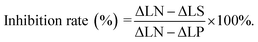Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleCreative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported Licence
Substituted 4-oxo-crotonic acid derivatives as a new class of protein kinase B (PknB) inhibitors: synthesis and SAR study†
Changliang
Xu‡
ab,
Xiaoguang
Bai‡
a,
Jian
Xu
a,
Jinfeng
Ren
a,
Yun
Xing
a,
Ziqiang
Li
a,
Juxian
Wang
a,
Jingjing
Shi
b,
Liyan
Yu
*a and
Yucheng
Wang
*a
aInstitute of Medicinal Biotechnology, Chinese Academy of Medical Science, Peking Union Medical College, Beijing 100050, China. E-mail: yly@cpcc.ac.cn; wyc9999@gmail.com; Fax: +86-010-6318-7118; Fax: +86-010-6316-5263; Tel: +86-010-6318-7118 Tel: +86-010-6316-5263
bJiangsu Protein Drug Engineering Laboratory, Food & Drug Analysis and Testing Center, Jiangsu Food & Pharmaceutical Science College, Huai'an 223003, Jiangsu, China. E-mail: clxu1986@163.com; Tel: +86-0517-87088209
First published on 17th January 2017
Abstract
Protein kinase B (PknB) is an essential serine/threonine protein kinase required for Mycobacterium tuberculosis (M. tb) cell division and cell-wall biosynthesis. A high throughput screen using PknB identified a (E)-4-oxo-crotonic acid inhibitor, named YH-8, which was used as a scaffold for SAR investigations. A significant improvement in enzyme affinity was achieved. The results indicated that the α,β-unsaturated ketone scaffold and “trans-” configuration are essential for the activity against PknB. And compounds with an aryl group, especially with electron-withdrawing substituents on benzene ring, exhibited four fold potency than that of YH-8.
1. Introduction
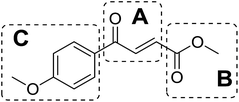
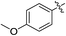
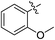
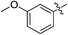
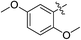
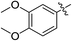
As an essential Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) serine/threonine protein kinase (STPK), protein kinase B (PknB) is highly conserved in Gram-positive bacteria and apparently required for mycobacterial growth.1–4 The knockout and overexpression of PknB can lead to alteration of growth rate and cell morphology of TB.5–8 The crystal structure of the kinase domain of PknB in complexes with an ATP analogue9 exhibits less than 30% similarity with eukaryotic and prokaryotic STPKs, which suggests that PknB may be a potential drug target for the tuberculosis kinases and not those of the host. Previously many high affinity inhibitors have also been reported for PknB.10YH-8, namely (E)-methyl-4-(4-methoxyphenyl)-4-oxobut-2-enoate (Fig. 1), was identified as a PknB inhibitor from a high throughput screen (HTS) of our compounds collection. Its majority anti-TB activity of minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) is falling in the 0.625–1.250 μmol L−1 range in vitro, which is significantly higher than other reported PknB inhibitors, such as amminopyrimidines, aminoguanidines and anthraquinones classes.11 Stability assay revealed that YH-8 was stable over 12 h in rat plasma samples, and the acute toxicity for the LD50 values in rat were 600 mg kg−1 (orally administered) and 200 mg kg−1 (vein injected).12 As a new unsaturated crotonic acid scaffold of YH-8 from all reported anti-TB chemical scaffolds,10,13 the previously results formed the starting point for our chemistry programme. In this study, we reported on the synthesis and structure–activity relationship (SAR) study of series of YH-8 derivatives as potential PknB inhibitors.
2. Chemical synthesis
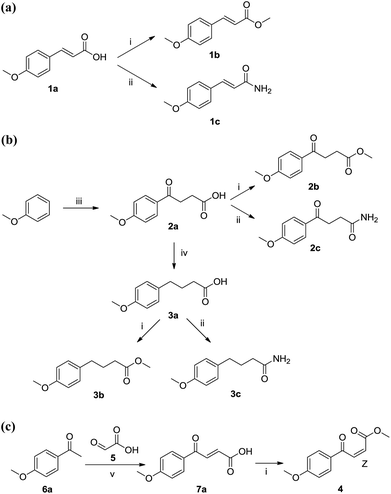
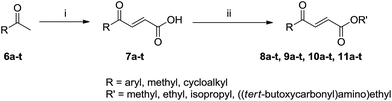
In Scheme 1, 7 compounds were firstly designed and synthesized based on the scaffold A ((E)-α,β-unsaturated ketone, Fig. 1) of YH-8 for SAR investigations. γ-Oxobenzenebutanoic acid 2a was prepared using Friedel–Crafts acylation of anisole with succinic anhydride catalyzed by Lewis acid of aluminum chloride in 80% yield.14 Reduction of 2a by triethylsilane in trifluoroacetic acid obtained 3a in 72% yield. Methyl esters 1b, 2b and 3b were synthesized from corresponding acids 1a, 2a and 3a in methanol catalyzed by concentrated sulfuric acid in 92–95% yields.15 According to literature method,16 the carboxylic acid group of 1a, 2a and 3a was firstly activated by treatment with isobutylchloroformate (IBCF), the product of which was then treated in situ with ammonia gas at −15 °C to give corresponding amides 1c, 2c and 3c in 75–85% yields. In Scheme 2, the 20 aromatic E-3-acylacrylic acid derivatives 7a–t were directly prepared from corresponding ketones 6a–t and glyoxylic acid in 50–75% yields.17 Esters 8a–t, 9a–t and 10a–t were obtained using the same method of 2a in around 40% yield. The “cis-” configuration (4, (Z)-methyl 4-(4-methoxyphenyl)-4-oxobut-2-enoate) of YH-8 (8a) was separated from a mixture of cis- and trans-products in 48% yield. Similarly, the carboxylic acid group of 7a–t was firstly activated by treatment with IBCF, the product of which was then treated in situ with N-Boc-ethanolamine to afford compounds 11a–t in 47–84% yields.3. Results and discussion
As a promising PknB inhibitor, the structure of YH-8 is markedly different from the reported PknB inhibitors. As shown in Fig. 1, YH-8 was characterized as a substituted (E)-4-oxo-crotonic acid scaffold with three parts, namely A ((E)-α,β-unsaturated ketone), B (ester) and C (aryl). We presumed each part should play a different role of the interactions between YH-8 and PknB ATP-binding site. In other words, firstly we should clarify which part is essential for the activity and which part is allowed to be modified for increasing potency. So, initial SAR study was performed mainly around the scaffold A ((E)-α,β-unsaturated ketone). As shown in Scheme 1-a, scaffold A was firstly deduced to methyl ester 1b and amide 1c from corresponding acid 1a, which lacks a carbonyl (ketone) group comparing with the α,β-unsaturated ketone of A. In Scheme 1-b, the carbon–carbon double bond of scaffold A was deduced to an alkane acid 2a by a Friedel–Crafts acylation reaction from anisole. The carbonyl (ketone) group of 2a was sequentially reduced to methylene of 3a. Both acids of 2a and 3a were also converted to corresponding methyl esters 2b & 3b and amides 2c & 3c. In Scheme 1-c, the “cis-” configuration (4) of YH-8, (Z)-methyl 4-(4-methoxyphenyl)-4-oxobut-2-enoate, was separated from a mixture of cis- and trans-products and characterized by 1H NMR. The JHH of “cis-” configuration is 3.6 Hz less than its “trans-” configuration. And the “cis-” configuration (4) is a yellow oil, whereas YH-8, namely 8a in this study, is a yellow solid.According to preliminary measurements, inhibitor concentration of 20 μM in the assay of percent inhibition of PknB was selected mainly because this concentration can cover and reflect the inhibitory rates rightly for all test compounds. Including carboxylic acid, esters and amides, ten compounds in Scheme 1 were tested for inhibitory activity against PknB at 20 μM along with YH-8. As shown in Table 1, eight compounds exhibit less than 10% inhibition against PknB comparing with YH-8 (52.1%). Only compounds 1a & 4 have a moderate inhibition (30.7% & 24.7%). The results show the α,β-unsaturated ketone scaffold and “trans-” configuration are essential for the activity of YH-8 against PknB.
| Compd. | Inhibitiona (%) | Compd. | Inhibitiona (%) | Compd. | Inhibitiona (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a Values represent the percent inhibition of PknB at 20 μM of the test compounds and are means of three independent experiments. | |||||
| 1a | 30.7 ± 1.6 | 2a | 3.3 ± 0.2 | 3a | 7.0 ± 0.5 |
| 1b | 1.7 ± 0.2 | 2b | 5.1 ± 1.6 | 3b | 5.6 ± 0.5 |
| 1c | 5.4 ± 0.6 | 2c | 8.7 ± 0.6 | 3c | 8.0 ± 0.7 |
| YH-8 (8a) | 52.1 ± 1.8 | 4 | 24.7 ± 1.5 | ||
Based on the findings above, the subsequent SAR study of YH-8 was carried out on modification of part B and C while maintaining the α,β-unsaturated ketone scaffold and “trans-” configuration. As shown in Scheme 2, series of compounds were synthesized from corresponding methyl ketones (6a–t). The structures of 8a–t, 9a–t, 10a–t, and 11a–t were shown in Table 2 and their PknB inhibitory activities were listed in Table 3. The data indicated that almost half of the tested compounds have comparable activity against PknB comparing with YH-8 (52.1%). Particularly, compounds 11a–t bearing a tert-butoxycarbonyl-aminoethyl group on part B generally show higher potency than that of other series. Among them, 11n–p exhibited much better activity (87.1%, 87.9% and 87.6%, respectively). Mostly, compounds bearing an aryl group on part C generally show higher potency than that substituted with alkyl analogues (8r–t, 9r–t, 10r–t and 11r–t). It indicated that the alkyl group on part C would be detrimental to the activity. For the aryl substituted compounds, 8–11g (61.4–70.7%) with 2,5-dimethoxyphenyl, 8–11h (62.1–68.3%) with 3,4-dimethoxyphenyl, 8–11m (61.3–73.6%) with naphthyl, 8–11n (61.3–73.6%) except 9n (49.0%) with 2,4-dichlorophenyl, 8–11o (59.1–87.9%) with 4-nitrophenyl, 8–11p (64.5–87.6%) with 4-bromophenyl and 8–11q (60.8–67.0%) with furyl exhibit higher activity than YH-8 of 52.1%. We speculated that the position of the substituted group on phenyl ring should be one of the factors that influence the binding between inhibitor and PknB ATP-binding site. Meanwhile, electron-withdrawing groups on phenyl ring should be beneficial to the potency. It maybe through the electron-withdrawing effect influence on the conjugation of scaffold A, which is known to be essential for the activity of YH-8 against PknB above.
| Compd. | Inhibitiona (%) | Compd. | Inhibitiona (%) | Compd. | Inhibitiona (%) | Compd. | Inhibitiona (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a Values represent the percent inhibition of PknB at 20 μM of the test compounds and are means of three independent experiments. | |||||||
| YH-8 (8a) | 52.1 ± 1.8 | 9a | 48.7 ± 4.9 | 10a | 41.1 ± 3.4 | 11a | 61.6 ± 2.8 |
| 8b | 47.8 ± 4.1 | 9b | 64.3 ± 7.7 | 10b | 11.2 ± 1.7 | 11b | 69.1 ± 4.5 |
| 8c | 60.5 ± 5.5 | 9c | 15.5 ± 2.3 | 10c | 72.8 ± 7.4 | 11c | 65.8 ± 5.5 |
| 8d | 54.2 ± 4.8 | 9d | 47.8 ± 7.1 | 10d | 38.0 ± 4.2 | 11d | 55.6 ± 2.7 |
| 8e | 62.1 ± 5.0 | 9e | 45.3 ± 3.7 | 10e | 56.2 ± 5.0 | 11e | 54.3 ± 3.7 |
| 8f | 63.1 ± 6.8 | 9f | 55.7 ± 7.0 | 10f | 42.6 ± 2.9 | 11f | 66.2 ± 4.9 |
| 8g | 70.7 ± 4.0 | 9g | 67.7 ± 5.0 | 10g | 61.4 ± 4.7 | 11g | 67.1 ± 5.4 |
| 8h | 65.6 ± 8.3 | 9h | 68.3 ± 5.4 | 10h | 63.9 ± 7.6 | 11h | 62.1 ± 4.8 |
| 8i | 45.4 ± 2.8 | 9i | 51.2 ± 1.4 | 10i | 60.6 ± 1.7 | 11i | 59.0 ± 4.5 |
| 8j | 39.0 ± 2.7 | 9j | 45.9 ± 3.2 | 10j | 43.1 ± 5.9 | 11j | 53.8 ± 5.3 |
| 8k | 48.6 ± 5.4 | 9k | 45.9 ± 6.1 | 10k | 19.5 ± 1.9 | 11k | 50.6 ± 5.6 |
| 8l | 59.1 ± 4.9 | 9l | 51.6 ± 7.8 | 10l | 45.5 ± 5.8 | 11l | 46.0 ± 2.6 |
| 8m | 62.8 ± 6.1 | 9m | 61.3 ± 4.6 | 10m | 61.6 ± 3.8 | 11m | 73.6 ± 4.0 |
| 8n | 57.0 ± 6.0 | 9n | 49.0 ± 3.9 | 10n | 57.1 ± 5.1 | 11n | 87.1 ± 4.3 |
| 8o | 65.1 ± 7.6 | 9o | 65.3 ± 8.5 | 10o | 59.1 ± 4.3 | 11o | 87.9 ± 5.3 |
| 8p | 66.7 ± 5.8 | 9p | 67.5 ± 5.7 | 10p | 64.5 ± 4.7 | 11p | 87.6 ± 5.8 |
| 8q | 63.2 ± 3.7 | 9q | 63.8 ± 6.2 | 10q | 60.8 ± 5.3 | 11q | 67.0 ± 4.6 |
| 8r | 32.6 ± 3.7 | 9r | 40.4 ± 4.2 | 10r | 38.3 ± 1.5 | 11r | 46.2 ± 5.4 |
| 8s | 33.2 ± 2.7 | 9s | 53.5 ± 6.8 | 10s | 42.7 ± 3.2 | 11s | 54.3 ± 4.0 |
| 8t | 36.9 ± 4.0 | 9t | 33.4 ± 5.8 | 10t | 43.7 ± 2.9 | 11t | 40.0 ± 3.4 |
Finally, the 50% inhibition concentrations (IC50) of compounds 11a–t were tested in Table 4. Among them, compounds 11a–c, f, g, i, m–q exhibit apparently higher IC50 activities than YH-8. Particularly, compounds 11n, 11o and 11p (IC50: 5.6 μM, 4.4 μM and 5.4 μM, respectively) with electron-withdrawing substituents on benzene ring show about fourfold more potent than that of YH-8 (IC50: 20.2 μM). Additionally, most IC50 values of compounds 11a–t in Table 4 consistently match with the corresponding inhibitory rates in Table 3. For example, the inhibitory rates of compounds 11o, 11p, 11n, 11f, 11a, 11e and 11t are 87.9%, 87.6%, 87.1%, 66.2%, 61.6%, 54.3% and 40.0%, respectively. And their corresponding IC50 values are 4.4, 5.4, 5.6, 10.5, 14.1, 19.1 and 38.4 μM, respectively.
| Compd. | IC50a (μM) | Compd. | IC50a (μM) | Compd. | IC50a (μM) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a Values are means of three independent experiments. b Not detected. | |||||
| 11a | 14.1 ± 2.7 | 11h | 17.7 ± 1.1 | 11o | 4.4 ± 0.6 |
| 11b | 10.2 ± 1.7 | 11i | 12.6 ± 2.7 | 11p | 5.4 ± 0.5 |
| 11c | 7.9 ± 1.4 | 11j | 17.3 ± 2.7 | 11q | 11.9 ± 1.7 |
| 11d | 19.6 ± 3.8 | 11k | 18.9 ± 2.4 | 11r | 45.5 ± 5.2 |
| 11e | 19.1 ± 1.1 | 11l | NDb | 11s | 27.9 ± 3.0 |
| 11f | 10.5 ± 1.7 | 11m | 10.6 ± 1.4 | 11t | 38.4 ± 3.3 |
| 11g | 8.1 ± 0.4 | 11n | 5.6 ± 0.7 | YH-8 | 20.2 ± 0.2 |
4. Conclusions
In summary, the starting HTS hit of YH-8 was optimized for potency against PknB, and total 87 compounds were synthesized for SAR investigations. The initial SAR study of YH-8 indicated the α,β-unsaturated ketone scaffold and “trans-” configuration are essential for the activity of YH-8 against PknB. According to this finding, other 80 YH-8 derivatives were synthesized and evaluated. The results showed that the compounds bearing an aryl group on part C and a tert-butoxycarbonyl-aminoethyl group on part B generally showed higher potency than other compounds and YH-8. Among these compounds, 11n–o and 11p with electron-withdrawing substituents on benzene ring exhibited about fourfold more potent than that of YH-8.5. Experimental section
Methods and materials
The chemicals were purchased from Aldrich Chemical Co., Sigma or Chemical Co. THF was distilled under argon from sodium-benzophenone ketyl and CH2Cl2 was distilled under argon from calcium hydride. The reaction products were purified by crystallization or flash column chromatography using a mixture of petroleum ether and ethyl acetate as the eluent. All melting points were obtained on a Mettler Toledo Melting Point MP70 apparatus (Mettler Toledo, Zurich, Switzerland) and are uncorrected. 1H-NMR spectra were recorded on Varian Inova-400 MHz, Varian Inova-500 MHz and SYS-600 MHz instruments (Varian, Palo Alto, CA, USA). The chemical shifts (δ) are reported in ppm relative to the internal reference standard tetramethylsilane (TMS) and the coupling constants (J values) have been reported in Hertz (Hz). MS data were obtained using time-of-flight mass spectrometer (TOF-MS) or Bruker microTOF-Q instrument (Bruker, Billerica, MA, USA). High resolution mass spectra (HRMS) were obtained on a Q-TOF Ultima ESI instrument (micrOTOF-Q II, Bruker Daltonics, Leipzig, Germany). Analysis by thin layer chromatography (TLC) was performed on silica gel plates (Merck, Billerica, MA, USA). Automated column chromatography was conducted over silica gel using a Companion Rf 200 automated chromatography system (Teledyne ISCO, Lincoln, NE, USA).General synthetic procedures
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 to give the corresponding ester.
1 to give the corresponding ester.
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) as a solvent system. After cooling, the solvent was evaporated. The residue was washed with ice-cold water by decantation or on a filter. The crude product was dried in air at 40 °C and recrystallized from ethyl acetate or purified by column chromatography over silica gel with elution of a mixture of petroleum ether and ethyl acetate (2
1) as a solvent system. After cooling, the solvent was evaporated. The residue was washed with ice-cold water by decantation or on a filter. The crude product was dried in air at 40 °C and recrystallized from ethyl acetate or purified by column chromatography over silica gel with elution of a mixture of petroleum ether and ethyl acetate (2![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) to give the corresponding acid. For the synthesis of compound 7s, catalytic amount of morpholine hydrochloride was used as a catalyst without acetic acid as a solvent at 120 °C for overnight.
1) to give the corresponding acid. For the synthesis of compound 7s, catalytic amount of morpholine hydrochloride was used as a catalyst without acetic acid as a solvent at 120 °C for overnight.
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 to give the corresponding ester.
1 to give the corresponding ester.
(E)-Methyl 3-(4-methoxyphenyl) acrylate (1b). Pale yellow solid (92%) yield, mp: 89.0–90.5 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.65 (d, J = 15.6 Hz, 1H), 7.49–7.47 (m, 2H), 6.92–6.89 (m, 2H), 6.31 (d, J = 15.6 Hz, 1H), 3.84 (s, 3H), 3.79 (s, 3H); HRMS (ESI) m/z calcd for C11H12O3Na [M + Na] 215.0684, found 215.0672.
(E)-3-(4-Methoxyphenyl) acrylamide (1c). Yellow solid (75%), mp: 188.2–189.7 °C. 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.61 (d, J = 15.5 Hz, 1H), 7.48–7.46 (m, 2H), 6.91–6.89 (m, 2H), 6.33 (d, J = 15.5 Hz, 1H), 5.54 (m, 2H), 3.84 (s, 3H); HRMS (ESI) m/z calcd for C10H11NO2Na [M + Na] 200.0687, found 200.0684.
4-(4-Methoxyphenyl)-4-oxobutanoic acid (2a)14. To a mixture of anisole (10.8 g, 100 mmol) and anhydrous aluminum chloride (32.0 g, 240 mmol) in nitrobenzene (150 mL) at 0–5 °C was added dropwise a solution of succinic anhydride (12.0 g, 120 mmol) in nitrobenzene (150 mL) and maintained the same temperature. After addition completed, the reaction mixture was stirred at room temperature for 1 h and then heated up to 60 °C for a further 3 h. The reaction mixture was cooled, poured into ice-cold water (800 mL) and the resulting precipitate was filtered, washed with water and hexane to give a crude, which was crystallized from methanol/ethyl acetate (1
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 9) to give a colorless crystal of 2a (16.7 g, 80%), mp: 150–151 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.98–7.96 (m, 2H), 6.96–6.94 (m, 2H), 3.88 (s, 3H), 3.29 (t, J = 6.8 Hz, 2H), 2.81 (t, J = 6.8 Hz, 2H); HRMS (ESI) m/z calcd for C11H12O4Na [M + Na] 231.0633, found 231.0625.
9) to give a colorless crystal of 2a (16.7 g, 80%), mp: 150–151 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.98–7.96 (m, 2H), 6.96–6.94 (m, 2H), 3.88 (s, 3H), 3.29 (t, J = 6.8 Hz, 2H), 2.81 (t, J = 6.8 Hz, 2H); HRMS (ESI) m/z calcd for C11H12O4Na [M + Na] 231.0633, found 231.0625.
Methyl 4-(4-methoxyphenyl)-4-oxobutanoate (2b). White solid (95%), mp: 48.1–49.4 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.98–7.96 (m, 2H), 6.95–6.93 (m, 2H), 3.87 (s, 3H), 3.71 (s, 3H), 3.28 (t, J = 6.8 Hz, 2H), 2.75 (t, J = 6.8 Hz, 2H); HRMS (ESI) m/z calcd for C11H14O4Na [M + Na] 245.0790, found 245.0779.
4-(4-Methoxyphenyl)-4-oxobutanamide (2c). White solid (80%), mp: 134.6–136.3 °C. 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 7.94–7.93 (m, 2H), 7.30 (s, 1H), 7.04–7.02 (m, 2H), 6.72 (s, 1H), 3.83 (s, 3H), 3.14 (t, J = 6.5 Hz, 2H), 2.41 (t, J = 6.5 Hz, 2H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 197.26, 173.36, 163.00, 130.10, 129.61, 113.83, 55.50, 32.85, 28.97; HRMS (ESI) m/z calcd for C11H14NO3Na [M + Na] 230.0793, found 230.0779.
4-(4-Methoxyphenyl) butanoic acid (3a). A mixture of 2a (3.12 g, 15.00 mmol) and triethylsilane (10.5 g, 90.0 mmol) in trifluoroacetic acid (20 mL) was heated to 50 °C under argon atmosphere for 5 h. After cooling, the solvent was evaporated in vacuum, then the reaction mass was diluted with water (100 mL) and EtOAc (100 mL) and stirred for 5 min. The aqueous layer was extracted with EtOAc (100 mL × 2) and the combined organic extracts were washed with saturated brine and dried over Na2SO4. After filtration, the solvent was removed under reduced pressure and then co-evaporated with hexanes (50 mL). The residue was treated by flash column chromatography on silica with a elution of hexanes/EtOAc 1
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 to give 3a as a colorless solid (2.10 g, 72%): mp 62.5–63.5 °C; 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.11–7.09 (m, 2H), 6.84–6.82 (m, 2H), 3.79 (s, 3H), 2.62 (t, J = 7.6 Hz, 2H), 2.36 (t, J = 7.6 Hz, 2H), 1.97–1.92 (m, 2H); HRMS (ESI) m/z calcd for C11H14O3Na [M + Na] 217.0841, found 217.0830.
1 to give 3a as a colorless solid (2.10 g, 72%): mp 62.5–63.5 °C; 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.11–7.09 (m, 2H), 6.84–6.82 (m, 2H), 3.79 (s, 3H), 2.62 (t, J = 7.6 Hz, 2H), 2.36 (t, J = 7.6 Hz, 2H), 1.97–1.92 (m, 2H); HRMS (ESI) m/z calcd for C11H14O3Na [M + Na] 217.0841, found 217.0830.
Methyl 4-(4-methoxyphenyl) butanoate (3b). Pale yellow oil (94%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.10–7.08 (m, 2H), 6.84–6.82 (m, 2H), 3.78 (s, 3H), 3.66 (s, 3H), 2.59 (t, J = 7.6 Hz, 2H), 2.32 (t, J = 7.6 Hz, 2H), 1.96–1.91 (m, 2H); HRMS (ESI) m/z calcd for C12H16O3Na [M + Na] 231.0997, found 231.0983.
4-(4-Methoxyphenyl) butanamide (3c). White solid (85%), mp: 121.6–123.3 °C. 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3): δ 7.10–7.08 (m, 2H), 6.83–6.82 (m, 2H), 5.57 (s, 1H), 5.41 (s, 1H), 3.78 (s, 3H), 2.61 (t, J = 7.5 Hz, 2H), 2.32 (t, J = 7.5 Hz, 2H), 1.96–1.91 (m, 2H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 174.04, 157.39, 133.67, 129.21, 113.68, 54.95, 34.49, 33.79, 27.11; HRMS (ESI) m/z calcd for C11H15NO2Na [M + Na] 216.1000, found 216.0987.
(Z)-Methyl 4-(4-methoxyphenyl)-4-oxobut-2-enoate (4) and (E)-methyl 4-(4-methoxyphenyl)-4-oxobut-2-enoate (8a or YH-8). To a solution of 7.40 g of glyoxylic acid (5.56 mL, 100 mmol) in acetic acid (100 mL) was added 5 (15.0 g, 100 mmol), and the resulting mixture was stirred at 120 °C overnight. After cooling, the solvent was evaporated. The residue was washed with ice-cold water (50 mL) by decantation or on a filter. The crude product was dried in air at 50 °C and recrystallized from ethyl acetate to give 7a ((E)-4-(4-methoxyphenyl)-4-oxobut-2-enoic acid) as a pale yellow powder (10.7 g, 52%), mp: 139.2–140.8 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 8.03–7.97 (m, 3H), 7.01–6.98 (m, 2H), 6.89 (d, J = 15.6 Hz, 1H), 3.90 (s, 3H); HRMS (ESI) m/z calcd for C11H10O4Na [M + H] 207.0657, found 207.0649 [M + H]. To a stirring solution of 7a (1.03 g, 5.00 mol) in methanol (10 mL) was added concentrated sulfuric acid (125 μL). The reaction mixture was refluxed overnight, then cooled, concentrated, diluted with sat. NaHCO3 solution, extracted with DCM, dried over Na2SO4 and concentrated in vacuum. The residue was purified by flash column chromatography on silica with an elution of hexanes/EtOAc 4
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 to give 4a and 8a, respectively. 4a as a yellow oil (0.53 g, 48%); 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.92–7.90 (m, 2H), 6.96–6.94 (m, 2H), 6.89 (d, J = 12.0 Hz, 1H), 6.26 (d, J = 12.0 Hz, 1H), 3.87 (s, 3H), 3.61 (s, 3H); 8a as a yellow solid (0.53 g, 48%), mp: 72.9–73.7 °C; 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 8.02–8.00 (m, 2H), 7.93 (d, J = 15.6 Hz, 1H), 6.99–6.97 (m, 2H), 6.88 (d, J = 15.6 Hz, 1H), 3.84 (s, 3H), 3.89 (s, 3H); HRMS (ESI) m/z calcd for C12H12O4Na [M + Na] 243.0633, found 243.0627 [M + Na].
1 to give 4a and 8a, respectively. 4a as a yellow oil (0.53 g, 48%); 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.92–7.90 (m, 2H), 6.96–6.94 (m, 2H), 6.89 (d, J = 12.0 Hz, 1H), 6.26 (d, J = 12.0 Hz, 1H), 3.87 (s, 3H), 3.61 (s, 3H); 8a as a yellow solid (0.53 g, 48%), mp: 72.9–73.7 °C; 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 8.02–8.00 (m, 2H), 7.93 (d, J = 15.6 Hz, 1H), 6.99–6.97 (m, 2H), 6.88 (d, J = 15.6 Hz, 1H), 3.84 (s, 3H), 3.89 (s, 3H); HRMS (ESI) m/z calcd for C12H12O4Na [M + Na] 243.0633, found 243.0627 [M + Na].
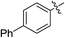
(E)-4-Oxo-4-phenylbut-2-enoic acid (7b). Yellow solid (74%), mp: 88.6–90.2 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 13.17 (s, 1H), 8.07–8.01 (m, 2H), 7.89 (d, J = 15.6 Hz, 1H), 7.74–7.70 (m, 1H), 7.61–7.57 (m, 2H), 6.69 (d, J = 15.6 Hz, 1H); HRMS (ESI) m/z calcd for C10H7O3 [M − H] 175.0395, found 175.0393 [M − H].
(E)-4-Oxo-4-(p-tolyl)but-2-enoic acid (7c). Yellow solid (76%), mp: 141.4–142.7 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 13.15 (s, 1H), 7.96–7.94 (m, 2H), 7.88 (d, J = 15.6 Hz, 1H), 7.40–7.38 (m, 2H), 6.67 (d, J = 15.6 Hz, 1H), 2.41 (s, 3H); HRMS (ESI) m/z calcd for C11H9O3 [M − H] 189.0552, found 189.0559 [M − H].
(E)-4-(4-Ethoxyphenyl)-4-oxobut-2-enoic acid (7d). Yellow solid (72%), mp: 150.3–151.7 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 13.09 (s, 1H), 8.04–8.01 (m, 2H), 7.89 (d, J = 15.6 Hz, 1H), 7.09–7.06 (m, 2H), 6.66 (d, J = 15.6 Hz, 1H), 4.15 (q, J = 7.2 Hz, 2H), 1.36 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 3H); HRMS (ESI) m/z calcd for C12H11O4 [M − H] 219.0657, found 219.0651 [M − H].
(E)-4-(2-Methoxyphenyl)-4-oxobut-2-enoic acid (7e). Yellow solid (73%), mp: 151.8–153.0 °C. 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 13.05 (s, 1H), 7.66–7.52 (m, 3H), 7.23–7.21 (m, 1H), 7.12–7.05 (m, 1H), 6.51 (d, J = 15.5 Hz, 1H), 3.88 (s, 3H); HRMS (ESI) m/z calcd for C11H10O4Na [M + Na] 229.0477, found 229.0467 [M + Na].
(E)-4-(3-Methoxyphenyl)-4-oxobut-2-enoic acid (7f). Yellow solid (71%), mp: 114.5–115.8 °C. 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 13.17 (s, 1H), 7.86 (d, J = 15.5 Hz, 1H), 7.66–7.61 (m, 1H), 7.53–7.46 (m, 2H), 7.30–7.27 (m, 1H), 6.68 (d, J = 15.5 Hz, 1H), 3.84 (s, 3H); HRMS (ESI) m/z calcd for C11H10O4Na [M + Na] 229.0477, found 229.0466 [M + Na].
(E)-4-(2,5-Dimethoxyphenyl)-4-oxobut-2-enoic acid (7g). Yellow solid (73%). Mp: 152.4–153.7 °C. 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 13.06 (s, 1H), 7.60 (d, J = 15.5 Hz, 1H), 7.23–7.15 (m, 2H), 7.09–7.08 (m, 1H), 6.52 (d, J = 15.5 Hz, 1H), 3.83 (s, 3H), 3.75 (s, 3H); HRMS (ESI) m/z calcd for C12H11O5 [M − H] 235.0606, found 235.0603 [M − H].
(E)-4-(3,4-Dimethoxyphenyl)-4-oxobut-2-enoic acid (7h). Yellow solid (75%). Mp: 183.1–184.3 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 13.11 (s, 1H), 7.93 (d, J = 15.6 Hz, 1H), 7.77–7.75 (m, 1H), 7.51–7.50 (m, 1H), 7.12–7.10 (m, 1H), 6.66 (d, J = 15.6 Hz, 1H), 3.87 (s, 3H), 3.84 (s, 3H); HRMS (ESI) m/z calcd for C12H11O5 [M − H] 235.0606, found 235.0610 [M − H].
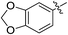
(E)-4-(Benzo[d][1,3]dioxol-5-yl)-4-oxobut-2-enoic acid (7i). Yellow solid (74%). Mp: 204.0–205.5 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 13.12 (s, 1H), 7.86 (d, J = 15.6 Hz, 1H), 7.74–7.72 (m, 1H), 7.50–7.49 (m, 1H), 7.09–7.07 (m, 1H), 6.65 (d, J = 15.6 Hz, 1H), 6.18 (s, 2H); MS-ESI (m/z): 219.06 [M − H].
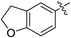
(E)-4-(2,3-Dihydrobenzofuran-5-yl)-4-oxobut-2-enoic acid (7j). Yellow solid (73%). Mp: 168.6–170.2 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CD3OD) δ 7.96–7.89 (m, 3H), 6.89–6.84 (m, 1H), 6.74 (d, J = 15.6 Hz, 1H), 4.68 (t, J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 3.30 (t, J = 8.8 Hz, 2H); HRMS (ESI) m/z calcd for C12H10O4Na [M + Na] 241.0477, found 241.0480 [M + Na].
(E)-4-([1,1′-Biphenyl]-4-yl)-4-oxobut-2-enoic acid (7k). Yellow solid (65%). Mp: 226.3–227.4 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 13.15 (s, 1H), 8.14–8.12 (m, 2H), 7.93 (d, J = 15.6 Hz, 1H), 7.90–7.88 (m, 2H), 7.79–7.77 (m, 2H), 7.54–7.50 (m, 2H), 7.46–7.43 (m, 1H), 6.76 (d, J = 15.6 Hz, 1H); HRMS (ESI) m/z calcd for C16H10O3 [M − H] 251.0708, found 251.0714 [M − H].
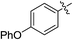
(E)-4-Oxo-4-(4-phenoxyphenyl)but-2-enoic acid (7l). Yellow solid (50%). Mp: 123.2–125.6 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 13.15 (s, 1H), 8.09–8.07 (m, 2H), 7.87 (d, J = 15.6 Hz, 1H), 7.50–7.46 (m, 2H), 7.30–7.26 (m, 1H), 7.17–7.15 (m, 2H), 7.09–7.07 (m, 2H), 6.67 (d, J = 15.6 Hz, 1H); HRMS (ESI) m/z calcd for C16H11O4 [M − H] 267.0657, found 267.0658 [M − H].
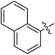
(E)-4-(Naphthalen-1-yl)-4-oxobut-2-enoic acid (7m). Yellow solid (55%). Mp: 150.1–151.7 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 13.21 (s, 1H), 8.47–8.45 (m, 1H), 8.23–8.21 (m, 1H), 8.08–8.04 (m, 2H), 7.70–7.60 (m, 4H), 6.61 (d, J = 15.6 Hz, 1H); HRMS (ESI) m/z calcd for C14H10O3Na [M + Na] 249.0528, found 249.0515 [M + Na].
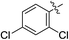
(E)-4-(2,4-Dichlorophenyl)-4-oxobut-2-enoic acid (7n). Yellow solid (58%). Mp: 201.3–202.8 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 13.30 (s, 1H), 7.81–7.80 (m, 1H), 7.70–7.68 (m, 1H), 7.61–7.58 (m, 1H), 7.32 (d, J = 16.0 Hz, 1H), 6.50 (d, J = 16.0 Hz, 1H); HRMS (ESI) m/z calcd for C10H6Cl2O3 [M − H] 242.9616, found 242.9612 [M − H].
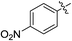
(E)-4-(4-Nitrophenyl)-4-oxobut-2-enoic acid (7o). Yellow solid (60%). Mp: 172.8–174.4 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 13.26 (s, 1H), 8.37–8.34 (m, 2H), 8.25–8.23 (m, 2H), 7.85 (d, J = 15.6 Hz, 1H), 6.71 (d, J = 15.6 Hz, 1H); HRMS (ESI) m/z calcd for C10H6NO5 [M − H] 220.0246, found 220.0261 [M − H].
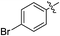
(E)-4-(4-Bromophenyl)-4-oxobut-2-enoic acid (7p). Yellow solid (64%). Mp: 161.1–163.4 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 13.18 (s, 1H), 6.97 (d, J = 15.6 Hz, 1H), 7.84 (d, J = 15.6 Hz, 1H), 7.97–7.95 (m, 2H), 7.79–7.77 (m, 2H); HRMS (ESI) m/z calcd for C10H6BrO3 [M − H] 253.9500, found 252.9489 [M − H].
(E)-4-(Furan-2-yl)-4-oxobut-2-enoic acid (7q). Brown solid (64%). Mp: 158.9–160.5 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 13.18 (s, 1H), 8.14 (s, 1H), 7.83–7.82 (m, 1H), 7.71 (d, J = 15.6 Hz, 1H), 6.85–6.78 (m, 1H), 6.74 (d, J = 15.6 Hz, 1H); HRMS (ESI) m/z calcd for C8H5O4 [M − H] 165.0188, found 165.0193 [M − H].
(E)-4-Oxohex-2-enoic acid (7r). White solid (54%). Mp: 123.5–125.7 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 13.13 (s, 1H), 6.80 (d, J = 16.0 Hz, 1H), 6.66 (d, J = 16.0 Hz, 1H), 2.34 (s, 3H); HRMS (ESI) m/z calcd for C5H5O3 [M − H] 113.0239, found 113.0244 [M − H].
(E)-4-Cyclohexyl-4-oxobut-2-enoic acid (7s). White solid (60%). Mp: 125.6–127.1 °C. 1HNMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 13.08 (s, 1H), 7.04 (d, J = 16.0 Hz, 1H), 6.60 (d, J = 16.0 Hz, 1H), 2.82–2.75 (m, 1H), 1.80–1.60 (m, 5H), 1.37–1.12 (m, 5H); HRMS (ESI) m/z calcd for C10H13O3 [M − H] 181.0865, found 181.0868 [M − H].
(E)-4-Cyclopropyl-4-oxobut-2-enoic acid (7t). White solid (65%), mp: 95.55–96.3 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 13.12 (s, 1H), 7.04 (d, J = 16.0 Hz, 1H), 6.70 (d, J = 16.0 Hz, 1H), 2.53–2.47 (m, 1H), 1.03–0.97 (m, 4H); MS-ESI (m/z): 163.04 [M + Na].
(E)-Methyl 4-oxo-4-phenylbut-2-enoate (8b). Yellow solid (45%), mp: 36.4–37.5 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 8.03–7.98 (m, 2H), 7.93 (d, J = 15.6 Hz, 1H), 7.66–7.59 (m, 1H), 7.54–7.50 (m, 2H), 6.90 (d, J = 15.6 Hz, 1H), 3.85 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 189.23, 165.38, 136.89, 136.01, 134.10, 131.21, 129.05, 128.84, 52.23; HRMS (ESI) m/z calcd for C11H10O3Na [M + Na] 213.0528, found 213.0538 [M + Na].
(E)-Methyl 4-oxo-4-(p-tolyl) but-2-enoate (8c). Yellow solid (46%), mp: 48.7–49.6 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.94–7.90 (m, 3H), 7.32–7.30 (m, 2H), 6.88 (d, J = 15.6 Hz, 1H), 3.85 (s, 3H), 2.44 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 188.54, 165.43, 144.83, 136.93, 133.57, 130.94, 129.63, 128.99, 52.20, 21.25; HRMS (ESI) m/z calcd for C12H12O3Na [M + Na] 227.0684, found 227.0691 [M + Na].
(E)-Methyl 4-(4-ethoxyphenyl)-4-oxobut-2-enoate (8d). Yellow solid (42%), mp: 81.7–83.2 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 8.03–7.97 (m, 2H), 7.94 (d, J = 15.6 Hz, 1H), 7.01–6.92 (m, 2H), 6.88 (d, J = 15.6 Hz, 1H), 4.13 (q, J = 7.2 Hz, 2H), 3.85 (s, 3H), 1.46 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 3H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 187.12, 165.51, 163.30, 137.03, 131.42, 130.53, 128.84, 114.72, 63.76, 52.19, 14.45; HRMS (ESI) m/z calcd for C13H14O4Na [M + Na] 257.0790, found 257.0778 [M + Na].
(E)-Methyl 4-(2-methoxyphenyl)-4-oxobut-2-enoate (8e). Yellow solid (47%), mp: 68.3–69.7 °C. 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 7.67 (d, J = 15.5 Hz, 1H), 7.65–7.56 (m, 2H), 7.24–7.22 (m, 1H), 7.10–7.07 (m, 1H), 6.59 (d, J = 15.5 Hz, 1H), 3.89 (s, 3H), 3.76 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 190.57, 165.62, 158.68, 140.77, 134.81, 130.14, 128.93, 126.80, 120.83, 112.69, 56.01, 52.19; HRMS (ESI) m/z calcd for C12H12O4Na [M + Na] 243.0633, found 243.0625 [M + Na].
(E)-Methyl 4-(3-methoxyphenyl)-4-oxobut-2-enoate (8f). Yellow solid (42%), mp: 58.4–60.0 °C. 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 7.95 (d, J = 15.5 Hz, 1H), 7.66–7.64 (m, 1H), 7.55–7.47 (m, 2H), 7.30–7.28 (m, 1H), 6.75 (d, J = 15.5 Hz, 1H), 3.84 (s, 3H), 3.79 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 188.95, 165.38, 159.62, 137.41, 136.85, 131.28, 130.22, 121.53, 120.37, 112.82, 55.39, 52.21; HRMS (ESI) m/z calcd for C12H12O4Na [M + Na] 243.0633, found 243.0616 [M + Na].
(E)-Methyl 4-(2,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-4-oxobut-2-enoate (8g). Yellow solid (43%). Mp: 74.4–75.7 °C. 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 7.68 (d, J = 15.5 Hz, 1H), 7.23–7.17 (m, 2H), 7.11–7.10 (m, 1H), 6.59 (d, J = 15.5 Hz, 1H), 3.84 (s, 3H), 3.76 (s, 3H), 3.75 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 190.19, 165.61, 153.15, 153.04, 140.71, 128.99, 127.07, 120.84, 114.35, 113.78, 56.50, 55.60, 52.20; HRMS (ESI) m/z calcd for C13H14O5Na [M + Na] 273.0739, found 273.0747 [M + Na].
(E)-Methyl 4-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-4-oxobut-2-enoate (8h). Yellow solid (46%). Mp: 97.7–99.0 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.01 (d, J = 15.2 Hz, 1H), 7.79–7.77 (m, 1H), 7.52–7.51 (m, 1H), 7.12–7.10 (m, 1H), 6.73 (d, J = 15.2 Hz, 1H), 3.88 (s, 3H), 3.84 (s, 3H), 3.78 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 186.98, 165.53, 154.07, 149.02, 136.77, 130.52, 129.02, 124.32, 110.95, 110.39, 55.85, 55.53, 52.16; HRMS (ESI) m/z calcd for C13H14O5Na [M + Na] 273.0739, found 273.0733 [M + Na].
(E)-Methyl 4-(benzo[d][1,3] dioxol-5-yl)-4-oxobut-2-enoate (8i). White solid (46%). Mp: 132.1–133.6 °C. 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 7.95 (d, J = 15.5 Hz, 1H), 7.75–7.73 (m, 1H), 7.52–7.51 (m, 1H), 7.10–7.08 (m, 1H), 6.71 (d, J = 15.5 Hz, 1H), 6.18 (s, 2H), 3.78 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 186.89, 165.46, 152.47, 148.30, 136.91, 130.79, 130.76, 126.25, 108.32, 107.66, 102.36, 52.19; MS-ESI (m/z): 235.15 [M + Na].
(E)-Methyl 4-(2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-5-yl)-4-oxobut-2-enoate (8j). Yellow solid (45%). Mp: 83.3–84.5 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.94–7.86 (m, 3H), 6.89–6.84 (m, 2H), 4.69 (t, J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 3.84 (s, 3H), 3.28 (t, J = 8.8 Hz, 2H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 186.85, 165.53, 164.89, 137.22, 131.11, 130.35, 129.32, 128.88, 126.36, 109.21, 72.45, 52.15, 28.25; HRMS (ESI) m/z calcd for C13H12O4Na [M + Na] 255.0633, found 255.0627 [M + Na].
(E)-Methyl 4-([1,1′-biphenyl]-4 yl)-4-oxobut-2-enoate (8k). Yellow solid (42%). Mp: 116.0–118.6 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.15–8.13 (m, 2H), 8.02 (d, J = 15.6 Hz, 1H), 7.90–7.88 (m, 2H), 7.81–7.75 (m, 2H), 7.55–7.51 (m, 2H), 7.47–7.43 (m, 1H), 6.78 (d, J = 15.6 Hz, 1H), 3.80 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 188.65, 165.43, 145.40, 138.65, 136.93, 134.85, 131.14, 129.64, 129.15, 128.64, 127.21, 127.07, 52.25; HRMS (ESI) m/z calcd for C17H14O3Na [M + Na] 289.0841, found 289.0836 [M + Na].
(E)-Methyl 4-oxo-4-(4-phenoxyphenyl) but-2-enoate (8l). Yellow solid (44%). Mp: 92.0–93.5 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.12–8.07 (m, 2H), 7.96 (d, J = 15.6 Hz, 1H), 7.52–7.46 (m, 2H), 7.31–7.25 (m, 1H), 7.19–7.14 (m, 2H), 7.11–7.06 (m, 2H), 6.74 (d, J = 15.6 Hz, 1H), 3.78 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 187.48, 165.45, 162.17, 154.64, 136.87, 131.64, 130.93, 130.44, 130.40, 125.08, 120.27, 117.29, 52.23; MS-ESI (m/z): 305.13 [M + Na].
(E)-Methyl 4-(naphthalen-1-yl)-4-oxobut-2-enoate (8m). Yellow oil (42%). 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.51–8.49 (m, 1H), 8.23–8.22 (m, 1H), 8.10–8.04 (m, 2H), 7.76 (d, J = 15.5 Hz, 1H), 7.71–7.60 (m, 3H), 6.69 (d, J = 15.5 Hz, 1H), 3.79 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 192.55, 165.34, 139.95, 133.59, 133.50, 133.45, 131.52, 129.96, 129.74, 128.65, 128.12, 126.65, 125.12, 124.72, 52.16; HRMS (ESI) m/z calcd for C15H12O3Na [M + Na] 263.0684, found 263.0674 [M + Na].
(E)-Methyl 4-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-4-oxobut-2-enoate (8n). Yellow solid (44%). Mp: 98.7–100.1 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.54 (d, J = 15.6 Hz, 1H), 7.50–7.44 (m, 2H), 7.38–7.36 (m, 1H), 6.69 (d, J = 15.6 Hz, 1H), 3.83 (s, 3H); HRMS (ESI) m/z calcd for C11H7Cl2O3 [M − H] 256.9789, found 256.9756 [M − H].
(E)-Methyl 4-(4-nitrophenyl)-4-oxobut-2-enoate (8o). Yellow solid (45%). Mp: 105.9–107.0 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 8.38–8.35 (m, 2H), 8.16–8.14 (m, 2H), 7.88 (d, J = 15.6 Hz, 1H), 6.95 (d, J = 15.6 Hz, 1H), 3.87 (s, 3H); HRMS (ESI) m/z calcd for C22H17N2O10 [2M − H] 469.0883, found 469.0875 [2M − H].
(E)-Methyl 4-(4-bromophenyl)-4-oxobut-2-enoate (8p). Yellow solid (46%). Mp: 77.8–79.0 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.87 (d, J = 15.6 Hz, 1H), 7.87–7.85 (m, 2H), 7.67–7.65 (m, 2H), 6.90 (d, J = 15.6 Hz, 1H), 3.85 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 188.50, 165.33, 136.60, 135.01, 132.12, 131.50, 130.84, 128.36, 52.27; HRMS (ESI) m/z calcd for C11H9BrO3Na [M + Na] 290.9633, found 290.9616 [M + Na].
(E)-Methyl 4-(furan-2-yl)-4-oxobut-2-enoate (8q). Yellow solid (44%). Mp: 90.7–92.8 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.77 (d, J = 15.6 Hz, 1H), 7.70–7.69 (m, 1H), 7.39–7.38 (m, 1H), 6.99 (d, J = 15.6 Hz, 1H), 6.63–6.62 (m, 1H), 3.85 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 175.46, 165.27, 151.97, 149.73, 136.10, 130.72, 121.68, 113.29, 52.24; HRMS (ESI) m/z calcd for C9H7O4 [M − H] 179.0362, found 179.0350 [M − H].
(E)-Methyl 4-oxopent-2-enoate (8r). White solid (41%). Mp: 61.9–63.2 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.02 (d, J = 16.0 Hz, 1H), 6.65 (d, J = 16.0 Hz, 1H), 3.81 (s, 3H), 2.35 (s, 3H); HRMS (ESI) m/z calcd for C6H7O3 [M − H] 127.0412, found 127.0392 [M − H].
(E)-Methyl 4-cyclohexyl-4-oxobut-2-enoate (8s). White solid (43%). Mp: 52.3–54.6 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.19 (d, J = 16.0 Hz, 1H), 6.71 (d, J = 16.0 Hz, 1H), 3.81 (s, 3H), 2.61–2.55 (m, 1H), 1.89–1.68 (m, 5H), 1.42–1.17 (m, 5H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 202.32, 165.59, 138.83, 129.68, 52.19, 47.97, 27.68, 25.37, 24.88; HRMS (ESI) m/z calcd for C11H16O3Na [M + Na] 219.0997, found 219.1006 [M + Na].
(E)-Methyl 4-cyclopropyl-4-oxobut-2-enoate (8t). Yellow oil (37%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 7.13 (d, J = 16.0 Hz, 1H), 6.79 (d, J = 16.0 Hz, 1H), 3.76 (s, 3H), 2.56–2.51 (m, 1H), 1.06–0.95 (m, 4H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 199.42, 165.61, 139.62, 129.80, 52.15, 19.44, 11.76; HRMS (ESI) m/z calcd for C8H10O3Na [M + Na] 177.0528, found 177.0520 [M + Na].
(E)-Ethyl 4-(4-methoxyphenyl)-4-oxobut-2-enoate (9a). Yellow solid (46%), mp: 41.2–42.7 °C. 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.06–8.05 (m, 2H), 7.99 (d, J = 15.5 Hz, 1H), 7.11–7.10 (m, 2H), 7.05–7.03 (m, 1H), 6.69 (d, J = 15.5 Hz, 1H), 4.18–4.16 (m, 2H), 3.88 (s, 3H), 3.28–3.24 (m, 2H), 1.37 (s, 9H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 187.14, 165.00, 163.95, 136.81, 131.36, 130.91, 129.00, 114.33, 60.93, 55.66, 13.99; HRMS (ESI) m/z calcd for C13H14O4Na [M + Na] 257.0790, found 257.0792 [M + Na].
(E)-Ethyl 4-oxo-4-phenylbut-2-enoate (9b). Yellow oil (46%). 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.05–8.03 (m, 2H), 7.95 (d, J = 15.5 Hz, 1H), 7.75–7.69 (m, 1H), 7.63–7.56 (m, 2H), 6.73 (d, J = 15.5 Hz, 1H), 4.25 (q, J = 7.0 Hz, 2H), 1.28 (t, J = 7.0 Hz, 3H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 189.15, 164.85, 136.64, 136.02, 134.01, 131.57, 128.99, 128.78, 60.98, 13.95; HRMS (ESI) m/z calcd for C11H10O3Na [M + Na] 213.0528, found 213.0538 [M + Na].
(E)-Ethyl 4-oxo-4-(p-tolyl) but-2-enoate (9c). Yellow oil (43%). 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 7.96–7.92 (m, 3H), 7.40–7.38 (m, 2H), 6.71 (d, J = 15.5 Hz, 1H), 4.25 (q, J = 7.0 Hz, 2H), 2.41 (s, 3H), 1.28 (t, J = 7.0 Hz, 3H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 188.51, 164.92, 144.77, 136.74, 133.58, 131.30, 129.60, 128.96, 60.97, 21.23, 13.98; HRMS (ESI) m/z calcd for C13H14O3Na [M + Na] 241.0841, found 241.0840 [M + Na].
(E)-Ethyl 4-(4-ethoxyphenyl)-4-oxobut-2-enoate (9d). Yellow solid (40%), mp: 54.4–55.7 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 8.03–7.97 (m, 2H), 7.92 (d, J = 15.6 Hz, 1H), 6.99–6.93 (m, 2H), 6.87 (d, J = 15.6 Hz, 1H), 4.30 (q, J = 7.2 Hz, 2H), 4.13 (q, J = 6.8 Hz, 2H), 1.46 (t, J = 6.8 Hz, 3H), 1.35 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 3H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 187.15, 165.02, 163.28, 136.90, 131.40, 130.88, 128.84, 114.72, 63.75, 60.94, 14.44, 14.02; HRMS (ESI) m/z calcd for C14H16O4Na [M + Na] 271.0946, found 271.0953 [M + Na].
(E)-Ethyl 4-(2-methoxyphenyl)-4-oxobut-2-enoate (9e). Yellow solid (41%), mp: 50.1–51.5 °C. 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 7.66 (d, J = 15.5 Hz, 1H), 7.64–7.57 (m, 2H), 7.24–7.22 (m, 1H), 7.10–7.07 (m, 1H), 6.57 (d, J = 15.5 Hz, 1H), 4.22 (q, J = 7.0 Hz, 2H), 1.26 (t, J = 7.0 Hz, 3H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 190.62, 165.11, 158.65, 140.68, 134.76, 130.10, 129.32, 126.81, 120.83, 112.70, 60.91, 56.00, 13.97; HRMS (ESI) m/z calcd for C13H14O4Na [M + Na] 257.0790, found 257.0778 [M + Na].
(E)-Ethyl 4-(3-methoxyphenyl)-4-oxobut-2-enoate (9f). Yellow oil (40%). 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 7.93 (d, J = 15.5 Hz, 1H), 7.68–7.62 (m, 1H), 7.55–7.47 (m, 2H), 7.30–7.28 (m, 1H), 6.73 (d, J = 15.5 Hz, 1H), 4.25 (q, J = 7.0 Hz, 2H), 3.85 (s, 3H), 1.28 (t, J = 7.0 Hz, 3H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 188.99, 164.88, 159.61, 137.42, 136.74, 131.65, 130.22, 121.52, 120.32, 112.82, 61.00, 55.39, 13.98; HRMS (ESI) m/z calcd for C13H14O4Na [M + Na] 257.0790, found 257.0793 [M + Na].
(E)-Ethyl 4-(2,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-4-oxobut-2-enoate (9g). Yellow solid (42%). Mp: 66.2–67.5 °C. 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 7.68 (d, J = 15.5 Hz, 1H), 7.22–7.17 (m, 2H), 7.11–7.10 (m, 1H), 6.57 (d, J = 15.5 Hz, 1H), 4.22 (q, J = 7.0 Hz, 2H), 3.84 (s, 3H), 3.75 (s, 3H), 1.26 (t, J = 7.0 Hz, 3H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 190.18, 165.10, 153.15, 153.02, 140.61, 129.35, 127.08, 120.76, 114.33, 113.77, 60.90, 56.46, 55.57, 13.96; HRMS (ESI) m/z calcd for C14H16O5Na [M + Na] 287.0895, found 287.0895 [M + Na].
(E)-Ethyl 4-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-4-oxobut-2-enoate (9h). Yellow solid (43%). Mp: 92.6–94.7 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.00 (d, J = 15.6 Hz, 1H), 7.79–7.77 (m, 1H), 7.52–7.51 (m, 1H), 7.13–7.10 (m, 1H), 6.72 (d, J = 15.6 Hz, 1H), 4.24 (q, J = 7.2 Hz, 2H), 3.88 (s, 3H), 3.84 (s, 3H), 1.28 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 3H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 187.09, 165.06, 154.08, 149.04, 136.75, 130.93, 129.04, 124.38, 111.01, 110.41, 60.95, 55.89, 55.57, 14.03; HRMS (ESI) m/z calcd for C14H16O5Na [M + Na] 287.0895, found 287.0878 [M + Na].
(E)-Ethyl 4-(benzo[d][1,3] dioxol-5-yl)-4-oxobut-2-enoate (9i). Yellow solid (45%). Mp: 90.8–93.0 °C. 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 7.93 (d, J = 15.5 Hz, 1H), 7.75–7.73 (m, 1H), 7.51–7.50 (m, 1H), 7.09–7.08 (m, 1H), 6.69 (d, J = 15.5 Hz, 1H), 6.18 (s, 2H), 4.24 (q, J = 7.0 Hz, 2H), 1.28 (t, J = 7.0 Hz, 3H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 186.88, 164.97, 152.45, 148.29, 136.74, 131.12, 130.79, 126.22, 108.30, 107.64, 102.36, 60.95, 14.01; MS-ESI (m/z): 249.13 [M + Na].
(E)-Ethyl 4-(2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-5-yl)-4-oxobut-2-enoate (9j). Yellow solid (44%). Mp: 57.7–59.4 °C. 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 7.96–7.89 (m, 3H), 6.92–6.90 (m, 1H), 6.69 (d, J = 15.5 Hz, 1H), 4.67 (t, J = 9.0 Hz, 2H), 4.24 (q, J = 7.0 Hz, 2H), 3.26 (t, J = 9.0 Hz, 2H), 1.28 (t, J = 7.0 Hz, 3H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 186.83, 165.03, 164.87, 137.03, 131.08, 130.70, 129.32, 128.85, 126.32, 72.43, 60.91, 28.25, 14.01; HRMS (ESI) m/z calcd for C14H14O4Na [M + Na] 269.0790, found 269.0791 [M + Na].
(E)-Ethyl 4-([1,1′-biphenyl]-4 yl)-4-oxobut-2-enoate (9k). Yellow solid (43%). Mp: 80.5–82.7 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.15–8.13 (m, 2H), 8.00 (d, J = 15.6 Hz, 1H), 7.90–7.88 (m, 2H), 7.78–7.76 (m, 2H), 7.55–7.51 (m, 2H), 7.47–7.43 (m, 1H), 6.76 (d, J = 15.6 Hz, 1H), 4.26 (q, J = 7.2 Hz, 2H), 1.29 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 3H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 188.63, 164.93, 145.38, 138.65, 136.74, 134.85, 131.51, 129.61, 129.13, 128.61, 127.19, 127.06, 61.02, 14.01; HRMS (ESI) m/z calcd for C18H16O3Na [M + Na] 303.0997, found 303.0990 [M + Na].
(E)-Ethyl 4-oxo-4-(4-phenoxyphenyl) but-2-enoate (9l). Yellow solid (41%). Mp: 53.7–55.5 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.12–8.06 (m, 2H), 7.94 (d, J = 15.6 Hz, 1H), 7.52–7.45 (m, 2H), 7.31–7.25 (m, 1H), 7.19–7.14 (m, 2H), 7.11–7.06 (m, 2H), 6.72 (d, J = 15.6 Hz, 1H), 4.24 (q, J = 7.2 Hz, 2H), 1.28 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 3H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 187.46, 164.93, 162.12, 154.65, 136.69, 131.59, 131.27, 130.75, 130.40, 125.04, 120.23, 117.27, 60.98, 13.99; HRMS (ESI) m/z calcd for C18H16O4Na [M + Na] 319.0946, found 319.0926 [M + Na].
(E)-Ethyl 4-(naphthalen-1-yl)-4-oxobut-2-enoate (9m). Yellow oil (42%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 8.52–8.50 (m, 1H), 8.05–8.03 (m, 1H), 7.94–7.88 (m, 1H), 7.87–7.85 (m, 1H), 7.74 (d, J = 15.6 Hz, 1H), 7.64–7.51 (m, 3H), 6.78 (d, J = 15.6 Hz, 1H), 4.30 (q, J = 7.2 Hz, 2H), 1.34 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 3H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 192.82, 164.88, 139.97, 133.66, 133.45, 132.00, 129.92, 129.72, 128.68, 128.15, 126.71, 125.10, 124.81, 61.03, 13.94; HRMS (ESI) m/z calcd for C16H14O3Na [M + Na] 277.0841, found 277.0837 [M + Na].
(E)-Ethyl 4-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-4-oxobut-2-enoate (9n). Yellow solid (43%). Mp: 67.3–69.2 °C. 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 7.81–7.80 (m, 1H), 7.70–7.69 (m, 1H), 7.61–7.59 (m, 1H), 7.39 (d, J = 16.0 Hz, 1H), 6.56 (d, J = 16.0 Hz, 1H), 4.22 (q, J = 7.0 Hz, 2H), 1.25 (t, J = 7.0 Hz, 3H); HRMS (ESI) m/z calcd for C12H10Cl2O3Na [M + Na] 294.9918, found 294.9918 [M + Na].
(E)-Ethyl 4-(4-nitrophenyl)-4-oxobut-2-enoate (9o). Yellow solid (42%). Mp: 69.4–71.5 °C. 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.38–8.35 (m, 2H), 8.27–8.25 (m, 2H), 7.93 (d, J = 15.5 Hz, 1H), 6.77 (d, J = 15.5 Hz, 1H), 4.26 (q, J = 7.0 Hz, 2H), 1.29 (t, J = 7.0 Hz, 3H); HRMS (ESI) m/z calcd for C24H21N2O10 [2M − H] 497.1196, found 497.1193 [2M − H].
(E)-Ethyl 4-(4-bromophenyl)-4-oxobut-2-enoate (9p). Yellow solid (44%). Mp: 62.3–64.7 °C. 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 7.99–7.97 (m, 2H), 7.91 (d, J = 15.5 Hz, 1H), 7.80–7.78 (m, 2H), 6.74 (d, J = 15.5 Hz, 1H), 4.25 (q, J = 7.0 Hz, 2H), 1.28 (t, J = 7.0 Hz, 3H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 188.50, 164.83, 136.42, 135.01, 132.10, 130.82, 128.33, 61.05, 14.00; HRMS (ESI) m/z calcd for C12H11BrO3Na [M + Na] 306.9769, found 306.9783 [M + Na].
(E)-Ethyl 4-(furan-2-yl)-4-oxobut-2-enoate (9q). Yellow solid (46%). Mp: 63.6–65.2 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.76 (d, J = 15.6 Hz, 1H), 7.71–7.67 (m, 1H), 7.38–7.37 (m, 1H), 6.98 (d, J = 15.6 Hz, 1H), 6.63–7.61 (m, 1H), 4.30 (q, J = 7.2 Hz, 2H), 1.35 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 3H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 175.50, 164.77, 151.98, 149.68, 135.96, 131.08, 121.59, 113.27, 61.03, 13.98; HRMS (ESI) m/z calcd for C10H10O4Na [M + Na] 217.0477, found 217.0456 [M + Na].
(E)-Ethyl 4-oxopent-2-enoate (9r). Yellow oil (40%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.00 (d, J = 16.0 Hz, 1H), 6.63 (d, J = 16.0 Hz, 1H), 4.25 (q, J = 7.2 Hz, 2H), 2.34 (s, 3H), 1.31 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 3H); MS-ESI (m/z): 165.09 [M + Na].
(E)-Ethyl 4-cyclohexyl-4-oxobut-2-enoate (9s). Yellow oil (39%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.14 (d, J = 16.0 Hz, 1H), 6.70 (d, J = 16.0 Hz, 1H), 4.26 (q, J = 7.2 Hz, 2H), 2.60–2.53 (m, 1H), 1.86–1.65 (m, 5H), 1.36–1.24 (m, 5H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 202.12, 165.01, 138.59, 130.00, 60.87, 47.89, 27.71, 25.37, 24.88, 13.88; HRMS (ESI) m/z calcd for C12H18O3Na [M + Na] 233.1154, found 233.1162 [M + Na].
(E)-Ethyl 4-cyclopropyl-4-oxobut-2-enoate (9t). Yellow oil (40%). 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.17 (d, J = 16.0 Hz, 1H), 6.71 (d, J = 16.0 Hz, 1H), 4.26 (q, J = 7.0 Hz, 2H), 2.22–2.17 (m, 1H), 1.32 (t, J = 7.0 Hz, 3H), 1.19–1.14 (m, 2H), 1.04–1.00 (m, 2H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 199.54, 165.16, 139.58, 130.26, 60.99, 19.37, 13.96, 11.77; MS-ESI (m/z): 191.22 [M + Na].
(E)-Isopropyl 4-(4-methoxyphenyl)-4-oxobut-2-enoate (10a). Yellow solid (45%), mp: 43.3–44.7 °C. 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.06–8.04 (m, 2H), 7.93 (d, J = 15.5 Hz, 1H), 7.11–7.09 (m, 2H), 6.67 (d, J = 15.5 Hz, 1H), 5.09–5.00 (m, 1H), 3.87 (s, 3H), 1.29 (s, 3H), 1.28 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 187.13, 164.50, 163.94, 136.66, 131.32, 129.01, 114.33, 68.53, 55.65, 21.49; HRMS (ESI) m/z calcd for C14H16O4Na [M + Na] 271.0946, found 271.0959 [M + Na].
(E)-Isopropyl 4-oxo-4-phenylbut-2-enoate (10b). Yellow oil (47%). 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.07–8.01 (m, 2H), 7.92 (d, J = 15.5 Hz, 1H), 7.74–7.70 (m, 1H), 7.62–7.57 (m, 2H), 6.70 (d, J = 15.5 Hz, 1H), 5.09–5.02 (m, 1H), 1.29 (s, 3H), 1.28 (s, 3H); HRMS (ESI) m/z calcd for C13H14O3Na [M + Na] 241.0841, found 241.0837 [M + Na].
(E)-Isopropyl 4-oxo-4-(p-tolyl) but-2-enoate (10c). Yellow solid (44%), mp: 60.2–61.9 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.92–7.86 (m, 3H), 7.32–7.30 (m, 2H), 6.85 (d, J = 15.6 Hz, 1H), 5.20–5.12 (m, 1H), 2.44 (s, 3H), 1.33 (s, 3H), 1.32 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 188.56, 164.43, 144.76, 136.65, 133.58, 131.71, 129.61, 128.96, 68.58, 21.48, 21.24; HRMS (ESI) m/z calcd for C14H16O3Na [M + Na] 255.0997, found 255.0982 [M + Na].
(E)-Isopropyl 4-(4-ethoxyphenyl)-4-oxobut-2-enoate (10d). Yellow solid (44%), mp: 38.6–40.5 °C. 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.04–8.02 (m, 2H), 7.93 (d, J = 15.5 Hz, 1H), 7.09–7.07 (m, 2H), 6.67 (d, J = 15.5 Hz, 1H), 5.11–4.99 (m, 1H), 4.15 (q, J = 7.0 Hz, 2H), 1.36 (t, J = 7.0 Hz, 3H), 1.29 (s, 3H), 1.28 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 187.07, 164.49, 163.25, 136.67, 131.34, 131.27, 128.84, 114.66, 68.51, 63.72, 21.48, 14.41; HRMS (ESI) m/z calcd for C15H18O4Na [M + Na] 285.1103, found 285.1107 [M + Na].
(E)-Isopropyl 4-(2-methoxyphenyl)-4-oxobut-2-enoate (10e). Yellow oil (43%). 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 7.65 (d, J = 15.5 Hz, 1H), 7.62–7.57 (m, 2H), 7.24–7.22 (m, 1H), 7.10–7.07 (m, 1H), 6.53 (d, J = 15.5 Hz, 1H), 5.05–5.00 (m, 1H), 3.89 (s, 3H), 1.27 (s, 3H), 1.26 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 190.64, 164.58, 158.62, 140.58, 134.71, 130.06, 129.73, 126.81, 120.82, 112.70, 68.46, 55.97, 21.46; HRMS (ESI) m/z calcd for C14H16O4Na [M + Na] 271.0946, found 271.0938 [M + Na].
(E)-Isopropyl 4-(3-methoxyphenyl)-4-oxobut-2-enoate (10f). Yellow oil (45%). 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 7.91 (d, J = 15.5 Hz, 1H), 7.67–7.61 (m, 1H), 7.54–7.47 (m, 2H), 7.30–7.28 (m, 1H), 6.70 (d, J = 15.5 Hz, 1H), 5.10–5.00 (m, 1H), 3.84 (s, 3H), 1.29 (s, 3H), 1.28 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 188.92, 164.34, 159.59, 137.42, 136.53, 132.05, 130.16, 121.47, 120.22, 112.82, 68.59, 55.34, 21.43; HRMS (ESI) m/z calcd for C14H16O4Na [M + Na] 271.0946, found 271.0932 [M + Na].
(E)-Isopropyl 4-(2,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-4-oxobut-2-enoate (10g). Yellow solid (40%). Mp: 43.5–45.7 °C. 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 7.66 (d, J = 15.5 Hz, 1H), 7.24–7.16 (m, 2H), 7.11–7.10 (m, 1H), 6.53 (d, J = 15.5 Hz, 1H), 5.08–4.99 (m, 1H), 3.84 (s, 3H), 3.75 (s, 3H), 1.27 (s, 3H), 1.25 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 190.20, 164.58, 153.15, 153.00, 140.52, 129.77, 127.09, 120.71, 114.34, 113.75, 68.46, 56.44, 55.56, 21.45; HRMS (ESI) m/z calcd for C15H18O5Na [M + Na] 301.1052, found 301.1062 [M + Na].
(E)-Isopropyl 4-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-4-oxobut-2-enoate (10h). Yellow solid (41%). Mp: 65.4–66.8 °C. 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 7.97 (d, J = 15.5 Hz, 1H), 7.78–7.76 (m, 1H), 7.51–7.50 (m, 1H), 7.12–7.11 (m, 1H), 6.69 (d, J = 15.5 Hz, 1H), 5.12–4.98 (m, 1H), 3.88 (s, 3H), 3.84 (s, 3H), 1.29 (s, 3H), 1.28 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 187.05, 164.55, 154.06, 149.03, 136.59, 131.31, 129.04, 124.35, 110.97, 110.38, 68.53, 55.87, 55.54, 21.50; HRMS (ESI) m/z calcd for C15H18O5Na [M + Na] 301.1052, found 301.1052 [M + Na].
(E)-Isopropyl 4-(Benzo[d][1,3] dioxol-5-yl)-4-oxobut-2-enoate (10i). Yellow solid (43%). Mp: 54.4–55.8 °C. 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 7.90 (d, J = 15.5 Hz, 1H), 7.74–7.72 (m, 1H), 7.51–7.50 (m, 1H), 7.09–7.08 (m, 1H), 6.66 (d, J = 15.5 Hz, 1H), 6.18 (s, 2H), 5.04 (m, 1H), 1.29 (s, 3H), 1.27 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 186.86, 164.46, 152.42, 148.27, 136.56, 131.51, 130.79, 126.17, 108.27, 107.62, 102.35, 68.53, 21.49; MS-ESI (m/z): 285.16 [M + Na].
(E)-Isopropyl 4-(2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-5-yl)-4-oxobut-2-enoate (10j). Yellow solid (41%). Mp: 65.6–66.9 °C. 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 7.97–7.86 (m, 3H), 6.91–6.89 (m, 1H), 6.64 (d, J = 15.5 Hz, 1H), 5.09–4.97 (m, 1H), 4.66 (t, J = 9.0 Hz, 2H), 3.25 (t, J = 9.0 Hz, 2H), 1.27 (s, 3H), 1.26 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 186.84, 164.85, 164.53, 136.88, 131.11, 131.07, 129.32, 128.84, 126.30, 109.18, 72.42, 68.48, 28.25, 21.49; HRMS (ESI) m/z calcd for C15H16O4Na [M + Na] 283.0946, found 283.0954 [M + Na].
(E)-Isopropyl 4-([1,1′-biphenyl]-4-yl)-4-oxobut-2-enoate (10k). Yellow solid (40%). Mp: 117.9–119.0 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 7.97–7.95 (m, 2H), 7.87–7.85 (m, 2H), 7.78–7.73 (m, 2H), 7.54–7.50 (m, 2H), 7.46–7.42 (m, 1H), 7.25 (d, J = 15.6 Hz, 1H), 6.37 (d, J = 15.6 Hz, 1H), 4.80 (m, 1H), 1.04 (s, 3H), 1.03 (s, 3H); MS-ESI (m/z): 317.21 [M + Na].
(E)-Isopropyl 4-oxo-4-(4-phenoxyphenyl) but-2-enoate (10l). Yellow solid (42%). Mp: 74.5–76.0 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.11–8.05 (m, 2H), 7.91 (d, J = 15.5 Hz, 1H), 7.53–7.45 (m, 2H), 7.31–7.24 (m, 1H), 7.19–7.14 (m, 2H), 7.11–7.06 (m, 2H), 6.69 (d, J = 15.5 Hz, 1H), 5.06–5.04 (m, 1H), 1.29 (s, 3H), 1.27 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 187.51, 164.45, 162.12, 154.65, 136.60, 131.67, 131.60, 130.76, 130.41, 125.05, 120.24, 117.29, 68.60, 21.50; HRMS (ESI) m/z calcd for C19H18O4Na [M + Na] 333.1103, found 333.1087 [M + Na].
(E)-Isopropyl 4-(naphthalen-1-yl)-4-oxobut-2-enoate (10m). Yellow oil (43%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 8.51–8.49 (m, 1H), 8.05–8.03 (m, 1H), 7.92–7.85 (m, 2H), 7.71 (d, J = 15.6 Hz, 1H), 7.66–7.50 (m, 3H), 6.75 (d, J = 15.6 Hz, 1H), 5.18–5.12 (m, 1H), 1.32 (s, 3H), 1.30 (s, 3H); HRMS (ESI) m/z calcd for C17H16O3Na [M + Na] 291.0997, found 291.1002 [M + Na].
(E)-Isopropyl 4-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-4-oxobut-2-enoate (10n). Yellow solid (45%). Mp: 58.0–60.1 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.51–7.44 (m, 3H), 7.37–7.35 (m, 1H), 6.63 (d, J = 16.0 Hz, 1H), 5.18–5.08 (m, 1H), 1.31 (s, 6H), 1.29 (s, 3H); HRMS (ESI) m/z calcd for C13H12Cl2O3Na [M + Na] 309.0061, found 309.0079 [M + Na].
(E)-Isopropyl 4-(4-nitrophenyl)-4-oxobut-2-enoate (10o). Yellow solid (44%). Mp: 81.5–82.7 °C. 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.42–8.34 (m, 2H), 8.29–8.21 (m, 2H), 7.90 (d, J = 15.5 Hz, 1H), 6.74 (d, J = 15.5 Hz, 1H), 5.09–5.04 (m, 1H), 1.30 (s, 3H), 1.28 (s, 3H); HRMS (ESI) m/z calcd for C13H12NO5 [M − H] 262.0715, found 262.0698 [M − H].
(E)-Isopropyl 4-(4-bromophenyl)-4-oxobut-2-enoate (10p). Yellow solid (41%). Mp: 101.7–102.5 °C. 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 7.98–7.96 (m, 2H), 7.89 (d, J = 15.5 Hz, 1H), 7.81–7.79 (m, 2H), 6.71 (d, J = 15.5 Hz, 1H), 5.10–4.99 (m, 1H), 1.29 (s, 3H), 1.28 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 188.54, 164.33, 136.32, 135.02, 132.10, 130.82, 128.30, 68.86, 21.49; HRMS (ESI) m/z calcd for C13H13BrO3Na [M + Na] 318.9946, found 318.9951 [M + Na].
(E)-Isopropyl 4-(furan-2-yl)-4-oxobut-2-enoate (10q). Yellow solid (42%). Mp: 41.7–43.4 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.73 (d, J = 15.6 Hz, 1H), 7.70–7.69 (m, 1H), 7.38–7.37 (m, 1H), 6.96 (d, J = 15.6 Hz, 1H), 6.63–6.62 (m, 1H), 5.19–5.10 (m, 1H), 1.33 (s, 6H), 1.31 (s, 1H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 175.53, 164.27, 151.98, 149.63, 135.83, 131.48, 121.50, 113.27, 68.66, 21.46; HRMS (ESI) m/z calcd for C10H10O4Na [M + Na] 231.0633, found 231.0632 [M + Na].
(E)-Isopropyl 4-oxopent-2-enoate (10r). Yellow oil (42%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 6.98 (d, J = 16.0 Hz, 1H), 6.61 (d, J = 16.0 Hz, 1H), 5.14–5.08 (m, 1H), 2.34 (s, 3H); MS-ESI (m/z): 179.14 [M + Na].
(E)-Isopropyl 4-cyclohexyl-4-oxobut-2-enoate (10s). Yellow oil (37%). 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.14 (d, J = 16.0 Hz, 1H), 6.67 (d, J = 16.0 Hz, 1H), 5.14–5.09 (m, 1H), 2.63–2.57 (m, 1H), 1.91–1.66 (m, 5H), 1.39–1.22 (m, 11H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 202.34, 164.57, 138.55, 130.46, 68.51, 47.74, 27.75, 25.37, 24.87, 21.44; MS-ESI (m/z): 247.20 [M + Na].
(E)-Isopropyl 4-cyclopropyl-4-oxobut-2-enoate (10t). Yellow oil (39%). 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.14 (d, J = 16.0 Hz, 1H), 6.69 (d, J = 16.0 Hz, 1H), 5.14–5.09 (m, 1H), 2.22–2.17 (m, 1H), 1.29 (s, 3H), 1.28 (s, 3H), 1.18–1.13 (m, 2H), 1.03–0.99 (m, 2H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 199.58, 164.66, 139.51, 130.71, 68.60, 21.47, 19.29, 11.71; HRMS (ESI) m/z calcd for C10H14O3Na [M + Na] 205.0841, found 205.0826 [M + Na].
(E)-2-((tert-Butoxycarbonyl) amino) ethyl 4-(4-methoxyphenyl)-4-oxobut-2-enoate (11a). White solid (81%), mp: 93.5–94.7 °C. 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.06–8.05 (m, 2H), 7.99 (d, J = 15.5 Hz, 1H), 7.11–7.10 (m, 2H), 7.05–7.03 (m, 1H), 6.69 (d, J = 15.5 Hz, 1H), 4.18–4.16 (m, 2H), 3.88 (s, 3H), 3.28–3.24 (m, 2H), 1.37 (s, 9H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 187.19, 164.92, 164.00, 155.71, 136.85, 131.38, 130.93, 129.01, 114.37, 77.85, 64.07, 55.71, 38.82, 28.19; HRMS (ESI) m/z calcd for C18H23NO6Na [M + Na] 372.1423, found 372.1441 [M + Na].
(E)-2-((tert-Butoxycarbonyl) amino) ethyl 4-oxo-4-phenylbut-2-enoate (11b). White solid (75%), mp: 95.5–96.8 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.08–8.02 (m, 2H), 7.97 (d, J = 15.6 Hz, 1H), 7.75–7.71 (m, 1H), 7.62–7.58 (m, 2H), 7.06–7.03 (m, 1H), 6.72 (d, J = 15.6 Hz, 1H), 4.18–4.16 (m, 2H), 3.28–3.24 (m, 2H), 1.37 (s, 9H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 189.33, 164.81, 155.71, 136.78, 136.02, 134.14, 131.59, 129.07, 128.82, 77.85, 64.14, 38.80, 28.19; HRMS (ESI) m/z calcd for C17H21NO5Na [M + Na] 342.1317, found 342.1320 [M + Na].
(E)-2-((tert-Butoxycarbonyl) amino) ethyl 4-oxo-4-(p-tolyl) but-2-enoate (11c). White solid (84%), mp: 88.7–91.4 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 7.99–7.95 (m, 3H), 7.41–7.39 (m, 2H), 7.06–7.03 (m, 1H), 6.70 (d, J = 15.6 Hz, 1H), 4.18–4.15 (m, 2H), 3.28–3.24 (m, 2H), 2.41 (s, 3H), 1.37 (s, 9H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 188.62, 164.85, 155.71, 144.88, 136.80, 133.58, 131.32, 129.65, 128.98, 77.85, 64.12, 38.80, 28.19, 21.21; HRMS (ESI) m/z calcd for C18H23NO5Na [M + Na] 356.1474, found 356.1469 [M + Na].
(E)-2-((tert-butoxycarbonyl) amino) ethyl 4-(4-ethoxyphenyl)-4-oxobut-2-enoate (11d). White solid (79%), mp: 96.5–97.6 °C. 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.05–8.03 (m, 2H), 7.98 (d, J = 15.5 Hz, 1H), 7.09–7.07 (m, 2H), 7.05–7.03 (m, 1H), 6.69 (d, J = 15.5 Hz, 1H), 4.22–4.10 (m, 4H), 3.28–3.25 (m, 2H), 1.42–1.31 (m, 12H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 187.13, 164.92, 163.31, 155.71, 136.86, 131.38, 130.87, 128.83, 114.71, 77.84, 64.07, 63.76, 38.81, 28.19, 14.43; HRMS (ESI) m/z calcd for C19H24NO6 [M − H] 362.1604, found 362.1595 [M − H].
(E)-2-((tert-Butoxycarbonyl) amino) ethyl 4-(2-methoxyphenyl)-4-oxobut-2-enoate (11e). White solid (84%), mp: 83.6–85.4 °C. 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 7.67 (d, J = 15.5 Hz, 1H), 7.64–7.55 (m, 2H), 7.24–7.22 (m, 1H), 7.11–7.06 (m, 1H), 7.01–7.99 (m, 1H), 6.55 (d, J = 15.5 Hz, 1H), 4.16–4.14 (m, 2H), 3.89 (s, 3H), 3.25–3.22 (m, 2H), 1.35 (s, 9H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 190.84, 165.05, 158.62, 155.67, 140.72, 134.69, 130.00, 129.37, 126.88, 120.81, 112.67, 77.78, 63.89, 55.98, 38.80, 28.15; HRMS (ESI) m/z calcd for C18H23NO6Na [M + Na] 372.1423, found 372.1424 [M + Na].
(E)-2-((tert-Butoxycarbonyl) amino) ethyl 4-(3-eethoxyphenyl)-4-oxobut-2-enoate (11f). White solid (81%), mp: 65.7–66.8 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 7.96 (d, J = 15.6 Hz, 1H), 7.66–7.64 (m, 1H), 7.55–7.48 (m, 2H), 7.31–7.28 (m, 1H), 7.06–7.03 (m, 1H), 6.71 (d, J = 15.6 Hz, 1H), 4.18–4.15 (m, 2H), 3.85 (s, 3H), 3.28–3.24 (m, 2H), 2.50 (s, 9H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 189.08, 164.79, 159.64, 155.71, 137.42, 136.78, 131.67, 130.26, 121.52, 120.37, 112.89, 77.85, 64.14, 55.43, 38.80, 28.18; MS-ESI (m/z): 372.20 [M + Na].
(E)-2-((tert-Butoxycarbonyl) amino) ethyl 4-(2,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-4-oxobut-2-enoate (11g). Yellow oil (81%). 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 7.68 (d, J = 15.5 Hz, 1H), 7.24–7.16 (m, 2H), 7.10–7.09 (m, 1H), 7.01–6.99 (m, 1H), 6.55 (d, J = 15.5 Hz, 1H), 4.16–4.14 (m, 2H), 3.84 (s, 3H), 3.75 (s, 3H), 3.25–3.22 (m, 2H), 1.36 (s, 9H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 190.44, 165.06, 155.69, 153.15, 152.99, 140.66, 129.44, 127.16, 120.69, 114.33, 113.73, 77.81, 63.89, 56.46, 55.60, 38.81, 28.16; HRMS (ESI) m/z calcd for C19H25NO7Na [M + Na] 402.1529, found 402.1519 [M + Na].
(E)-2-((tert-Butoxycarbonyl) amino) ethyl 4-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-4-oxobut-2-enoate (11h). Orange solid (69%), mp: 100.0–101.7 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.02 (d, J = 15.6 Hz, 1H), 7.80–7.77 (m, 1H), 7.53–7.52 (m, 1H), 7.13–7.11 (m, 1H), 7.06–7.03 (m, 1H), 6.71 (d, J = 15.6 Hz, 1H), 4.18–4.16 (m, 2H), 3.88 (s, 3H), 3.85 (s, 3H), 3.28–3.24 (m, 2H), 1.37 (s, 9H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 187.08, 164.95, 155.71, 154.10, 149.05, 136.73, 130.91, 129.03, 124.35, 110.99, 110.42, 77.84, 64.05, 55.90, 55.56, 38.81, 28.19; HRMS (ESI) m/z calcd for C19H25NO7Na [M + Na] 402.1529, found 402.1540 [M + Na].
(E)-2-((tert-Butoxycarbonyl) amino) ethyl 4-(benzo[d][1,3] dioxol-5-yl)-4-oxobut-2-enoate (11i). Brown solid (68%), mp: 115.0–117.4 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 7.96 (d, J = 15.6 Hz, 1H), 7.76–7.73 (m, 1H), 7.52–7.51 (m, 1H), 7.11–7.09 (m, 1H), 7.06–7.03 (m, 1H), 6.68 (d, J = 15.6 Hz, 1H), 6.18 (s, 2H), 4.17–4.14 (m, 2H), 3.28–3.24 (m, 2H), 1.37 (s, 9H); MS-ESI (m/z): 386.16 [M + Na].
(E)-2-((tert-Butoxycarbonyl) amino) ethyl 4-(2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-5-yl)-4-oxobut-2-enoate (11j). White solid (67%), mp: 106.0–107.6 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.00–7.96 (m, 2H), 7.93–7.90 (m, 1H), 7.06–7.03 (m, 1H), 6.94–6.92 (m, 1H), 6.68 (d, J = 15.6 Hz, 1H), 4.68 (t, J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 4.17–4.15 (m, 2H), 3.29–3.24 (m, 4H), 1.37 (s, 9H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 186.90, 164.95, 164.92, 155.71, 137.09, 131.12, 130.72, 129.32, 128.92, 126.33, 109.22, 77.84, 72.46, 64.06, 38.81, 28.26, 28.19; HRMS (ESI) m/z calcd for C19H23NO6Na [M + Na] 384.1423, found 384.1416 [M + Na].
(E)-2-((tert-Butoxycarbonyl) amino) ethyl 4-([1,1′-biphenyl]-4-yl)-4-oxobut-2-enoate (11k). Yellow solid (62%), mp: 87.4–89.1 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.16–8.14 (m, 2H), 8.03 (d, J = 15.6 Hz, 1H), 7.91–7.89 (m, 2H), 7.81–7.76 (m, 2H), 7.57–7.51 (m, 2H), 7.51–7.44 (m, 1H), 7.08–7.05 (m, 1H), 6.75 (d, J = 15.6 Hz, 1H), 4.20–4.17 (m, 2H), 3.30–3.25 (m, 2H), 1.38 (s, 9H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 188.70, 164.85, 155.71, 145.43, 138.64, 136.78, 134.86, 131.52, 129.62, 129.16, 129.11, 128.65, 127.22, 127.08, 127.05, 77.86, 64.15, 38.82, 28.19; MS-ESI (m/z): 418.15 [M + Na].
(E)-2-((tert-Butoxycarbonyl) amino) ethyl 4-oxo-4-(4-phenoxyphenyl) but-2-enoate (11l). Brown solid (60%), mp: 76.4–78.7 °C. 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.10–8.08 (m, 2H), 7.97 (d, J = 15.5 Hz, 1H), 7.50–7.47 (m, 2H), 7.29–7.28 (m, 1H), 7.22–7.13 (m, 2H), 7.10–7.08 (m, 2H), 7.05–7.03 (m, 1H), 6.71 (d, J = 15.5 Hz, 1H), 4.18–4.16 (m, 2H), 3.28–3.24 (m, 2H), 1.37 (s, 9H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 187.50, 164.85, 162.16, 155.70, 154.64, 136.71, 131.59, 131.27, 130.75, 130.41, 125.06, 120.24, 117.29, 77.84, 64.10, 38.81, 28.18; MS-ESI (m/z): 434.19 [M + Na].
(E)-2-((tert-Butoxycarbonyl) amino) ethyl 4-(naphthalen-1-yl)-4-oxobut-2-enoate (11m). Yellow solid (57%), mp: 74.7–76.0 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.92–8.90 (m, 1H), 8.46–8.44 (m, 1H), 8.24–8.19 (m, 2H), 8.08–8.02 (m, 4H), 7.75 (d, J = 15.6 Hz, 1H), 7.72–7.58 (m, 6H), 7.42 (d, J = 12.0 Hz, 1H), 7.04–7.01 (m, 1H), 6.83–6.81 (m, 1H), 6.64 (d, J = 15.6 Hz, 1H), 6.37 (d, J = 12.0 Hz, 1H), 4.18–4.15 (m, 2H), 3.89–3.86 (m, 2H), 3.26–3.24 (m, 2H), 3.04–3.00 (m, 2H), 1.35 (s, 9H), 1.34 (s, 9H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 193.07, 164.83, 155.69, 140.06, 133.74, 133.45, 132.10, 129.81, 129.71, 128.73, 128.21, 126.77, 125.05, 124.84, 77.82, 64.17, 38.77, 28.16; MS-ESI (m/z): 392.20 [M + Na].
(E)-2-((tert-Butoxycarbonyl) amino) ethyl 4-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-4-oxobut-2-enoate (11n). Yellow solid (56%), mp: 54.6–56.3 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 7.82–7.81 (m, 1H), 7.69–7.67 (m, 1H), 7.62–7.59 (m, 1H), 7.41 (d, J = 16.0 Hz, 1H), 7.02–6.99 (m, 1H), 6.52 (d, J = 16.0 Hz, 1H), 4.16–4.13 (m, 2H), 3.24–3.20 (m, 2H), 1.35 (s, 9H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 188.53, 164.73, 155.69, 136.41, 135.02, 132.12, 130.79, 128.37, 77.85, 64.15, 38.79, 28.18; HRMS (ESI) m/z calcd for C17H19Cl2NO5Na [M + Na] 410.0538, found 410.0560 [M + Na].
(E)-2-((tert-Butoxycarbonyl) amino) ethyl 4-(4-nitrophenyl)-4-oxobut-2-enoate (11o). Yellow solid (55%), mp: 86.6–88.5 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.43–8.34 (m, 2H), 8.27–8.25 (m, 2H), 7.96 (d, J = 15.6 Hz, 1H), 7.06–7.03 (m, 1H), 6.76 (d, J = 15.6 Hz, 1H), 4.19–4.17 (m, 2H), 3.28–3.24 (m, 2H), 1.37 (s, 9H); HRMS (ESI) m/z calcd for C17H19N2O7 [M − H] 363.1193, found 363.1201 [M − H].
(E)-2-((tert-Butoxycarbonyl) amino) ethyl 4-(4-bromophenyl)-4-oxobut-2-enoate (11p). Yellow solid (53%), mp: 86.6–88.5 °C. 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 7.99–7.97 (m, 2H), 7.94 (d, J = 15.5 Hz, 1H), 7.81–7.79 (m, 2H), 7.05–7.03 (m, 1H), 6.73 (d, J = 15.5 Hz, 1H), 4.18–4.16 (m, 2H), 3.28–3.24 (m, 2H), 1.37 (s, 9H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 188.53, 164.73, 155.69, 136.41, 135.02, 132.12, 130.79, 128.37, 77.85, 64.15, 38.79, 28.18; MS-ESI (m/z): 420.10 [M + Na].
(E)-2-((tert-Butoxycarbonyl) amino) ethyl 4-(furan-2-yl)-4-oxobut-2-enoate (11q). White solid (55%), mp: 86.6–88.5 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.16–8.15 (m, 1H), 7.84–7.83 (m, 1H), 7.78 (d, J = 15.6 Hz, 1H), 7.04–7.01 (m, 1H), 6.84–6.82 (m, 1H), 6.78 (d, J = 15.6 Hz, 1H), 4.18–4.15 (m, 2H), 3.27–3.23 (m, 2H), 1.37 (s, 9H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 175.54, 164.69, 155.70, 151.97, 149.77, 149.74, 136.01, 131.08, 121.66, 121.62, 113.29, 77.85, 64.10, 38.79, 28.18; HRMS (ESI) m/z calcd for C15H19NO6Na [M + Na] 332.1110, found 332.1105 [M + Na].
(E)-2-((tert-Butoxycarbonyl) amino) ethyl 4-oxopent-2-enoate (11r). White solid (51%), mp: 96.7–98.6 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 7.02–7.00 (m, 1H), 6.90 (d, J = 16.0 Hz, 1H), 6.72 (d, J = 16.0 Hz, 1H), 4.15–4.12 (m, 2H), 3.24–3.20 (m, 2H), 2.35 (s, 3H), 1.37 (s, 9H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 198.33, 165.15, 155.67, 140.21, 131.14, 77.84, 63.99, 38.77, 28.19, 27.88; HRMS (ESI) m/z calcd for C12H19NO5Na [M + Na] 280.1161, found 280.1162 [M + Na].
(E)-2-((tert-Butoxycarbonyl) amino) ethyl 4-cyclohexyl-4-oxobut-2-enoate (11s). Yellow solid (48%), mp: 70.1–72.8 °C. 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.19 (d, J = 16.0 Hz, 1H), 6.70 (d, J = 16.0 Hz, 1H), 4.79 (s, 1H), 4.27–4.25 (m, 2H), 3.45–3.44 (m, 2H), 2.61–2.56 (m, 1H), 1.88–1.79 (m, 5H), 1.44 (s, 9H), 1.40–1.19 (m, 5H); MS-ESI (m/z): 348.22 [M + Na].
(E)-2-((tert-Butoxycarbonyl) amino) ethyl 4-cyclopropyl-4-oxobut-2-enoate (11t). White solid (47%), mp: 70.1–73.4 °C. 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.19 (d, J = 16.0 Hz, 1H), 6.72 (d, J = 16.0 Hz, 1H), 4.79 (s, 1H), 4.28–4.26 (m, 2H), 3.45–3.44 (m, 2H), 2.22–2.17 (m, 1H), 1.44 (s, 9H), 1.21–1.14 (m, 2H), 1.06–1.02 (m, 2H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 199.61, 165.08, 155.68, 139.64, 130.24, 77.83, 63.99, 38.77, 19.39, 11.74; HRMS (ESI) m/z calcd for C14H21NO5Na [M + Na] 306.1317, found 306.1309 [M + Na].
In vitro protein kinase assay12
The inhibition rates and IC50 values of target compounds were determined by a non-radioactive assay using Promega ‘Kinase Glo’ plus Luminescent Kinase assay kit. The assay was carried out in a 96-well plate and the reaction mixture was prepared: 3 μM PknB12 in buffer (25 mL Tris–HCl pH 7.4, 5 mM MgCl2, 2 mM MnCl2) containing the compound at various concentrations. Following inculation at 4 °C for 30 min, ATP was added to the reaction buffer at the final concentration of 100 μM, and the plates were conducted at 37 °C for 3 hours. Multilabel Plate Reader (PE Envision) was used to measure the intensity of luminescence signal with addition of 50 μL Kinase Glo reagent. The inhibition rates were calculated by the following formula and the IC50 values were calculated using the GraphPad Prism5 software.ΔLN: luminescence intensity of negative control; ΔLS: luminescence intensity of sample; ΔLP: luminescence intensity of positive control.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing financial interests.Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Science and Technology Project of China (No. 2014ZX09201001-011), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81373452, 81302644, 81473098, 81473099 and 30970038), and the National Infrastructure of Microbial Resources (No. NIMR-2016-03). Liyan Yu is supported by Xiehe Scholar.Notes and references
- P. Barthe, G. V. Mukamolova, C. Roumestand and M. Cohen-Gonsaud, Structure, 2010, 18, 606–615 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. M. Kang, D. W. Abbott, S. T. Park, C. C. Dascher, L. C. Cantley and R. N. Husson, Genes Dev., 2005, 19, 1692–1704 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. Sharma, M. Gupta, A. Krupa, N. Srinivasan and Y. Singh, FEBS J., 2006, 273, 2711–2721 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Dasgupta, P. Datta, M. Kundu and J. Basu, Microbiology, 2006, 152, 493–504 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. Fernandez, B. Saint-Joanis, N. Barilone, M. Jackson, B. Gicquel, S. T. Cole and P. M. Alzari, J. Bacteriol., 2006, 188, 7778–7784 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Ortiz-Lombardía, F. Pompeo, B. Boitel and P. Alzari, J. Biol. Chem., 2003, 278, 13094–13100 CrossRef PubMed.
- A. Narayan, P. Sachdeva, K. Sharma, A. K. Saini, A. K. Tyagi and Y. Singh, Physiol. Genomics, 2007, 29, 66–75 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Villarino, R. Duran, A. Wehenkel, P. Fernandez, P. England, P. Brodin, S. T. Cole, U. Zimny-Arndt, P. R. Jungblut, C. Cerveñansky and P. M. Alzari, J. Mol. Biol., 2005, 350, 953–963 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. A. Young, B. Delagoutte, J. A. Endrizzi, A. M. Falick and T. Alber, Nat. Struct. Biol., 2003, 10, 168–174 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Seal, P. Yogeeswari, D. Sriram, O. S. D. D. Consortium and D. J. Wild, J. Cheminf., 2013, 14(5), 2–11 Search PubMed.
- Y. Xing, B. Huang, J. Xu, L. L. Zhao, S. Y. Si, Y. C. Wang, X. F. You and L. Y. Yu, Microbiology, 2014, 41, 646–653 CAS.
- Q. Zhai, J. Pang, G. Li, C. Li, X. Yang, L. Yu, Y. Wang, J. Li and X. You, Acta Pharm. Sin. B, 2015, 5, 467–472 CrossRef PubMed.
- A. Koul, E. Arnoult, N. Lounis, J. Guillemont and K. Andries, Nature, 2011, 469, 483–490 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Žari, M. Kudrjashova, T. Pehk, M. Lopp and T. Kanger, Org. Lett., 2014, 16, 1740–1743 CrossRef PubMed.
- A. J. Hirsh, B. F. Molino, J. Zhang, N. Astakhova, W. B. Geiss, B. J. Sargent, B. D. Swenson, A. Usyatinsky, M. J. Wyle, R. C. Boucher, R. T. Smith, A. Zamurs and M. R. Johnson, J. Med. Chem., 2006, 49, 4098–4115 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- N. V. Tolstoluzhsky, N. Y. Gorobets, N. N. Kolos and S. M. Desenko, J. Comb. Chem., 2008, 10, 893–896 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Srinivas, C. M. Haricharan Raju and P. V. R. Acharyulu, Org. Process Res. Dev., 2004, 8, 291–292 CrossRef CAS.
Footnotes |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available: NMR spectra of synthesized compounds. See DOI: 10.1039/c6ra24953a |
| ‡ These authors contributed equally to this work. |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 |