DOI:
10.1039/C6RA20150D
(Paper)
RSC Adv., 2016,
6, 98026-98034
Simultaneous in situ and ex situ growth of ultra-long Si3N4 nanobelts with different optical properties
Received
9th August 2016
, Accepted 29th September 2016
First published on 30th September 2016
Abstract
In situ and ex situ growth of ultra-long Si3N4 nanobelts (NBs) was simultaneously achieved via an effective method with the raw materials of graphite, nanosilicon and nanosilica. In situ growth of ultra-long Si3N4 NBs on the surface of the powder mixture resulted in a cross-section of 30–50 nm in thickness and 100–250 nm in width, and a length that can grow up to several millimeters. The width and thickness of the NBs obtained on the inner walls of the crucible, namely ex situ growth of Si3N4 NBs, are in the range of 200–500 nm and 50–200 nm, respectively. A vapor–solid (VS) mechanism was proposed for the growth mode of the in situ growth of Si3N4 NBs, while VS and vapor–liquid–solid (VLS) mechanisms simultaneously existed in the growth of the Si3N4 NBs obtained on the inner walls of the crucible. This method provides an effective way of preparing Si3N4 NBs on an industrial scale. The room-temperature photoluminescence (PL) spectra show that the synthesized α-Si3N4 NBs both had two strong emissions peaks, but the PL spectrum of the ex situ NBs shows an obvious red-shift compared to that of the in situ NBs, making it a potential material for applications in special optoelectronic nanodevices.
1. Introduction
Silicon nitride (Si3N4) is one of the most important ceramics applied in a number of applications, such as high-temperature electronics and structural materials, due to its unique mechanical property, good chemical inertness and strong resistance against thermal shock.1–6 One-dimensional (1-D) Si3N4 nanomaterials could be used widely in nanocomposites and nanoelectronics because of their superior photoelectric and mechanical properties for quantum confinement effects.7–9 Numerous methods are employed to synthesize 1-D Si3N4 nanomaterials, including pyrolysis of polymeric precursors, chemical vapor deposition, carbothermal reduction and the sol–gel method.10–13 In addition, ultra-long 1-D Si3N4 nanomaterials (with lengths in the order of millimeters or even centimeters) could be more available compared to short ones in some particular fields, such as connections for devices and reinforcements for composites, which have attracted considerable attention by researchers in recent years.14,15 For example, single-crystalline Si3N4 nanomaterials with lengths up to several millimeters were synthesized by Yang et al. through thermal decomposition of a polysilazane preceramic polymer using FeCl2 powder as a catalyst, and they also fabricated ultra-long α-Si3N4 NBs by catalyst-assisted crystallization of polymer-derived amorphous silicon carbonitride (SiCN).16,17 Lin et al. prepared ultra-long Si3N4 nanomaterials with N2 as the nitrogen source, SiO or a mixture of Si and SiO2 as the silicon source, N2 and Ar as the barrier gas, and CH4 as the reducing gas under superatmospheric pressure conditions.6 Although research about the preparation of ultra-long Si3N4 nanomaterials has been making great progress, these methods all involve preceramic polymers, catalysts, or severe demands of materials and equipment, including CH4 as a gaseous reactant and superatmospheric pressure conditions, which limit further research and applications of Si3N4 nanomaterials. According to our survey, up to now the simultaneous in situ and ex situ preparation of ultra-long Si3N4 nanomaterials was rarely reported by a simple method only using solid raw materials.
In this paper, in situ and ex situ synthesis of ultra-long Si3N4 nanomaterials, several millimeters in length, were successfully achieved by an effective and simple method, which has been used to synthesize ultra-long SiC nanowires.14 The possible growth mechanisms for in situ and ex situ growth of ultra-long Si3N4 nanomaterials were also proposed, and this simple and effective method provides a promising means of fabricating ultra-long Si3N4 nanomaterials on an industrial scale. In addition, the optical properties of in situ and ex situ Si3N4 nanobelts were investigated.
2. Experimental
The experimental procedure is similar to that reported previously.14 The commercially available nanosilicon (100 nm, Hefei Kaier Nanometer Energy & Technology Co., Ltd, China), nanosilica (25 nm, Aladdin Industrial Corporation) and graphite flakes (20 μm, Qingdao Tiansheng Graphite Co., Ltd, China) were used as the raw materials. The powder was mixed as follows: 13.92 wt% nanosilicon, 29.83 wt% nanosilica and 56.25 wt% graphite (G). The powder mixture was ball-milled in ethanol for 6 h with SiC balls and then dried in a rotary evaporator. A ceramic crucible (60 mm × 30 mm × 30 mm) was used to hold the powder mixture (1 g) and then the crucible was placed into a tube corundum furnace. High-purity nitrogen gas was introduced into the furnace at a rate of 50 mL min−1 before heating. The furnace was heated up from room temperature to 300 °C at a speed of 3 °C min−1 and maintained for 10 min, and then heated up to 800 °C at 3 °C min−1 and maintained for 10 min, and then further heated up to 1450–1550 °C at 5 °C min−1 and maintained for 2 h. High-purity nitrogen gas was kept flowing during the experimental process. The furnace was first cooled to 500 °C at a rate of 5 °C min−1 and then naturally cooled to room temperature after the heating was terminated. The final products, looking like white wool, were found on the inner walls of the crucible and on the surface of the powder mixture.
The morphology, structure, and composition of the obtained products were characterized using scanning electron microscopy (SEM, HELIOS NanoLab 600i, America), X-ray powder diffraction (XRD, X’PERT PRO MPD, Holland), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR, Spectrum Two, America), transmission electron microscopy and high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (TEM and HRTEM, Tecnai G2-F30, America) equipped with energy dispersive spectroscopy (EDS). Photoluminescence (PL) measurements of the samples were analyzed on an ultraviolet-visible spectrophotometer (Labram HR800) with a 325 nm He–Cd laser as the excitation source.
3. Results and discussion
3.1 Effect of temperature on the formation of Si3N4 nanomaterials
The effect of preparation temperature on the product was first investigated and the photographs of the products obtained at different preparation temperatures are shown in Fig. 1. At 1450 °C, just a few strands of white wool were obtained on the inner walls of the crucible and short strands of white wool were obtained on the surface of the powder mixture suggesting that ultra-long Si3N4 nanomaterials could not be produced below or even at this temperature. A similar phenomenon was observed at 1550 °C, but with a different color powder mixture (gray at 1450 °C and white at 1550 °C), while the color of the crucible indicated that the preparation temperature at 1550 °C was too high to synthesize ultra-long Si3N4 nanomaterials. In situ and ex situ growth of ultra-long Si3N4 nanomaterials simultaneously occurred at 1500 °C, and it is reasonable to believe that 1500 °C was a suitable and relatively low temperature for the preparation of in situ and ex situ grown ultra-long Si3N4 nanomaterials.
 |
| | Fig. 1 Photographs of the products obtained at different preparation temperatures; (a) 1450 °C, (b) 1550 °C and (c) 1500 °C. | |
3.2 Phase composition, morphology and microstructure of the as-synthesized products
The strands of white wool were seen on the inner walls of the crucible and on the surface of the powder mixture after 2 h at 1500 °C under N2. The crystalline phase of the products was characterized by XRD, as shown in Fig. 2, and it was found to be composed of only α-Si3N4. To further confirm the composition, FTIR measurements were performed on the obtained white wool strands and a typical FTIR transmittance spectrum is shown in Fig. 3. It can be seen that a broad band in the range of 800–1100 cm−1 belongs to the Si–N stretching vibration mode of α-Si3N4, similar to previous literature reports.18–20 In addition, the absorption peaks around 400–700 cm−1 can also be attributed to the crystalline structure of α-Si3N4.19 Furthermore, some absorption peaks display a blue shift compared to those of the bulk α-Si3N4, such as 1016 cm−1 and 885 cm−1, which might be a result of the effect of the nanosize and surface states.19 Therefore, it can be concluded that the white wool strands were α-Si3N4 based on analysis of the XRD pattern and the FTIR spectrum.
 |
| | Fig. 2 Typical XRD pattern of the synthesized products obtained at 1500 °C for 2 h. | |
 |
| | Fig. 3 Typical FTIR spectrum of the synthesized products obtained at 1500 °C for 2 h. | |
The morphology of the white cotton-like products was characterized by SEM. As shown in Fig. 4, it can be seen that the lengths of the nanomaterials, both on the inner walls of the crucible and surface of the powder mixture, are in the range of hundreds to thousands of micrometers. The white wool-like products obtained on the surface of the powder mixture, namely by in situ growth, were analyzed using SEM and the images are shown in Fig. 4a and b. From the SEM images it can be seen that the white cotton-like products were both straight and curved NBs grown randomly. The high-magnification SEM image (Fig. 4b) suggests that the NBs had a smooth surface, but that the width and thickness of the NBs fluctuated from 100 nm to 200 nm and 30 nm to 50 nm, respectively. A width distribution histogram of the NBs in Fig. 4a provides an average width of 166 nm and a main distribution range of 110–170 nm (Fig. 4c). As for the products obtained on the inner walls of the crucible, namely by ex situ growth, the typical SEM images are shown in Fig. 4d and e. Similar to the morphology of the NBs obtained on the surface of the powder mixture, the NBs were both straight and curved NBs grown randomly, but the width and thickness of the NBs ranged from 200 nm to 550 nm and 50 nm to 200 nm, respectively. Fig. 4f shows a width distribution histogram of the NBs in Fig. 4d, and provides an average width of 426 nm and a main distribution range of 230–550 nm. Meanwhile, the yield and lengths of the NBs obtained on the inner walls of the crucible are larger than those of the NBs on the surface of powder mixture.
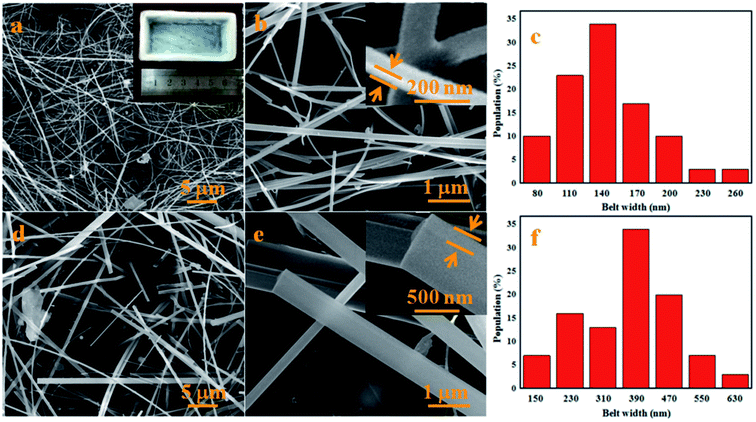 |
| | Fig. 4 Typical SEM images of the products obtained at 1500 °C for 2 h; (a) low-magnification and macroscopic morphology and (b) high-magnification SEM images of the products obtained on the surface of the powder mixture, namely by in situ growth, (c) belt width distribution histogram of the NBs in (a), (d) low- and (e) high-magnification SEM images of the products obtained on the inner walls of the crucible, namely by ex situ growth and (f) belt width distribution histogram of the NBs in (d). | |
Further details of the microstructure and morphology of the obtained NBs can be revealed by TEM and HRTEM as shown in Fig. 5. The TEM and HRTEM images of the NBs obtained on the surface of the powder mixture, namely by in situ growth, are shown in Fig. 5a and b. From the TEM images, it can be seen that the width of the nanobelt (NB) was about 160 nm and that the NB had a smooth surface without a shell film. The annotations in Fig. 5b show the marked lattice fringes with d-spacing values of 0.56 nm and 0.67 nm, which are consistent with the (001) and (100) planes of α-Si3N4.21–23 Furthermore, the composition of the NB was measured by EDS under HRTEM and a typical EDS spectrum is shown in Fig. 5c. It can be seen that the NB was composed of Si and N without any other elements indicating that the product was Si3N4. Typical TEM and HRTEM images obtained of the inner walls of the crucible, namely by ex situ growth, are shown in Fig. 6a and b. It can be seen that the width of the NB without a shell film was about 400 nm, and that the lattice fringes were consistent with the (001) and (100) planes of α-Si3N4 similar to those of the in situ grown NBs from the previous images. Moreover, a typical EDS spectrum obtained from the NB is shown in Fig. 6c suggesting that it was composed of Si and N elements only.
 |
| | Fig. 5 Typical TEM and HRTEM images and the EDS spectrum of the products obtained at 1500 °C for 2 h. (a) TEM and (b) HRTEM images of the products obtained on the surface of the powder mixture, namely by in situ growth. (c) The EDS spectrum of the products obtained on the surface of the powder mixture, namely in situ growth. | |
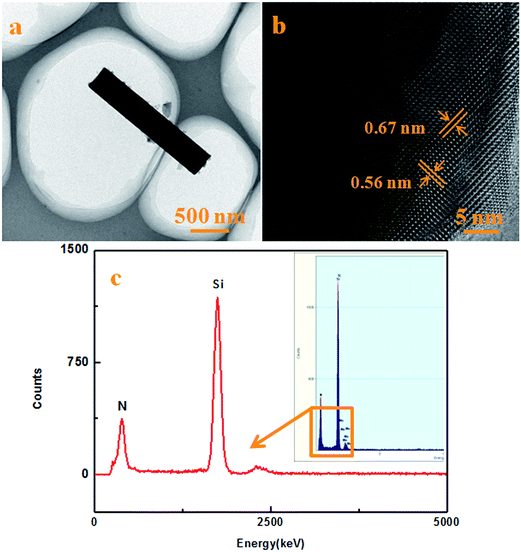 |
| | Fig. 6 Typical TEM and HRTEM images and the EDS spectrum of the products obtained at 1500 °C for 2 h. (a) TEM and (b) HRTEM images of the products obtained on the inner walls of the crucible, namely by ex situ growth. (c) The EDS spectrum of the products obtained on the inner walls of the crucible, namely by ex situ growth. | |
The combination of the XRD patterns (Fig. 2), FTIR spectra (Fig. 3), HRTEM observations (Fig. 5b and 6b) and EDS spectra (Fig. 5c and 6c), suggest that both in situ and ex situ grown NBs are composed of α-Si3N4.
3.3 Growth mechanisms of Si3N4 NBs obtained at different sites
With regards to the growth mechanisms of nanomaterials, some fundamental growth models have been proposed, such as VS, VLS, solid–liquid–solid (SLS) and oxide assisted growth (OAG). These mechanisms all contain some unique features.24–27 For example, droplets located at the tips of the NBs should be observed when VLS and SLS growth mechanisms are employed to illustrate the growth model of the products. Meanwhile, there should be a dense and uniform oxide layer instead of metal, playing an important role in nucleation and growth processes of the NBs, when an OAG mechanism is used to disclose the growth model of the NBs without a metal catalyst, in which a layer of film should also be found on the surface of the nanomaterials.28–30
According to the images of the NBs and the unique features of these growth mechanisms, VLS, SLS and OAG growth mechanisms are not suitable to explain the growth process of ultra-long Si3N4 NBs obtained on the surface of the powder mixture since there were no droplets, oxide layer or a layer of film found in the products.31–33 Therefore, in situ growth of ultra-long Si3N4 NBs would be produced via the VS mechanism due to the fact that no metal catalyst was employed in the present experiment and no droplets were found on the tips of the nanomaterials. However, a phenomenon, namely the higher yield and longer lengths of the NBs obtained on the inner walls of the crucible compared to those of the NBs obtained on the surface of the powder mixture, should be noted and a more detailed analysis was employed as shown in Fig. 7. It is worth noting that there are some droplets located at the tips of the NBs as shown in Fig. 7a and b, while there were no droplets found in Fig. 4 and the reason can be concluded to be that the droplets easily fell off during the treatment of the samples, as they just existed at the tips of the NBs and only some fractures of the NBs are shown in Fig. 4. In addition, the elemental composition of the droplet was confirmed by using EDS attached to the SEM apparatus. The EDS spectrum of the droplet consists of Si, N, C, O, Au and Fe elements, in which the Au element should come from the treatment of samples. As no catalysts were employed, the Fe element should come from the crucible, which contains alumina and a small amount of impurities consisting of Fe2O3 and SiO2. Fe2O3 would reduce to active Fe nanoclusters under the reductive gas from the reaction system, including CO.14 The gaseous mixture containing Si and C elements (e.g., SiO and CO) was transported to the inner walls of the crucible and the elements were preferably absorbed and then it dissolved into active Fe nanoclusters to promote the nucleation and growth of nanomaterials.14 Furthermore, SiO2 contained in the crucible could also participate in the reaction of formation of nanomaterials and alumina may also behave as a novel and highly effective mediator playing an important role in controlling the concentration of gas containing Si.14 In order to confirm the above analysis, some comparative experiments have been done and the products are shown in Fig. 8a. Some pieces of graphite paper were affixed to the inner walls of the crucible to identify the source of the catalyst and the microstructure of products, as shown in Fig. 8. The white wool strands obtained on the graphite paper were analyzed by SEM and there were found to be no droplets on the tips of the NBs as shown in Fig. 8c, while some droplets were seen on the tips of the NBs grown on the crucible as shown in Fig. 8b. No droplets were found on the tips of the NBs taken from the surface of the powder mixture as shown in Fig. 8d, which confirmed that the Fe element comes from the crucible. Therefore, a combination of mechanisms, both VS and VLS, were proposed to disclose the growth of Si3N4 NBs obtained on the inner walls of the crucible owing to the small amount of Fe2O3. Meanwhile, the growth process of the Si3N4 NBs can be described as shown in Fig. 9.
 |
| | Fig. 7 Detailed analysis of the products obtained on the inner walls of the crucible; SEM images (a) and (b) and EDS spectra (c) of the tip of the Si3N4 NB. | |
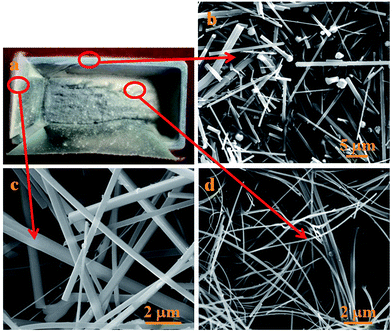 |
| | Fig. 8 Analysis of the products obtained from the comparative experiment; macroscopic morphology of the products (a) and SEM images of the products grown at different places: on the inner walls of the crucible (b), on the surface of graphite paper (c) and on the surface of the powder mixture (d). | |
 |
| | Fig. 9 Illustrations of the possible growth process of Si3N4 ultra-long NBs. | |
Firstly, the raw materials would chemically react with each other to prepare for post-nucleation as the temperature rises and the following reactions may take place during this period similarly to in previous literature.34,35
| | |
2Si(s) + O2(g) → 2SiO(g)
| (1) |
| | |
2C(s) + O2(g) → 2CO(g)
| (2) |
| | |
SiO2(s) + Si(s) → 2SiO(g)
| (3) |
| | |
SiO2(s) + C(s) → SiO(g) + CO(g)
| (4) |
| | |
SiO2(s) + CO(g) → SiO(g) + CO2(g)
| (5) |
| | |
CO2(g) + C(s) → 2CO(g)
| (6) |
It should be noted that the initial reaction temperature of the above reactions might drop due to the effect of the nanosize.36 The changes in Gibbs free energy of reactions (1) and (2) are both negative, while the changes in Gibbs free energy of the other reactions are positive at low temperatures (below 900 K) without taking into account the effect of the nanosize based on thermodynamic data.37 Reactions (1) and (2) could take place spontaneously at low temperatures from the view of thermodynamics, while other reactions would occur later. The nucleation would take place under suitable conditions as the reaction is carried out and the following reactions may take place to form Si3N4 nuclei as shown in Fig. 9(III), while some liquid alloy would be formed on the inner walls of crucible.
| | |
3SiO(g) + 3C(g) + 2N2(g) = Si3N4(s) + 3CO(g)
| (7) |
| | |
3SiO(g) + 3CO(g) + 2N2(g) = Si3N4(s) + 3CO2(g)
| (8) |
| | |
3SiO2(s) + 6C(g) + 2N2(g) = Si3N4(s) + 6CO(g)
| (9) |
| | |
3SiO2(s) + 6CO(g) + 2N2(g) = Si3N4(s) + 6CO2(g)
| (10) |
Based on thermodynamics calculations and thermodynamic data, the change in Gibbs free energy of reaction (7) is always below zero at the reaction temperature and the change in Gibbs free energy of reaction (8) is negative until the reaction temperature is high enough, without taking into account the effect of size, while the changes in Gibbs free energy of other reactions are both positive without taking into account the effect of nanosize. Therefore, it is reasonable to believe that reaction (7) may be mainly responsible for the formation of Si3N4 nuclei, owing to a lower change in Gibbs free energy compared to that of reaction (8), and then provides the reactant gas CO for the subsequent reactions (8) and (10). After the Si3N4 nuclei are formed, Si3N4 NBs may subsequently grow along a fixed axis as shown in Fig. 9(IV). Therefore, the last stage is Si3N4 NB growth along the axis direction, and the NBs would subsequently grow along a fixed direction for as long as the reactant gas is continuously generated.
The reason for the different morphologies of the in situ and ex situ grown NBs, with different widths and thicknesses, can be attributed to a different degree of supersaturation of gas in different reaction sites. Therefore the saturated liquid alloy would contain a higher amount of Si and C and form a larger droplet compared to that formed with no catalyst with the increase in temperature, which leads to a larger width and thickness of the NBs. The reason for the formation of Si3N4 without SiC should also be noted. SiC might be formed in the present system due to the presence of Si, SiO, CO, C and SiO2, while no SiC was found in the Si3N4 nanostructures. The reason can be attributed to the fact that Si3N4 is more stable than the SiC phase under N2 conditions and that Si3N4 would be preferentially formed over SiC according to previous literature.38,39 The following reactions (11)–(15) might take place to form SiC and reaction (12) would be mainly responsible for the formation of SiC nucleation and the growth of SiC nanowires.40 However, owing to a lower change in Gibbs free energy compared to that of reaction (12), reaction (7) would take place easily from a thermodynamic point of view. In addition, the change in Gibbs free energy of reaction (7) is the lowest among the reactions (11)–(13) and (15), while reaction (14) might be suppressed due to a lower concentration of SiO compared to that of CO, which is generated by graphite in excess, and reaction (15) may be limited by the presence of N2. Therefore, Si3N4 is more easily formed in the present system without SiC, in which SiC is suppressed both in the formation of nucleation and growth.
| | |
Si(s,l) + C(s) → SiC(s)
| (11) |
| | |
SiO(g) + 2C(s) → SiC(s) + CO(g)
| (12) |
| | |
SiO(g) + 3CO(g) → SiC(s) + 2CO2(g)
| (13) |
| | |
3SiO(g) + CO(g) → SiC(s) + 2SiO2(s)
| (14) |
| | |
Si3N4(s) + 3C(s,g) = 3SiC(s) + 2N2(g)
| (15) |
3.4 Optical properties of in situ and ex situ Si3N4 NBs
The room-temperature PL spectra of α-Si3N4 NBs obtained on the inner walls of the ceramic crucible (marked as ex situ NBs) and on the surface of the powder mixture (marked as in situ NBs) are shown in Fig. 10 with a black and a red line. Both of the NBs show visible luminescence giving a broad range emission band between 400 and 700 nm with three obvious peaks, which are located at 442 nm (2.81 eV), 553 nm (2.24 eV) and 699 nm (1.77 eV) for the black line, and were focused on 441 nm (2.82 eV), 550 nm (2.25 eV) and 682 nm (1.82 eV) for the red line. It should be noted that the obvious emission concentrated at about 1.8 eV should be ascribed to electronic recombination transition between the intrinsic conduction band edge and the N4+ level or between two N dangling bonds.41 Based on the preliminary work, the peak positions ranging from 2.0 to 3.2 eV can be attributed to defect energy levels, such as those of Si–Si, N–N, ![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) Si and
Si and ![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N dangling bonds.42,43 As for the emission around 2.25 and 2.8 eV, the reason could be ascribed to the presence of surface oxygen species, which leads to the formation of Si–O–Si and N–Si–O structure defects, and introduces Si–O–Si and N–Si–O defective gap states.42,44 Compared to the PL spectra of the in situ NBs, those of the ex situ NBs show an obvious red-shift and the following sentences could explain these phenomena. It is worth noting the larger size of the ex situ NBs with a width of 426 nm compared to those of the in situ NBs. It has been revealed by some reports that the band gap reduces, resulting in a red-shift of the emission spectrum, when the size of the nanostructure is increased.45 Although the content is too low to be tested in a single NB by EDS, we speculate that the ex situ NBs might contain a small amount of Al coming from the alumina crucible, which has also been verified by the report of Gao et al.46 As for the doping mechanism of Al, it can be attributed to the generation of two types of defects with N4+ and the silicon dangling bond (K0) by reaction (16).46 In consequence, the distinctive optical properties of these NBs can be ascribed to the larger size of the NBs and incorporation of small amount of Al into the NBs, providing a promising method for preparing Si3N4 NBs with desired optical properties.
N dangling bonds.42,43 As for the emission around 2.25 and 2.8 eV, the reason could be ascribed to the presence of surface oxygen species, which leads to the formation of Si–O–Si and N–Si–O structure defects, and introduces Si–O–Si and N–Si–O defective gap states.42,44 Compared to the PL spectra of the in situ NBs, those of the ex situ NBs show an obvious red-shift and the following sentences could explain these phenomena. It is worth noting the larger size of the ex situ NBs with a width of 426 nm compared to those of the in situ NBs. It has been revealed by some reports that the band gap reduces, resulting in a red-shift of the emission spectrum, when the size of the nanostructure is increased.45 Although the content is too low to be tested in a single NB by EDS, we speculate that the ex situ NBs might contain a small amount of Al coming from the alumina crucible, which has also been verified by the report of Gao et al.46 As for the doping mechanism of Al, it can be attributed to the generation of two types of defects with N4+ and the silicon dangling bond (K0) by reaction (16).46 In consequence, the distinctive optical properties of these NBs can be ascribed to the larger size of the NBs and incorporation of small amount of Al into the NBs, providing a promising method for preparing Si3N4 NBs with desired optical properties.| |
 | (16) |
 |
| | Fig. 10 PL spectra of α-Si3N4 NBs obtained at different places under excitation of a 325 nm He–Cd laser at room temperature. | |
4. Conclusions
Several millimeter long in situ and ex situ grown Si3N4 NBs were successfully prepared using simple raw materials via an effective method. Si3N4 NBs obtained on the surface of the powder mixture, namely by in situ growth, have a uniform cross-section of 30–50 nm in thickness and 100–200 nm in width, while the width and thickness of the ex situ grown Si3N4 NBs obtained on the inner walls of the crucible range from 200 nm to 500 nm and 50 nm to 200 nm, respectively. The growth process of Si3N4 NBs obtained on the surface of the powder mixture can be attributed to the VS mechanism, while combined mechanisms of VS and VLS were proposed to disclose the growth of Si3N4 NBs obtained on the inner walls of the crucible, which offers great potential for industrial fabrication of ultra-long Si3N4 NBs. The PL spectra of α-Si3N4 NBs at room temperature show two strong emission peaks, based on which a possible emission mechanism is also proposed with a larger size and a small amount of Al playing a role.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Science Foundation (51202048, 51372047, 11402252, 11421091, 91216301 and 51525201) of China, and National Key Laboratory of Science and Technology on Advanced Composites in Special Environments, KL.PYJH.2016.001.
References
- F. Munakata, K. Matsuo, K. Furuya, Y. Akimune, J. Ye and I. Ishikawa, Appl. Phys. Lett., 1999, 74, 3498–3500 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. J. Bai, J. Bian, C. G. Wang, B. Zhu, Y. X. Qi, Y. X. Wang and G. L. Geng, J. Mater. Chem., 2005, 15, 4832–4837 RSC.
- Y. Zhang, J. Zang, L. Dong, X. Cheng, Y. Zhao and Y. Wang, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2014, 2, 17815–17819 CAS.
- Z. Huang, F. Chen, Q. Shen and L. Zhang, RSC Adv., 2016, 6, 7568–7574 RSC.
- J. Huang, S. Zhang, Z. Huang, Y. G. Liu and M. Fang, CrystEngComm, 2013, 15, 785–790 RSC.
- L. W. Lin and Y. H. He, CrystEngComm, 2012, 14, 3250–3256 RSC.
- Z. W. Pan, Z. R. Dai and Z. L. Wang, Science, 2001, 291, 1947–1949 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Zang, Z. H. Xu, R. A. Webb and X. Li, Nano Lett., 2010, 11, 241–244 CrossRef PubMed.
- H. Liu, Z. Huang, J. Huang, M. Fang, Y. G. Liu, X. Wu and S. Zhang, Sci. Rep., 2015, 5, 3504 Search PubMed.
- W. Yang, H. Wang, S. Liu, Z. Xie and L. An, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2007, 111, 4156–4160 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. W. Yin, Y. Bando, Y. C. Zhu and Y. B. Li, Appl. Phys. Lett., 2003, 83, 3584–3586 CrossRef CAS.
- F. Wang, G. Q. Jin and X. Y. Guo, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2006, 110, 14546–14549 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- F. Wang, G. Q. Jin and X. Y. Guo, Mater. Lett., 2006, 60, 330–333 CrossRef CAS.
- P. Hu, S. Dong, K. Gui, X. Deng and X. Zhang, RSC Adv., 2015, 5, 66403–66408 RSC.
- F. Gao, W. Yang, Y. Fan and L. An, Nanotechnology, 2008, 19, 105602 CrossRef PubMed.
- W. Yang, Z. Xie, J. Li, H. Miao, L. Zhang and L. An, J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2005, 88, 1647–1650 CrossRef CAS.
- W. Yang, L. Zhang, Z. Xie, J. Li, H. Miao and L. An, Appl. Phys. A, 2005, 80, 1419–1423 CrossRef CAS.
- N. Wada, S. A. Solin, J. Wong and S. Prochazka, J. Non-Cryst. Solids, 1981, 43, 7–15 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Huang, Z. Huang, S. Yi, Y. G. Liu, M. Fang and S. Zhang, Sci. Rep., 2013, 3, 17250 Search PubMed.
- E. Theodossiu, H. Baumann, W. Matz and A. Mücklich, Phys. Status Solidi A, 2002, 194, 47–55 CrossRef CAS.
- G. Shen, Y. Bando, B. Liu, C. Tang, Q. Huang and D. Golberg, Chem.–Eur. J., 2006, 12, 2987–2993 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Hu, Y. Bando, Z. Liu, F. Xu, T. Sekiguchi and J. Zhan, Chem.–Eur. J., 2004, 10, 554–558 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. M. El-Sheikh, Y. M. Ahmed, E. M. Ewais and J. F. Al-Sharab, J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2010, 93, 2082–2091 CAS.
- Y. Xu, C. Cao, Z. Chen, J. Li, F. Wang and H. Cai, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2006, 110, 3088–3092 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Mizuhara, M. Noguchi, T. Ishihara, A. Satoh, K. Hiramatsu and Y. Takita, J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 1991, 74, 846–848 CrossRef CAS.
- J. J. Niu and J. N. Wang, Chem. Vap. Deposition, 2007, 13, 396–400 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Wang, J. Liu, B. Cheng, J. Yu and Q. Wang, Nanotechnology, 2006, 17, 3989 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. L. Li, Y. Liang and Z. Q. Hu, J. Mater. Sci., 1996, 31, 2677–2682 CrossRef CAS.
- G. Y. Li, X. D. Li, H. Wang and Z. Q. Li, Appl. Phys. A, 2008, 93, 471–475 CrossRef CAS.
- R. Q. Zhang, Y. Lifshitz and S. T. Lee, Adv. Mater., 2003, 15, 635–640 CrossRef CAS.
- M. A. Rodriguez, N. S. Makhonin, J. A. Escriña, I. P. Borovinskava, M. I. Osendi, M. F. Barba and J. S. Moya, Adv. Mater., 1995, 7, 745–747 CrossRef CAS.
- I. C. Jung, S. H. Cho, S. W. Na, J. Lee, H. S. Lee and W. S. Cho, Mater. Lett., 2007, 61, 4843–4846 CrossRef CAS.
- S. X. Ren, F. Q. Ji and X. L. He, Adv. Mater. Res., 2011, 148, 1347–1350 Search PubMed.
- C. H. Liang, G. W. Meng, L. D. Zhang, Y. C. Wu and Z. Cui, Chem. Phys. Lett., 2000, 329, 323–328 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Zhang, X. Huang, G. Wen, X. Geng, J. Zhu, T. Zhang and H. Bai, Nanotechnology, 2010, 21, 385601 CrossRef PubMed.
- A. M. Morales and C. M. Lieber, Science, 1998, 279, 208–211 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- I. Barin and G. Platzki, Thermochemical Date of Pure Substances, VCH, Weinheim, 3rd edn, 1995 Search PubMed.
- W. Yang, Z. Xie, H. Miao, L. Zhang, H. Ji and L. An, J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2005, 88, 466–469 CAS.
- H. J. Seifert, J. Peng, H. L. Lucas and F. Aldinger, J. Alloys Compd., 2001, 320, 251–261 CrossRef CAS.
- R. Wu, B. Zha, L. Wang, K. Zhou and Y. Pan, Phys. Status Solidi A, 2012, 209, 553–558 CrossRef CAS.
- N. Zhu, Z. Peng, C. Wang, Z. Fu and H. Miao, Solid State Sci., 2009, 11, 1094–1097 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Ahmad, J. Zhao, C. Pan and J. Zhu, J. Cryst. Growth, 2009, 311, 4486–4490 CrossRef CAS.
- C. M. Mo, L. Zhang, C. Xie and T. Wang, J. Appl. Phys., 1993, 73, 5185–5188 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Liu, Y. Zhou, W. Shi, L. Zhao, B. Sun and T. Ye, Mater. Lett., 2004, 58, 2397–2400 CrossRef CAS.
- J. S. Wu and D. F. Xue, Nanoscale Res. Lett., 2011, 6, 14 Search PubMed.
- F. Gao, Y. Wang, L. Zhang, W. Yang and L. An, J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2010, 93, 1364–1367 CAS.
|
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 |
Click here to see how this site uses Cookies. View our privacy policy here. 

![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) Si and
Si and ![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N dangling bonds.42,43 As for the emission around 2.25 and 2.8 eV, the reason could be ascribed to the presence of surface oxygen species, which leads to the formation of Si–O–Si and N–Si–O structure defects, and introduces Si–O–Si and N–Si–O defective gap states.42,44 Compared to the PL spectra of the in situ NBs, those of the ex situ NBs show an obvious red-shift and the following sentences could explain these phenomena. It is worth noting the larger size of the ex situ NBs with a width of 426 nm compared to those of the in situ NBs. It has been revealed by some reports that the band gap reduces, resulting in a red-shift of the emission spectrum, when the size of the nanostructure is increased.45 Although the content is too low to be tested in a single NB by EDS, we speculate that the ex situ NBs might contain a small amount of Al coming from the alumina crucible, which has also been verified by the report of Gao et al.46 As for the doping mechanism of Al, it can be attributed to the generation of two types of defects with N4+ and the silicon dangling bond (K0) by reaction (16).46 In consequence, the distinctive optical properties of these NBs can be ascribed to the larger size of the NBs and incorporation of small amount of Al into the NBs, providing a promising method for preparing Si3N4 NBs with desired optical properties.
N dangling bonds.42,43 As for the emission around 2.25 and 2.8 eV, the reason could be ascribed to the presence of surface oxygen species, which leads to the formation of Si–O–Si and N–Si–O structure defects, and introduces Si–O–Si and N–Si–O defective gap states.42,44 Compared to the PL spectra of the in situ NBs, those of the ex situ NBs show an obvious red-shift and the following sentences could explain these phenomena. It is worth noting the larger size of the ex situ NBs with a width of 426 nm compared to those of the in situ NBs. It has been revealed by some reports that the band gap reduces, resulting in a red-shift of the emission spectrum, when the size of the nanostructure is increased.45 Although the content is too low to be tested in a single NB by EDS, we speculate that the ex situ NBs might contain a small amount of Al coming from the alumina crucible, which has also been verified by the report of Gao et al.46 As for the doping mechanism of Al, it can be attributed to the generation of two types of defects with N4+ and the silicon dangling bond (K0) by reaction (16).46 In consequence, the distinctive optical properties of these NBs can be ascribed to the larger size of the NBs and incorporation of small amount of Al into the NBs, providing a promising method for preparing Si3N4 NBs with desired optical properties.








