Thermal stability enhancement of hydrogen bonded semicrystalline thermoplastics achieved by combination of aramide chemistry and supramolecular chemistry†
Abstract
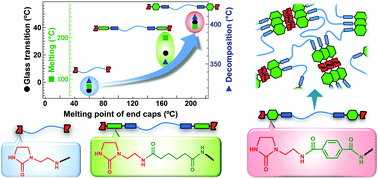
Thermo-stability enhancement of supramolecular thermoplastics is a meaningful task to enable more application for their usage at high temperatures. An inspiration from aromatic polyamide (aramide) led us to prepare multi-block semicrystalline supramolecular polymers bearing an amorphous dicarboxylic central block and end caps composed of a hydrogen bonding unit (UDETA) and an aramide unit (NHCO-phenyl ring-OCHN). We also prepared three other semicrystalline materials to demonstrate thermal property tuning by simply varying the end caps. The thermal properties of the semicrystalline compounds, including glass transition temperature (Tg) and melting point (Tm) measured by differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), decomposition temperature (Td) measured by thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), and softening temperature (Tsoftening) measured by dynamic mechanical analysis (DMA), were systematically varied depending on the thermal features of the end caps. Especially, Tm and Td were found to be higher than 200 °C and 400 °C, respectively, when both hydrogen bonding and aramide fragments were present. Melt viscosity investigated by rheology was lower than 1 Pa s for each compound due to the low molecular weight of the components (nearly 1200 g mol−1 or less), which is desirable for practical melt processing. Interestingly, shear thinning behavior was observed only in the aramide unit incorporated compound among all the compounds. This indicates a highly clusterable nature of the aramide fragments, which was also supported by the data of its larger flow activation energy than other compounds bearing no aramide fragments. Between Tg and Tm, a large elastic plateau region was observed in the DMA measurements for all compounds, despite their low molecular weight, meaning that the flexible strands are effectively connected into a network through crystallized end-capping groups.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...