Layer like porous materials with hierarchical structure
Abstract
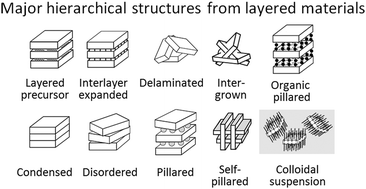
Many chemical compositions produce layered solids consisting of extended sheets with thickness not greater than a few nanometers. The layers are weakly bonded together in a crystal and can be modified into various nanoarchitectures including porous hierarchical structures. Several classes of 2-dimensional (2D) materials have been extensively studied and developed because of their potential usefulness as catalysts and sorbents. They are discussed in this review with focus on clays, layered transition metal oxides, silicates, layered double hydroxides, metal(IV) phosphates and phosphonates, especially zirconium, and zeolites. Pillaring and delamination are the primary methods for structural modification and pore tailoring. The reported approaches are described and compared for the different classes of materials. The methods of characterization include identification by X-ray diffraction and microscopy, pore size analysis and activity assessment by IR spectroscopy and catalytic testing. The discovery of layered zeolites was a fundamental breakthrough that created unprecedented opportunities because of (i) inherent strong acid sites that make them very active catalytically, (ii) porosity through the layers and (iii) bridging of 2D and 3D structures. Approximately 16 different types of layered zeolite structures and modifications have been identified as distinct forms. It is also expected that many among the over 200 recognized zeolite frameworks can produce layered precursors. Additional advances enabled by 2D zeolites include synthesis of layered materials by design, hierarchical structures obtained by direct synthesis and top-down preparation of layered materials from 3D frameworks.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Hierarchically-structured porous materials: from basic understanding to applications

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...