Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleCreative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported Licence
Inhibition of the key enzyme of sialic acid biosynthesis by C6-Se modified N-acetylmannosamine analogs†
Olaia
Nieto-Garcia‡
a,
Paul R.
Wratil‡
b,
Long D.
Nguyen
b,
Verena
Böhrsch
a,
Stephan
Hinderlich
*c,
Werner
Reutter
*b and
Christian P. R.
Hackenberger
*ad
aLeibniz-Institut für Molekulare Pharmakologie, Robert-Roessle-Strasse 10, 13125 Berlin, Germany
bInstitut für Laboratoriumsmedizin, Klinische Chemie und Pathobiochemie, Charié-Universitätsmedizin Berlin, Arnimalee 22, 14195 Berlin, Germany. E-mail: werner.reutter@charite.de
cBeuth Hochschule für Technik Berlin, Department Life Sciences & Technology, Seestrase 64, 13347 Berlin, Germany. E-mail: hinderlich@beuth-hochschule.de
dHumboldt Universität zu Berlin, Department Chemie, Brook-Taylor-Strasse 2, 12489, Berlin, Germany. E-mail: hackenbe@fmp-berlin.de
First published on 19th February 2016
Abstract
Synthetically accessible C6-analogs of N-acetylmannosamine (ManNAc) were tested as potential inhibitors of the bifunctional UDP-N-acetylglucosamine-2-epimerase/N-acetylmannosamine kinase (GNE/MNK), the key enzyme of sialic acid biosynthesis. Enzymatic experiments revealed that the modification introduced at the C6 saccharide position strongly influences the inhibitory potency. A C6-ManNAc diselenide dimer showed the strongest kinase inhibition in the low μM range among all the substrates tested and successfully reduced cell surface sialylation in Jurkat cells.
Introduction
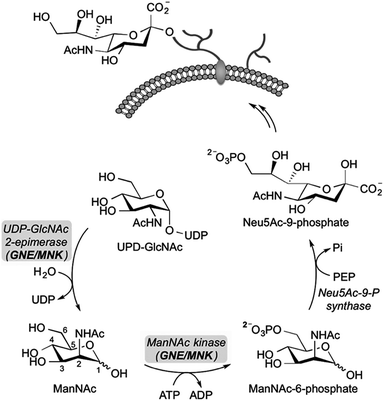
Sialic acid is an essential component of the periphery of the glycocalyx. Sialylated glycoconjugates are involved in a broad range of cell functions and biological interactions including recognition of pathogens and immune regulation, among others.1–3 For instance, it is known that the influenza virus invades host cells through sialic acid recognition.4 Many tumor cells show an altered glycosylation pattern with increased expression of sialic acids on their surface.5,6 Assumingly, this oversialylation may act as a shield to protect these tumor cells from immune recognition.7,8 Nowadays, the elucidation of the precise role of sialic acids in glycan-mediated cellular interactions is a field of growing interest. For studying cell-surface glycosylation metabolic oligosaccharide-engineering (MOE) is a well-established tool to modify and visualize sialic acids on the cell membrane even in living animals.9 By this strategy, unnatural N-acetylmannosamine (ManNAc) analogs can be efficiently incorporated into membrane glycoconjugates utilizing the sialic acid biosynthetic pathway, which can be subsequently labeled with bioorthogonal reactions.9–12 Regarding sialic acid expression, inhibitors of sialyltransferases, a group of enzymes that facilitate the transfer of sialic acid onto glycoconjugates in the Golgi lumen, were reported to efficiently reduce cell surface sialylation in vitro13,14 and in vivo.15 Another promising approach for the study of sialic acid related biological processes is the development of inhibitors targeting the de novo biosynthesis of this sugar. The key enzyme of sialic acid biosynthesis is the bifunctional UDP-N-acetylglucosamine-2-epimerase/N-acetylmannosamine kinase (GNE/MNK), which consequently serves as an important regulator of cell surface sialylation in mammals.16 Specifically, the GNE domain of the enzyme first isomerizes UPD-N-acetylglucosamine (UPD-GlcNAc) into ManNAc, which is then phosphorylated at the 6-hydroxy position under consumption of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) by the MNK domain (Scheme 1).To date, known GNE/MNK inhibitors were synthesized based on unnatural monosaccharides, including N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc), UDP-GlcNAc and ManNAc analogs (Fig. 1).17–23
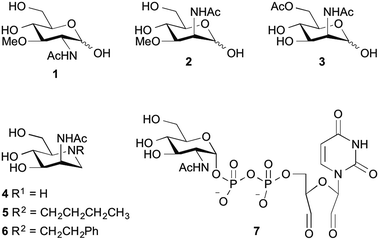
Among all reported inhibitors, only 3-O-methyl-N-acetyl-glucosamine (1) and the methylated ManNAc analog 2 were tested in eukaryotic cells. For instance, the methylated GlcNAc analog 1 at 1 mM final concentration reduced the incorporation rate of N-GlcNAc and N-ManNAc into glycoproteins by 70% in HepG2 cells.17 More recently, the methylated ManNAc analog 2 showed reduction of cell surface sialylation to 20% using 500 μM final concentration of the inhibitor in culture medium.22 Other reported inhibitors, including 6-O-Ac-ManNAc (3), iminosugars 4–6 and 2′,3′-dialdehydo-UPD-N-acetylglucosamine (7) were tested with either the purified ManNAc kinase (3 at 5 mM final concentration) or UDP-GlcNAc-2-epimerase/MNK kinase (4–6 at 1 mM; 7 at 300 μM) and showed an inhibition of the corresponding enzyme by 60%, 70% and 93%, respectively.18,20,23 Despite these studies, the need of high inhibitor concentrations for an efficient reduction of cell surface sialylation limits the applicability for further studies, especially for in vivo experiments, and points towards the need of novel potent inhibitors for sialic acid de novo biosynthesis.
In this manuscript, we report the synthesis and evaluation of sulfur and selenium-based C6-derivatives of N-acetylmannosamine as potential inhibitors of the human MNK. We hypothesized that C6-ManNAc derivatives cannot be phosphorylated by MNK, making them competitive inhibitors for this enzyme. Our concept was supported by investigating the crystal structure of human MNK in complex with its natural substrate, ManNAc.23 The geometry of the active site revealed that only the hydroxyl moiety at the C6 position of ManNAc is sterically accessible for substrate modifications. For this purpose, we planned to access C6-modified ManNAc analogs, in which larger selenium or sulfur atoms replaced the oxygen at position C6, presumably leading to a better blockage of the binding pocket. Furthermore, we reasoned that these C6-modifications would be promising for inhibitory studies in living cells in contrast to compound 3, in which the acetylated C6-hydroxyl group is cleaved by endogenous esterases.
Results and discussion
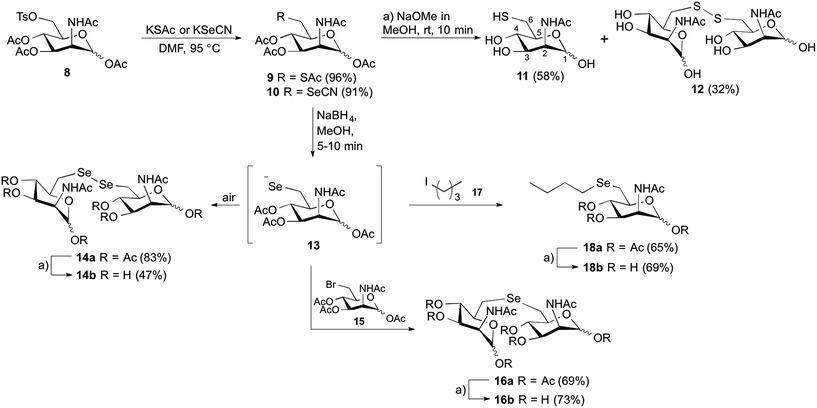
The synthetic strategy was designed to be versatile and accessible from previously described tosylated ManNAc 8 (Scheme 2),24 which can react with appropriate S- or Se-nucleophiles. Considering the S-derivatives, the peracetylated thiol derivative 9 was obtained from 8 by nucleophilic substitution employing potassium thioacetate. In order to obtain water-soluble compounds suitable for enzymatic in vitro assays, simultaneous deprotection of S- and O-acetyl groups was carried out using standard basic conditions; however, to avoid epimerization at position C2 it was crucial to limit the time of basic deprotection with sodium methoxide to 10 min.25 We observed the formation of thiol 11 and the disulfide 12 based on the 1H-NMR shift of the protons at position C6,26 which were both isolated and employed in further enzymatic MNK-assays. To prepare the corresponding C6-Se-ManNAc-analogues, we employed the same electrophilic building block 8 from above. After reaction with nucleophilic potassium selenocyanate as the Se-source, compound 10 was obtained in 91% yield after purification. The chemoselective reduction of selenocyanate in presence of O-acetyl groups was ensured by using sodium borohydride, followed by acidification and stirring under inert atmosphere. Although the selenol could be observed after the acidification as a minor peak by UPLC-MS analysis, the high oxidation potential of the selenolate prevented the isolation of the corresponding selenol. Instead, the diselenide dimer 14a was obtained in 83% yield and analyzed by 77Se NMR, displaying the characteristic shift for diselenides at 319–323 ppm. The treatment with sodium methoxide in methanol and subsequent neutralization afforded the unprotected seleno sugar-dimer 14b in a moderate yield of 47%, most likely due to the cleavage of the labile C–Se bond as previously reported.27 With compounds 11, 12 and 14b in hand we tested the inhibitory effect in an MNK activity assay. Human MNK was expressed in BL21-CodonPlus (DE3)-RIL Escherichia coli (Stragene) and purified according to an established method.23 The half maximal inhibitory concentrations (IC50) of modified ManNAc analogs for MNK activity have been measured in vitro using a coupled optical assay based on consumption of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH, details in ESI†). Herein, purified enzyme was incubated with ManNAc (125 μM), the natural substrate for the kinase, ATP and varying concentrations of the previously synthesized C6-modified ManNAc analogs 11, 12 and 14b. With an IC50 value of 8.5 μM, the diselenide 14b showed the strongest inhibition of enzyme activity among all tested substances (Table 1, entries 1–3 and Fig. 2A). Encouraged by these results, we also prepared the selenoethers 16b and 18b, to further probe the influence of the second selenium atom as well as the second sugar moiety on enzyme activity. Thereby, we took advantage of the nucleophilic properties of the selenolate anion precursor 13 to access the selenoethers. Seleno cyanate 10 was reductively cleaved with sodium borohydride for 5–10 min (monitored by TLC) and the high reactive selenolate anion 13 was caught in situ by Ac3-6-Br-ManNAc (15) or 1-iodopentane (17) (Scheme 2). An excess of the electrophiles was used to decrease the formation of the diselenide 14a. The desired seleno compounds 16a and 18a were isolated in 69% and 65%, respectively. The treatment with sodium methoxide delivered unprotected seleno sugars 16b and 18b as described for 14b before. MNK activity studies with selenoethers revealed significantly lower inhibition in comparison to the diselenide 14b (Table 1, entry 4 and 5).| Entry | Compound | IC50 (mM) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 11 | >10 |
| 2 | 12 | 4.2 (±0.7) |
| 3 | 14b | 8.5 × 10−3 (±1.9 × 10−3) |
| 4 | 16b | 3.0 (±0.7) |
| 5 | 18b | 1.9 (±0.5) |
The performed MNK activity studies for the sulfur and seleno analogs 11, 12, 14b, 16b and 18b indicated that a combination of a diselenide bond together with an additional ManNAc unit is highly beneficial for the enzyme inhibition. In the homodimeric ManNAc derivatives the backbone structure of ManNAc appears twice, giving two potential binding partners for the ManNAc-binding site of MNK. Consequently, this leads to a stochiometrical advantage for dimeric inhibitors, and therefore increases their inhibitory potential compared to monosaccharide ManNAc analogs that have been previously reported as MNK inhibitors.17–23 Comparing the results of the enzymatic studies with 14b and 16b, the length and type of the selenide-linker is apparently of great importance for MNK inhibition. The C–Se–Se–C linker in 14b is longer, but also could be more flexible than the C–Se–C linker in 16b. This feature as well as the length and the angle of the C–Se bond could be essential for successful positioning of the inhibitor into the active binding pocket of the MNK.28 In addition, different van der Waals interactions and H-bonding properties of selenium and sulfur atoms could play a role for protein binding.23 Even though they share a high structural similarity, compound 12 had an approximately 500-fold higher IC50 in comparison to 14b.
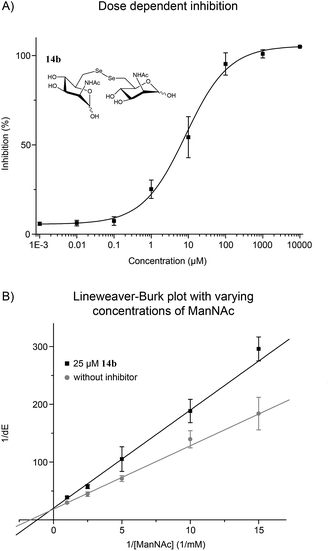
With the potent diselenide compound 14b in hand, we further studied the binding properties of this potent MNK inhibitor, which is to our knowledge the strongest MNK inhibitor reported to date. Diselenide 14b inhibited MNK activity in a dose dependent manner (Fig. 2A). Additionally, we performed the enzymatic assay in presence of 14b (25 μM) and different concentrations of ManNAc and confirmed a competitive inhibition of 14b for ManNAc. The inhibitor constant (Ki) value obtained was 15.7 μM (Fig. 2B). Additionally, we tested if diselenide 14b influenced the GNE activity of the bifunctional GNE/MNK. Analysis of GNE/MNK in mouse liver cytosol revealed an IC50 of 14b for inhibiting the GNE activity in the range of 200 μM (details in ESI†). This result indicates that the main inhibitory effect of 14b on sialic acid biosynthesis is due to MNK inhibition, although the GNE activity appears to be influenced by the diselenide 14b, likely due to an allosteric effect of the binding of the inhibitor to the MNK domain. To evaluate the specificity of the inhibitor towards other sugar kinases, we performed further inhibition studies using human GlcNAc kinase (GNK) and hexokinase (HK) from yeast (details in ESI†). The IC50 of 14b for GNK activity was about 1.7 mM, and higher than 5 mM for HK activity, respectively, indicating that the effects of 14b on these other sugar kinases are non-specific and negligible.
At this stage, we also wanted to evaluate the stability of the diselenide 14b in presence of thiol-containing reducing agents like dithiothreitol (DTT) or glutathione (GSH) to address the application of our compounds in living cells. Therefore, the possible reduction of the diselenide bond was monitored by 77Se NMR using a solution of 60 mM concentration of 14b in an aqueous saturated DTT solution at room temperature. Immediately after the addition of 14b to the DTT solution, a characteristic signal for the selenol compound at −48.1 ppm was observed and a major peak at 294 ppm related to the diselenide. Concretely, the integration of diselenide/selenol peaks gave a 90![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10 ratio (details in ESI†). Due to the most stable oxidation state, in the time period between 15 min and 5 h, only signals from the diselenide were detected. In the case of saturated GSH solution, using the same procedure as before, only diselenide 14b was detected after incubation at 60 mM.
10 ratio (details in ESI†). Due to the most stable oxidation state, in the time period between 15 min and 5 h, only signals from the diselenide were detected. In the case of saturated GSH solution, using the same procedure as before, only diselenide 14b was detected after incubation at 60 mM.
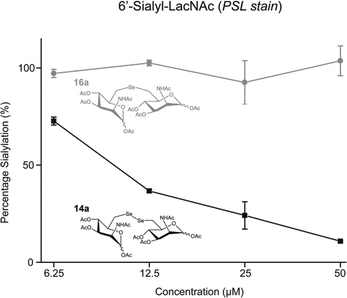
Encouraged by the strong in vitro inhibition of 14b and its high stability in the presence of reducing agents, we evaluated the capability of this substance to reduce cell surface sialylation. Due to the fact that peracetylated ManNAc derivatives are known to have better membrane permeability,29 the corresponding peracetylated diselenide 14a was used as a prodrug like precursor of 14b for cell experiments. Additionally, selenide 16a was chosen as a control because it shares high structural similarity to 14a, but had only weak effects on the enzyme activity of MNK (Table 1). Jurkat cells were treated for 72 h with different concentrations of peracetylated diselenide 14a and selenide 16a. First, the cytotoxicity of 14a as well as 16a was evaluated using the AlamarBlue© cell viability assay. Up to a concentration of 50 μM in culture medium, diselenide 14a exposed negligible cytotoxicity (details in ESI†). However, at a final concentration of 100 μM cell viability was reduced by approximately 70%. Therefore, the following experiments on cell surface sialylation were limited to an inhibitor concentration of 50 μM in culture medium. In the same concentration range, selenide 16a reduced cell viability by up to 25%. Cell surface sialylation was evaluated by measuring the expression of 6′-sialyl-N-acetyllactosamine (6′-sialyl-LacNAc) via flow cytometry using fluorescein isothiocyanate-conjugated Polyporus squamosus lectin (FITC–PSL).22,30 Only treatment with diselenide 14a led to a significant reduction of sialic acid expression in tested cells. At a final concentration of 50 μM in cell culture medium, the 6′-sialyl-LacNAc entity was reduced by approximately 85% (Fig. 3).
As expected, selenide 16a did not alter cell surface sialylation at tested conditions. Total inhibition of cell surface 6′-sialyl-LacNAc expression was not observed. This is most likely due to uptake and reutilization of sialic acids from the serum supplement and its conversion to CMP-sialic acid independent of GNE/MNK activity.31 A slow turnover of sialylated glycoproteins could additionally contribute to this finding.32
Conclusions
In summary, the performed enzymatic assays showed that diselenide 14b is a potent MNK inhibitor both in vitro and in cellulo with an IC50 value of 8.5 μM, representing the strongest inhibition of all previously reported MNK inhibitors. The homodimeric structure including a diselenide linker introduced at position C6 proved to be highly beneficial for the inhibitory activity of the compound. Finally, we demonstrated that the peracetylated diselenide 14a was successfully capable of reducing cell surface sialylation in Jurkat cells. With the C6-modified ManNAc analogs presented in this work new insight could be attained into inhibition of the key enzyme of sialic acid biosynthesis, the GNE/MNK. We hope that strong GNE/MNK inhibitors like the described 14a/14b, pave the way for future studies elucidating the effects of GNE/MNK inhibition in vivo.Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge support from the DFG (SFB 765 and SPP 1623 to CPRH), the Fonds der Chemischen Industrie (FCI to CPRH), the Einstein Foundation (to CPRH), the DAAD (postdoctoral scholarship to ONG), the Sonnenfeld-Stiftung Berlin (to WR) and the Elfriede and Roland Schauer Stiftung (to WR), Dr Natali Wisbrun for the supply of mouse liver and Prof. H. J. Gabius for providing FITC-conjugated Polyporus squamosus lectin.References
- A. Varki, FASEB J., 1997, 11, 248 CAS.
- S. Kelm and R. Schauer, Int. Rev. Cytol., 1997, 175, 137 CAS.
- R. Schauer, Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol., 2009, 19, 507 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. J. Russell and R. G. Webster, Cell, 2005, 123, 368 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. J. Kim and A. Varki, Glycoconjugate J., 1997, 14, 569 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Chen and M. Fukuda, Methods Enzymol., 2006, 416, 371 CAS.
- V. P. Bhavanandan, Glycobiology, 1991, 1, 493 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. Chen and J. F. Liang, Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm., 2012, 81, 339 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- For a review on MOE, see: (a) O. T. Keppler, R. Horstkorte, M. Pawlita, C. Schmidt and W. Reutter, Glycobiology, 2001, 11, 11R–18R CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) D. H. Dube and C. R. Bertozzi, Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol., 2003, 7, 616 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) J. Du, M. A. Meledeo, Z. Wang, H. S. Khanna, V. D. Paruchuri and K. J. Yarema, Glycobiology, 2009, 19, 1382 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (d) B. J. Beahm and C. R. Bertozzi, Imaging Cell-Surface in Animals with Bioorthogonal Chemistry, ed. T. Endo, P. H. Seeberger, G. W. Hart, C.-H. Wong and T. Taniguchi, Glycoscience: Biology and Medicine, Springer, Japan, 2014 Search PubMed.
- (a) H. Kayser, R. Zeitler, C. Kannicht, D. Grunow, R. Nuck and W. Reutter, J. Biol. Chem., 1992, 267, 16934–16938 CAS; (b) K. Mahal, K. J. Yarema and C. R. Bertozzi, Science, 1997, 276, 1125 CrossRef PubMed.
- (a) E. Saxon and C. R. Bertozzi, Science, 2000, 287, 2007 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) J. A. Prescher, D. H. Dube and C. R. Bertozzi, Nature, 2004, 430, 873 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Möller, V. Bohrsch, J. Bentrop, J. Bender, S. Hinderlich and C. P. Hackenberger, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2012, 51, 5986 CrossRef PubMed.
- C. D. Rillahan, A. Antonopoulos, C. T. Lefort, R. Sonon, P. Azadi, K. Ley, A. Dell, S. M. Haslam and J. C. Paulson, Nat. Chem. Biol., 2012, 8, 661 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. D. Rillahan, S. J. Brown, A. C. Register, H. Rosen and J. C. Paulson, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2011, 50, 12534 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. S. Macauley, B. M. Arlian, C. D. Rillahan, P. C. Pang, N. Bortell, M. C. G. Marcondes, S. M. Haslam, A. Dell and J. C. Paulson, J. Biol. Chem., 2014, 289, 35149 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- O. T. Keppler, S. Hinderlich, J. Langner, R. Schwartz-Albiez, W. Reutter and M. Pawlita, Science, 1999, 284, 1372 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. Zeitler, A. Giannis, S. Danneschewski, E. Henk, T. Henk, C. Bauer, W. Reutter and K. Sandhoff, Eur. J. Biochem., 1992, 204, 1165 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Blume, H. Chen, W. Reutter, R. R. Schmidt and S. Hinderlich, FEBS Lett., 2002, 521, 127 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- F. Stolz, M. Reiner, A. Blume, W. Reutter and R. R. Schmidt, J. Org. Chem., 2004, 69, 665 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Al-Rawi, S. Hinderlich, W. Reutter and A. Giannis, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2004, 43, 4366 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Zhu, F. Stolz and R. R. Schmidt, J. Org. Chem., 2004, 69, 7367 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. R. Wratil, S. Rigol, B. Solecka, G. Kohla, C. Kannicht, W. Reutter, A. Giannis and L. D. Nguyen, J. Biol. Chem., 2014, 289, 32056 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Martinez, L. D. Nguyen, S. Hinderlich, R. Zimmer, E. Tauberger, W. Reutter, W. Saenger, H. Fan and S. Moniot, J. Biol. Chem., 2012, 287, 13656 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Tosylated ManNAc 8 was prepared according to the protocol reported in: R. Thomson and M. von Itzstein, Carbohydr. Res., 1995, 274, 29 CrossRef CAS.
- For a proposed mechanism of C-2 base catalyzed epimerization of ManNAc, see: T. Toida, I. R. Vlahov, A. E. Smith, R. E. Hileman and R. J. Linhardt, J. Carbohydr. Chem., 1996, 15, 351 CrossRef CAS.
- As an example of 1H NMR assigment for the protons at position 6 of C6-thiol and C6-disulfide modified piranoses, see: M. Guillemineau, S. Singh, M. Grossutti and F. I. Auzanneau, Carbohydr. Res., 2010, 345, 2723 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- V. Fourniere and I. Cumpstey, Tetrahedron Lett., 2010, 51, 2127 CrossRef CAS.
- For the values of bond angles and lengths in diselenides and selenoethers, see: (a) C. Paulmier, Selenium Reagents and Intermediates in Organic Synthesis, Pergamon Press, Oxford, 1st edn, 1986 Search PubMed; to compare the bond angles and lengths in dimethyl ether, thioether and selenothers, see: (b) D. R. Lide, Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, 74th edn, 1994 Search PubMed; for a discussion of the significant differences between C–O, C–S and C–Se in saccharides, see: (c) S. André, K. E. Kövér, H.-J. Gabius and L. Szilágyi, Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett., 2015, 25, 931 CrossRef PubMed and ref. 27.
- M. B. Jones, H. Teng, J. K. Rhee, N. Lahar, G. Baskaran and K. J. Yarema, Biotechnol. Bioeng., 2004, 85, 394 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Mo, H. C. Winter and I. J. Goldstein, J. Biol. Chem., 2000, 275, 10623 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) C. Oetke, S. Hinderlich, R. Brossmer, W. Reutter, M. Pawlita and O. T. Keppler, Eur. J. Biochem., 2001, 268, 4553 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) C. D. Rillahan, A. Antonopoulos, C. T. Lefort, R. Sonon, P. Azadi, K. Ley, A. Dell, S. M. Haslam and J. C. Paulson, Nat. Chem. Biol., 2012, 8, 661 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. Mendla, J. Baumkötter, C. Rosenau, B. Ulrich-Bott and M. Cantz, Biochem. J., 1988, 250, 261 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
Footnotes |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available. See DOI: 10.1039/c5sc04082e |
| ‡ Both authors contributed equally to this work. |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 |