New α-glucosidase inhibitors from a marine sponge-derived fungus, Aspergillus sp. OUCMDZ-1583†
Fandong Konga,
Chengying Zhaoa,
Jiejie Haoa,
Cong Wanga,
Wei Wanga,
Xiaolong Huangb and
Weiming Zhu*a
aKey Laboratory of Marine Drugs, Ministry of Education of China, School of Medicine and Pharmacy, Ocean University of China, Qingdao 266003, China. E-mail: weimingzhu@ouc.edu.cn; Fax: +86-532-82031268; Tel: +86-532-82031268
bCollege of Agriculture, Hainan University, Haikou 570228, China
First published on 27th July 2015
Abstract
Eighteen new compounds named aspergones A–Q (1–17) and 6-O-demethylmonocerin (18), along with five known analogues (19–23), were isolated from the fermentation broth of Aspergillus sp. OUCMDZ-1583 associated with an unidentified marine sponge (XD10410) from the Xisha Islands of China. The structures, including the absolute configurations, were unambiguously elucidated by spectroscopic, X-ray crystallographic, chemical, and Mosher’s methods along with quantum ECD calculations. Compounds 1, 2, 5, 10, 11, 14–18, and 21–23 showed α-glucosidase inhibition with IC50 values of 2.36, 1.65, 1.30, 2.37, 2.70, 1.36, 1.54, 2.21, 2.26, 0.027, 1.65, 1.19 and 1.74 mM, respectively (with acarbose as the positive control; IC50 = 0.95 mM), among which compound 18 is 35 times more potent than acarbose. In addition, compounds 18 and 21 exhibited inhibitory activity against the influenza A (H1N1) virus with IC50 values of 172.4 and 175.5 μM, respectively (with ribavirin as the positive control; IC50 = 137.3 μM).
Introduction
Microorganisms continue to play an important role in the search for novel and bioactive compounds for drug development.1,2 However, with the deepening of research on terrestrial microbial natural products, the discovery of new entities from these microorganisms is increasingly difficult due to chemical redundancy.3 As a result, many natural product chemists turned their attention to marine counterparts, especially marine fungi, which are supposed to be a tremendous resource for drug discovery with their specialised niches.4,5 With this trend in mind, and as a continuation of our investigations on structurally new and bioactive natural products of marine fungal origin,6–9 an endozoic fungus, Aspergillus sp. OUCMDZ-1583, was isolated from an unidentified marine sponge (XD10410) from the Xisha Islands of China. The EtOAc extract of the fermentation broth showed α-glucosidase inhibition with an IC50 value of 0.97 mg mL−1, while the IC50 value of acarbose (the positive control) was 0.61 mg mL−1. Chemical examination of the fermentation broth resulted in the isolation and identification of eighteen new compounds that we named aspergones A–Q (1–17) and 6-O-demethylmonocerin (18), as well as five known compounds: epoxyquinol (19),10 7-O-demethylmonocerin (20),11 (+)-monocerin (21),11,12 fusarentin 6-methyl ether (22),11 and 6,7-O-dimethyl-4R-hydroxy-10-epifusarentin (23)13 (Table S1, ESI†).Results and discussion
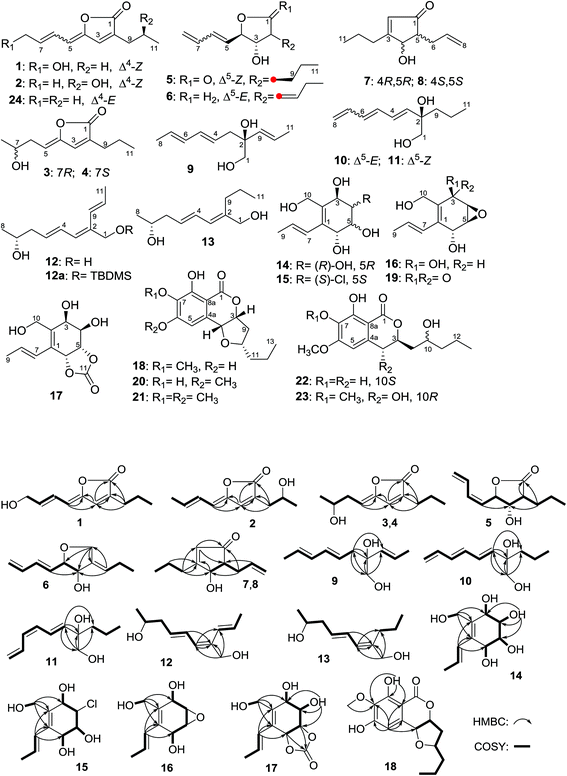
Aspergone A (1) was obtained as a brown oil, with a molecular formula of C11H14O3, which was established from an HRESIMS peak of m/z 195.1014 [M + H]+. The IR spectrum of 1 showed the presence of a lactone carbonyl (1777 cm−1), and a hydroxy group (3377 cm−1). The 1H and 13C NMR data (Table 1 and 2) along with the HSQC spectrum showed the presence of one triplet methyl (δC/H 13.7/0.91), three methylenes including an oxygenated one, six olefinic carbons (where four were protonated), and one lactone carbonyl (δC 170.1). These data were similar to the known 5-(E)-but-2-enylidene-3-propyl-5H-furan-2-one (24)14 except for an oxygenated methylene (δC/H 63.3/4.24) replacing the corresponding methyl signals, indicating the hydroxylation of C-8 in 1. This deduction was further evidenced by the COSY cross-peaks from H-5 (δH 5.67) to H2-8 (δH 4.24) through H-6 (δH 6.74) and H-7 (δH 6.04) and from H2-9 (δH 2.31) to H3-11 (δH 0.91) through H2-10 (δH 1.57) as well as the HMBC correlations of H-3 (δH 6.96) to C-1 (δC 170.1), C-2 (δC 134.4), C-4 (δC 148.0), and C-9 (δC 27.4), H-6 to C-4, H-5 to C-3 (δC 136.6) and C-4, and of H-9 to C-1, C-2, and C-3 (Fig. 1). The E- and Z-geometries of the Δ6- and Δ4-double bonds could be deduced from the large JH-6,H-7 value (16.3 Hz) (Table 2) and the NOE difference experiment (Fig. 2), respectively. The H-3 signal (δH 6.96) was significantly enhanced when the H-5 signal (δH 5.67) was irradiated.| Position | 1b,c | 2b,d | 3 and 4b,c | 5b,d | 6a,d | 7 and 8b,c | 9a,c | 10a,c | 11a,c | 12a,c | 13a,c | 14a,c | 15a,d | 16a,c | 17a,c | 18b,c |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a Recorded in DMSO-d6.b Recorded in CDCl3.c Measured using a JEOL JNM-ECP 600 spectrometer, and the δC values of C-4a, C-8a, C-12, C-13 and 7-OMe for 18 were 131.4 (C), 101.3 (C), 19.2 (CH2), 14.1 (CH3) and 60.9 (CH3), respectively.d Measured using an Agilent 500 MHz DD2 spectrometer. | ||||||||||||||||
| 1 | 170.1, C | 171.1, C | 170.8, C | 175.9, C | 70.1, CH2 | 206.9, C | 68.7, CH2 | 69.0, CH2 | 68.9, CH2 | 62.4, CH2 | 65.0, CH2 | 133.4, C | 134.8, C | 131.2, C | 126.0, C | 168.2, C |
| 2 | 134.4, C | 129.7, C | 134.1, C | 47.6, CH | 140.2, C | 128.9, CH | 75.0, C | 75.2, C | 75.3, C | 135.7, C | 140.9, C | 135.8, C | 135.4, C | 133.2, C | 140.2, C | |
| 3 | 136.6, CH | 139.3, CH | 137.0, CH | 78.4, CH | 74.1, CH | 180.7, C | 41.0, CH2 | 140.8, CH | 141.6, CH | 126.7, CH | 124.3, CH | 68.5, CH | 73.3, CH | 65.5, CH | 67.4, CH | 81.5, CH |
| 4 | 148.0, C | 146.2, C | 149.8, C | 79.4, CH | 86.6, CH | 76.7, CH | 125.1, CH | 132.2, CH | 123.6, CH | 127.6, CH | 128.1, CH | 68.7, CH | 69.0, CH | 54.5, CH | 69.8, CH | 74.3, CH |
| 5 | 111.2, CH | 113.8, CH | 110.4, CH | 126.0, CH | 132.9, CH | 55.3, CH | 134.7, CH | 134.2, CH | 128.8, CH | 132.6, CH | 130.8, CH | 68.3, CH | 75.6, CH | 54.3, CH | 77.9, CH | 108.1, CH |
| 6 | 123.8, CH | 124.9, CH | 35.8, CH2 | 135.0, CH | 131.8, CH | 31.7, CH2 | 131.3, CH | 128.3, CH | 130.8, CH | 43.1, CH2 | 43.2, CH2 | 67.9, CH | 73.4, CH | 62.7, CH | 75.5, CH | 155.4, C |
| 7 | 137.1, CH | 136.5, CH | 67.6, CH | 131.1, CH | 136.9, CH | 135.3, CH | 128.6, CH | 137.8, CH | 132.9, CH | 66.6, CH | 66.7, CH | 127.7, CH | 126.9, CH | 128.3, CH | 126.0, CH | 134.9, C |
| 8 | 63.3, CH2 | 19.0, CH3 | 23.4, CH3 | 121.7, CH2 | 118.2, CH2 | 117.4, CH2 | 18.1, CH3 | 117.4, CH2 | 118.5, CH2 | 23.6, CH3 | 23.6, CH3 | 128.0, CH | 129.6, CH | 127.0, CH | 130.2, CH | 155.6, C |
| 9 | 27.4, CH2 | 35.0, CH2 | 27.2, CH2 | 30.4, CH2 | 125.7, CH | 32.9, CH2 | 133.3, CH | 40.0, CH2 | 40.0, CH2 | 125.8, CH | 30.4, CH2 | 19.3, CH3 | 19.3, CH3 | 19.2, CH3 | 19.2, CH3 | 39.1, CH2 |
| 10 | 21.0, CH2 | 66.3, CH | 21.0, CH2 | 19.9, CH2 | 21.9, CH2 | 20.2, CH2 | 135.2, CH | 16.8, CH2 | 16.8, CH2 | 125.7, CH | 22.1, CH2 | 58.1, CH2 | 57.5, CH2 | 56.8, CH2 | 58.2, CH2 | 78.7, CH |
| 11 | 13.7, CH3 | 23.3, CH3 | 13.8, CH3 | 13.9, CH3 | 14.6, CH3 | 14.0, CH3 | 17.9, CH3 | 15.2, CH3 | 15.2, CH3 | 19.3, CH3 | 14.6, CH3 | 154.8, C | 38.1, CH2 | |||
| Position | 1b,c | 2b,d | 3 and 4 b,c | 5b,d | 6a,d | 7 and 8b,c | 9a,c | 10a,c | 11a,c | 12a,c | 13a,c | 14a,c | 15a,d | 16a,c | 17a,c | 18b,c |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a Recorded in DMSO-d6.b Recorded in CDCl3.c Measured using a JEOL JNM-ECP 600 spectrometer, and the δH values of H-12, H-13, HO-8 and 7-OMe for 18 were 1.41 (m)/1.33 (m), 0.90 (t, J = 7.5 Hz, 3H), 11.5 (s) and 3.97 (s3H), respectively.d Measured using an Agilent 500 MHz DD2 spectrometer. | ||||||||||||||||
| 1 | 4.27, d (12.5) | 3.45, d (11.7) | 3.25, d (12.0) | 3.26, d (12.5) | 4.07, s | 3.87, s | ||||||||||
| 4.18, d (12.5) | 3.43, d (11.7) | 3.21, d (12.0) | 3.22, d (12.5) | |||||||||||||
| 2 | 2.62, m | 5.87, s | ||||||||||||||
| 3 | 6.96, s | 7.15, s | 6.99, s | 3.97 dd (7.8, 8.9) | 4.22, dd (5.5, 5.4) | 2.31, m; 2.32, m | 5.79, d (14.8) | 5.82, d (15.0) | 6.03, d (11.6) | 5.97, d (11.0) | 4.17, dd (5.3, 4.9) | 4.24, dd (10.6, 7.5) | 4.52, dd (5.1, 3.2) | 4.24, dd (4.8, 3.6) | 5.02, m | |
| 4 | 4.98, dd (7.8, 7.8) | 4.09, dd (5.4, 5.4) | 4.45, d (3.0) | 5.48, dt (14.5, 7.4) | 6.23, dd (14.8, 10.7) | 6.68, dd (15.0, 12.4) | 6.51, dd (15.0, 11.2) | 6.26, dd (15.4, 11.0) | 3.60, m | 3.66, dd (10.6, 10.6) | 3.35, dd (3.2, 4.0) | 3.55, m | 4.49, d (3.0) | |||
| 5 | 5.67, d (11.6) | 5.71, d (11.3) | 5.26, t (8.2) | 5.41, dd (10.2, 7.8) | 5.71, dd (15.7, 6.7) | 2.37, m | 6.08, dd (14.5, 11.0) | 6.28, dd (14.8, 10.7) | 6.03, dd (11.3, 12.4) | 5.70, m | 5.62, dt (15.4, 7.5) | 3.55, m | 3.34, m | 3.28, dd (4.0, 1.9) | 4.81, dd (9.6, 7.6) | 6.60, s |
| 6 | 6.74, dd (16.3, 11.6) | 6.52, dd (15.6, 11.3) | 2.55, m; 2.49, m | 6.31, dd (10.2, 11.3) | 6.21, dd (15.7, 10.2) | 2.56, ddd (14.6, 6.0, 6.2) 2.21, ddd (14.6, 7.9, 7.4) | 6.02, dd (14.4, 10.2) | 6.19, dd (14.8, 10.2) | 5.93, dd (11.2, 11.3) | 2.24, m; 2.14, m | 2.19, m; 2.10, m | 4.23, dd (4.0, 4.0) | 3.99, dd (6.5, 6.5) | 4.45, dd (7.7, 1.9) | 5.60, d (7.6) | |
| 7 | 6.04, dt (16.3, 4.9) | 5.99, dq (15.6, 6.8) | 3.96, m | 6.68, ddd (16.6, 11.3, 10.3) | 6.32, ddd (17.0, 10.2, 10.2) | 5.75, m | 5.62, dq (14.4, 6.9) | 6.36, ddd, (17.1, 10.2, 10.2) | 6.82, ddd (16.7, 11.2, 10.4) | 3.65, m | 3.62, m | 6.34, dd (15.7, 1.6) | 6.15, d (16.2) | 6.36, d (15.8) | 6.42, br.d (16.3) | |
| 8 | 4.24, d (4.9) | 1.84, d (7.1) | 1.23, d (6.1) | 5.37, br.d (16.6); 5.30, br.d (10.3) | 5.21 br.d (17.0); 5.07 br.d (10.2) | 5.11, br.d (17.0); 5.03, br.d (10.5) | 1.73, d (6.9) | 5.20, d (17.1); 5.06, d (10.2) | 5.24, d (16.7); 5.15, (10.4) | 1.03, d (6.1) | 1.02, d (6.2) | 5.94, dq (15.7, 6.7) | 5.82, m | 5.91, dq (15.8, 6.7) | 5.93, dq (16.3, 6.8) | |
| 9 | 2.31, t (7.5) | 2.53, dd (15.0, 7.9); 2.46, dd (15.0, 3.9) | 2.32, t (7.6) | 1.84, m; 1.58, m | 5.36, t (7.3) | 2.49, m; 2.36, m | 5.44, d (15.5) | 1.41, m; 1.42, m | 1.43, m; 1.41, m | 6.49, dd (16.6, 1.5) | 2.07, t (7.3) | 1.77, dd (1.6, 6.7) | 1.73, d (5.5) | 1.76, d (6.7) | 1.80, dd (6.6, 1.5) | 2.56, ddd, (14.6, 8.7, 6.4); 2.13, ddd (14.6, 6.0, 1.4) |
| 10 | 1.57, m | 4.04, m | 1.59, m | 1.57, m; 1.51, m | 2.12, m | 1.56, m; 1.62, m | 5.73, dq (15.5, 6.6) | 1.30, m; 1.18, m | 1.30, m; 1.18, m | 5.72, m | 1.37, m | 4.18, dd (12.0, 5.8); 3.92, dd (12.0, 5.8) | 4.11, s | 4.16, dd (6.0, 11.7); 4.13, dd (6.0, 11.7) | 4.31, dd (12.4, 4.7); 3.95, dd (12.4, 4.7) | 4.10, m |
| 11 | 0.91, t (7.6) | 1.21, d (6.4) | 0.95, t (7.8) | 0.96, t (7.3) | 0.91, t (7.7) | 0.95, t (7.4) | 1.72, d (6.6) | 0.83, t (7.3) | 0.83, t (6.7) | 1.76, dd (6.8, 1.5) | 0.86, t (7.6) | 1.68, m; 1.55, m | ||||
| 3-OH | 5.27, d (5.5) | 4.51, d (5.3) | 5.39, d (7.5) | 5.13, d (5.1) | 5.14, d (4.8) | |||||||||||
| 4-OH | 4.27, d (5.9) | 5.47, d (5.9) | ||||||||||||||
| 5-OH | 4.41, d (5.4) | 5.41, d (5.6) | ||||||||||||||
| 6-OH | 4.44, d (4.0) | 5.09, d (6.5) | 5.16, d (7.7) | |||||||||||||
| 10-OH | 4.64, t (5.8) | 4.37, t (5.4) | 4.35, t (6.) | 4.91, t (4.9) | ||||||||||||
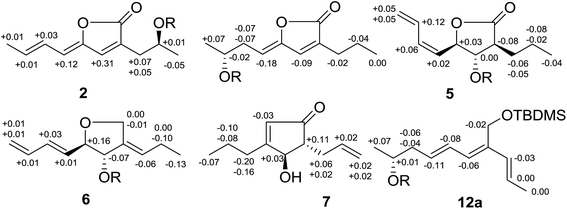
Aspergone B (2) has the same molecular formula as 1, with an HRESIMS peak at m/z 217.0832 [M + Na]+, and similar 13C NMR data (Table 1). The difference was that hydroxymethine (δC/H 66.3/4.04) and methyl (δC/H 19.0/1.84) signals replaced the corresponding hydroxymethylene and methylene signals of 1. HMBC correlations from H-3 (δH 7.15) to C-1 (δC 171.1), C-2 (δC 129.7) and C-4 (δC 146.2), H2-9 (δH 2.46, 2.53) to C-1, C-2 and C-3 (δC 139.3), and from H3-8 (δH 1.84) to C-6 (δC 124.9) and C-7 (δC 136.5) along with the 1H–1H COSY data of H2-9/H-10 (δH 4.04)/H3-11 (δH 1.21) suggested that the hydroxy group was located at C-10 in 2. The E- and Z-geometries of the Δ6- and Δ4-double bonds could be deduced from the large JH-6,H-7 value (15.6 Hz) (Table 1) and the NOE difference experiment (Fig. 2), respectively. The H-5 signal (δH 5.71) was significantly enhanced when the H-3 signal (δH 7.15) was irradiated. The absolute configuration of C-10 was determined by the modified Mosher’s method.15 The Δδ values between the (S)-MTPA ester (2b) and (R)-MTPA ester (2a) clearly indicated the 10S-configuration (Fig. 3).
Aspergones C (3) and D (4) were initially obtained as a racemic mixture, as shown by the zero value of the specific rotation, and with the same molecular formula of C11H16O3 as established from an HRESIMS peak at m/z 219.0988 [M + Na]+. Although the 1H and 13C NMR data revealed the presence of the same furan-2(5H)-one nucleus as 1, the remaining portion was slightly different. 1H–1H COSY data (ESI†) and HMBC correlations of H-7 (δH 3.96) to C-5 (δC 110.4) and H-5 (δH 5.26) to C-3 (δC 137.0) and C-4 (δC 149.8) revealed that a 3-hydroxybutylidene group in 3 and 4 replaced the corresponding 4-hydroxybutenylidene group in 1. The Z-geometry of the Δ4-double bond was deduced from the NOE enhancements of the H-5 signal after the irradiation of H-3 (δH 6.99) (Fig. 2). Upon chiral chromatography on a CHIRAPAK IA HPLC column, optically pure 3 and 4 were obtained. The distribution of Δδ values between the (S)- and (R)-MTPA esters (3a and 3b) indicated the 7R-configuration of 3 (Fig. 3). Therefore, the absolute configuration of 4 was determined to be 7S.
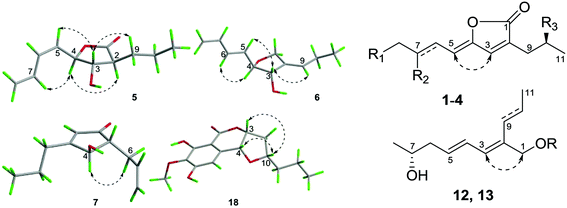
The molecular formula of aspergone E (5) was established as C11H16O3 from an HRESIMS peak at m/z 219.0989 [M + Na]+, with four degrees of unsaturation. Strong IR absorptions at 1769 and 1645 cm−1 implied the presence of lactone carbonyl and double bond functional groups. 1H–1H COSY cross-peaks from H2-8 (δH 5.30, 5.37) through H-7 (δH 6.68), H-6 (δH 6.31), H-5 (δH 5.41), H-4 (δH 4.98), H-3 (δH 3.97), H-2 (δH 2.62), H2-9 (δH 1.84, 1.58) and H2-10 (δH 1.57, 1.51) to H3-11 (δH 0.96), and HMBC correlations from H-2 and H2-9 to C-1 (δC 175.9), indicated a 4-(but-1,3-dienyl)-3-hydroxy-2-propylbutyrrolactone structure (Fig. 2). The Z-geometry of the Δ5-double bond could be determined by the JH-5,H-6 value (10.2 Hz, Table 2) and the NOE enhancement of H-7 after the irradiation of H-4. Furthermore, NOE enhancements of H-5 and H-9 were observed when H-3 was irradiated, while the H-2 signal was enhanced after the irradiation of H-4, indicating the trans-orientations of both H-2 and H-4 with H-3 (Fig. 2). The distribution of Δδ values between the (S)- and (R)-MTPA esters (5a and 5b) indicated the 3S-configuration (Fig. 3). Thus, the absolute configuration of 5 was determined to be 2S, 3S, and 4R.
The molecular formula of aspergone F (6) was established as C11H16O2 from an HRESIMS peak at m/z 203.1037 [M + Na]+, with one oxygen less than that of 5. Comparison of the 13C NMR data between 6 and 5 (Table 1) revealed that an olefinic quaternary carbon, an olefinic methine and an oxygenated methylene signal in 6 replaced the corresponding sp3-methine, sp3-methylene and ester carbonyl signals in 5. Two separate 1H–1H COSY systems of H-3/H-4/H-5/H-6/H-7/H-8 and H-9/H-10/H-11 (ESI†) were observed in 6, indicating that a propylidene group replaced the propyl group in 5. The key HMBC data from H2-1 (δH 4.27, 4.18) to C-2 (δC 140.2), C-4 (δC 86.6) and C-9 (δC 125.7) and from H-9 (δH 5.36) to C-1 (δC 70.1) confirmed the replacement of the carbonyl group in 5 by a –CH2– group in 6. The E-geometry of the Δ5-double bond was deduced from the large JH-5,H-6 value (15.7 Hz, Table 2) and the NOE enhancement of H-6 (δH 6.21) after the irradiation of H-4 (δH 4.09) (Fig. 2). The NOE enhancements of H-5 (δH 5.71) and H-9 after the irradiation of H-3 (δH 4.22) (Fig. 2) indicated the trans-orientation of H-3 and H-4 and the E-geometry of the Δ2(9)-double bond. The distribution of Δδ values between the (S)- and (R)-MTPA esters (6a and 6b) indicated the 3S-configuration (Fig. 3). Thus, the absolute configuration of 6 was determined as 3S and 4R.
Aspergones G (7) and H (8) were initially isolated as a racemic mixture and the molecular formula was established as C11H16O2 on the basis of an HRESIMS peak at m/z 203.1038 [M + Na]+. The strong UV and IR absorptions at a λmax value of 223 nm and νmax values of 1703 and 1614 cm−1, respectively, indicated the presence of a conjugated enone moiety, which was further supported by the HMBC correlations from an olefinic proton (δH-2 5.87) to a sp2-quaternary carbon (δC-3 180.7) and a carbonyl carbon (δC-1 206.9). 1H–1H COSY (Fig. 1) and HSQC data indicated the presence of two isolated spin systems, CH(4)–CH(5)–CH2(6)–CH(7)–CH2(8) and CH3(11)–CH2(10)–CH2(9). The key HMBC correlations of H-4 (δH 4.45) to C-1, C-2 (δC 128.9), C-5 (δC 55.3), C-6 (δC 31.7) and C-9 (δC 32.9) linked these three moieties as 5-allyl-4-hydroxy-3-propylcyclopent-2-en-1-one. When H-4 was irradiated, the H2-6 (δH 2.56, 2.21) signals were enhanced, indicating a trans-orientation between H-4 and H-5 (δH 2.37). Chiral HPLC separation on a CHIRAPAK IA column afforded the optically pure D-isomer (7) and L-isomer (8). The distribution of Δδ values between the (S)- and (R)-MTPA esters (7a and 7b) indicated the 4R-configuration (Fig. 3). Thus, the absolute configuration of 7 was determined to be 4R and 5R. As a consequence, the absolute configuration of 8 was determined to be 4S and 5S.
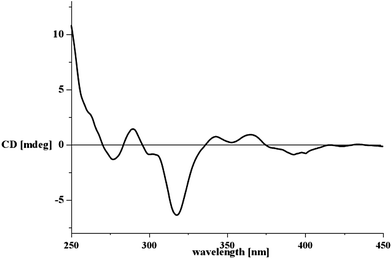
Aspergone I (9) had an HRESIMS peak at m/z 205.1195 [M + Na]+, corresponding to a molecular formula of C11H18O2. Its 1D NMR revealed two methyls (δC 17.9 & 18.1), an oxygenated methylene (δC 68.7), six olefinic methines and an oxygenated quaternary carbon (δC 75.0) (Table 1). 1H–1H COSY and HSQC data indicated the presence of CH3(8)–CH(7)–CH(6)–CH(5)–CH(4)–CH2(3) and CH(9)–CH(10)–CH3(11) units (Fig. 1). HMBC correlations (Fig. 1) from H2-1 (δH 3.45, 3.43) to C-2 (δC 75.0), C-3 (δC 41.0) and C-9 (δC 133.3) and from H2-3 (δH 2.31, 2.32) to C-1 (δC 68.7), C-2 and C-9 connected these structural moieties as 2-propenylocta-4,6-diene-1,2-diol (Fig. 1). The large J values of H-4/H-5 (14.5 Hz), H-6/H-7 (14.4 Hz) and H-9/H-10 (15.5 Hz) (Table 2) indicated that all the Δ4,6,9-double bonds have an E-geometry. The absolute configuration was assigned using the in situ dimolybdenum CD method.16,17 After the addition of Mo2(OAc)4 to a DMSO solution of 9, a metal complex auxiliary chromophore was generated. Because the contribution from the inherent CD was subtracted, the Cotton effect observed in the induced CD spectrum originates solely from the chirality of the vic-diol moiety. The negative Cotton effect observed at 320 (Δε −0.64) and 400 (Δε −0.10) nm in the induced CD spectrum (Fig. 5) revealed the 2S-configuration according to Snatzke’s empirical rule.18 The structure of 9 was therefore elucidated as (2S,4E,6E)-2-(E-propenyl)octa-4,6-diene-1,2-diol.
Aspergone J (10) has the same molecular formula of C11H18O2 as 9, with an HRESIMS peak at m/z 205.1196 [M + Na]+. NMR comparison revealed that a methylene and an olefinic methylene of 10 replaced the methyl and olefinic methine of 9. The 1H–1H COSY spectrum of 10 further indicated a hexatrienyl group and propyl group in place of the hexadienyl and propenyl groups in 9, which was also supported by the key HMBC correlations from H-3 (δH 5.79) to C-1 (δC 69.0), C-2 (δC 75.2) and C-9 (δC 40.0). The E-geometries of the Δ3,5-double bonds could be deduced from the J values of H-3/H-4 (14.8 Hz) and H-5/H-6 (14.8 Hz) (Table 2), and the same sign of the [α]D value (−55.3) as that of 9 (−34.8) implied the same 2R-configuration; therefore the structure is (2R,3E,5E)-2-propylocta-3,5,7-triene-1,2-diol.
Aspergone K (11) also has the molecular formula C11H18O2, based on an HRESIMS peak at m/z 205.1195 [M + Na]+. The NMR data and 1H–1H COSY and HMBC coupling modes, along with the [α]D value (−64.5), were very similar to those of 10, indicating almost the same structure. The only difference was found to be the Z-geometry of the Δ5-double bond, as deduced from the relatively small JH-5,H-6 value (11.3 Hz). Thus, the structure of 11 was determined as (2R,3E,5Z)-2-propylocta-3,5,7-triene-1,2-diol.
The molecular formula of aspergone L (12) was also established as C11H18O2 from an HRESIMS peak at m/z 205.1196 [M + H]+. 1D NMR, 1H–1H COSY and HSQC data indicated an oxygenated methylene, a 5-hydroxyhex-2-en-1-ylidene (CH3(8)–CH(7)–CH2(6)–CH(5)–CH(4)–CH(3)), a propenyl (CH(9)–CH(10)–CH3(11)), and an olefinic quaternary carbon. The key HMBC correlations of H-3 (δH 6.03) to C-1 (δC 62.4), C-2 (δC 135.7) and C-9 (δC 125.8) along with H2-1 (δH 4.07) to C-2, C-3 (δC 126.7) and C-9 connected the above structural moieties as 2-propenylocta-2,4-diene-1,7-diol (Fig. 2). All the geometries of the Δ2,4,9-double bonds were assigned as E according to the large J values of H-4/H-5 (15.0 Hz) and H-9/H-10 (16.6 Hz) (Table 2) and the NOESY cross-peak between H-3 and H2-1 (Fig. 2). To determine the absolute configuration of 12, the 1-O-t-butyldimethylsilyl (TBDMS) derivative (12a) and the (R)- and (S)-MTPA esters of 12a were prepared. The distribution of Δδ values between the (S)- and (R)-MTPA esters (12aa and 12ab) indicated the 7R-configuration (Fig. 3). Thus, compound 12 was determined to be (7R,2E,4E)-2-(E-propenyl)octa-2,4-diene-1,7-diol.
The molecular formula of aspergone M (13) was established as C11H20O2 from an HRESIMS peak at m/z 207.1350 [M + Na]+, equivalent to 12 with an additional H2 unit. Comparison of the 1H and 13C NMR data between 13 and 12 revealed that their structures were only different in the replacement of the propenyl group in 12 with a propyl group in 13. This deduction was further supported by the 1H–1H COSY connectivity of H3-11/H2-10/H2-9 and the key HMBC correlations of H2-1 (δH 3.87) to C-2 (δC 140.9), C-3 (δC 124.3) and C-9 (δC 30.4). The E-geometries of both the Δ2- and Δ4-double bonds were assigned from the large JH-4,H-5 (15.4 Hz) and the NOESY cross-peak of H-3 (δH 5.97) with H2-1 (Fig. 2). The close specific rotation value of 13 to that of 12 (−36.7 vs. −30.5) implied the same 7R-configuration. Thus, compound 13 was elucidated as (7R,2E,4E)-2-propylocta-2,4-diene-1,7-diol.
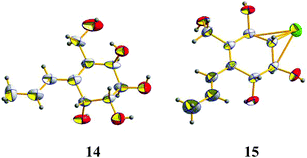
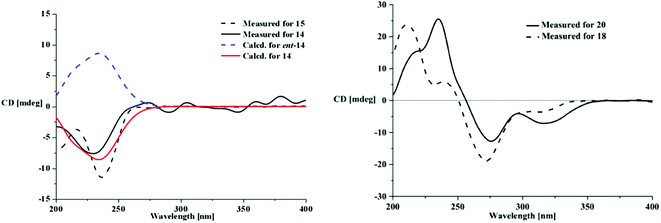
Aspergone N (14) had a molecular formula of C10H16O5, as determined from an HRESIMS peak at m/z 239.0888 [M + Na]+, with three degrees of unsaturation. The IR spectrum of 14 showed the absorption of the double bonds (1645 cm−1) and the hydroxy groups (3287 cm−1). The 1H and 13C NMR along with the HSQC data revealed the presence of a doublet methyl, an oxygenated methylene, four oxygenated methines, two vicinal olefinic methines, two olefinic quaternary carbons, and five hydroxy groups. This accounted for two degrees of unsaturation, indicating the presence of a cyclic nucleus in 14. 1H–1H COSY correlations reveal the presence of CH(–OH)(3)–CH(–OH)(4)–CH(–OH)(5)–CH(–OH)(6), CH3(9)–CH(8)–CH(7), and CH2(–OH)(10) moieties. HMBC correlations from H-7 (δH 6.34) to C-1 (δC 133.4), C-2 (δC 135.8) and C-6 (δC 67.9) and from H2-10 (δH 4.18, 3.92) to C-1, C-2, and C-3 (δC 68.5) connected these moieties as 2-hydroxymethyl-1-propenyl-1-cyclohexene-3,4,5,6-tetraol. The large JH-7,H-8 value (15.7 Hz) suggested an E-Δ7-double bond. The relative configurations of C-3–C-6 and the geometry of the Δ7-double bond were supported by X-ray single crystal diffraction (Fig. 4). The absolute configurations of all the chiral centers were assigned as R by ECD calculations of 14 and ent-14 using the time-dependent density functional theory (TD-DFT) method at the B3LYP/6-31G(d) level.19 The results showed that the measured CD curve matches well with the calculated ECD curve for 14 and is the opposite to that of ent-14 (Fig. 6).
Aspergone O (15) was isolated as a colorless orthorhombic crystal with a molecular formula of C10H15ClO4 on the basis of an HRESIMS peak at m/z 257.0548 [M + Na]+, indicating the substitution of –Cl for –OH relative to 14. In addition, we noted that there was one hydroxy signal less, and the 1H–1H COSY and HMBC coupling patterns were similar to 14 except for the lack of a COSY correlation between 4-OH and 4-CH, supporting the substitution of 4-Cl in 15 for 4-OH in 14. The large JH-7,H-8 value (16.2 Hz) indicated an E-geometry of the Δ7-double bond. The similar CD data to that of 14 (Fig. 6) indicated a (3R,4S,5S,6R)-configuration of 15 that was further confirmed by single-crystal X-ray diffraction (Fig. 4) with a small Flack parameter (0.05(7)) and a heavy chlorine atom in the molecule.20,21 Thus, aspergone O (15) was identified as (3R,4S,5S,6R,7E)-4-chloro-2-hydroxymethyl-1-propenylcyclohex-1-ene-3,5,6-triol.
Aspergone P (16) had a molecular formula of C10H14O4 as determined from its HRESIMS peak at m/z 221.0780 [M + Na]+, which is equivalent to 14 minus a H2O unit. The absence of two hydroxy proton signals and the upfield oxygenated methine carbon signals (δC 54.5, 54.3) indicated the replacement of two hydroxy groups by an epoxy group. This epoxidation was deduced to occur at C-4 and C-5 according to the 1H–1H COSY of OH-3/H-3/H-4/H/5/H-6/OH-6 and the HMBC correlations from H-3 (δH 4.52) to C-1 (δC 131.2) along with H-6 (δH 4.45) to C-2 (δC 133.2), C-4 (δC 54.5) and C-7 (δC 128.3). The large JH-7,H-8 value (15.8 Hz) suggested an E-geometry of the Δ7-double bond. The absolute configuration of 16 was defined by its chemical transformation into 15. After adding hydrochloric acid to a methanol solution of 16, compound 15 was yielded as the major product (Fig. S120†) which showed identical [α]D, NMR and MS data to those of the natural product, indicating a (3R,4R,5S,6R)-configuration of 16. This result also indicated that compound 15 might be an artifact formed under acidic conditions in the fermentation process.
The molecular formula of aspergone Q (17) was established as C11H14O6 from an HRESIMS peak at m/z 265.0680 [M + Na]+. The NMR data (Table 1 and 2) of 17 are similar to those of 14, except for the absence of two hydroxy proton signals and the presence of an additional carbonate carbonyl signal (δC 154.8), suggesting that two hydroxy groups of 14 were esterified to form a cyclic carbonate. HMBC correlations of H-5 (δH 4.81) and H-6 (δH 5.60) to C-11 (δC 154.8) and H-7 (δH 6.42) to C-6 (δC 75.5) supported the theory that the 5,6-dihydroxy group formed a cyclic carbonate in 17 (Fig. 2). Treatment of 17 in 1% aqueous sodium hydroxide yielded compound 14 which showed identical [α]D, NMR and MS data to the natural product, indicating a (3R,4R,5S,6R)-configuration of 17.
Compound 18 was found to have the molecular formula C15H18O6, as established from an HRESIMS peak at m/z 295.1171 [M + H]+. Apart from the phenyl motif, the 1H and 13C NMR data (Table 1 and 2) were nearly identical to the known compound 20,11 indicating a similar structure which is isomeric in the phenyl motif. The HSQC data revealed the presence of five aromatic quaternary carbons, one aromatic methine (δC/H 108.1/6.60), three oxygenated methines, three methylenes, one methyl (δC/H 14.1/0.90), one methoxyl (δC/H 60.9/3.97), and one ester carbonyl group (δC 168.2). The key HMBC correlations from a phenolic hydroxy proton (δHO-8 11.5) to three aromatic quaternary carbons (δC-7,8,8a 134.9, 155.6, 101.3) and the methoxy protons (δH 3.97) to a relative upfield oxygenated aromatic quaternary carbon (δC-7 134.9) revealed that O-methylation occurred at 7-OH in 18 as opposed to 6-OH in 20. The relative configuration was established from the NOE data and the comparison of NMR data with 20, especially the vicinal coupling constants. The small JH-3,H-4 value (3.0 Hz) (Table 2) along with the NOESY correlations from H-10 (δH 4.10) to H-3 (δH 5.02) and H-4 (δH 4.49) indicated the same cis-orientation of H-3, H-4 and H-10 as in 20. The similar CD spectra of 18 and 20 (Fig. 5) revealed the same (3R,4R,10S)-configuration. Because the absolute configuration of 20 has been resolved by chemical synthesis11 and furthermore by Cu-Kα radiated X-ray single crystal diffraction (Fig. S107†) with a small Flack parameter (0.0(3)) in this paper, the structure of compound 18 could be clearly elucidated as 6-O-demethylmonocerin.
All the isolated compounds (1–23) were evaluated for antiviral activity against the H1N1 flu virus, as well as α-glucosidase inhibition, by previously described methods.6,22 Only compounds 18 and 21 exhibited anti-H1N1 activities, with IC50 values of 172.4 μM and 175.5 μM, respectively (with ribavirin as the positive control; IC50 = 137.3 μM), while the other compounds were not active against H1N1. These data suggested that the tetrahydrofuran moiety and the methoxy group located at C-7 in the isocoumarins were required for antiviral activity against the influenza A H1N1 virus. In addition, compounds 1, 2, 5, 10, 11, 14–18, and 21–23 showed α-glucosidase inhibition with IC50 values of 2.36, 1.65, 1.30, 2.37, 2.70, 1.36, 1.54, 2.21, 2.26, 0.027, 1.65, 1.19 and 1.74 mM, respectively (with acarbose as the positive control; IC50 = 0.95 mM) (Table 3). The results showed that compound 18 is 35 times more potent than the positive control, which supports the idea that marine fungi might be a promising source for drug discovery. Compounds 1–23 were also tested for their cytotoxicities against A549 and K562 tumor cells, and against MCF-7 cells, by the MTT23 and CCK-8 (ref. 24) methods, respectively. Their antimicrobial activities against Escherichia coli, Enterobacter aerogenes, Bacillus subtilis, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Candida albicans were also evaluated, by an agar dilution method.25 However, none of the compounds showed any activity against the tested tumor cells and pathogens.
| Compound | Acarbose | 1 | 2 | 5 | 10 | 11 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 21 | 22 | 23 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IC50 (mM) | 0.95 | 2.36 | 1.65 | 1.30 | 2.37 | 2.70 | 1.36 | 1.54 | 2.21 | 2.26 | 0.027 | 1.65 | 1.19 | 1.74 |
Experimental section
General experimental procedures
Optical rotations were measured using a JASCO P-1020 digital polarimeter, and UV spectra were measured using a Beckman DU 640 spectrophotometer. CD data were collected using a JASCO J-715 spectropolarimeter. IR spectra were taken using a Nicolet Nexus 470 spectrophotometer with KBr discs. 1H NMR, 13C NMR, DEPT, HMQC, HSQC, HMBC, COSY and NOESY spectra were acquired using a JEOL JNM-ECP 600 spectrometer or an Agilent 500 MHz DD2 spectrometer using TMS as an internal standard or residual solvent signals for referencing. HR-ESI-MS spectra were determined using a Q-TOF ULTIMA GLOBAL GAA076 LC mass spectrometer. Semi-preparative HPLC was carried out using an ODS column (YMC-pack ODS-A, 10 × 250 mm, 5 μm, 4 mL min−1) and a πNAP column (COSMOSIL-pack, 10 × 250 mm, 5 μm, 4 mL min−1). Sea salt used was made by the evaporation of seawater collected in Laizhou Bay (Weifang Haisheng Chemical Factory). Thin layer chromatography (TLC) and column chromatography (CC) were performed on plates precoated with silica gel GF254 (10–40 μm, Qingdao Marine Chemical Factory) and Sephadex LH-20 (Amersham Biosciences), respectively. Vacuum-liquid chromatography (VLC) utilized silica gel H (Qingdao Marine Chemical Factory).Fungal material and fermentation
The fungus Aspergillus sp. OUCMDZ-1583 was isolated from a piece of sponge (XD10410) from the Xisha Islands of China in August 2010. After it was ground into a powder, the sample (1 g) was diluted to 10−2 g mL−1 with sterile water, 100 μL of which was deposited on a PDA (200 g potato, 20 g glucose, and 20 g agar per liter of tap water) plate containing chloramphenicol (100 μg mL−1) as a bacterial inhibitor. A single colony was transferred onto another PDA plate and was identified according to its morphological characteristics and ITS gene sequences (GenBank accession no. KM056275, ESI†). A reference culture of Aspergillus sp. OUCMDZ-1583 maintained at −80 °C is deposited in our laboratory. The isolate was cultured on slants of PDA medium at 28 °C for 5 days. Plugs of agar supporting the mycelium growth were cut and transferred aseptically to 200 × 1000 mL Erlenmeyer flasks each containing 300 mL of liquid medium (2% mannitol, 2% maltose, 1% glucose, 1% monosodium glutamate, 0.3% yeast extract, 0.05% corn meal, 0.05% KH2PO4, 0.03% MgSO4, 1.75% Na2HPO4·2H2O, 1.05% C4H2O7·H2O, and 3.3% sea salt; pH 7.0). The flasks were incubated at room temperature under static conditions for 30 days.Extraction and isolation
The cultures (50 L) were filtered through cheesecloth to separate the mycelial mass from the aqueous layer. The filtrate was then extracted three times with 3-fold volumes of EtOAc, while the mycelium was extracted with acetone. After removing some of the acetone by evaporation under vacuum, the obtained aqueous acetone solution was extracted three times with equal volumes of EtOAc. The combined EtOAc extracts were dried under vacuum to produce 28.7 g of extract. The EtOAc extract was subjected to chromatography with a silica gel VLC column, eluting with a stepwise gradient of 0%, 20%, 40%, 60%, 80% and 100% MeOH in CH2Cl2 (v/v), to give 20 fractions (fractions 1–20). Fraction 1 (1.2 g) was subjected to Sephadex LH-20 chromatography (5 × 200 cm) with CH2Cl2–MeOH (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) to afford two subfractions (1.1 and 1.2). Fraction 1.1 (106 mg) was further purified by HPLC on a πNAP column (70% MeOH/H2O, v/v) to give compounds 23 (tR 11.8 min; 20 mg) and 21 (tR 16.0 min; 24 mg). Fraction 1.2 (234 mg) was subjected to HPLC on an ODS column (55% MeOH/H2O, v/v) to yield 20 (tR 9.5 min, 16.3 mg), 2 (tR 9.7 min, 10.2 mg), 1 (tR 12.6 min, 7.6 mg) and 18 (tR 13.8 min, 7.6 mg). Fraction 2 (3.4 g) was eluted with CH2Cl2–MeOH (100
1) to afford two subfractions (1.1 and 1.2). Fraction 1.1 (106 mg) was further purified by HPLC on a πNAP column (70% MeOH/H2O, v/v) to give compounds 23 (tR 11.8 min; 20 mg) and 21 (tR 16.0 min; 24 mg). Fraction 1.2 (234 mg) was subjected to HPLC on an ODS column (55% MeOH/H2O, v/v) to yield 20 (tR 9.5 min, 16.3 mg), 2 (tR 9.7 min, 10.2 mg), 1 (tR 12.6 min, 7.6 mg) and 18 (tR 13.8 min, 7.6 mg). Fraction 2 (3.4 g) was eluted with CH2Cl2–MeOH (100![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) and was subjected to reversed-phase C18 silica column chromatography eluting with a stepwise gradient of 30% to 100% MeOH in H2O to obtain four subfractions (2.1–2.4). Fraction 2.1 (247 mg) was further separated into three subfractions (2.1.1–2.1.3) by Sephadex LH-20 chromatography (5 × 200 cm) eluting with CH2Cl2–MeOH (1
1) and was subjected to reversed-phase C18 silica column chromatography eluting with a stepwise gradient of 30% to 100% MeOH in H2O to obtain four subfractions (2.1–2.4). Fraction 2.1 (247 mg) was further separated into three subfractions (2.1.1–2.1.3) by Sephadex LH-20 chromatography (5 × 200 cm) eluting with CH2Cl2–MeOH (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1, v/v). Fraction 2.1.1 (56 mg) was subjected to HPLC on an ODS column (55% MeOH/H2O, v/v) to yield fraction 2.1.1.1, which was further purified by HPLC on a πNAP column (50% MeOH/H2O, v/v) to give compound 5 (tR 17.0 min; 8.2 mg) and a racemic mixture of 7 and 8 (tR 14.7 min; 16 mg) that was further subjected to HPLC on a CHIRAPAK IA column (75% n-C6H14/EtOH, v/v) to give the optically pure 7 (tR 5.7 min; 7.1 mg) and 8 (tR 5.9 min; 8.3 mg). Fraction 2.1.2 (78 mg) was subjected to HPLC on an ODS column (35% MeCN/H2O, v/v) to yield a racemic mixture of 3 and 4 (tR 7.7 min; 24 mg) that was further purified on a CHIRAPAK IA column (75% n-C6H14/EtOH, v/v) to give optically pure 3 (tR 6.9 min; 11.3 mg) and 4 (tR 7.8 min; 10.9 mg). Fraction 2.1.3 (39 mg) was subjected to HPLC on an ODS column (50% MeOH/H2O, v/v) to yield compound 6 (tR 21.3 min; 11.3 mg). Fractions 15–20 (4.2 g) were combined and re-chromatographed on Sephadex LH-20 (5 × 200 cm, MeOH) to afford four subfractions (Fr. 15.1–Fr. 15.4). Fraction 15.4 (706 mg) was subjected to HPLC on an ODS column (25% MeOH/H2O, v/v) to give 17 (tR 6.2 min; 76 mg), 14 (tR 4.0 min; 22 mg) and subfraction 15.4.1. Fraction 15.4.1 (215 mg) was fractionated by silica gel CC using petroleum ether–EtOAc (4
1, v/v). Fraction 2.1.1 (56 mg) was subjected to HPLC on an ODS column (55% MeOH/H2O, v/v) to yield fraction 2.1.1.1, which was further purified by HPLC on a πNAP column (50% MeOH/H2O, v/v) to give compound 5 (tR 17.0 min; 8.2 mg) and a racemic mixture of 7 and 8 (tR 14.7 min; 16 mg) that was further subjected to HPLC on a CHIRAPAK IA column (75% n-C6H14/EtOH, v/v) to give the optically pure 7 (tR 5.7 min; 7.1 mg) and 8 (tR 5.9 min; 8.3 mg). Fraction 2.1.2 (78 mg) was subjected to HPLC on an ODS column (35% MeCN/H2O, v/v) to yield a racemic mixture of 3 and 4 (tR 7.7 min; 24 mg) that was further purified on a CHIRAPAK IA column (75% n-C6H14/EtOH, v/v) to give optically pure 3 (tR 6.9 min; 11.3 mg) and 4 (tR 7.8 min; 10.9 mg). Fraction 2.1.3 (39 mg) was subjected to HPLC on an ODS column (50% MeOH/H2O, v/v) to yield compound 6 (tR 21.3 min; 11.3 mg). Fractions 15–20 (4.2 g) were combined and re-chromatographed on Sephadex LH-20 (5 × 200 cm, MeOH) to afford four subfractions (Fr. 15.1–Fr. 15.4). Fraction 15.4 (706 mg) was subjected to HPLC on an ODS column (25% MeOH/H2O, v/v) to give 17 (tR 6.2 min; 76 mg), 14 (tR 4.0 min; 22 mg) and subfraction 15.4.1. Fraction 15.4.1 (215 mg) was fractionated by silica gel CC using petroleum ether–EtOAc (4![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 6, v/v) to afford 15 (35.5 mg), 16 (106.5 mg) and 19 (5.4 mg). Fractions 6 and 7 (1.3 g) were combined and chromatographed on Sephadex LH-20 (5 × 200 cm, MeOH) to afford three subfractions (Fr. 6.1–Fr. 6.3). Fraction 6.1 (78 mg) was subjected to HPLC on an ODS column (55% MeOH/H2O, v/v) to yield compounds 24 (tR 6.7 min; 24.3 mg) and 22 (tR 9.9 min; 14.7 mg). Fraction 6.2 (108 mg) was subjected to HPLC on an ODS column (50% MeOH/H2O, v/v) to yield compounds 9 (tR 26.6 min; 18.3 mg), 10 (tR 27.9 min; 3.7 mg) and 11 (tR 30.5 min; 4.5 mg). Fraction 6.3 (94 mg) was separated by HPLC on an ODS column (50% MeOH/H2O, v/v) to yield compounds 12 (tR 11.7 min; 18.3 mg) and 13 (tR 13.9 min; 3.5 mg).
6, v/v) to afford 15 (35.5 mg), 16 (106.5 mg) and 19 (5.4 mg). Fractions 6 and 7 (1.3 g) were combined and chromatographed on Sephadex LH-20 (5 × 200 cm, MeOH) to afford three subfractions (Fr. 6.1–Fr. 6.3). Fraction 6.1 (78 mg) was subjected to HPLC on an ODS column (55% MeOH/H2O, v/v) to yield compounds 24 (tR 6.7 min; 24.3 mg) and 22 (tR 9.9 min; 14.7 mg). Fraction 6.2 (108 mg) was subjected to HPLC on an ODS column (50% MeOH/H2O, v/v) to yield compounds 9 (tR 26.6 min; 18.3 mg), 10 (tR 27.9 min; 3.7 mg) and 11 (tR 30.5 min; 4.5 mg). Fraction 6.3 (94 mg) was separated by HPLC on an ODS column (50% MeOH/H2O, v/v) to yield compounds 12 (tR 11.7 min; 18.3 mg) and 13 (tR 13.9 min; 3.5 mg).
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) ε) 325 (3.67) and 208 (3.09) nm; IR (KBr) νmax 3377, 2984, 1777, 1715 cm−1; 1H and 13C NMR data, see Tables 1 and 2; HRESIMS m/z 195.1014 [M + H]+ (calcd for C11H15O3, 195.1016).
ε) 325 (3.67) and 208 (3.09) nm; IR (KBr) νmax 3377, 2984, 1777, 1715 cm−1; 1H and 13C NMR data, see Tables 1 and 2; HRESIMS m/z 195.1014 [M + H]+ (calcd for C11H15O3, 195.1016).![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) ε) 324.8 (3.63) and 208.6 (3.11) nm; IR (KBr) νmax 3416, 2972, 1766, 1641 cm−1; 1H and 13C NMR data, see Tables 1 and 2; HRESIMS m/z 217.0832 [M + Na]+ (calcd for C11H14O3Na, 217.0832).
ε) 324.8 (3.63) and 208.6 (3.11) nm; IR (KBr) νmax 3416, 2972, 1766, 1641 cm−1; 1H and 13C NMR data, see Tables 1 and 2; HRESIMS m/z 217.0832 [M + Na]+ (calcd for C11H14O3Na, 217.0832).![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) ε) 275.2 (3.80) and 201.6 (3.10) nm; IR (KBr) νmax 3420, 2918, 1676, 1645 cm−1; 1H and 13C NMR data, see Tables 1 and 2; HRESIMS m/z 219.0988 [M + Na]+ (calcd for C11H16O3Na, 219.0992).
ε) 275.2 (3.80) and 201.6 (3.10) nm; IR (KBr) νmax 3420, 2918, 1676, 1645 cm−1; 1H and 13C NMR data, see Tables 1 and 2; HRESIMS m/z 219.0988 [M + Na]+ (calcd for C11H16O3Na, 219.0992).![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) ε) 275.2 (3.80) and 201.6 (3.10) nm; IR (KBr) νmax 3420, 2918, 1676, 1645 cm−1; 1H and 13C NMR data, see Tables 1 and 2; HRESIMS m/z 219.0988 [M + Na]+ (calcd for C11H16O3Na, 219.0992).
ε) 275.2 (3.80) and 201.6 (3.10) nm; IR (KBr) νmax 3420, 2918, 1676, 1645 cm−1; 1H and 13C NMR data, see Tables 1 and 2; HRESIMS m/z 219.0988 [M + Na]+ (calcd for C11H16O3Na, 219.0992).![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) ε) 225.2 (3.78) and 204.3 (3.17) nm; CD (c 0.1, MeOH) λmax (Δε) 226.5 (+1.05) and 209 (+2.35) nm; IR (KBr) νmax 3420, 2966, 1769, 1645 cm−1; 1H and 13C NMR data, see Tables 1 and 2; HRESIMS m/z 219.0989 [M + Na]+ (calcd for C11H16O3Na, 219.0992).
ε) 225.2 (3.78) and 204.3 (3.17) nm; CD (c 0.1, MeOH) λmax (Δε) 226.5 (+1.05) and 209 (+2.35) nm; IR (KBr) νmax 3420, 2966, 1769, 1645 cm−1; 1H and 13C NMR data, see Tables 1 and 2; HRESIMS m/z 219.0989 [M + Na]+ (calcd for C11H16O3Na, 219.0992).![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) ε) 225.5 (3.75) and 203.6 (3.50) nm; CD (c 0.1, MeOH) λmax (Δε) 217.5 (+3.20) and 210.5 (−0.87) nm; IR (KBr) νmax 3443, 2966, 1680, 1645 cm−1; 1H and 13C NMR data, see Tables 1 and 2; HRESIMS m/z 203.1037 [M + Na]+ (calcd for C11H16O2Na, 203.1043).
ε) 225.5 (3.75) and 203.6 (3.50) nm; CD (c 0.1, MeOH) λmax (Δε) 217.5 (+3.20) and 210.5 (−0.87) nm; IR (KBr) νmax 3443, 2966, 1680, 1645 cm−1; 1H and 13C NMR data, see Tables 1 and 2; HRESIMS m/z 203.1037 [M + Na]+ (calcd for C11H16O2Na, 203.1043).![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) ε) 223 (3.38) and 203.5 (2.99) nm; CD (c 0.05, MeOH) λmax (Δε) 235 (+1.96) and 207 (−0.51) nm; IR (KBr) νmax 3404, 2960, 1703, 1614 cm−1; 1H and 13C NMR data, see Tables 1 and 2; HRESIMS m/z 203.1038 [M + Na]+ (calcd for C11H16O2Na, 203.1043).
ε) 223 (3.38) and 203.5 (2.99) nm; CD (c 0.05, MeOH) λmax (Δε) 235 (+1.96) and 207 (−0.51) nm; IR (KBr) νmax 3404, 2960, 1703, 1614 cm−1; 1H and 13C NMR data, see Tables 1 and 2; HRESIMS m/z 203.1038 [M + Na]+ (calcd for C11H16O2Na, 203.1043).![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) ε) 223 (3.38) and 203.5 (2.99) nm; CD (c 0.05, MeOH) λmax (Δε) 235 (−2.06) and 207 (+0.54) nm; IR (KBr) νmax 3404, 2960, 1703, 1614 cm−1; 1H and 13C NMR data, see Tables 1 and 2; HRESIMS m/z 203.1038 [M + Na]+ (calcd for C11H16O2Na, 203.1043).
ε) 223 (3.38) and 203.5 (2.99) nm; CD (c 0.05, MeOH) λmax (Δε) 235 (−2.06) and 207 (+0.54) nm; IR (KBr) νmax 3404, 2960, 1703, 1614 cm−1; 1H and 13C NMR data, see Tables 1 and 2; HRESIMS m/z 203.1038 [M + Na]+ (calcd for C11H16O2Na, 203.1043).![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) ε) 229.5 (3.45) and 204 (2.94) nm; CD (c 0.05, MeOH) λmax (Δε) 233.5 (+0.99) and 209 (+0.40) nm; IR (KBr) νmax 3420, 2918, 1676, 1645 cm−1; 1H and 13C NMR data, see Tables 1 and 2; HRESIMS m/z 205.1195 [M + Na]+ (calcd for C11H18O2Na, 205.1199).
ε) 229.5 (3.45) and 204 (2.94) nm; CD (c 0.05, MeOH) λmax (Δε) 233.5 (+0.99) and 209 (+0.40) nm; IR (KBr) νmax 3420, 2918, 1676, 1645 cm−1; 1H and 13C NMR data, see Tables 1 and 2; HRESIMS m/z 205.1195 [M + Na]+ (calcd for C11H18O2Na, 205.1199).![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) ε) 253 (3.34), 263 (3.57) and 274 (3.38) nm; CD (c 0.1, MeOH) λmax (Δε) 273 (+2.23) and 258.5 (−0.51) nm; IR (KBr) νmax 3420, 2949, 1680, 1641 cm−1; 1H and 13C NMR data, see Tables 1 and 2; HRESIMS m/z 205.1196 [M + Na]+ (calcd for C11H18O2Na, 205.1199).
ε) 253 (3.34), 263 (3.57) and 274 (3.38) nm; CD (c 0.1, MeOH) λmax (Δε) 273 (+2.23) and 258.5 (−0.51) nm; IR (KBr) νmax 3420, 2949, 1680, 1641 cm−1; 1H and 13C NMR data, see Tables 1 and 2; HRESIMS m/z 205.1196 [M + Na]+ (calcd for C11H18O2Na, 205.1199).![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) ε) 253 (3.44), 263 (3.48) and 274 (3.38) nm; CD (c 0.05, MeOH) λmax (Δε) 265 (+2.54) and 249 (−0.70) nm; IR (KBr) νmax 3392, 2964, 1676, 1645 cm−1; 1H and 13C NMR data, see Tables 1 and 2; HRESIMS m/z 205.1195 [M + Na]+ (calcd for C11H18O2Na, 205.1199).
ε) 253 (3.44), 263 (3.48) and 274 (3.38) nm; CD (c 0.05, MeOH) λmax (Δε) 265 (+2.54) and 249 (−0.70) nm; IR (KBr) νmax 3392, 2964, 1676, 1645 cm−1; 1H and 13C NMR data, see Tables 1 and 2; HRESIMS m/z 205.1195 [M + Na]+ (calcd for C11H18O2Na, 205.1199).![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) ε) 258.5 (3.79), 269.5 (3.87) and 280 (3.77) nm; CD (c 0.1, MeOH) λmax (Δε) 276 (+2.43) and 261.5 (−1.10) nm; IR (KBr) νmax 3389, 2918, 1649, 1614 cm−1; 1H and 13C NMR data, see Tables 1 and 2; HRESIMS m/z 205.1196 [M + Na]+ (calcd for C11H18O2Na, 205.1199).
ε) 258.5 (3.79), 269.5 (3.87) and 280 (3.77) nm; CD (c 0.1, MeOH) λmax (Δε) 276 (+2.43) and 261.5 (−1.10) nm; IR (KBr) νmax 3389, 2918, 1649, 1614 cm−1; 1H and 13C NMR data, see Tables 1 and 2; HRESIMS m/z 205.1196 [M + Na]+ (calcd for C11H18O2Na, 205.1199).![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) ε) 233 (3.72), 239 (3.74) and 248.5 (3.57) nm; CD (c 0.1, MeOH) λmax (Δε) 251.5 (+0.26) and 234 (−0.55) nm; IR (KBr) νmax 3389, 2918, 1649, 1614 cm−1; 1H and 13C NMR data, see Tables 1 and 2; HRESIMS m/z 207.1350 [M + Na]+ (calcd for C11H20O2Na, 207.1356).
ε) 233 (3.72), 239 (3.74) and 248.5 (3.57) nm; CD (c 0.1, MeOH) λmax (Δε) 251.5 (+0.26) and 234 (−0.55) nm; IR (KBr) νmax 3389, 2918, 1649, 1614 cm−1; 1H and 13C NMR data, see Tables 1 and 2; HRESIMS m/z 207.1350 [M + Na]+ (calcd for C11H20O2Na, 207.1356).![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) ε) 239.5 (3.39), 206 (3.03) nm; CD (c 0.05, MeOH) λmax (Δε) 230.5 (−1.02) nm; IR (KBr) νmax 3287, 2910, 1645, 1443 cm−1; 1H and 13C NMR data, see Tables 1 and 2; HRESIMS m/z 239.0888 [M + Na]+ (calcd for C10H16O5Na, 239.0890).
ε) 239.5 (3.39), 206 (3.03) nm; CD (c 0.05, MeOH) λmax (Δε) 230.5 (−1.02) nm; IR (KBr) νmax 3287, 2910, 1645, 1443 cm−1; 1H and 13C NMR data, see Tables 1 and 2; HRESIMS m/z 239.0888 [M + Na]+ (calcd for C10H16O5Na, 239.0890).![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) ε) 238 (3.58), 206 (3.18) nm; CD (c 0.05, MeOH) λmax (Δε) 236.5 (−1.67) nm; IR (KBr) νmax 3392, 2925, 1657, 1443 cm−1; 1H and 13C NMR data, see Tables 1 and 2; HRESIMS m/z 257.0548 and 259.0518 [M + Na]+ (calcd for C10H15O4ClNa, 257.0551 and 257.0522).
ε) 238 (3.58), 206 (3.18) nm; CD (c 0.05, MeOH) λmax (Δε) 236.5 (−1.67) nm; IR (KBr) νmax 3392, 2925, 1657, 1443 cm−1; 1H and 13C NMR data, see Tables 1 and 2; HRESIMS m/z 257.0548 and 259.0518 [M + Na]+ (calcd for C10H15O4ClNa, 257.0551 and 257.0522).![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) ε) 238 (3.48), 206.5 (2.90) nm; CD (c 0.1, MeOH) λmax (Δε) 232 (−1.54) nm; IR (KBr) νmax 3350, 2921, 1660, 1446 cm−1; 1H and 13C NMR data, see Tables 1 and 2; HRESIMS m/z 221.0780 [M + Na]+ (calcd for C10H14O4Na, 221.0784).
ε) 238 (3.48), 206.5 (2.90) nm; CD (c 0.1, MeOH) λmax (Δε) 232 (−1.54) nm; IR (KBr) νmax 3350, 2921, 1660, 1446 cm−1; 1H and 13C NMR data, see Tables 1 and 2; HRESIMS m/z 221.0780 [M + Na]+ (calcd for C10H14O4Na, 221.0784).![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) ε) 238 (3.36), 205.5 (2.97) nm; CD (c 0.05, MeOH) λmax (Δε) 231 (−1.29) nm; IR (KBr) νmax 3350, 2921, 1660, 1446 cm−1; 1H and 13C NMR data, see Tables 1 and 2; HRESIMS m/z 265.0680 [M + Na]+ (calcd for C11H14O6Na, 265.0683).
ε) 238 (3.36), 205.5 (2.97) nm; CD (c 0.05, MeOH) λmax (Δε) 231 (−1.29) nm; IR (KBr) νmax 3350, 2921, 1660, 1446 cm−1; 1H and 13C NMR data, see Tables 1 and 2; HRESIMS m/z 265.0680 [M + Na]+ (calcd for C11H14O6Na, 265.0683).![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) ε) 219 (3.58), 232.5 (3.53), 274 (3.37), 309 (3.02) nm; CD (c 0.1, MeOH) λmax (Δε) 274 (−2.23), 242 (+0.62), and 212.5 (+2.68) nm; IR (KBr) νmax 3335, 2956, 1660, 1468, 1376 cm−1; 1H and 13C NMR data, see Tables 1 and 2; HRESIMS m/z 295.1171 [M + H]+ (calcd for C15H19O6, 295.1176).
ε) 219 (3.58), 232.5 (3.53), 274 (3.37), 309 (3.02) nm; CD (c 0.1, MeOH) λmax (Δε) 274 (−2.23), 242 (+0.62), and 212.5 (+2.68) nm; IR (KBr) νmax 3335, 2956, 1660, 1468, 1376 cm−1; 1H and 13C NMR data, see Tables 1 and 2; HRESIMS m/z 295.1171 [M + H]+ (calcd for C15H19O6, 295.1176).Preparation of 12-O-tert-butyldimethylsilylaspergone L (12a)
tert-Butyldimethylsilyl chloride (TBDMSCl) (6.7 mg) was added to a mixture of compound 12 (4.1 mg) and imidazole (10 mg) in DMF (1.5 mL). The reaction mixture was stirred at r.t. for 2 h. Then the reaction mixture was quenched with H2O and extracted three times with EtOAc. The EtOAc layers were combined and separated by semipreparative HPLC on an ODS column (100% MeOH) to afford 12a (tR 4.4 min, 3.4 mg) as one product (Fig. S119†).Preparation of MTPA esters
Compound 2 (1 mg for each) was reacted with either R-(−)- or S-(+)-MTPA chloride (10 μL) in anhydrous pyridine (500 μL) for 6 h. The reaction mixture was quenched with H2O and extracted three times with CH2Cl2. The organic layers were combined and separated by semipreparative HPLC on an ODS column (80% MeOH/H2O, v/v) to afford the S-MTPA ester 2a (1.2 mg, tR 10.2 min) and R-MTPA ester 2b (0.8 mg, tR 10.3 min), respectively. By the same procedure, the S-MTPA esters 3a, 5a, 6a, 7a, and 12aa and R-MTPA esters 3b, 5b, 6b, 7b, and 12ab were also prepared.Chemical transformation of 16 to 15
To a solution of compound 16 (2 mg) in MeOH (1 mL) was added 15 μL concentrated HCl (37%). After stirring at r.t. for 1 h, the reaction mixture was subjected to HPLC separation on an ODS column (10% MeOH/H2O, v/v) to yield 15 (tR 15.5 min, 1.2 mg).Chemical transformation of 17 to 14
To a solution of compound 17 (2 mg) in methanol (1 mL) was added 500 μL NaOH solution (2%). After stirring at r.t. for 5 h, the reaction was neutralized to pH 7 using 1 M HCl. The obtained mixture was concentrated and then added to 1.5 mL H2O. The H2O layer was extracted twice with 3 mL EtOAc and the combined EtOAc extracts were concentrated and purified by HPLC on an ODS column (20% MeOH/H2O, v/v) to yield 14 (tR 4.6 min, 1.5 mg).X-ray crystal data for 14 and 15
Colorless crystals of 14 and 15 were obtained in MeOH–H2O (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1, v/v). Crystal data of 14 were obtained using a Bruker APEX DUO area detector diffractometer with graphite monochromatic Cu-Kα radiation (λ = 1.54178 Å). Crystal data of 15 were obtained using a Bruker Smart CCD area detector diffractometer with graphite monochromatic Mo-Kα radiation (λ = 0.71073 Å) (ESI†).
1, v/v). Crystal data of 14 were obtained using a Bruker APEX DUO area detector diffractometer with graphite monochromatic Cu-Kα radiation (λ = 1.54178 Å). Crystal data of 15 were obtained using a Bruker Smart CCD area detector diffractometer with graphite monochromatic Mo-Kα radiation (λ = 0.71073 Å) (ESI†).
Conclusion
In conclusion, eighteen new compounds (1–18) were isolated from the marine sponge-derived Aspergillus sp. strain OUCMDZ-1583. Compounds 5, 14 and 18 displayed comparable or stronger α-glucosidase inhibition than acarbose (IC50 = 0.95 mM) with IC50 values of 1.30, 1.37 and 0.027 mM, respectively. In addition, the α-glucosidase inhibition of fusarentin 6-methyl ether (22) was reported here for the first time with an IC50 value of 1.19 mM.Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from NSFC (No. 21172204, 41376148 & 81373298), from 863 programs of China (No. 2012AA092104 & 2013AA092901), from NSFC-Shandong Joint Fund for Marine Science Research Centers (No. U1406402), and from the Special Fund for Marine Scientific Research in the Public Interest of China (No. 201405038).References
- F. Pietra, Nat. Prod. Rep., 1997, 14, 453–464 RSC.
- J. W. Blunt, B. R. Copp, R. A. Keyzers, M. H. Munro and M. R. Prinsep, Nat. Prod. Rep., 2013, 30, 237–323 RSC.
- R. K. Pettit, Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 2009, 83, 19–25 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. E. Rateb and R. R. Ebel, Nat. Prod. Rep., 2011, 28, 290–344 RSC.
- M. Saleem, M. S. Ali, S. Hussain, A. Jabbar, M. Ashraf and Y. S. Lee, Nat. Prod. Rep., 2007, 24, 1142–1152 RSC.
- Y. Q. Fan, Y. Wang, P. P. Liu, P. Fu, T. H. Zhu, W. Wang and W. M. Zhu, J. Nat. Prod., 2013, 76, 1328–1336 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. K. Zheng, Z. H. Xu, Y. Wang, K. Hong, P. P. Liu and W. M. Zhu, J. Nat. Prod., 2010, 73, 1133–1137 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. B. Zhuang, X. C. Teng, Y. Wang, P. P. Liu, G. Q. Li and W. M. Zhu, Org. Lett., 2011, 13, 1130–1133 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- F. Kong, Y. Wang, P. Liu, T. Dong and W. M. Zhu, J. Nat. Prod., 2014, 77, 132–137 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Li and J. A. Porco, J. Org. Chem., 2005, 70, 6053–6065 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- B. Fang, X. Xie, C. Zhao, P. Jing, H. Li, Z. Wang, J. Gu and X. She, J. Org. Chem., 2013, 78, 6338–6343 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. K. Kwon, Y. E. Lee and E. Lee, Org. Lett., 2008, 10, 2995–2996 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- W. Zhang, K. Krohn, S. Draeger and B. Schulz, J. Nat. Prod., 2008, 71, 1078–1081 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Johansson, B. Köpcke, H. Anke and O. Sterner, J. Antibiot., 2002, 55, 104–106 CrossRef CAS.
- R. Ueoka, Y. Nakao, S. Kawatsu, J. Yaegashi, Y. Matsumoto, S. Matsunaga, K. Furihata, R. W. van Soest and N. Fusetani, J. Org. Chem., 2009, 74, 4203–4207 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. Di Bari, G. Pescitelli, C. Pratelli, D. Pini and P. Salvadori, J. Org. Chem., 2001, 66, 4819–4825 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Górecki, E. Jabłońska, A. Kruszewska, A. Suszczyńska, Z. Urbańczyk-Lipkowska, M. Gerards, J. W. Morzycki, W. J. Szczepek and J. Frelek, J. Org. Chem., 2007, 72, 2906–2916 CrossRef PubMed.
- S. Chen, F. Ren, S. Niu, X. Liu and Y. Che, J. Nat. Prod., 2014, 77, 9–14 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. J. Stephens, J. J. Pan and K. J. Krohn, J. Org. Chem., 2007, 72, 7641–7649 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. A. Beutler, K. L. McCall, K. Herbert, D. L. Herald, G. R. Pettit, T. Johnson, R. H. Shoemaker and M. R. Boyd, J. Nat. Prod., 2000, 63, 657–661 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. D. Flack, Acta Crystallogr., Sect. A: Found. Crystallogr., 1983, 39, 876–881 CrossRef.
- S. V. Nampoothiri, A. Prathapan, O. L. Cherian, K. G. Raghu, V. V. Venugopalan and A. Sundaresan, Food Chem. Toxicol., 2011, 49, 125–131 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. Mosmann, Immunol. Methods, 1983, 65, 55–63 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Xiong, X. Q. Chen, H. Wei and H. Xiao, Arch. Med. Sci., 2015, 11, 301–306 CAS.
- L. L. Zaika, J. Food Saf., 1988, 9, 97–118 CrossRef PubMed.
Footnote |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available: Bioassay protocols used, the NMR spectra of compounds 19–23, the ITS gene sequences of Aspergillus sp. OUCMDZ-1583. CCDC 995363 and 995361. For ESI and crystallographic data in CIF or other electronic format see DOI: 10.1039/c5ra11185d |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 |