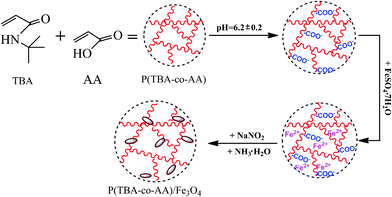
In situ synthesis of magnetic poly(N-tert-butyl acrylamide-co-acrylic acid)/Fe3O4 nanogels for magnetic resonance imaging
Di Zhaoa,
Xueting Lia,
Xiaodi Shi*a,
Kai Yea,
Weiyi Liua,
Gao Qiub and
Xihua Lu*ab
aCollege of Chemistry, Chemical Engineering and Biotechnology, Donghua University, Shanghai 201620, China. E-mail: luxihua@dhu.edu.cn; Fax: +862167792776; Tel: +862167792776
bState Key Laboratory for Modification of Chemical Fibers and Polymer Materials, College of Materials Science and Engineering, Donghua University, Shanghai 201620, China
First published on 20th June 2016
Abstract
Poly(N-tert-butylacrylamide-co-acrylic acid)/Fe3O4 (P(TBA-co-AA)/Fe3O4) nanogels have been synthesized successfully by two steps: firstly, poly(N-tert-butylacrylamide-co-acrylic acid) (P(TBA-co-AA)) nanogels were synthesized through emulsion precipitation polymerization by using N-tert-butylacrylamide (TBA) and acrylic acid (AA) as reactive monomers; then P(TBA-co-AA)/Fe3O4 nanogels were synthesized by in situ oxidation of Fe2+ into Fe3O4 nanoparticles inside the networks of the P(TBA-co-AA) nanogels. The prepared P(TBA-co-AA)/Fe3O4 nanogels were about 70 nm in dry state, and 118.9 nm in aqueous solution with a low polydispersity index (PDI) of 0.124. The small size and low PDI of the magnetic nanogels could be applied in living body. Besides, the nanogels had good superparamagnetic property, and high r2 relaxivity value of about 512.01 mM−1 s−1. These magnetic properties endowed the nanogels with a new ability to be applied in T2-style imaging. In short, this work would provide the possibility of using the P(TBA-co-AA)/Fe3O4 nanogels as contrast agents for high resolution of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
1. Introduction
Magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs) have been used incrementally in the biomedical field,1–5 among which iron oxide is the most commonly used because of its stability and low level of toxicity.6 For example, Fe3O4 nanoparticles have been researched7,8 and applied as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) contrast agents because they can improve r2 relaxivity.9–11 However, they may aggregate easily owing to their tiny sizes and high surface energy, and cause blockages in blood vessels when they are injected into veins.12,13 Moreover, the surfaces of commonly used Fe3O4 nanoparticles are hydrophobic6,12 which is incompatible with the human environment. And there is growing evidence that iron accumulation in brain may associate with Parkinson's disease.14 All these defects above of Fe3O4 nanoparticles limit their applications in practice.Nanogels are in the range of 10–1000 nm with three-dimensional network nanostructures which have good biocompatibility and stimuli-responsive.15,16 Therefore, many researchers used nanogels to encapsulate the Fe3O4 nanoparticles to avoid their aggregation and form protective layers to improve their hydrophilicity.14,17,18 The traditional method to synthesize magnetic hybrid nanogels is prepare Fe3O4 nanoparticles first, and then coat Fe3O4 nanoparticles with nanogel shells.18,19 However, that method could easily cause aggregation and low encapsulation efficiency of Fe3O4.20 In situ synthesis of Fe3O4 nanoparticles in the interior of nanogels is an alternative approach for the magnetic nanogels,21 in which the nanogels could be used as nanoreactors to avoid the aggregation, and maintain the structure and content of Fe3O4 nanoparticles.22
N-tert-Butylacrylamide (TBA) is an important material to synthesize copolymer nanogels, which can enhance the rigidity of molecular chain and then decrease the phase transition temperature and salt resistance.23,24 TBA-based nanogels have good biocompatibility and their mean size is smaller than other isonomic nanogels under the same reactive situation for hydrophobicity of TBA, thus they are more suitable as an intravenous injection for living body. Therefore, we described a novel magnetic nanogels preparation technology. In this work, TBA and acrylic acid (AA) were used as monomers to synthesize P(TBA-co-AA) nanogels, in which TBA was used as nanogels frameworks and ionized AA was used to attract more Fe2+ inside the networks of the nanogels. Then Fe2+ was oxidized to form Fe3O4 nanoparticles in networks of the nanogels, in which FeSO4·7H2O was used as iron source to provide Fe2+.25 The whole synthesis process was showed in Fig. 1. The prepared magnetic nanogels had a small size, a low polydispersity index (PDI) value, a good superparamagnetic property, and a high r2 relaxivity value by using P(TBA-co-AA) nanogels as polymer shell to in situ synthesize Fe3O4 nanoparticles.
2. Experiment
2.1. Materials
N-tert-Butylacrylamide (TBA, 97%), acrylic acid (AA, 99%), sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS, ≧99%), N,N′-methylenebisacrylamide (BIS, 99%), and ammonium persulfate (APS, ≧98%) were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich. NaOH, FeSO4·7H2O, NaNO2, NH3·H2O (28 wt%), and pure Fe3O4 nanoparticles (nm) were A.R. grade and purchased from Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd. All reagents were used without further purification. Ultrapure water (UPW) was 18.2 MΩ cm and prepared by Direct-Q 3UV System from Shanghai Tongdi Co., Ltd.2.2. Preparation of P(TBA-co-AA) nanogels
Approximately 1.50 g of TBA, 0.10 g of AA, 0.08 g of SDS, and 0.04 g of BIS were dissolved in 145 mL of UPW, and stirred the system at 400 rpm for 2 h at room temperature by electric-heated thermostatic water bath under a N2 atmosphere. Then the solution was maintained at 60 °C for 30 min, 5 mL of APS at a concentration of 0.008 g mL−1 was injected into the system. The reaction was kept for 4 h, and the nanogels were purified by dialysis bag (molecular weight cutoff of 8000–14![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 Da) with plenty of deionized water at room temperature for a week. The deionized water was replaced with fresh water three times a day.
000 Da) with plenty of deionized water at room temperature for a week. The deionized water was replaced with fresh water three times a day.
2.3. Preparation of P(TBA-co-AA)/Fe3O4 nanogels
0.2 M of NaOH was used to regulate the pH of P(TBA-co-AA) nanogels to 6.2 ± 0.2. Then 0.0695 g of FeSO4·7H2O was mixed with 50 mL of the nanogels above, and stirred at 200 rpm at room temperature for 12 h by mechanical stirrer under a N2 atmosphere. After dialyzing the nanogels for 3 h, 0.052 g of NaNO2 was mixed with the solution under the N2 atmosphere. 0.5 h later, the stirring rate was improved to 600 rpm and 5 mL of NH3·H2O was quickly injected into the system. The reaction was kept for 3 h at room temperature. The whole process was operated in the dark condition and the resulting magnetic nanogels were purified by the same method as the dialysis of P(TBA-co-AA) nanogels.2.4. Characterizations
The hydrodynamic particle size and monodispersity of the samples were measured with dynamic light scattering (DLS, BI-200SM, Brookhaven Co., Ltd., USA) equipped with a standard 633 nm laser, the test temperature was 25 °C, the pH was 7.4 ± 0.1, and the concentration was 0.1 g mL−1. The chemical functional groups of the samples were determined using Fourier transform infrared (FTIR, Nicolet6700, Thermo Fisher Technology Co., Ltd., USA), the samples were freeze dried and KBr was mixed before the testing. The morphology and size of the particles were characterized with transmission electron microscope (TEM, JEM-2100, JEOL Co., Ltd., JPN), the samples were diluted to 50 mg mL−1 and tested in dry state with 200 kV. The Fe concentration of the magnetic sample was analyzed using inductively coupled plasma-atomic emission spectroscopy (ICP-AES, Prodigy, Leeman Co., Ltd., USA). The crystalline structure of samples were determined using X-ray diffraction (XRD, D/Max-2550 PC, Rigaku Co., Ltd., JPN), the scan range (2θ) was from 20 to 70°. The magnetic properties were examined using vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM, Lakeshore7407, Trend Limited Co., Ltd., USA) at 300 K. T2 relaxometry was performed by a 0.5 T NMI20-Analyst NMR Analyzing and Imaging system (Shanghai Niumag Co., Ltd., CHN) using a wrist receiver coil with a Carr–Purcell–Meiboom–Gill (CPMG) sequence, the P(TBA-co-AA)/Fe3O4 nanogels were diluted in UPW with Fe concentration in the range of up to 0.05 mM. The instrumental parameters were set at point resolution = 156 mm × 156 mm, section thickness = 0.6 mm, TR = 5500 ms, TE = 0.2 ms, and number of excitation = 1. The r2 relaxivity was calculated by a linear fit of the inverse T2 (1/T2) relaxation time as a function of Fe concentration.3. Results and discussion
3.1. Chemical and crystal structures
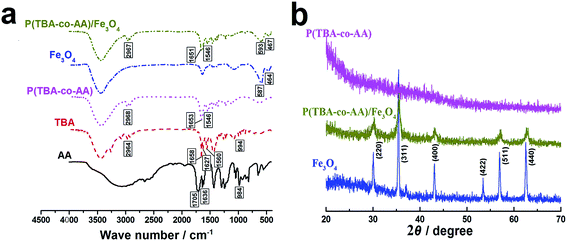
FTIR characterization was applied to characterize the chemical structures of the prepared P(TBA-co-AA)/Fe3O4 nanogels. And FTIR spectra of AA, TBA, the P(TBA-co-AA) nanogels, pure Fe3O4 nanoparticles were used as control samples. As was shown in Fig. 2a, the bands at 2964–2968 cm−1 could be attributed to stretching and bending vibrations of C–H groups.26 The characteristic band at 1705 cm−1 was assigned to the C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O stretching of AA. The bands at 1651–1658 cm−1 and 1546–1560 cm−1 were regarded as amide I (C
O stretching of AA. The bands at 1651–1658 cm−1 and 1546–1560 cm−1 were regarded as amide I (C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O stretching) and amide II (N–H bending), respectively.26,27 The characteristic bands at 1627–1636 cm−1 and 984–994 cm−1 assigned to C
O stretching) and amide II (N–H bending), respectively.26,27 The characteristic bands at 1627–1636 cm−1 and 984–994 cm−1 assigned to C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C of AA and TBA, which could not be found in the spectra of the P(TBA-co-AA) and P(TBA-co-AA)/Fe3O4 nanogels, indicating that the AA and TBA monomers totally formed the P(TBA-co-AA) and P(TBA-co-AA)/Fe3O4 nanogels in the process of polymerization.28,29 Two characteristic bands for Fe–O stretching observed at 587–593 cm−1 and 464–467 cm−1 were found in the Fe3O4 spectra. Moreover, the two characteristic bands of Fe3O4 were found in the P(TBA-co-AA)/Fe3O4 nanogels spectra but didn't appear in the P(TBA-co-AA) nanogels spectra which confirmed presence of Fe3O4 in the magnetic P(TBA-co-AA)/Fe3O4 nanogels.27,30
C of AA and TBA, which could not be found in the spectra of the P(TBA-co-AA) and P(TBA-co-AA)/Fe3O4 nanogels, indicating that the AA and TBA monomers totally formed the P(TBA-co-AA) and P(TBA-co-AA)/Fe3O4 nanogels in the process of polymerization.28,29 Two characteristic bands for Fe–O stretching observed at 587–593 cm−1 and 464–467 cm−1 were found in the Fe3O4 spectra. Moreover, the two characteristic bands of Fe3O4 were found in the P(TBA-co-AA)/Fe3O4 nanogels spectra but didn't appear in the P(TBA-co-AA) nanogels spectra which confirmed presence of Fe3O4 in the magnetic P(TBA-co-AA)/Fe3O4 nanogels.27,30
 | ||
| Fig. 2 FTIR spectra of AA, TBA, P(TBA-co-AA), pure Fe3O4 and P(TBA-co-AA)/Fe3O4 (a). XRD patterns of Fe3O4, P(TBA-co-AA) and P(TBA-co-AA)/Fe3O4 nanogels (b). | ||
Meanwhile, XRD spectra also confirmed the encapsulation of crystal Fe3O4. Fig. 2b were the XRD patterns of pure Fe3O4 nanoparticles, the P(TBA-co-AA) and P(TBA-co-AA)/Fe3O4 nanogels. The P(TBA-co-AA) nanogels revealed an amorphous structure and did not show any crystal peaks. And the pure Fe3O4 nanoparticles exhibited strong diffraction peaks and indexed to (220), (311), (400), (422), (511) and (533) planes of spinel cubic structure of Fe3O4 (Joint Committee on Powder Diffraction Standards (JCPDS) card number 88-0315). In contrast, the P(TBA-co-AA)/Fe3O4 nanogels exhibited apparent diffraction peaks at 2θ = 30.081 (220), 35.598 (311), 43.205 (400), 57.200 (511) and 62.761 (400).27,31 This evidence indicated that the crystal structures of Fe3O4 particles were kept in the magnetic nanogels.
3.2. Morphology and size characterizations
Fig. 3a and b were TEM photos of the P(TBA-co-AA) and P(TBA-co-AA)/Fe3O4 nanogels, respectively. The P(TBA-co-AA) nanogels were spherical, and the P(TBA-co-AA)/Fe3O4 nanogels were near-spherical. Moreover, the dry mean sizes of P(TBA-co-AA) nanogels and P(TBA-co-AA)/Fe3O4 nanogels were measured to be about 50 nm and 70 nm, respectively. Apparently, the mean size of P(TBA-co-AA)/Fe3O4 nanogels was bigger than the other one, this was probably because the Fe3O4 nanoparticles were synthesized and contained in the interior of the nanogels. And from the higher magnification TEM photo in Fig. 3b, the P(TBA-co-AA)/Fe3O4 nanogels were filled with Fe3O4 nanoparticles. However, the magnetic nanogels with 70 nm in diameter were still small sizes which could be applied for more tissues imaging in vivo. Besides, the P(TBA-co-AA) nanogels could improve the hydrophilicity and stability of magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs), thus they could not be identified easily by macrophage when they were injected into vein, which could increase the half-time of phagocytosis and the time of contract imaging.32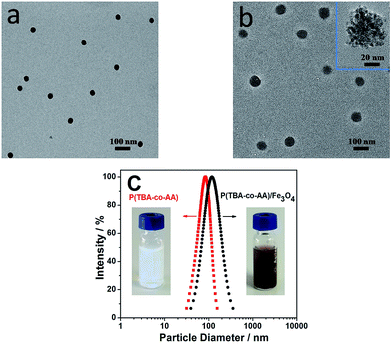 | ||
| Fig. 3 TEM photos of P(TBA-co-AA) (a) and P(TBA-co-AA)/Fe3O4 nanogels (b). Particle size distribution of P(TBA-co-AA) and P(TBA-co-AA)/Fe3O4 nanogels (c). | ||
Fig. 3c showed the hydrodynamic mean sizes and PDI values of the P(TBA-co-AA) and P(TBA-co-AA)/Fe3O4 nanogels which were characterized by DLS. They were measured to be 82.1 nm and 118.9 nm, respectively. And the PDI values were 0.085 and 0.124 accordingly. Meanwhile, magnetic nanogels had a quite small PDI value, indicating that the nanogels had uniform size distribution. And the hydrodynamic mean size of the P(TBA-co-AA)/Fe3O4 nanogels was bigger than the other one, this result was in consistent with the dates measured by TEM. Besides, the particle size distribution of P(TBA-co-AA) nanogels (red parabola) and P(TBA-co-AA)/Fe3O4 nanogels (black parabola) in Fig. 3c, showed both nanogels had a very narrow size distribution range. And photos (Fig. 3c, inset) showed the P(TBA-co-AA) nanogel sample was light blue and the P(TBA-co-AA)/Fe3O4 nanogel sample was puce.
3.3. Magnetic properties
Photos of the different states of the P(TBA-co-AA)/Fe3O4 nanogels which clearly showed their magnetic behavior were shown in Fig. 4a. The nanogel dispersion was puce and turbid (left), when magnets were placed near to the sample after 1–2 h, the suspension became clear and transparent (right). And the magnetic nanogels were collected at the vial wall because of the attraction from the magnets. However, when the magnets were removed and ultrasonic was afforded, the sample turned back to its original state. The process above was repeatable which showed the P(TBA-co-AA)/Fe3O4 nanogels kept a good magnetic performance and good dispersion at aqueous media. What's more, the synthesized Fe3O4 nanoparticles can be encapsulated by the network of the P(TBA-co-AA) nanogels. And the content of Fe element of the nanogels was 1.73 μg mL−1.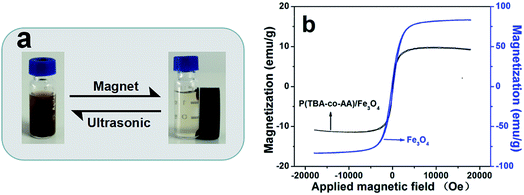 | ||
| Fig. 4 Photos of the P(TBA-co-AA)/Fe3O4 nanogels (a) and magnetization curves for Fe3O4 and P(TBA-co-AA)/Fe3O4 nanogels (b). | ||
The magnetization curves of the pure Fe3O4 nanoparticles (blue line) and the prepared P(TBA-co-AA)/Fe3O4 nanogels (black line) were shown in Fig. 4b. Yang Yudong33 reported that the superparamagnetic magnetic particles had a huge magnetism in a weak external magnetic field but had no magnetism without the outer magnetic field. As shown in Fig. 4b, no hysteresis loop was observed, and both coercivity (Hc) and remanence (Mr) were measured to be zero, meaning these samples had a superparamagnetic property.34,35 Thus the magnetic nanogels could be used to improve the clarity of T2-style magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Besides, the magnetization values of Fe3O4 and P(TBA-co-AA)/Fe3O4 were found to be 83.3 emu g−1 and 10.1 emu g−1. These values were similar to previously reported work of nanogels-based MNPs.27,36
3.4. r2 relaxivity measurements
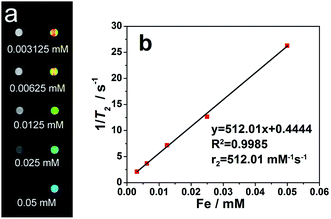
Fig. 5 showed the transverse relaxation time (T2) of water protons in an aqueous solution of the P(TBA-co-AA)/Fe3O4 nanogels. From the T2-weighted MRI (Fig. 5a), it showed that the P(TBA-co-AA)/Fe3O4 sample was able to induce the decrease of the MR signal intensity with the increase of Fe concentration. By linear fitting of the T2 relaxation rate (1/T2) as a function of Fe concentration (Fig. 5b), the r2 relaxivity of the P(TBA-co-AA)/Fe3O4 nanogels was estimated to be 512.01 mM−1 s−1. It is easy to find that the value is higher than that of other Fe3O4 nanoparticles coated with polymer shells,37,38 which was essential for the prepared P(TBA-co-AA)/Fe3O4 nanogels to be used as good T2 negative contrast agent for sensitive MRI applications with small dose.4. Conclusions
In summary, a new method was developed to prepare the P(TBA-co-AA)/Fe3O4 nanogels which had a very low PDI value of 0.124, the hydrodynamic and dry mean size were 118.9 nm and 70 nm, respectively. The magnetization value and the r2 relaxivity of the P(TBA-co-AA)/Fe3O4 nanogels were 10.1 emu g−1 and 512.01 mM−1 s−1. Moreover, the P(TBA-co-AA)/Fe3O4 nanogels had a superparamagnetic property and a significant contrast enhancement in T2-weighted MRI, meaning the magnetic nanogels had high sensitivity and clear imaging as MRI contrast agent.Acknowledgements
The authors thank for financial supports by National Nature Science Foundation of China (51473032, 51503034), Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (CUSF-DH-D-2016024, 2232015D3-12) and Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality for Yangfan Program (15YF1400700).References
- J. Z. Zhu, C. Peng, W. J. Sun, Z. B. Yu, B. Q. Zhou, D. Li, Y. Luo, L. Ding, M. W. Shen and X. Y. Shi, J. Mater. Chem. B, 2015, 3, 8684–8693 RSC.
- S. Veintemillas-Verdaguer, O. Bomati-Miguel and M. P. Morales, Scr. Mater., 2002, 47, 589–593 CrossRef CAS.
- M. B. Gongalsky, Y. V. Kargina, L. A. Osminkina, A. M. Perepukhov, M. V. Gulyaev, A. N. Vasiliev, Y. A. Pirogov, A. V. Maximychev and V. Y. Timoshenko, Appl. Phys. Lett., 2015, 107, 233702 CrossRef.
- P. Granitzer, K. Rumpf, Y. Tian, G. Akkaraju, J. Coffer, P. Poelt and M. Reissner, Appl. Phys. Lett., 2013, 102, 193110 CrossRef.
- M. Pirhayati, H. Veisi and A. Kakanejadifard, Rsc Adv., 2016, 6, 27252–27259 RSC.
- P. Tartaj, M. D. Morales, S. Veintemillas-Verdaguer, T. Gonzalez-Carreno and C. J. Serna, J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys., 2003, 36, 182–197 CrossRef.
- S.-C. Lee, C.-M. Fu and F.-H. Chang, Appl. Phys. Lett., 2013, 103, 163104 CrossRef.
- F. Gao, H. Qu, Y. Duan, J. Wang, X. Song, T. Ji, L. Cao, G. Nie and S. Sun, Rsc Adv., 2014, 4, 6657–6663 RSC.
- Y. Wu, H. Yang, Y. Lin, Z. Zheng and X. Ding, Mater. Lett., 2016, 169, 218–222 CrossRef CAS.
- V. Patsula, L. Kosinova, M. Lovric, L. Ferhatovic Hamzic, M. Rabyk, R. Konefal, A. Paruzel, M. Slouf, V. Herynek, S. Gajovic and D. Horak, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2016, 8, 7238–7247 Search PubMed.
- W. Chen, X. Wen, G. Zhen and X. Zheng, RSC Adv., 2015, 5, 69307–69311 RSC.
- X.-H. Peng, X. Qian, H. Mao, A. Y. Wang, Z. Chen, S. Nie and D. M. Shin, Int. J. Nanomed., 2008, 3, 311–321 CAS.
- T. Ogawa, H. Kura and M. Takahashi, Scr. Mater., 2011, 64, 1067–1070 CrossRef CAS.
- J. S. Weinstein, C. G. Varallyay, E. Dosa, S. Gahramanov, B. Hamilton, W. D. Rooney, L. L. Muldoon and E. A. Neuwelt, J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab., 2010, 30, 15–35 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. S. Yao, W. B. Zhang, X. Z. Yang, J. Liu and H. T. Liu, Biomater. Sci., 2014, 2, 1761–1767 RSC.
- S. Y. Li, D. L. Lin, J. F. Zhou and L. S. Zha, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2016, 120, 4902–4908 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Wang, D. C. Niu, Q. Wu, S. Bao, T. Su, X. H. Liu, S. J. Zhang and Q. G. Wang, Biomaterials, 2015, 53, 349–357 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. B. Na, I. C. Song and T. Hyeon, Adv. Mater., 2009, 21, 2133–2148 CrossRef CAS.
- R. Salehi, S. Rasouli and H. Hamishehkar, Int. J. Pharm., 2015, 487, 274–284 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. L. Xu, S. A. Majetich and S. A. Asher, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2002, 124, 13864–13868 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. G. Zhang, S. Q. Xu and E. Kumacheva, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2004, 126, 7908–7914 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. L. Rogach, D. Nagesha, J. W. Ostrander, M. Giersig and N. A. Kotov, Chem. Mater., 2000, 12, 2676–2685 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Gao, W.-L. Xue, Z.-X. Zeng and X.-r. Fan, J. Chem. Eng. Data, 2015, 60, 2273–2279 CrossRef CAS.
- K. Yoshimatsu, B. K. Lesel, Y. Yonamine, J. M. Beierle, Y. Hoshino and K. J. Shea, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2012, 51, 2405–2408 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. F. Yan, X. Zhang and Y. Y. Sun, Colloids Surf., B, 2014, 113, 302–311 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. F. Chen, L. Jiang and Y. Dan, J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 2011, 121, 3322–3331 CrossRef CAS.
- F.-Y. Chou, C.-M. Shih, M.-C. Tsai, W.-Y. Chiu and S. J. Lue, Polymer, 2012, 53, 2839–2846 CrossRef CAS.
- K. Boram, S. Hye In and C. Bong Geun, BioChip J., 2014, 8, 8–14 CrossRef.
- S. M. Elsaeed, R. K. Farag and N. S. Maysour, J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 2012, 124, 1947–1955 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Gupta, P. Paul, N. Kumar, S. Baxi and D. P. Das, J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2014, 430, 221–228 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. Hernandez and C. Mijangos, Macromol. Rapid Commun., 2009, 30, 176–181 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. L. Immordino, F. Dosio and L. Cattel, Int. J. Nanomed., 2006, 1, 297–315 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. D. Yang, Prog. Mod. Biomed., 2007, 7, 1387–1390 CAS.
- H. C. Gu, H. Xu, N. H. Tong, C. Li and Y. Lu, J. Magn. Magn. Mater., 2007, 311, 125–130 CrossRef.
- M. M. Lakouraj, F. Mojerlou and E. N. Zare, Carbohydr. Polym., 2014, 106, 34–41 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- F.-Y. Chou, J.-Y. Lai, C.-M. Shih, M.-C. Tsai and S. J. Lue, Colloids Surf., B, 2013, 104, 66–74 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Li, L. Zheng, H. Cai, W. Sun, M. Shen, G. Zhang and X. Shi, Biomaterials, 2013, 34, 8382–8392 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. C. Li, Y. He, S. W. J. Sun, Y. Luo, H. D. Cai, Y. Q. Pan, M. W. Shen, J. D. Xia and X. Y. Shi, Biomaterials, 2014, 35, 3666–3677 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 |