The effect of amino substituents on the interactions of quinazolone derivatives with c-KIT G-quadruplex: insight from molecular dynamics simulation study for rational design of ligands†
Abstract
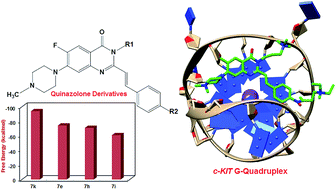
Stabilization of G-quadruplex structures in the oncogenic promoter regions with small molecules has attracted considerable attention as a promising target for cancer therapy. To discover such small molecules, understanding the nature of interactions between the ligand and G-quadruplex is of paramount importance. To precisely investigate how these interactions can be influenced by varying different substituents, binding interactions of some quinazolone derivatives (QDs) with c-KIT G-quadruplex were studied by molecular dynamics (MD) simulation. The results revealed that the QD–NH–CO– arrangement in quinazolone derivatives improve binding affinity toward c-KIT G-quadruplex and the amino substituents play a crucial role in hydrogen bond formation and electrostatic interactions with the phosphate backbone of the G-quadruplex. We also proposed a new derivative of quinazolone (7k) with a terminal amino substituent instead of a 3-phenyl group. The binding free energy analysis suggested that this derivative stabilizes the c-KIT G-quadruplex much better than other derivatives. Furthermore, the calculated changes in solvent-accessible surface area (ΔSASA) were consistent with the binding free energy calculations. Our studies provide insight into the effect of different substituents on binding interactions between the ligand and G-quadruplex which can pave the way to rational ligand design.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...