months.
Structure determination
High-quality single crystals were selected by an optical microscope and mounted on glass fibers with epoxy, and then the crystal data was collected on a Bruker SMART APEX II 4K CCD diffractometer with Mo Kα radiation (λ = 0.71073 Å) at 296 K. Lorentz and polarization factors were used to collect the date, and the absorption corrections were completed with multi-scan method.49 All structure determinations were based on direct method and refined through the full-matrix least-squares on F2 by SHELXTL crystallographic program package.50 The final structures were checked with PLATON program,49 and no other higher symmetries elements were found. Crystallographic data and refinements of the title compounds were summarized in Table 1. The isotropic displacement parameters and atomic coordinates, as well as the results of the bond valence sum (BVS) calculations are given in Table S1 in the ESI.† The bond angles and selected bond distances are shown in Table S2 in the ESI.†| a R1 = Fo − Fc/Fo and wR2 = [w(Fo2 − Fc2)2/wFo4]1/2 for Fo2 > 2σ(Fo2). | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Empirical formula | BaCu2GeS4 | BaCu2GeSe4 | BaCu2SiSe4 | BaCu2SnS4 | BaCu2SnSe4 |
| fw | 465.25 | 652.85 | 608.35 | 511.35 | 698.95 |
| Crystal system | Trigonal | Trigonal | Trigonal | Trigonal | Orthorhombic |
| Space group | P3121 | P3121 | P3221 | P3221 | Ama2 |
| a (Å) | 6.2092(8) | 6.5014(6) | 6.4188(19) | 6.353(3) | 11.101(10) |
| b (Å) | 6.2092(8) | 6.5014(6) | 6.4188(19) | 6.353(3) | 11.189(10) |
| c (Å) | 15.520(4) | 16.266(3) | 16.083(10) | 15.788(14) | 6.728(6) |
| Z, V (Å3) | 3, 518.20(19) | 3, 595.42(16) | 3, 573.9(5) | 3, 551.8(6) | 4, 835.7(13) |
| Dc (g cm−3) | 4.473 | 5.462 | 5.281 | 4.616 | 5.555 |
| μ (mm−1) | 17.089 | 32.160 | 29.673 | 15.358 | 29.945 |
| GOF on F2 | 1.031 | 1.054 | 0.920 | 0.876 | 1.018 |
| R1, wR2 (I > 2σ(I))a | 0.0185, 0.0366 | 0.0281, 0.0659 | 0.0264, 0.0437 | 0.0258, 0.0569 | 0.0251, 0.0527 |
| R1, wR2 (all data)a | 0.0214, 0.0373 | 0.0287, 0.0663 | 0.0310, 0.0449 | 0.0317, 0.0594 | 0.0265, 0.0532 |
| Absolute structure parameter | 0.05(3) | 0.09(4) | 0.07(4) | −0.04(5) | 0.06(3) |
| Largest diff. peak and hole (e Å−3) | 1.306, −1.117 | 1.135, −1.207 | 0.846, −0.809 | 0.831, −0.945 | 1.041, −1.691 |
Powder X-ray diffraction
All the compounds were ground to micro-crystals for the powder XRD measurement. The PXRD data were collected on a Bruker D2 X-ray diffractometer equipped with a diffracted beam monochromator set for Cu Kα radiation (λ = 1.5418 Å) at room temperature. The 2θ range was 10–70° with a step size of 0.02° and a fixed counting time of 1 s per step. Seen from Fig. S1 in the ESI,† it can be found that no obvious byproducts was observed and the experimental powder XRD patterns of title compounds are in agreement with the calculated ones derived from the single-crystal data.UV-vis-near IR diffuse-reflectance and IR spectroscopy
The diffuse-reflectance spectra of title compounds were collected by a Shimadzu SolidSpec-3700DUV spectrophotometer in the wavelength range of 190–2600 nm at room temperature. Then the reflectance spectra were converted to absorption spectra with the Kubelka–Munk function.51 In addition, IR spectra were also measured with a Shimadzu IR Affinity-1 Fourier transform infrared spectrometer in wavenumber range from 450 to 4000 cm−1 using picked single-crystals mixed with KBr pellets.Raman spectroscopy
The Raman spectra of the crushed crystals of title compounds were collected on a LABRAM HR Evolution spectrometer equipped with a CCD detector using 532 nm radiation from a diode laser. For each sample, crystals were simply placed on a small glass slide and a 50× objective lens was used to choose the area of the crystal specimens to be measured. The grating was set to be 600 gr per mm. The maximum power of 60 mW and beam diameter of 35 μm were used. The spectrum was collected using an integration time of 5 s.Second-harmonic generation measurement
By the Kurtz and Perry method,52 powder SHG responses of title compounds were investigated by a Q-switch Ho:Tm:Cr:YAG laser (2.09 μm, 3 Hz, 50 ns). Polycrystalline samples of the title compounds were ground and sieved into distinct size ranges (0–38, 38–55, 55–88, 88–105, 105–155, 155–200, and 200–250 μm). Then, the samples were pressed between two glass slides in 1 mm thick and secured by a 1 mm thick silicone insole with an 8 mm diameter hole. In the end, they were placed into a light-tight box and irradiated by a pulsed infrared beam and measured with the detector. Oscilloscope was used to record the intensity of the frequency-doubled output emitted from the samples.Theoretical calculation
Through density functional theory (DFT) calculations tests, we investigated the electronic structures, total and partial density of states (T/PDOS) and optical properties of BaCu2MIVQ4 (MIV = Si, Ge, and Sn; Q = S, Se). The ab initio DFT method calculations were performed by the plane wave pseudopotential implemented in the CASTEP package.53 The local density approximations (LDA) with CA–PZ functional,54,55 a 900 eV cutoff energy for the plane-wave basis set and norm-conserving pseudopotentials (NCP)56 was employed in all computations. The Brillouin zone was integrated using Monkhorst–Pack-generated sets of k-points and we determined 3 × 3 × 2 k-point meshes for the former four target compounds and a 4 × 4 × 2 for BaCu2SnSe4. The configurations for diverse electron orbital generating pseudopotentials were Ba 5p6 6s2, Cu 3p6 3d10 4s1, Si 3s2 3p2, Ge 4s2 4p2, Sn 5s2 5p2, S 3s2 3p4 and Se 4s2 4p4 and the other calculating parameters used in the calculations and convergent criteria were set by the default values of the CASTEP code. To explore the contributions from different structural units to the NLO coefficients, the SHG density method was performed by using the effective SHG: Virtual-Electron (VE) and Virtual-Hole (VH).2 At a zero frequency, the formula of second-order NLO coefficients can be derived as57| χαβγ = χαβγ(VE) + χαβγ(VH) | (1) |
 | (2) |
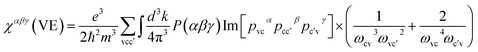 | (3) |
Results and discussion
Crystal structure
Although all title compounds have the similar formula BaCu2MIVQ4, they crystallize in the different polar space groups. Among them, BaCu2SnSe4 crystallizes in the Ama2 space group of orthorhombic system, whereas other four compounds crystallize in the trigonal system. In other words, while through the simple element substitution (Sn to Ge, or Se to S) in BaCu2SnSe4, they show obvious structural transformation from orthorhombic to trigonal system. Note that BaCu2GeS4 and BaCu2GeSe4 crystallize in the P3121 space group, while BaCu2SiSe4 and BaCu2SnS4 crystallize in the mirror symmetry P3221 space group. The current crystal date is consistent with the previously reported phases.45–48BaCu2SiSe4
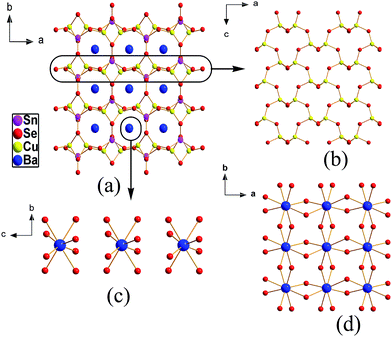
It crystallizes in a polar trigonal space group P3221 with Z = 3 and its asymmetric unit consists of one Ba, one Cu, one Si, two Se atoms. It exhibits a 3D framework structure built up of isolated [SiSe4] tetrahedra and edge or corner-sharing linked [CuSe4] ligands with charge-balanced Ba cations located at the framework tunnels (Fig. 1a). The isolated [SiSe4] ligands are approximately regular tetrahedra with d(Si–Se) = 2.263(2) to 2.269(2) Å, which is comparable to those of other known seleno-silicates.58,59 The distorted [CuSe4] units with d(Cu–Se) = 2.428(5) to 2.539(1) Å link together by sharing corners and edges to form the 3D tunnel structure. Note that two types (type I and type II) of tunnels that formed with the interconnection of the [CuSe4] units are interestingly found, such as six-member ring (6-MR) and 4-MR (Fig. 2a). In addition, the [BaSe8] polyhedra only locate within the 6-MR tunnels and show two types of connection modes: (i) exist in the isolation (Fig. 2b); (ii) link with each other by sharing Se corners to form the isolated [BaSe6]n chains (Fig. 2c). Each [BaSe8] unit is linked with eight other [BaSe8] units by sharing corners and edges in the b–c plane. Then, the [BaSe8] ligands in the different tunnels still interlink by sharing corners and edges to make up framework structure.BaCu2GeSe4
It crystallizes in the trigonal P3121 space group that shows the mirror symmetry compared with the structure of BaCu2SiSe4. Seen from its structure, the [CuSe4] units with d(Cu–Se) = 2.427(1) to 2.541(2) Å link with isolated [GeSe4] units with d(Ge–Se) = 2.352(16) to 2.361(15) Å to form two types of 3D tunnel structure (6-MR and 4-MR), which is similar with the structural features in BaCu2SiSe4. In addition, the existence patterns of [BaSe8] polyhedra in BaCu2GeSe4 are in consistence with that in BaCu2SiSe4. Note that the arrangement direction of [GeSe4] units in BaCu2GeSe4 is opposite with that in the BaCu2SiSe4, thus, it show mirror symmetry structure with that of BaCu2SiSe4.BaCu2SnSe4
It crystallizes in a polar orthorhombic space group Ama2 with Z = 4 and one crystallographically unique Ba, one Sn, one Cu, three Se atoms locate in its asymmetric unit. Seen from its structure (Fig. 3a), the irregular [CuSe4] with d(Cu–Se) = 2.431(3) to 2.546(2) Å are firstly linked with each other by sharing corners and edges to form the layer structure in the ac plane (Fig. 3b). Then, isolated [SnSe4] tetrahedra with d(Sn–Se) = 2.509(3)–2.545(2) Å as further bridge with these layers form the 3D tunnel structure along the c-axis, which may generate a wide range of applications for this compound, such as conductive material, heat-transfer material, ionic absorption, and photocatalysis.60–62 The Ba atoms exist inside the tunnels and are linked with eight Se atoms showing d(Ba–Se) range from 3.311(2) to 3.409(2) Å to form distorted [BaSe8] polyhedra, which is close to those of other related compounds, including BaGa4Se7 (3.429–3.861 Å)21 and Ba7Sn3Se13 (3.183–3.761 Å).63 Each [BaSe8] unit is linked with six other [BaSe8] units by sharing corners and edges in the b–c plane. Note that the [BaSe8] polyhedra exist isolated in the same tunnel (Fig. 3c), but the [BaSe8] polyhedra in the different tunnels connect together by sharing corners and edges to make up framework structure (Fig. 3d).Structural comparison
In view of their similar structures among the four compounds (BaCu2SiSe4, BaCu2GeS4, BaCu2GeSe4, BaCu2SnS4), we have chosen the BaCu2SiSe4 and BaCu2SnSe4 as the representatives to discuss their structural comparison and the results can be extended to all of title compounds. In comparison with the structures of BaCu2SiSe4 and BaCu2SnSe4, they have some similarities: all of them have the [BaSe8] octahedra and isolated [MIVSe4] (MIV = Si and Sn) tetrahedra in their structures. However, they still have several obviously different features in their structures: (i) the asymmetric unit and Z (number of molecules in a unit cell) of BaCu2SiSe4 have five crystallographically distinct sites and Z = 3, which are different from those of BaCu2SnSe4 (6 and Z = 4); (ii) the [BaSe8] units are more highly distorted in BaCu2SnSe4 than those in BaCu2SiSe4, owing to the largest difference (Δd) between Ba–Se that Δd (Ba–Se) = 0.098 Å in BaCu2SnSe4 is larger than that (0.066 Å) in BaCu2SiSe4; (iii) the [CuSe4] units link together to make up the tunnel structure in BaCu2SiSe4, whereas the [CuSe4] units connect with each other to form layer structure in BaCu2SnSe4; (iv) note that the [BaSe8] polyhedra exist in isolation in each tunnel of BaCu2SnSe4, but in BaCu2SiSe4, the [BaSe8] polyhedra show two types of connection modes: isolation and chain; (v) each [BaSe8] unit is linked with six other [BaSe8] units in BaCu2SnSe4, which is different from that each [BaSe8] polyhedron connects with eight other [BaSe8] units in BaCu2SiSe4. Similarly, the main structural differences as mentioned above are also found between BaCu2SnSe4 and other compounds. Interestingly, previous researches show that the structures of metal chalcogenides can be changed with the different M or Q atoms in crystal structures.44 Therefore, this observation indicates that the slight change of cation size would result in different structure features, and future structure prediction should be devoted considerable attentions to the different chalcogen atoms (Fig. 4).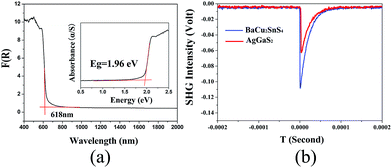 | ||
| Fig. 4 (a) Experimental band gap of BaCu2SnS4; (b) SHG intensities of BaCu2SnS4 versus AgGaS2 at the particle size of 55–88 μm. | ||
Optical properties
The diffuse-reflectance UV-vis-NIR spectra of title compounds (Fig. S3 in the ESI†) were measured, and the spectral results show that the experimental band gaps are 2.62 eV for BaCu2SiSe4, 2.47 eV for BaCu2GeS4, 1.88 eV for BaCu2GeSe4, 1.96 eV for BaCu2SnS4 and 1.72 eV for BaCu2SnSe4, respectively. Among them, BaCu2SiSe4 and BaCu2GeS4 have larger band gaps, which are comparable to those of commercial AGS (2.64 eV). The other three compounds have relatively narrow band gaps that are still comparable to those of other typical IR NLO crystals, such as ZnGeP2 (1.65 eV) and AgGaSe2 (1.75 eV). IR spectra of title compounds were also measured on the micro-crystal powders, and the results (Fig. S2 in the ESI†) reveal that all of them have wide transmission regions from 4000–450 cm−1, namely, 2.5–22 μm, that cover the two important atmospheric transparent windows of 3–5 and 8–12 μm, which are comparable to the IR absorption edges of other IR NLO powdered compounds such as BaGa4Se7 (∼18 μm),21 LiCdGeS4 (∼22 μm),35 AGS (∼23 μm),64 SnGa4S7 (∼25 μm),65 Li4HgGe2S7 (∼22 μm)66 and CsCd4Ga5S12 (∼25 μm).23 Raman spectra (Fig. 5) also further verify that title compounds have the wide IR transmission region and no absorption peaks in the region of 450–1000 cm−1 (10–22 μm). As for the selenides, the obvious absorption peaks include BaCu2SiSe4 (221.5 cm−1), BaCu2GeSe4 (275 cm−1) and BaCu2SnSe4 (195 cm−1), which can be assigned to the characteristic absorptions of the Si–Se, Ge–Se, and Sn–Se modes, respectively. As for the sulfides, the absorption peaks for BaCu2GeS4 and BaCu2SnS4 are 367.5 and 337.5 cm−1 that correspond to the Ge–S and Sn–S bonding interactions, respectively. The intensive peak positions for the family of BaCu2MIVQ4 are affected by the tetravalent (IV) metals, and the peak positions slightly shifted towards the short wavelength with the change of the MIV cations (from Si to Sn).44 By comparing the absorption peaks of sulphides (BaCu2GeS4 and BaCu2SnS4) and selenides (BaCu2SiSe4, BaCu2GeSe4 and BaCu2SnSe4), the peak positions shifted towards the short wavelength when the anion Q vary from S to Se. SHG responses for title compounds were also systemically measured with a 2.09 μm Q-switch laser in different particle sizes at room temperature and commercial AGS crystal was used as a reference. Among them, BaCu2SnS4 has a good SHG response that is about 1.6 times that of benchmark AGS in the particle size range 55–88 μm (Fig. S4 in the ESI†) and the other four compounds show the weak SHG responses about 0.3 times of AGS in the particle size range 55–88 μm. Note that SHG intensities were decreased with the increase of particle sizes for all of title compounds, which indicates that they exhibit the non-phase matching behavior.Theoretical studies
First-principles computations were adopted to better understand the electronic structures of the title compounds. Based on the theoretical electronic structures (Fig. S5 in the ESI†), the highest point of the valence band (VB) and the lowest point of the conduction band (CB) locate at the different points for BaCu2SnSe4, which indicates that it is an indirect band gap compound, whereas the other four compounds are direct band gap semiconductors. Calculated results show that the theoretical band gaps are 1.53 eV for BaCu2GeS4, 1.31 eV for BaCu2GeSe4, 1.63 eV for BaCu2SiSe4, 1.09 eV for BaCu2SnS4 and 1.07 eV for BaCu2SnSe4 (Fig. 6a for BaCu2SnS4, Fig. S5† for other compounds, respectively), respectively. The calculated band gaps are lower than the experimental values, which can be attributed to the discontinuity of exchange–correlation energy of the GGA functional.67,68 Moreover, the PDOS of title compounds were also obtained (Fig. S6 in the ESI†). From the PDOS of BaCu2SnS4 (Fig. 6b), the region in the valence bands from −8 eV to Fermi level is mainly occupied by Cu-3d and S-3p states. Meanwhile, the bottom of conduction bands is derived from the S-3p and Sn-5s orbitals. As for the other four compounds, their T/PDOS were also achieved and familiar with that of BaCu2SnS4. Moreover, SHG coefficients (dij) for title compounds were also calculated. Since BaCu2SiSe4, BaCu2GeS4, BaCu2GeSe4 and BaCu2SnS4 belong to 32 point group that allows for five nonzero coefficients in the SHG tensor and only two are independent: d11 = −d12 = −d26 and d14 = −d25. However, the allowed coefficients from five to three were reduced by Kleinman symmetry,69 and results the condition that d14 = −d25 = 0, so the four compounds only have one independent NLO tensor (d11). The theoretical SHG coefficients (dij) are d11 = 0.28 pm V−1 for BaCu2GeS4, d11 = 5.62 pm V−1 for BaCu2GeSe4, d11 = 4.18 pm V−1 for BaCu2SiSe4, and d11 = 12.09 pm V−1 for BaCu2SnS4, respectively. In addition, BaCu2SnSe4 belongs to mm2 group that has three unequal NLO coefficients: d31 = 1.76, d32 = −12.65 and d33 = −10.13 pm V−1. In comparison with their calculated SHG coefficients (dij) values, it can be found that BaCu2GeS4, BaCu2GeSe4, and BaCu2SiSe4 are smaller than that of BaCu2SnS4, which are also consistent with their experimental results. Unfortunately, the SHG experimental observation (0.3× AgGaS2) is smaller than that (d32 = −12.65 pm V−1) of BaCu2SnSe4, which may be by its narrow optical bandgap (1.72 eV) and long shortwave absorption edge (up to 1 μm). Thus, the SHG light (1045 nm) was likely to be weaken under the fundamental light (2090 nm), and then lead to the low SHG intensity. We believe that the precise SHG effect may be obtained by the long wavelength laser (e.g. carbon dioxide laser) for BaCu2SnSe4. Note that BaCu2SnS4 exhibits a comparable SHG coefficient (12.09 pm V−1) to that of commercial AGS (11 pm V−1). Meanwhile, SHG density method was also used to investigate the origin of SHG responses for title compounds. The contributions of VE and VH to the total SHG coefficients were obtained using the band-resolved method, and the results were listed in Table S3 in the ESI.† As for BaCu2SnS4, the VH and VE contributions were about 90.01% (d11) and 9.99% (d11), respectively. Therefore, we chose the occupied and unoccupied of VH to investigate the mainly origin of the SHG response for BaCu2SnS4. Fig. 6c and d plot the occupied and unoccupied states of VH and clearly showing that the SHG effect of BaCu2SnS4 was derived from the [CuS4] and [SnS4] tetrahedra. In addition, the contributions of VE and VH for other four compounds were similar to that of BaCu2SnS4 (Fig. S7 in the ESI†), which indicate that their origins of SHG effects are mainly derived from the cooperative contribution of the [CuQ4] and [MQ4] units. | ||
| Fig. 6 (a) Calculated band gap of BaCu2SnS4; (b) PDOS of BaCu2SnS4; (c) SHG-density of BaCu2SnS4 at VH occupied; (d) SHG-density of BaCu2SnS4 at VH unoccupied. | ||
Conclusions
In summary, a family of NCS quaternary BaCu2MIVQ4 (MIV = Si, Ge, and Sn; Q = S, Se) were successfully synthesized and characterized. Interestingly, title compounds crystallize in different space groups. Among them, BaCu2GeS4 and BaCu2GeSe4 crystallize in the trigonal space group P3121 that are mirror symmetric with BaCu2SiSe4 and BaCu2SnS4 (space group P3221), while BaCu2SnSe4 crystallizes in the orthorhombic space group Ama2. In BaCu2SnSe4, irregular [CuSe4] units are firstly linked with each other by sharing corners and edges to form a 2D layer structure in the ac plane, and then the isolated [SnSe4] tetrahedra as a bridge connect with these layers to form a 3D tunnel structure along the c-axis. Different from the structure that all the [BaSe8] units of BaCu2SnSe4 existed in the same tunnel structure in isolation in BaCu2SnSe4, other four title compounds exhibit two types of tunnel structure (I, 4-MR and II, 6-MR) with the isolated [BaSe8] units and [BaSe6]n chains existed in the tunnel II. Raman and IR spectra indicate that their IR absorption edges can reach to 22 μm, which covers the two critical atmospheric transparent windows (3–5 and 8–14 μm). Experimental band gaps of BaCu2SiSe4 and BaCu2GeS4 are 2.47 and 2.62 eV, respectively, and larger than those of other typical materials, which imply that they may exhibit the large LDTs and are applied in the high-power laser system. In addition, the results of SHG measurements indicate that BaCu2SnS4 has a good SHG response about 1.6 times of that AGS in the particle size range 55–88 μm. The overall research results indicate that BaCu2SnS4 has a promising application as a potential NLO material in the IR region.Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Western Light Foundation of CAS (Grant No. XBBS201318), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51402352, 51425206, 91622107), Fund of Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Materials Chemistry and Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences (2008DP173016).Notes and references
- R. J. Seymour and F. Zernike, Appl. Phys. Lett., 1976, 29, 705 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Lin, M. H. Lee, Z. P. Liu, C. T. Chen and C. J. Pickard, Phys. Rev. B: Condens. Matter Mater. Phys., 1999, 60, 13380 CrossRef CAS.
- C. T. Chen, B. C. Wu, A. D. Jiang and G. M. You, Sci. China, Ser. B, 1985, 28, 235 Search PubMed.
- G. D. Boyd, T. J. Bridges, C. K. N. Patel and E. Buehler, Appl. Phys. Lett., 1972, 21, 553 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Q. Sun, P. Shan, H. Chen, X. W. Liu, H. D. Liu, S. L. Chen, Y. A. Cao, Y. F. Kong and J. J. Xu, CrystEngComm, 2014, 16, 10497 RSC.
- T. T. Tran, H. Yu, J. M. Rondinelli, K. R. Poeppelmeier and P. S. Halasyamani, Chem. Mater., 2016, 28, 5238 CrossRef CAS.
- S. G. Zhao, P. F. Gong, L. Bai, X. Xu, S. Q. Zhang, Z. H. Sun, Z. S. Lin, M. C. Hong, C. T. Chen and J. H. Luo, Nat. Commun., 2014, 5, 4019 CAS.
- H. P. Wu, S. L. Pan, K. R. Poeppelmeier, H. Y. Li, D. Z. Jia, Z. H. Chen, X. Y. Fan, Y. Yang, J. M. Rondinelli and H. S. Luo, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2011, 133, 7786 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. P. Wu, H. W. Yu, Z. H. Yang, X. L. Hou, X. Su, S. L. Pan, K. R. Poeppelmeier and J. M. Rondinelli, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2013, 135, 4215 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. Li, Y. Wang, B. H. Lei, S. J. Han, Z. H. Yang, K. R. Poeppelmeier and S. L. Pan, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2016, 138, 9101 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. W. Yu, H. P. Wu, S. L. Pan, Z. H. Yang, X. L. Hou, X. Su, Q. Jing, K. R. Poeppelmeier and J. M. Rondinelli, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2014, 136, 1264 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. G. Zhao, P. F. Gong, S. Y. Luo, S. J. Liu, L. N. Li, M. A. Asghar, T. Khan, M. C. Hong, Z. S. Lin and J. H. Luo, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2015, 137, 2207 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Zhang, X. Su, S. L. Pan, Z. Wang, H. Zhang, Z. H. Yang, B. B. Zhang, L. Y. Dong, Y. Wang, F. F. Zhang and Y. Yang, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2014, 118, 11849 CAS.
- H. P. Wu, S. L. Pan, H. W. Yu, D. Z. Jia, A. M. Chang, H. Y. Li, F. F. Zhang and X. Huang, CrystEngComm, 2012, 14, 799 RSC.
- T. X. Zhu, X. G. Chen and J. G. Qin, Front. Chem. Sci. Eng., 2011, 6, 1 CrossRef.
- P. F. Bordui and M. M. Fejer, Annu. Rev. Mater. Sci., 1993, 23, 321 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Jayaraman, V. Narayanamurti, H. Kasper, M. Chin and R. Maines, Phys. Rev. B: Solid State, 1976, 14, 3516 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Harasaki and K. Kato, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys., Part 1, 1997, 36, 700 CrossRef CAS.
- G. Catella, L. Shiozawa, J. Hietanen, R. Eckardt, R. Route, R. Feigelson, D. Cooper and C. Marquardt, Appl. Opt., 1993, 32, 3948 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. J. Mei, P. F. Gong, Z. S. Lin, K. Feng, J. Y. Yao, F. Q. Huang and Y. C. Wu, CrystEngComm, 2014, 16, 6836 RSC.
- J. Y. Yao, D. J. Mei, L. Bai, Z. S. Lin, W. L. Yin, P. Z. Fu and Y. C. Wu, Inorg. Chem., 2010, 49, 9212 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- G. M. Li, K. Wu, Q. Liu, Z. H. Yang and S. L. Pan, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2016, 138, 7422 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Lin, L. J. Zhou and L. Chen, Chem. Mater., 2012, 24, 3406 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Lin, L. Chen, J. S. Yu, H. Chen and L. M. Wu, Chem. Mater., 2017, 29, 499 CrossRef CAS.
- G. M. Li, Q. Liu, K. Wu, Z. H. Yang and S. L. Pan, Dalton Trans., 2017, 46, 2778 RSC.
- X. S. Lin, G. Zhang and N. Ye, Cryst. Growth Des., 2009, 9, 1186 CAS.
- Z. Z. Luo, C. S. Lin, W. L. Zhang, H. Zhang, Z. Z. He and W. D. Cheng, Chem. Mater., 2013, 26, 1093 CrossRef.
- S. P. Guo, Y. Chi and G. C. Guo, Coord. Chem. Rev., 2016, 335, 44 CrossRef.
- F. Liang, L. Kang, Z. S. Lin and Y. C. Wu, Cryst. Growth Des., 2017, 17, 2254 CAS.
- Y. Kim, I.-s. Seo, S. W. Martin, J. Baek, P. Shiv Halasyamani, N. Arumugam and H. Steinfink, Chem. Mater., 2008, 20, 6048 CrossRef CAS.
- I. Chung, M. G. Kim, J. I. Jang, J. Q. He, J. B. Ketterson and M. G. Kanatzidis, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2011, 50, 10867 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- I. Chung and M. G. Kanatzidis, Chem. Mater., 2013, 26, 849 CrossRef.
- Z. M. Ma, F. Weng, Q. R. Wang, Q. Tang, G. H. Zhang, C. Zheng, R. P. S. Han and F. Q. Huang, RSC Adv., 2014, 4, 28937 RSC.
- C. D. Morris, H. Li, H. Jin, C. D. Malliakas, J. A. Peters, P. N. Trikalitis, A. J. Freeman, B. W. Wessels and M. G. Kanatzidis, Chem. Mater., 2013, 25, 3344 CrossRef CAS.
- J. A. Brant, D. J. Clark, Y. S. Kim, J. I. Jang, J. H. Zhang and J. A. Aitken, Chem. Mater., 2014, 26, 3045 CrossRef CAS.
- J. H. Liao, G. M. Marking, K. F. Hsu, Y. Matsushita, M. D. Ewbank, R. Borwick, P. Cunningham, M. J. Rosker and M. G. Kanatzidis, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2003, 125, 9484 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. A. Rosmus, J. A. Brant, S. D. Wisneski, D. J. Clark, Y. S. Kim, J. I. Jang, C. D. Brunetta, J. H. Zhang, M. N. Srnec and J. A. Aitken, Inorg. Chem., 2014, 53, 7809 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- N. Zhen, K. Wu, Y. Wang, Q. Li, W. H. Gao, D. W. Hou, Z. H. Yang, H. D. Jiang, Y. J. Dong and S. L. Pan, Dalton Trans., 2016, 45, 10681 RSC.
- N. Ding, D. Y. Chung and M. G. Kanatzidis, Chem. Commun., 2004, 1170 RSC.
- K. Wu, X. Su, Z. H. Yang and S. L. Pan, Dalton Trans., 2015, 44, 19856 RSC.
- K. Wu, S. Pan and Z. Yang, RSC Adv., 2015, 5, 33646 RSC.
- J. W. Lekse, M. A. Moreau, K. L. McNerny, J. Yeon, P. S. Halasyamani and J. A. Aitken, Inorg. Chem., 2009, 48, 7516 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. Wu, Z. H. Yang and S. L. Pan, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2016, 55, 6713 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. Wu, Z. H. Yang and S. L. Pan, Chem. Mater., 2016, 28, 2795 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Tampier and D. Johrendt, Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem., 2001, 627, 312 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Assoud, N. Soheilnia and H. Kleinke, Chem. Mater., 2005, 17, 2255 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Teske and O. Vetter, Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem., 1976, 426, 281 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Teske, Z. Naturforsch., B: J. Chem. Sci., 1979, 34, 386 Search PubMed.
- A. Spek, J. Appl. Crystallogr., 2003, 36, 7 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Bruker and A. Saint, Acta Crystallogr., Sect. A: Found. Crystallogr., 2008, 64, 112 CrossRef PubMed.
- P. Kubelka, Z. Tech. Phys., 1931, 12, 593 Search PubMed.
- S. Kurtz and T. Perry, J. Appl. Phys., 1968, 39, 3798 CrossRef CAS.
- S. J. Clark, M. D. Segall, C. J. Pickard, P. J. Hasnip, M. I. Probert, K. Refson and M. C. Payne, Z. Kristallogr., 2005, 220, 567 CAS.
- J. P. Perdew and A. Zunger, Phys. Rev. C: Nucl. Phys., 1981, 23, 5048 CrossRef CAS.
- D. M. Ceperley and B. Alder, Phys. Rev. Lett., 1980, 45, 566 CrossRef CAS.
- D. Hamann, M. Schlüter and C. Chiang, Phys. Rev. Lett., 1979, 43, 1494 CrossRef CAS.
- B. B. Zhang, M. H. Lee, Z. H. Yang, Q. Jing and S. L. Pan, Appl. Phys. Lett., 2015, 106, 031906 CrossRef.
- W. L. Yin, K. Feng, R. He, D. J. Mei, Z. S. Lin, J. Y. Yao and Y. C. Wu, Dalton Trans., 2012, 41, 5653 RSC.
- Z. Z. Luo, C. S. Lin, H. H. Cui, W. L. Zhang, H. Zhang, H. Chen, Z. Z. He and W. D. Cheng, Chem. Mater., 2015, 27, 914 CrossRef CAS.
- J. J. Suk, H. D. Won and L. J. Sung, Catal. Today, 2007, 120, 174 CrossRef.
- D. Huang, C. Persson, Z. P. Ju, M. F. Dou, C. M. Yao and J. Guo, Europhys. Lett., 2014, 105, 37007 CrossRef.
- J. D. Beasley, Appl. Opt., 1994, 33, 1000 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Assoud and H. Kleinke, Chem. Mater., 2005, 17, 4509 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Okorogu, S. Mirov, W. Lee, D. Crouthamel, N. Jenkins, A. Y. Dergachev, K. Vodopyanov and V. Badikov, Opt. Commun., 1998, 155, 307 CrossRef CAS.
- Z. Z. Luo, C. S. Lin, H. H. Cui, W. L. Zhang, H. Zhang, Z. Z. He and W. D. Cheng, Chem. Mater., 2014, 26, 2743 CrossRef CAS.
- K. Wu, Z. H. Yang and S. L. Pan, Chem. Commun., 2017, 53, 3010 RSC.
- L. Sham and M. Schlüter, Phys. Rev. Lett., 1983, 51, 1888 CrossRef.
- A. J. Cohen, P. Mori-Sanchez and Y. Weitao, Phys. Rev. B, 2008, 77, 115123 CrossRef.
- D. Kleinman, Phys. Rev., 1962, 126, 1977 CrossRef CAS.
Footnote |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available: CIF file; checkcif; atomic coordinates, isotropic displacement parameters; selected bond lengths and angles; powder XRD patterns and IR spectra; particle size versus SHG intensity for BaCu2SnS4 and AgGaS2; absorption spectra of title compounds; calculated electronic structures; projected density of states; calculated SHG density. CCDC 1540053, 1540054, 1540055, 1540056 and 1540057 for BaCu2SiSe4, BaCu2GeS4, BaCu2GeSe4, BaCu2SnS4 and BaCu2SnSe4, respectively. For ESI and crystallographic data in CIF or other electronic format see DOI: 10.1039/c7ra05022d |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 |