Direct reuse of Cu-laden wastewater for non-edible oil hydrolysis: basic mechanism of metal extraction and fatty acid production†
Abstract
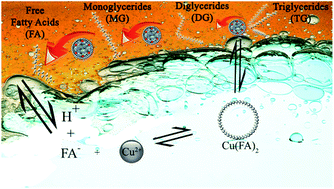
Fatty acids are platform chemicals to produce various useful chemicals and fuels. Hydrolysis of waste cooking oil using synthetic copper wastewater as the water and catalyst source to produce fatty acids was studied by carrying out reactions at 200–250 °C, water/acylglyceride molar ratio of 30 : 1–90 : 1, and CuSO4 concentration of 250–1500 mg kg−1. Comparison between catalytic and non-catalytic systems was also evaluated. Increasing temperature influenced fatty acid yield, acylglycerides conversion, and copper removal by enhancing fatty acid deprotonation. Minimum loss of fatty acids by micellar solubilization mechanism was achieved by using CuSO4 in the concentration range of 250–750 mg kg−1. Copper was transferred into the fatty acid product during the process by ion exchange mechanism. Considerable copper removal from the aqueous phase (98.87%) was achieved by 5 times recycling of the aqueous phase product into the hydrolysis process of pristine waste cooking oil. Direct utilization of copper-containing wastewater for industrial processes such as oil hydrolysis offers a potential symbiotic approach in industrial wastewater management and production of valuable chemicals.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...