Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleSequential palladium catalyzed coupling–cyclocondensation–coupling (C3) four-component synthesis of intensively blue luminescent biarylsubstituted pyrazoles†
Melanie
Denißen
a,
Jan
Nordmann
a,
Julian
Dziambor
a,
Bernhard
Mayer
a,
Walter
Frank
b and
Thomas J. J.
Müller
*a
aInstitut für Organische Chemie und Makromolekulare Chemie, Heinrich-Heine-Universität Düsseldorf, Universitätsstraße 1, 40225 Düsseldorf, Germany. E-mail: ThomasJJ.Mueller@uni-duesseldorf.de
bInstitut für Anorganische Chemie und Strukturchemie, Heinrich-Heine-Universität Düsseldorf, Universitätsstraße 1, 40225 Düsseldorf, Germany
First published on 30th March 2015
Abstract
1-, 3-, and 5-Biarylsubstituted pyrazoles can be efficiently prepared by a microwave-assisted consecutive four-component synthesis based upon a sequential Pd-catalyzed coupling–condensation–coupling (C3), a one-pot sequence which concatenates Sonogashira alkynylation and Suzuki arylation intercepted by pyrazole forming cyclocondensation of the ynone intermediate. This diversity-oriented approach enables tailoring, fine-tuning and optimization of absorption and emission properties towards high fluorescence quantum yields in solution up to Φf = 0.97. The increased luminescence intensity stemming from biaryl substitution can be rationalized by ground and excited state computations on the DFT level of theory, which nicely reproduce the experimental data of absorption and emission.
Introduction
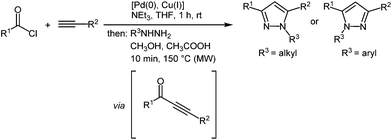
Pyrazoles are omnipresent in many fields of science and technology. Although they are rarely found in nature,1 they have applications as pesticides in crop protection2 and their biological activities encompass analgesic, anti-inflammatory, sedative, antipyretic, and antispasmodic activity.3 In addition, these heterocycles are known as pluripotent ligands4 in coordination chemistry. Furthermore, pyrazoles have also aroused interest due their photophysical properties and applications such as optical brighteners as additives in detergents,5 UV-stabilizer for polystyrene,6 and highly selective fluorescence sensors.7 Quite some derivatives display large Stokes shifts and emission at short wavelength, i.e. blue luminescence, which remains an ongoing challenge in OLED technologies.8 Hence, novel syntheses of pyrazoles are highly attractive evergreens for organic chemists.The interesting photophysical properties of pyrazoles as fluorophores and the challenge to access tailor-made π-systems by diversity-oriented syntheses (DOS)9 such as multicomponent reactions (MCR) have prompted us to develop a regioselective consecutive three-component Sonogashira coupling–cyclocondensation (C2) synthesis of 1,3,5-substitued pyrazoles in a one-pot fashion (Scheme 1).10 All 1,3,5-substituted pyrazoles are highly fluorescent dyes with large Stokes shifts and moderate quantum yields.
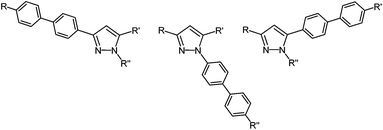
It is known that biphenyl is essentially coplanar in the first excited state S1, while the phenyl rings are distorted from coplanarity by ∼44° in the electronic ground state S0.11,12 This peculiar aspect was successfully considered for designing fluorescent chemosensors.13 For increasing fluorescence quantum yields we envisioned the implementation of extended delocalization by employing a DOS approach to biaryl pyrazoles. Therefore, biaryl substitution on the pyrazole core in 1-, 3-, and 5-position (Fig. 1) could guide the way for combining the photophysical characteristics of biaryls with pyrazole based emitters supported by systematic quantitative structure–activity relationship (QSAR) studies.
Modular, flexible and reactivity-based procedures are currently highly topical methodologies in one-pot syntheses of heterocycles.14 Conceptually, instead of applying biaryl starting materials to the ynone strategy we considered a DOS approach based upon sequential catalysis.15 In the sense of a self-relay catalysis16 the initially employed catalyst source should catalyze a subsequent catalytic step without further addition of the metal complexes. As a consequence a straightforward one-pot process furnishing diversely functionalized molecules can be envisioned. In addition, the combined advantages of MCR and sequential catalysis enhance the synthetic and catalytic efficiency and efficacy.17 In this context sequential Pd-catalyzed processes15 should pave the way to expanded pyrazoles in the sense of de novo generation-functionalization of the pyrazole core. Therefore, the concatenation of the C2 sequence with a concluding Suzuki–Miyaura coupling in a one-pot fashion promises a highly modular access to intensely fluorescent biarylsubstituted pyrazoles (Scheme 2).
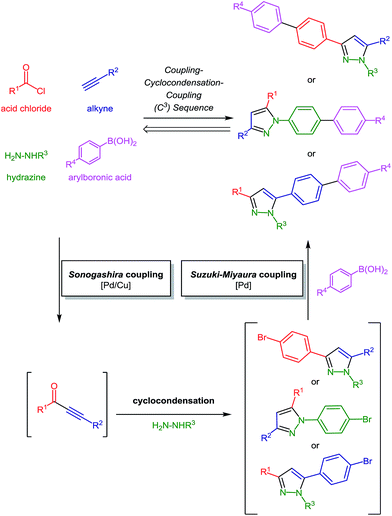 | ||
| Scheme 2 Retrosynthetic analysis of biarylsubstituted substituted pyrazoles via coupling–condensation–coupling (C3) one-pot transforms. | ||
Here, we report a novel sequentially Pd-catalyzed C3-synthesis of biarylsubstituted pyrazoles in a consecutive four-component fashion. In addition, the photophysical properties in solution are reported and discussed in the light of DFT-computational studies.
Results and discussion
Synthesis
For establishing the sequentially Pd(0)-catalyzed microwave-assisted C3-four-component synthesis of 1,3,5-substituted pyrazoles containing biaryl units we first set out to place the dormant bromine functionality in the alkynyl part. Based upon previous studies on one-pot sequences with terminal Suzuki coupling9b the addition of 20 mol% of triphenylphosphane is necessary to stabilize the catalytically active Pd(0) species.Therefore, upon coupling various (hetero)aroyl chlorides 1 with p-bromophenyl acetylene (2a) the expected alkynones are formed that were subsequently cyclocondensed with hydrazines 3 and then, still within the same reaction vessel and without further addition of metal complexes, different boronic acids 4 were coupled to give the desired 5-biarylsubstituted pyrazoles 5 in moderate to good yields (Scheme 3, Table 1). The structures of the compounds 5 were unambiguously assigned by 1H and 13C NMR spectroscopy and mass spectrometry.
| Entry | Acid chloride 1 | Hydrazine 3 | Boronic acid 4 | 5-Biarylsubstituted pyrazoles 5 (yield) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| a Employed as N2H4·H2O. | ||||
| 1 | R1 = C6H5 (1a) | R3 = CH3 (3a) | R4 = 4-MeC6H4 (4a) |
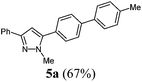
|
| 2 | 1a | 3a | R4 = C6H5 (4b) |
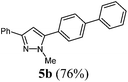
|
| 3 | 1a | 3a | R4 = 2-Me-4-FC6H3 (4c) |
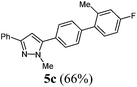
|
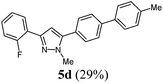
| 4 | R1 = 2-FC6H4 (1b) | 3a | 4a |
|
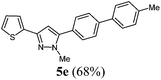
| 5 | R1 = 2-thienyl (1c) | 3a | 4a |
|
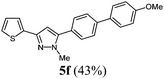
| 6 | 1c | 3a | R4 = 4-MeOC6H4 (4d) |
|
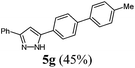
| 7 | 1a | R3 = H (3b)a | 4a |
|
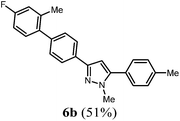
However, these optimized reaction conditions (Scheme 3) cannot be directly transposed to the synthesis of 3-substituted pyrazoles starting from 4-bromo benzoyl chloride (1d). The model reaction with acid chloride 1d, phenyl acetylene (2b), methyl hydrazine (3a), and phenyl boronic acid (4b) in THF gives rise to the formation of the desired 3-substituted pyrazole 6a only in 26% (2 h for the Sonogashira coupling step) and 39% (17.5 h for the Sonogashira coupling step). However, changing the solvent to 1,4-dioxane considerably improves the overall yield of product 6a with a Sonogashira coupling time of 2 h.
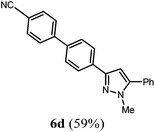
When applying these conditions to the C3-four-component sequence of 4-bromo benzoyl chloride (1d), alkynes 2, methyl hydrazine (3a), and arylboronic acids 4 3-biarylsubstituted pyrazoles 6 can be obtained in good yields (Scheme 4, Table 2). The structures of the compounds 6 were unambiguously assigned by 1H and 13C NMR spectroscopy and mass spectrometry.
The substitution pattern of the pyrazole core can be varied by the choice of different alkynes 2 and boronic acids 4. In addition to aryl substituents a butyl substituent can be uneventfully introduced in the 5-position (Table 2, entry 3). Electron neutral and electron withdrawing aryl boronic acids (Table 2, entry 4) are well tolerated in the reaction sequence. Sterically hindered boronic acids can also be coupled (Table 2, entry 2).
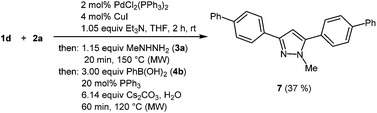
In the sense of a consecutive C3-pseudo-five-component synthesis starting from 4-bromo benzoyl chloride (1d), p-bromophenyl acetylene (2a), methyl hydrazine (3a), and phenyl boronic acid (4b) the 3,5-bis(biphenyl) 1-methyl pyrazole (7) was obtained in 37% yield, i.e. an average yield of 72% per step in this three-step one-pot process (Scheme 5). The structure of compound 7 was unambiguously assigned by 1H and 13C NMR spectroscopy and mass spectrometry.
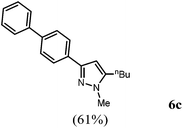
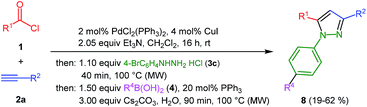
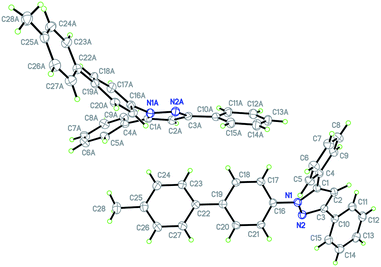
Finally, we also planned to couple a bromophenyl substituent in the 1-position. However, the standard conditions for the synthesis of 3- and 5-biphenylic substituted pyrazoles 5 and 6 were found to be unsuitable for accessing this substitution pattern. The problem already arose in the pyrazole formation step. Careful optimization of these first two steps revealed dichloromethane as a solvent with a reaction time of 16 h at room temperature for the Sonogashira step and subsequent cyclocondensation with dielectric heating at 100 °C for 40 min gave 1-p-bromophenyl-3,5-diphenylpyrazole in 61% yield. These modifications were then employed in the consecutive four-component synthesis to give 1-biarylsubstituted pyrazoles 8 in moderate to good yields (Scheme 6, Table 3). The structures of the compounds 8 were unambiguously assigned by 1H and 13C NMR spectroscopy and mass spectrometry, and later by an X-ray crystal structure analysis of compound 8b (Fig. 2). Although, in the cases of the pyrazoles 5, 6, and 7 exclusively the regioisomers arising from the Michael addition of the inner nitrogen atom of the hydrazines were formed, the regioselectivity for aryl hydrazines was inverted giving preferentially the products arising from the Michael addition of the outer nitrogen atom. For compounds 8e–h the minor regioisomer could be identified and quantified by 1H NMR spectroscopy. The regioselectivity in these cases lies between 6![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 and 22
1 and 22![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 in favor of the depicted regioisomers.
1 in favor of the depicted regioisomers.
| Entry | Acid chloride 1 | Alkyne 2 | Boronic acid 4 | 1-Biarylsubstituted pyrazoles 8 (yield) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| a The ratio of regioisomers, rr, was determined by intergration of the characteristic proton signal of the methine group. | ||||
| 1 | 1a | 2b | 4b |
|
| 2 | 1a | 2b | 4a |
|
| 3 | 1a | 2b | 4e |
|
| 4 | 1a | 2b | 2-Bpin-5-methyl-thio-phene (4f) |
|
| 5 | R1 = 4-MeOC6H4 (1e) | 2b | 4a |
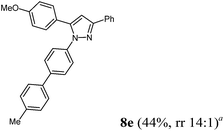
|
| 6 | R1 = 2-ClC6H4 (1f) | 2b | 4a |
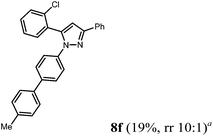
|
| 7 | 1c | 2b | 4a |
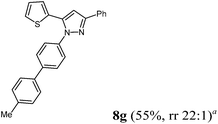
|
| 8 | 1a | 2d | 4a |
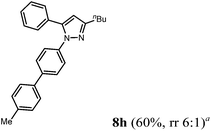
|
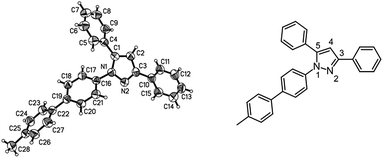 | ||
| Fig. 2 Diagram of the structure of the molecules of compound 8b in the crystal; 30% probability ellipsoids (enumeration of the pyrazole core on the left). | ||
This sequence also allows the use of boronic acid esters (Table 3, entry 4) besides the usually employed boronic acids without changing the reaction conditions. Besides structural elucidation by spectroscopy the solid state structure of the pyrazole 8b was additionally corroborated by single crystal X-ray analysis (Fig. 2).18
The X-ray diffractional and DFT-computed (upon employing a solvent model, vide infra) torsional angles of the phenyl substituents are in good agreement (Table 4). In contrast to the optimized calculated solution geometry only for the phenyl substituent in position 3 of the pyrazole core the crystal structure reveals a considerable twist out of coplanarity, which can be most likely attributed to crystal packing of compound 8b.
| Torsion angels [°] | ||
|---|---|---|
| θ X-ray | θ calc. | |
| N(1)–C(1)–C(4)–C(5) | 35.0(3) | 45 |
| N(2)–C(3)–C(10)–C(15) | −26.1(3) | 4 |
| N(2)–N(1)–C(16)–C(21) | 44.8(2) | 48 |
| C(20)–C(19)–C(22)–C(27) | 26.3(2) | 37 |
The crystal packing of the molecules of pyrazole 8b reveals an acentric structure (space group Pca21) (Fig. 3). The sheer number of π-systems suggests many intermolecular π–π-interactions to be present in the solid. However, only van der Waals interactions can be observed. A closer inspection reveals van der Waals interactions of one distinct molecule to entirely ten nearest neighbors which cannot be specified in more detail here. As a special feature only a coordinated multiple T-shape interaction can be found (Fig. 4).
Photophysical properties and calculated electronic structure
All solutions of the synthesized biarylsubstituted pyrazoles 5–8 show a remarkable blue fluorescence in solution upon eyesight. Therefore, the photophysical properties were determined by UV/Vis and static fluorescence spectroscopy (Table 5). For comparison to simple arylsubstituted pyrazoles we prepared 1-methyl-3,5-diphenylpyrazole (9) according to our previously published protocol (for experimental details see ESI†).10a The longest wavelength absorption maxima λmax,abs of the 3- and 5-biarylsubstituted pyrazoles 5–7 are found in a broad range from 263.0 to 306.5 nm with a molar extinction coefficients ε between 33![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 to 44
000 to 44![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 L cm−1 mol−1. As a consequence of the large extended π-electron conjugation the 3,5-bis(biphenyl) substituted pyrazole 7 display a particularly high molar extinction coefficient ε of 62
000 L cm−1 mol−1. As a consequence of the large extended π-electron conjugation the 3,5-bis(biphenyl) substituted pyrazole 7 display a particularly high molar extinction coefficient ε of 62![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 500 L cm−1 mol−1. The absorption maxima of the 1-aryl substituted compounds 8 ranges between 256.5 and 311.0 nm with molar extinction coefficients ε of 18
500 L cm−1 mol−1. The absorption maxima of the 1-aryl substituted compounds 8 ranges between 256.5 and 311.0 nm with molar extinction coefficients ε of 18![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 900 to 39
900 to 39![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 900 L cm−1 mol−1. In general the high molar extinction coefficients ε can be ascribed to the dominance of π–π* transitions. The absorption maximum of the simple pyrazole 9 is hypsochromically shifted in comparison to the consanguineous biarylsubstituted pyrazoles 5b, 6a, and 7 as a consequence of the extended π-system by biaryl substitution. The absorption maximum of 9 could be detected at 254.0 nm with a molar extinction coefficient of 28
900 L cm−1 mol−1. In general the high molar extinction coefficients ε can be ascribed to the dominance of π–π* transitions. The absorption maximum of the simple pyrazole 9 is hypsochromically shifted in comparison to the consanguineous biarylsubstituted pyrazoles 5b, 6a, and 7 as a consequence of the extended π-system by biaryl substitution. The absorption maximum of 9 could be detected at 254.0 nm with a molar extinction coefficient of 28![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 800 L cm−1 mol−1. The transition at highest energy of pyrazole 8a (257.0 nm) can be assigned to the absorption of the pyrazole core as in the case of the simple pyrazole 9.
800 L cm−1 mol−1. The transition at highest energy of pyrazole 8a (257.0 nm) can be assigned to the absorption of the pyrazole core as in the case of the simple pyrazole 9.
| Compound | Absorption maxima λmax,abs (ε)a [nm] (L cm−1 mol−1) | Emission maxima λmax,em (Φf)b [nm] (a.u.) | Stokes-shift Δ![[small nu, Greek, tilde]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/i_char_e0e1.gif) c [cm−1] c [cm−1] |
|---|---|---|---|
a Recorded in CH2Cl2 UVASOL (in the absorption maxima sh stands for shoulder).
b Recorded in CH2Cl2 UVASOL. Quantum yields Φf were determined with p-terphenyl as a standard in cyclohexane UVASOL, Φ = 0.89.21,22
c Δ![[small nu, Greek, tilde]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/i_char_e0e1.gif) = λmax,abs − λmax,em [cm−1]. = λmax,abs − λmax,em [cm−1].
|
|||
| 5a | 273.5 (40![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 100) 100) |
357.0 (0.77) | 9400 |
| 5b | 268.5 (36![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 700) 700) |
359.0 (0.77) | 8600 |
| 5c | 263.0 (38![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 400) 400) |
344.5 (0.67) | 9000 |
| 5d | 281.0 (34![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 200) 200) |
351.5 (0.97) | 7100 |
| 5e | 285.0 (44![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000) 000) |
382.0 (0.35) | 8900 |
| 5f | 289.0 (43![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 300) 300) |
363.0 (0.80) | 7100 |
| 5g | 285.0 (42![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000) 000) |
343.5 (0.86) | 6000 |
| 6a | 283.5 (35![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 600) 600) |
344.5 (0.49) | 6300 |
| 6b | 267.5 (35![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 800) 800) |
338.5 (0.83) | 7800 |
| 6c | 286.0 (33![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000) 000) |
347.0 (0.27) | 6200 |
| 6d | 306.5 (36![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 600) 600) |
384.0 (0.10) | 6600 |
| 7 | 288.5 (62![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 500) 500) |
367.0 (0.07) | 7400 |
| 8a | 257.0 (36![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 300), 293.0 sh (25 300), 293.0 sh (25![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000) 000) |
385.0 (0.41) | 8200 |
| 8b | 257.0 (32![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000), 296.0 sh (23 000), 296.0 sh (23![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000) 000) |
388.0 (0.33) | 8000 |
| 8c | 257.0 (27![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 400), 307.5 (18 400), 307.5 (18![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 900) 900) |
387.0 (0.12) | 6700 |
| 8d | 268.5 (29![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 500) 500) |
385.0 (0.29) | 11![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 300 300 |
| 8e | 261.5 (39![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 900), 288.0 sh (29 900), 288.0 sh (29![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 600), 311.0 sh (20 600), 311.0 sh (20![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 500) 500) |
386.5 (0.37) | 6300 |
| 8f | 256.5 (27![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 260), 296.0 (28 260), 296.0 (28![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 404) 404) |
388.5 (0.35) | 8000 |
| 8g | 272.5 (39![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 600) 600) |
394.0 (0.30) | 11![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 300 300 |
| 8h | 286.0 (22![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 900) 900) |
382.5 (0.33) | 8800 |
| 9 | 254.0 (28![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 800) 800) |
338.5 (0.40) | 9800 |
For the emission maxima λmax,em 3- and 5-biarylsubstituted pyrazoles 5–7 span a wider range (λmax,em 338.5–394.0 nm) than the 1-biarylsubstituted pyrazoles 8 (λmax,em 382.5–394.0 nm). In comparison the diphenyl derivative 9 possesses an emission maximum at 338.5 nm. The observed large Stokes shift of 9800 cm−1 arises from the well-established pronounced conformational change in the pyrazole core upon excitation.19 While the relative fluorescence quantum yields Φf of 3- and 5-biarylsubstituted pyrazoles 5–7 are with the exceptions of compounds 6d and 7 generally high (Φf = 0.27–0.97), 1-aryl substituted compounds 8 lie with Φf = 0.12–0.41 generally lower. Moreover, in comparison of the simple pyrazole 9 (Φf = 0.40) with the consanguineous series pyrazoles 5b, 6a, and 8a as well as 7 the fluorescence quantum yields of 5b (Φf = 0.77) and 6a (Φf = 0.49) have increased, it remains identical for 8a (Φf = 0.41), however, strongly decreases for the bis(biphenyl) compound 7 (Φf = 0.07).
For all substitution patterns the Stokes shifts Δ![[small nu, Greek, tilde]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/i_char_e0e1.gif) are very pronounced and are found between 6000 and 11
are very pronounced and are found between 6000 and 11![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 300 cm−1. The occurrence of large Stokes shifts can be generally attributed to two mechanistic pathways based on the excited state properties of the molecules. Either the geometry of the molecule changes considerably in the excited state or a reorganization of solvent molecules after excitation becomes responsible.19 This latter solvent effect increases for molecules with larger excited state dipole moments than in their ground state.20 3,5-Diarylsubstituted pyrazoles are known for their strongly polar nature in the excited state.6 For 3- and 5-biarylsubstituted pyrazoles 5–7 one distinct maximum can be detected in the absorption spectra (Fig. 5 and 6). However 1-biarylsubstituted pyrazoles 8 often show an additional characteristic shoulder around 300 nm (Fig. 5). The direct comparison of the absorption and emission properties of the regioisomers 5b and 6a reveals significant differences (Fig. 6). While the absorption maximum of compound 6a is shifted bathochromically in comparison to pyrazole 5b by 2000 cm−1 the emission maximum appears with a hypsochromic shift of 1200 cm−1. So, this shift causes a smaller Stokes shift. This shift of 5b can be rationalized by planarization of the biphenyl unit in the excited state.
300 cm−1. The occurrence of large Stokes shifts can be generally attributed to two mechanistic pathways based on the excited state properties of the molecules. Either the geometry of the molecule changes considerably in the excited state or a reorganization of solvent molecules after excitation becomes responsible.19 This latter solvent effect increases for molecules with larger excited state dipole moments than in their ground state.20 3,5-Diarylsubstituted pyrazoles are known for their strongly polar nature in the excited state.6 For 3- and 5-biarylsubstituted pyrazoles 5–7 one distinct maximum can be detected in the absorption spectra (Fig. 5 and 6). However 1-biarylsubstituted pyrazoles 8 often show an additional characteristic shoulder around 300 nm (Fig. 5). The direct comparison of the absorption and emission properties of the regioisomers 5b and 6a reveals significant differences (Fig. 6). While the absorption maximum of compound 6a is shifted bathochromically in comparison to pyrazole 5b by 2000 cm−1 the emission maximum appears with a hypsochromic shift of 1200 cm−1. So, this shift causes a smaller Stokes shift. This shift of 5b can be rationalized by planarization of the biphenyl unit in the excited state.
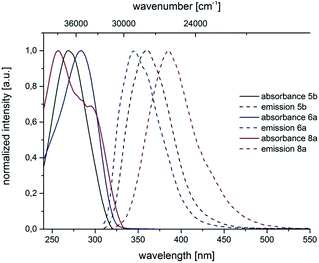 | ||
| Fig. 5 Selected normalized absorption and emission spectra of biarylsubstituted pyrazoles 5b, 6a and 8a (recorded in CH2Cl2 UVASOL at T = 293 K, λexc = 290.0 nm). | ||
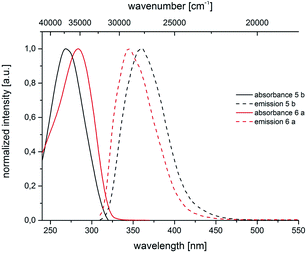 | ||
| Fig. 6 Normalized absorption and emission spectra of pyrazoles 5b and 6a (recorded in CH2Cl2 UVASOL at T = 293 K, λexc = 290.0 nm). | ||
The substituent effects on the fluorescence quantum yields are quite substantial. While cyano substitution (compounds 6d and 8c) causes a significant decrease of Φf, a similar, yet smaller tendency due to additional rotational degrees of freedom23 can be observed for n-butyl substituted pyrazoles 6c and 8h, and pyrazoles with a thienyl substituent in a remote position as in compound 8d or in 5-position (compound 8g). For the two sanguineous 3-thienyl pyrazoles 5e and 5f the remote para-substituent of the biaryl moiety exerts a distinct difference. While the methyl substituent only leads to a mediocre quantum yield the methoxy substituent displays a significant magnitude. Interestingly, the 2-phenyl congener 5a possesses substantially higher fluorescence efficiency than the 2-thienyl derivative 5e. However, most remarkably are the effects of remote (compounds 5c and 6b) and ortho-fluorophenyl substitution (compound 5d) at the position 3 and 5 of the pyrazole core. Indeed the 3-(ortho-fluorophenyl) substituted pyrazole 5d almost reaches unity for the fluorescence efficiency. In summary redshifted emission and highest quantum yields for the solution emission can be obtained upon placing biaryl substituents in the 3- or 5-positions of the pyrazole core.
The observed tunable photophysical behavior of the different series of biarylsubstituted pyrazoles calls for a deeper understanding of the electronic structure, in particular, the nature of relevant longest wavelength transition. Therefore, the geometries of the electronic ground state structures of the pyrazoles 5c, 6d, and 8b were optimized on the DFT level of theory using Gaussian09 (ref. 24) with the B3LYP functional25 and the Pople 6-311G(d,p) basis set.26 Since all experimental photophysical data were obtained in dichloromethane solutions the calculations were carried out applying the Polarizable Continuum Model (PCM) with dichloromethane as a solvent.27 All minimum structures were unambiguously confirmed by analytical frequency analysis.
The inspection of the equilibrium ground state structures for all three different substitution patterns reveals that the torsional angles θcalc. between the phenyl residues in 3- and 5-position and the adjacent C(1)–N(5) or C(3)–N(4)-atoms only show marginal differences (Fig. 7). Even for the 1-biarylsubstituted pyrazole 8b the torsional angle remains in the same range. While the 3-phenyl substituents adopt an almost coplanar orientation with the pyrazole core (θcalc. = 2–4°) the aromatic substituent in 5-position is considerably twisted out of coplanarity (θcalc. = 45–47°). The ground state equilibrium geometries of the biaryl moieties in all three substituent positions are inherently and expectedly not coplanar28 and dihedral angles between the two arene rings are found at θcalc. = 36–37° for 6d and 8b and at θcalc. = 55° for 5c, the latter as a steric effect of the ortho-methyl group. Therefore the electronic communication can be expected to be more efficient biphenyl cores without ortho-substitution.
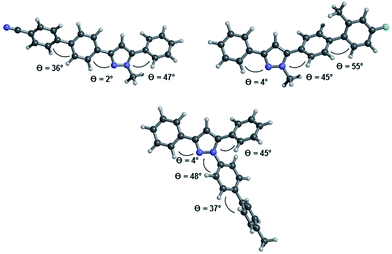 | ||
| Fig. 7 Optimized geometries at the B3LYP 6-311G(d,p) level of DFT theory for the pyrazole structures 6d (top left), 5c (top right), and 8b (bottom). | ||
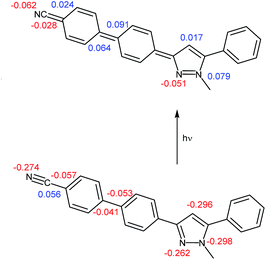
A closer inspection of the coefficient densities in the Kohn–Sham frontier molecular orbitals of pyrazole 6d reveals that the HOMO's coefficient density is largely localized on the pyrazole core and the 3-aryl substituent (Fig. 8). Furthermore, the remote benzonitrile substituent and the 5-phenyl substituent only bear marginal coefficient density. In contrast, the coefficient density in the LUMO representing cum grano salis the Franck–Condon state upon excitation is almost completely inverted. The major density is now localized on the terminal benzonitrile moiety and its adjacent phenylene fragment, whereas just marginal residual density is found on the pyrazole core and none on the 5-phenyl substituent. Significant coefficient density on the 3-phenylene moiety both in HOMO and LUMO indicates a sufficient overlap between the ground and presumed excited state wavefunctions required for substantial transition dipole moment.
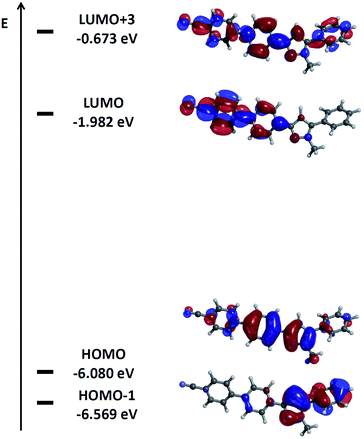 | ||
| Fig. 8 Selected DFT-computed (B3LYP 6-311G(d,p)) Kohn–Sham frontier molecular orbitals of pyrazole 6d. | ||
The optimized structures for the pyrazoles 5c, 6d, and 8b were submitted to TD-DFT calculations for assigning the absorption characteristics (Table 6). All calculations were performed for dichloromethane as a solvent. Furthermore, the hybrid exchange-correlation functional CAM-B3LYP29 was implemented and a non-equilibrium solvation30 for the state specific solvation of the vertical excitation was included. The computed results are in good agreement with the experimentally determined values. Expectedly, the longest wavelength absorption maxima for the structures 6d and 8b appearing around 300 nm result from dominant HOMO → LUMO transitions. The absorption maximum of pyrazole 5c is shifted hypsochromically due to a considerable torsion by the ortho-tolyl substituent. In this case the dominant contribution not only arises from the HOMO → LUMO transition but also from the HOMO−1 → LUMO transition. For 1-biarylsubstituted pyrazoles 8 second maxima are often detected in experimental absorption spectra. For elucidation of this behavior the oscillatory strength of the first ten excited states of 8b were compared. The inspection reveals that the absorption at lower wavelengths not only consists of one but also of two different excited states, in particular, the excited states S3 and S4 are apparently superimposed.
| Structure | Experimental λmax,abs [nm] | Computed λmax,abs [nm] (most dominant contributions) |
|---|---|---|
| 5c | 263 | 256 (HOMO−1 → LUMO (45%)), (HOMO → LUMO (39%)) |
| 6d | 307 | 298 (HOMO → LUMO (86%)) |
| 8b | 257 | 243 (HOMO → LUMO +1 (20%)) |
| 245 (HOMO → LUMO +2 (32%)) | ||
| 296 | 278 (HOMO → LUMO (85%)) |
In addition the geometry of the vibrationally relaxed excited state (S1)31 of structure 6d was optimized by a gas phase DFT calculation using the program package Turbomole32,33 with the B3LYP functional and the TZVP basis set.34 COSMO (Conductor-like Screening Model)35 has not been implemented for excited state calculations so far, thus, no solvent model computations were performed. It is also noteworthy to mention that the vibrationally relaxed S1 state possess a coplanar geometry of the central pyrazole core. This is different with respect to simple substituted and annellated pyrazoles where butterfly and kite conformations are considered to be the origin of large Stokes shifts.19 The vibrationally relaxed ground state (S0) geometry, optimized with Gaussian09 with a similar basis set employing dichloromethane as a solvent, differs at first glance from the geometry of the excited state only in the dihedral angle between the two rings of the biaryl substituent. As a consequence of excitation the biphenyl moiety planarizes with a torsional angle θcalc.,exc = 13° (θcalc.,ground = 36°). A closer inspection of the optimized vibrationally relaxed S1 state structure reveals far more distinct geometry changes. In the pyrazole core the nitrogen–nitrogen bond N4–N5 is contracted, whereas the nitrogen–carbon bonds C1–N5 and C3–N4 are elongated upon excitation (Fig. 9, Table 7).
| Bonds | S0 | S1 |
|---|---|---|
| C1–C2 | 1.39 | 1.37 |
| C1–N5 | 1.37 | 1.39 |
| N4–N5 | 1.34 | 1.32 |
| C3–N4 | 1.34 | 1.37 |
| C3–C8 | 1.47 | 1.43 |
| C8–C18 | 1.40 | 1.42 |
| C17–C18 | 1.39 | 1.37 |
| C16–C17 | 1.40 | 1.43 |
| C16–C19 | 1.48 | 1.44 |
| C19–C20 | 1.41 | 1.43 |
| C20–C21 | 1.39 | 1.37 |
| C21–C22 | 1.40 | 1.42 |
| C22–C25 | 1.43 | 1.41 |
| C25–N26 | 1.16 | 1.16 |
In addition, the carbon–carbon bonds in the biaryl residue indicate rather bond length alternation between single and double bonds than typical aromatic bond lengths. This also plausibly rationalizes the biphenyl planarization upon excitation. Also the carbon–carbon bond C22–C25 ligating the nitrile group to the phenylene moiety is slightly contracted to 1.41 Å. While the pyrazole nitrogen atom N5 bears a partial charge of −0.30 in the ground state, it is slightly positively charged (0.08) in the excited state. However, nitrogen atom N4 is obviously not affected by this charge transfer. Yet, adjacent carbon atoms to the nitrogen atoms reveal an inverse behavior. In the nitrile group with nitrogen atom N26 receives a lower negative partial charge in the excited state whereas the partial charge of the nitrile carbon atom C25 alters from positive to negative. In conclusion the dipolar nature of the first excited state of 6d is evident (Fig. 9).
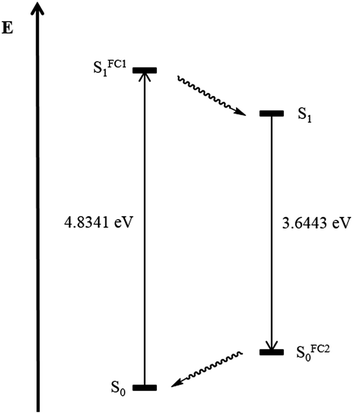
The calculation of the emission maximum of 6d of λem,calc. = 374 nm, performed with Turbomole with TZVP on the geometry optimized structure of the excited state as confirmed by a numerical frequency analysis,36 reproduces the experimental value of λem,exp = 385 nm in good agreement. The measured and the computed absorption maximum of pyrazole 5d are representative for this class of pyrazoles. In this case the dominant contribution arises from the HOMO → LUMO transition (Table 8).
| Experimental [nm] | Computed [nm] | Transition dipole moment | |
|---|---|---|---|
| λ max,abs (5d) | 281 | 256 (HOMO → LUMO (50%)) | 10.6 |
| λ max,em (5d) | 352 | 340 | 20.6 |
In addition the geometry of the vibrationally relaxed excited state (S1)31 of structure 5d was optimized with Gaussian09 with a similar basis set employing dichloromethane as a solvent. The calculation of the emission maximum of pyrazole 5d of λem,calc. = 340 nm, reproduces the experimental value of λem,exp = 352 nm in good agreement. Fig. 10 summarizes the results of the theoretical analysis. The transition dipole moment after excitation from the electronic ground state S0 to the Franck–Condon state SFC11 (Δμ = 10.6 SI) differs extremely from the transition dipole moment from the electronic relaxed excited state S1 to the Franck–Condon state SFC20 (Δμ = 20.1 SI).
Conclusions
A microwave-assisted consecutive four-component synthesis of biarylsubstituted pyrazoles based upon a sequentially Pd-catalyzed coupling–condensation–coupling (C3) was successfully established. A particular feature of this one-pot sequence is the sequential use of the palladium catalyst without further catalyst addition for both the Sonogashira alkynylation and the Suzuki arylation. The absorption and emission properties can be tailored, fine-tuned and optimized towards high fluorescence quantum yields as a consequence of the diversity oriented nature of this process. Indeed, biaryl substituents improve the overall favorable photophysical properties of arylsubstituted pyrazoles giving rise to bright blue solution emissive molecular materials. Most favorably for achieving a redshifted emission with concomitant high fluorescence quantum yields the biaryl substituents should be placed in position 5 or 3 of the pyrazole core. The electronic structure of the first excited state can be plausibly rationalized and also reproduced by ground and excited state computations on the DFT level of theory. Further studies directed to exploit this novel synthetic approach and the efficient option of optimizing the electronic properties in functional organic materials and also in matrices are currently underway.Experimental
General considerations
All reactions were carried out in flame-dried glassware under nitrogen atmosphere. Reagents and catalyst were purchased reagent-grade and used without further purification. Besides triethylamine was dried with calcium hydride and stored over potassium hydroxide under nitrogen atmosphere. Solvents were dried by a solvent purification system. Dielectric heating was performed in a single mode microwave cavity producing continuous irradiation at 2450 MHz.Further purification of the compounds was performed with flash column chromatography (silica gel 60, mesh 230–400). TLC: silica coated aluminium plates (60, F254). 1H, 13C, DEPT and NOESY NMR spectra were recorded in CDCl3, CDCl2 or acetone-d6 on 300 MHz (Bruker AVIII) or 600 MHz (Bruker Avance III-600) NMR spectrometers. The assignments of Cquat, CH, CH2 and CH3 nuclei were based on DEPT spectra. The elemental analyses were carried out in the microanalytical laboratory on a Perkin Elmer Series II Analyser 2400 of the Pharmazeutisches Institut of the Heinrich-Heine-Universität Düsseldorf. Mass spectra were recorded with a GC/MS-spectrometer Finnigan Trace DSQ with Finnigan Trace GC Ultra (Thermo Electron Corp.) or the ESI spectrometer Ion-Trap-API-mass spectrometer Finnigan LCQDeca (Thermo Quest). High resolution mass spectra were measured on a UHR-QTOF maxis 4G (Bruker Daltonics). Infrared spectra were recorded with a Shimadzu IR Affinity-1 with ATR technique. The intensities of signals are abbreviated as s (strong), m (medium) and w (weak). Absorption spectra were recorded in CH2Cl2 or cyclohexane UVASOL at 293 K on Perkin Elmer UV/VIS/NIR Lambda 19 Spectrometer. Emission spectra were recorded in CH2Cl2 or cyclohexane UVASOL at 293 K on a Perkin Elmer LS55 spectrometer. The melting points were determined with Reichert Thermovar with Kofler technique and they were not corrected.
Synthetic procedures
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 (v/v)) to give the desired pyrazoles 5.
1 (v/v)) to give the desired pyrazoles 5.
| Entry | Acid chloride 1 mg (mmol) | Alkyne 2a mg (mmol) | Hydrazine 3 mg (mmol) | Boronic acid 4 mg (mmol) | 5-Biarylsubstituted pyrazoles 5 mg (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a PdCl2(PPh3)2 (28.0 mg, 0.04 mmol), CuI (15.4 mg, 0.08 mmol), Et3N (207.4 mg, 2.05 mmol), Cs2CO3 (1.95 g, 4.50 mmol), PPh3 (104.1 mg, 0.40 mmol). | |||||
| 1 | 142 (1.00) of 1a | 182 (1.05) of 2a | 51.9 (1.10) of 3a | 204 (1.50) of 4a | 217 (67) of 5a |
| 2 | 141 (1.00) of 1a | 182 (1.05) of 2a | 50.9 (1.10) of 3a | 183 (1.50) of 4b | 229 (76) of 5b |
| 3a | 281 (2.00) of 1a | 362 (2.00) of 2a | 101.4 (2.20) of 3a | 464 (3.00) of 4c | 451 (66) of 5c |
| 4 | 160 (1.00) of 1b | 182 (1.05) of 2a | 51.4 (1.10) of 3a | 205 (1.50) of 4a | 100 (29) of 5d |
| 5 | 148 (1.00) of 1c | 181 (1.05) of 2a | 53.0 (1.10) of 3a | 205 (1.50) of 4a | 227 (69) of 5e |
| 6 | 150 (1.00) of 1c | 183 (1.05) of 2a | 52.4 (1.10) of 3a | 229 (1.50) of 4d | 147 (43) of 5f |
| 7 | 141 (1.00) of 1a | 181 (1.05) of 2a | 56.1 (1.10) of 3b | 205 (1.50) of 4a | 140 (45) of 5g |
![[small nu, Greek, tilde]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/i_char_e0e1.gif) [cm−1] 3024 (w), 2980 (w), 2918 (w), 1601 (w), 1485 (m), 1460 (m), 1438 (w), 1358 (w), 1290 (w), 1188 (w), 1115 (w), 1002 (m), 954 (m), 912 (w), 853 (m), 814 (s), 793 (s), 762 (s), 739 (m), 687 (s), 671 (m). GC-MS (m/z (%)): 326 (2), 325 (25), 324 ([M+], 100), 321 (2), 320 (3), 294 (2), 239 (2), 215 (4), 194 (4), 193 (7), 192 (3), 171 (3), 162 (15), 161 (4), 154 (4), 153 (3), 130 (3), 118 (3), 117 (3), 104 (3), 89 (3), 77 (5). UV/Vis (CH2Cl2): λmax [nm] (ε [L cm−1 mol−1]) = 273.5 (40
[cm−1] 3024 (w), 2980 (w), 2918 (w), 1601 (w), 1485 (m), 1460 (m), 1438 (w), 1358 (w), 1290 (w), 1188 (w), 1115 (w), 1002 (m), 954 (m), 912 (w), 853 (m), 814 (s), 793 (s), 762 (s), 739 (m), 687 (s), 671 (m). GC-MS (m/z (%)): 326 (2), 325 (25), 324 ([M+], 100), 321 (2), 320 (3), 294 (2), 239 (2), 215 (4), 194 (4), 193 (7), 192 (3), 171 (3), 162 (15), 161 (4), 154 (4), 153 (3), 130 (3), 118 (3), 117 (3), 104 (3), 89 (3), 77 (5). UV/Vis (CH2Cl2): λmax [nm] (ε [L cm−1 mol−1]) = 273.5 (40![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 100). Emission (CH2Cl2): λmax [nm] (Φf) = 357.0 (0.77). Stokes shift [cm−1] = 9400. Anal. calcd for C23H20N2 (324.4): C 85.15, H 6.21, N 8.63; found C 85.23, H 6.17, N 8.75%.
100). Emission (CH2Cl2): λmax [nm] (Φf) = 357.0 (0.77). Stokes shift [cm−1] = 9400. Anal. calcd for C23H20N2 (324.4): C 85.15, H 6.21, N 8.63; found C 85.23, H 6.17, N 8.75%.
![[small nu, Greek, tilde]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/i_char_e0e1.gif) [cm−1] 3028 (w), 2936 (w), 1601 (w), 1483 (m), 1460 (m), 1439 (w), 1360 (w), 1279 (w), 1186 (w), 1113 (w), 1003 (m), 957 (w), 918 (w), 849 (m), 799 (m), 766 (s), 737 (m), 694 (s), 675 (m). EI-MS (m/z (%)): 311.1 (31), 310 ([M+], 100), 273 (3), 232 (5), 179 (6), 155 (9), 135 (7), 116 (3), 77 (5). UV/Vis (CH2Cl2): λmax [nm] (ε [L cm−1 mol−1]) = 268.5 (36
[cm−1] 3028 (w), 2936 (w), 1601 (w), 1483 (m), 1460 (m), 1439 (w), 1360 (w), 1279 (w), 1186 (w), 1113 (w), 1003 (m), 957 (w), 918 (w), 849 (m), 799 (m), 766 (s), 737 (m), 694 (s), 675 (m). EI-MS (m/z (%)): 311.1 (31), 310 ([M+], 100), 273 (3), 232 (5), 179 (6), 155 (9), 135 (7), 116 (3), 77 (5). UV/Vis (CH2Cl2): λmax [nm] (ε [L cm−1 mol−1]) = 268.5 (36![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 700). Emission (CH2Cl2): λmax [nm] (Φf) = 359.0 (0.77). Stokes shift [cm−1] = 8600. Anal. calcd for C22H18N2 (310.4): C 85.13, H 5.85, N 9.03; found C 84.92, H 5.88, N 8.77%.
700). Emission (CH2Cl2): λmax [nm] (Φf) = 359.0 (0.77). Stokes shift [cm−1] = 8600. Anal. calcd for C22H18N2 (310.4): C 85.13, H 5.85, N 9.03; found C 84.92, H 5.88, N 8.77%.
![[small nu, Greek, tilde]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/i_char_e0e1.gif) [cm−1] 3026 (w), 2940 (w), 1609 (w), 1481 (m), 1460 (m), 1439 (w), 1360 (w), 1269 (m), 1223 (m), 1192 (w), 1150 (m), 1119 (w), 1003 (m), 955 (m), 909 (w), 850 (m), 799 (m), 766 (s), 685 (s), 683 (m). GC-MS (m/z (%)): 343 ([M+ + H], 25), 342 ([M+], 100), 183 ([C13H10F+], 13), 157 ([C10H9N2], 7), 118 ([C8H5F+], 22), 91 ([C7H7+], 9), 77 ([C6H5+], 19), 65 ([C5H5+], 2), 51 ([C4H3+], 4). UV/Vis (CH2Cl2): λmax [nm] (ε [L cm−1 mol−1]) = 263.0 (38
[cm−1] 3026 (w), 2940 (w), 1609 (w), 1481 (m), 1460 (m), 1439 (w), 1360 (w), 1269 (m), 1223 (m), 1192 (w), 1150 (m), 1119 (w), 1003 (m), 955 (m), 909 (w), 850 (m), 799 (m), 766 (s), 685 (s), 683 (m). GC-MS (m/z (%)): 343 ([M+ + H], 25), 342 ([M+], 100), 183 ([C13H10F+], 13), 157 ([C10H9N2], 7), 118 ([C8H5F+], 22), 91 ([C7H7+], 9), 77 ([C6H5+], 19), 65 ([C5H5+], 2), 51 ([C4H3+], 4). UV/Vis (CH2Cl2): λmax [nm] (ε [L cm−1 mol−1]) = 263.0 (38![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 400). Emission (CH2Cl2): λmax [nm] (Φf) = 344.5 (0.67). Stokes shift [cm−1] = 9000. Anal. calcd for C23H19N2F (342.4): C 80.68, H 5.59, N 8.18; found C 80.58, H 5.52, N 7.9%.
400). Emission (CH2Cl2): λmax [nm] (Φf) = 344.5 (0.67). Stokes shift [cm−1] = 9000. Anal. calcd for C23H19N2F (342.4): C 80.68, H 5.59, N 8.18; found C 80.58, H 5.52, N 7.9%.
![[small nu, Greek, tilde]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/i_char_e0e1.gif) [cm−1] 3022 (w), 2345 (w), 1481 (m), 1468 (m), 1433 (w), 1354 (w), 1258 (w), 1206 (w), 1190 (w), 1043 (w), 961 (w), 854 (m), 808 (s), 756 (s), 737 (m), 692 (m). GC-MS (m/z (%)): 343 ([M+ + H], 25), 342 ([M+], 100), 299 ([C23H17N2F+], 4), 206 (2), 193 (4), 181 (3), 178 (3), 171 (15), 165 (4), 152 (3), 148 (2), 136 (2), 122 (4), 102 (3). UV/Vis (CH2Cl2): λmax [nm] (ε [L cm−1 mol−1]) = 281.0 (34
[cm−1] 3022 (w), 2345 (w), 1481 (m), 1468 (m), 1433 (w), 1354 (w), 1258 (w), 1206 (w), 1190 (w), 1043 (w), 961 (w), 854 (m), 808 (s), 756 (s), 737 (m), 692 (m). GC-MS (m/z (%)): 343 ([M+ + H], 25), 342 ([M+], 100), 299 ([C23H17N2F+], 4), 206 (2), 193 (4), 181 (3), 178 (3), 171 (15), 165 (4), 152 (3), 148 (2), 136 (2), 122 (4), 102 (3). UV/Vis (CH2Cl2): λmax [nm] (ε [L cm−1 mol−1]) = 281.0 (34![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 200). Emission (CH2Cl2): λmax [nm] (Φf) = 351.5 (0.97). Stokes shift [cm−1] = 7100. Anal. calcd for C23H19N2F (342.4): C 80.68, H 5.59, N 8.18; found C 79.08, H 5.43, N 8.01%.
200). Emission (CH2Cl2): λmax [nm] (Φf) = 351.5 (0.97). Stokes shift [cm−1] = 7100. Anal. calcd for C23H19N2F (342.4): C 80.68, H 5.59, N 8.18; found C 79.08, H 5.43, N 8.01%.
![[small nu, Greek, tilde]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/i_char_e0e1.gif) [cm−1] 3019 (w), 2930 (w), 1489 (m), 1477 (m), 1439 (m), 1396 (m), 1375 (m), 1285 (m), 1221 (m, C–S), 1180 (w), 1105 (w), 1005 (m), 843 (m), 795 (s), 741 (m), 694 (s), 681 (m). GC-MS (m/z (%)): 330 ([M+], 100), 287 (7), 239 ([C14H11N2S+], 2), 165 ([C13H9+], 18), 91 ([C7H7+], 8), 77 ([C6H5+], 2), 65 ([C5H5+], 4), 51 ([C4H3+], 3). UV/Vis (CH2Cl2): λmax [nm] (ε [L cm−1 mol−1]) = 285.0 (44
[cm−1] 3019 (w), 2930 (w), 1489 (m), 1477 (m), 1439 (m), 1396 (m), 1375 (m), 1285 (m), 1221 (m, C–S), 1180 (w), 1105 (w), 1005 (m), 843 (m), 795 (s), 741 (m), 694 (s), 681 (m). GC-MS (m/z (%)): 330 ([M+], 100), 287 (7), 239 ([C14H11N2S+], 2), 165 ([C13H9+], 18), 91 ([C7H7+], 8), 77 ([C6H5+], 2), 65 ([C5H5+], 4), 51 ([C4H3+], 3). UV/Vis (CH2Cl2): λmax [nm] (ε [L cm−1 mol−1]) = 285.0 (44![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000). Emission (CH2Cl2): λmax [nm] (Φf) = 382.0 (0.35). Stokes shift [cm−1] = 8900. Anal. calcd for C21H18N2S (330.5): C 76.33, H 5.49, N 8.48; found C 76.11, H 5.35, N 8.47%.
000). Emission (CH2Cl2): λmax [nm] (Φf) = 382.0 (0.35). Stokes shift [cm−1] = 8900. Anal. calcd for C21H18N2S (330.5): C 76.33, H 5.49, N 8.48; found C 76.11, H 5.35, N 8.47%.
![[small nu, Greek, tilde]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/i_char_e0e1.gif) [cm−1] 3030 (w), 2938 (w), 2839 (w), 1603 (m), 1516 (m), 1487 (m), 1443 (m), 1369 (w), 1285 (m), 1261 (m), 1248 (m), 1178 (m), 1117 (w), 1026 (m), 1001 (m), 920 (m), 849 (m), 810 (s), 779 (s), 752 (w), 700 (s), 642 (m). GC-MS (m/z (%)): 348 (8). 347 (24), 346 (100), 332 (5), 331 (23), 304 (3), 303 (15), 258 (2), 174 (2), 173 (16), 152 (19), 139 (4), 130 (3), 117 (3), 110 (2). UV/Vis (CH2Cl2): λmax [nm] (ε [L cm−1 mol−1]) = 289.0 (43
[cm−1] 3030 (w), 2938 (w), 2839 (w), 1603 (m), 1516 (m), 1487 (m), 1443 (m), 1369 (w), 1285 (m), 1261 (m), 1248 (m), 1178 (m), 1117 (w), 1026 (m), 1001 (m), 920 (m), 849 (m), 810 (s), 779 (s), 752 (w), 700 (s), 642 (m). GC-MS (m/z (%)): 348 (8). 347 (24), 346 (100), 332 (5), 331 (23), 304 (3), 303 (15), 258 (2), 174 (2), 173 (16), 152 (19), 139 (4), 130 (3), 117 (3), 110 (2). UV/Vis (CH2Cl2): λmax [nm] (ε [L cm−1 mol−1]) = 289.0 (43![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 300). Emission (CH2Cl2): λmax [nm] (Φf) = 363.0 (0.80). Stokes shift [cm−1] = 7100. Anal. calcd for C21H18N2OS (346.5): C 72.80, H 5.24, N 8.09; found C 72.62, H 5.01, N 7.86%.
300). Emission (CH2Cl2): λmax [nm] (Φf) = 363.0 (0.80). Stokes shift [cm−1] = 7100. Anal. calcd for C21H18N2OS (346.5): C 72.80, H 5.24, N 8.09; found C 72.62, H 5.01, N 7.86%.
![[small nu, Greek, tilde]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/i_char_e0e1.gif) [cm−1] 3030 (w), 2940 (w), 2859 (w), 1605 (w), 1489 (m), 1458 (m), 1377 (w), 1290 (w), 1180 (m), 1115 (w), 1005 (w), 968 (m), 849 (m), 814 (s), 795 (s), 762 (s), 741 (w), 689 (s). EI-MS (m/z (%)): 311 ([M+], 21), 310 (100), 298 (6), 281 (6), 265 (6), 189 (4), 165 (7), 155 (9), 154 (5), 140 (3), 104 (2), 89 (2), 77 (2). UV/Vis (CH2Cl2): λmax [nm] (ε [L cm−1 mol−1]) = 285.0 (42
[cm−1] 3030 (w), 2940 (w), 2859 (w), 1605 (w), 1489 (m), 1458 (m), 1377 (w), 1290 (w), 1180 (m), 1115 (w), 1005 (w), 968 (m), 849 (m), 814 (s), 795 (s), 762 (s), 741 (w), 689 (s). EI-MS (m/z (%)): 311 ([M+], 21), 310 (100), 298 (6), 281 (6), 265 (6), 189 (4), 165 (7), 155 (9), 154 (5), 140 (3), 104 (2), 89 (2), 77 (2). UV/Vis (CH2Cl2): λmax [nm] (ε [L cm−1 mol−1]) = 285.0 (42![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000). Emission (CH2Cl2): λmax [nm] (Φf) = 343.5 (0.86). Stokes shift [cm−1] = 6000. HRMS calcd for C22H18N2 + H+: 311.1543; found 311.1546.
000). Emission (CH2Cl2): λmax [nm] (Φf) = 343.5 (0.86). Stokes shift [cm−1] = 6000. HRMS calcd for C22H18N2 + H+: 311.1543; found 311.1546.
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 (v/v)) to give the desired pyrazoles 6.
1 (v/v)) to give the desired pyrazoles 6.
| Entry | Acid chloride 1d mg (mmol) | Alkyne 2 mg (mmol) | Methylhydrazine 3a mg (mmol) | Boronic acid 4 mg (mmol) | 3-Biarylsubstituted pyrazoles 6 mg (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a PdCl2(PPh3)2 (21.0 mg, 0.03 mmol), CuI (11.4 mg, 0.06 mmol), Et3N (159 mg, 1.57 mmol), Cs2CO3 (1.47 g, 4.50 mmol), PPh3 (79.1 mg, 0.30 mmol). b PdCl2(PPh3)2 (28.0 mg, 0.04 mmol), CuI (15.2 mg, 0.08 mmol), Et3N (212 mg, 2.10 mmol), Cs2CO3 (1.96 mg, 6.0 mmol), PPh3 (105 mg, 0.40 mmol). | |||||
| 1 | 226 (1.00) of 1d | 106.4 (1.00) of 2b | 51.3 (1.10) | 183 (1.50) of 4b | 207 (66) of 6a |
| 2a | 330 (1.50) of 1d | 179 (1.50) of 2c | 77.1 (1.70) | 325 (2.10) of 4c | 274 (51) of 6b |
| 3b | 444 (2.00) of 1d | 170 (2.00) of 2d | 104 (2.20) | 367 (3.00) of 4b | 356 (61) of 6c |
| 4b | 439 (2.00) of 1d | 205 (2.00) of 2b | 101 (2.20) | 407 (2.80) of 4e | 395 (59) of 6d |
![[small nu, Greek, tilde]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/i_char_e0e1.gif) [cm−1] 3030 (w), 2926 (w), 1598 (w), 1578 (w), 1481 (m), 1460 (m), 1352 (w), 1279 (w), 1188 (w), 1119 (w), 1007 (m), 957 (m), 918 (w), 847 (m), 791 (m), 768 (s), 760 (s), 694 (s). GC-MS (m/z (%)): 311 (25), 310 ([M+], 100), 265 (3), 179 (3), 178 (2), 155 (13), 152 (5), 130 (3), 118 (10), 103 (5), 91 (4), 77 (9). UV/Vis (CH2Cl2): λmax [nm] (ε [L cm−1 mol−1]) = 283.5 (35
[cm−1] 3030 (w), 2926 (w), 1598 (w), 1578 (w), 1481 (m), 1460 (m), 1352 (w), 1279 (w), 1188 (w), 1119 (w), 1007 (m), 957 (m), 918 (w), 847 (m), 791 (m), 768 (s), 760 (s), 694 (s). GC-MS (m/z (%)): 311 (25), 310 ([M+], 100), 265 (3), 179 (3), 178 (2), 155 (13), 152 (5), 130 (3), 118 (10), 103 (5), 91 (4), 77 (9). UV/Vis (CH2Cl2): λmax [nm] (ε [L cm−1 mol−1]) = 283.5 (35![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 600). Emission (CH2Cl2): λmax [nm] (Φf) = 344.5 (0.49). Stokes shift [cm−1] = 6300. Anal. calcd for C22H18N2 (310.4): C 85.13, H 5.85, N 9.03; found C 84.92, H 5.88, N 8.77%.
600). Emission (CH2Cl2): λmax [nm] (Φf) = 344.5 (0.49). Stokes shift [cm−1] = 6300. Anal. calcd for C22H18N2 (310.4): C 85.13, H 5.85, N 9.03; found C 84.92, H 5.88, N 8.77%.
![[small nu, Greek, tilde]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/i_char_e0e1.gif) [cm−1] 3049 (w), 2951 (w), 1609 (w), 1585 (w), 1481 (m), 1437 (m), 1350 (w), 1265 (w), 1223 (m), 1007 (w), 943 (w), 854 (m), 822 (s), 787 (s), 745 (m), 691 (m). GC-MS (m/z (%)): 357 (26), 356 (100), 226 (2), 207 (2), 183 (6), 178 (11), 177 (5), 170 (5), 169 (2), 146 (2), 132 (4), 118 (3), 115 (3), 91 (5), 77 (2). UV/Vis (CH2Cl2): λmax [nm] (ε [L cm−1 mol−1]) = 267.5 (35
[cm−1] 3049 (w), 2951 (w), 1609 (w), 1585 (w), 1481 (m), 1437 (m), 1350 (w), 1265 (w), 1223 (m), 1007 (w), 943 (w), 854 (m), 822 (s), 787 (s), 745 (m), 691 (m). GC-MS (m/z (%)): 357 (26), 356 (100), 226 (2), 207 (2), 183 (6), 178 (11), 177 (5), 170 (5), 169 (2), 146 (2), 132 (4), 118 (3), 115 (3), 91 (5), 77 (2). UV/Vis (CH2Cl2): λmax [nm] (ε [L cm−1 mol−1]) = 267.5 (35![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 800). Emission (CH2Cl2): λmax [nm] (Φf) = 338.5 (0.83). Stokes shift [cm−1] = 7800. HRMS calcd for C24H21FN2 + H+: 357.1762; found 357.1763.
800). Emission (CH2Cl2): λmax [nm] (Φf) = 338.5 (0.83). Stokes shift [cm−1] = 7800. HRMS calcd for C24H21FN2 + H+: 357.1762; found 357.1763.
![[small nu, Greek, tilde]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/i_char_e0e1.gif) [cm−1] 3053 (w), 2953 (w), 2928 (w), 2859 (w), 1597 (w), 1491 (m), 1466 (m), 1439 (m), 1368 (w), 1292 (w), 1119 (w), 1007 (m), 959 (m), 847 (m), 806 (m), 785 (m), 764 (s), 729 (s), 696 (s). GC-MS (m/z (%)): 291 (14), 290 (61), 249 (18), 248 (100), 247 (70), 232 (2), 206 (3), 203 (8), 202 (12), 179 (4), 178 (5), 165 (3), 153 (3), 152 (7), 125 (3), 124 (26), 115 (2), 77 (2), 69 (4), 54 (2). UV/Vis (CH2Cl2): λmax [nm] (ε [L cm−1 mol−1]) = 286.0 (33
[cm−1] 3053 (w), 2953 (w), 2928 (w), 2859 (w), 1597 (w), 1491 (m), 1466 (m), 1439 (m), 1368 (w), 1292 (w), 1119 (w), 1007 (m), 959 (m), 847 (m), 806 (m), 785 (m), 764 (s), 729 (s), 696 (s). GC-MS (m/z (%)): 291 (14), 290 (61), 249 (18), 248 (100), 247 (70), 232 (2), 206 (3), 203 (8), 202 (12), 179 (4), 178 (5), 165 (3), 153 (3), 152 (7), 125 (3), 124 (26), 115 (2), 77 (2), 69 (4), 54 (2). UV/Vis (CH2Cl2): λmax [nm] (ε [L cm−1 mol−1]) = 286.0 (33![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000). Emission (CH2Cl2): λmax [nm] (Φf) = 347.0 (0.27). Stokes shift [cm−1] = 6200. Anal. calcd for C20H22N2 (290.4): C 82.72, H 7.64, N 9.65; found C 82.50, H 7.51, N 9.73%.
000). Emission (CH2Cl2): λmax [nm] (Φf) = 347.0 (0.27). Stokes shift [cm−1] = 6200. Anal. calcd for C20H22N2 (290.4): C 82.72, H 7.64, N 9.65; found C 82.50, H 7.51, N 9.73%.
![[small nu, Greek, tilde]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/i_char_e0e1.gif) [cm−1] 3038 (w), 2999 (w), 2949 (w), 2222 (m), 1603 (m), 1483 (m), 1472 (m), 1458 (m), 1437 (m), 1354 (w), 1283 (w), 1186 (m), 1119 (w), 1003 (w), 959 (m), 910 (w), 826 (s), 791 (s), 762 (s), 746 (m), 689 (m), 673 (m). EI/MS (m/z (%)): 337 (3), 336 (25), 335 (100), 334 (7), 292 (3), 290 (2), 204 (2), 167 (7), 151 (2), 118 (3), 103 (3), 77 (2), 44 (2), 43 (3). UV/Vis (CH2Cl2): λmax [nm] (ε [L cm−1 mol−1]) = 306.5 (36
[cm−1] 3038 (w), 2999 (w), 2949 (w), 2222 (m), 1603 (m), 1483 (m), 1472 (m), 1458 (m), 1437 (m), 1354 (w), 1283 (w), 1186 (m), 1119 (w), 1003 (w), 959 (m), 910 (w), 826 (s), 791 (s), 762 (s), 746 (m), 689 (m), 673 (m). EI/MS (m/z (%)): 337 (3), 336 (25), 335 (100), 334 (7), 292 (3), 290 (2), 204 (2), 167 (7), 151 (2), 118 (3), 103 (3), 77 (2), 44 (2), 43 (3). UV/Vis (CH2Cl2): λmax [nm] (ε [L cm−1 mol−1]) = 306.5 (36![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 600). Emission (CH2Cl2): λmax [nm] (Φf) = 384.0 (0.10). Stokes shift [cm−1] = 6600. Anal. calcd for C23H17N3 (335.4): C 82.36, H 5.11, N 12.53; found C 82.18, H 4.81, N 12.40%.
600). Emission (CH2Cl2): λmax [nm] (Φf) = 384.0 (0.10). Stokes shift [cm−1] = 6600. Anal. calcd for C23H17N3 (335.4): C 82.36, H 5.11, N 12.53; found C 82.18, H 4.81, N 12.40%.
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1, v/v) to give 142 mg (37%) of pyrazole 7 as beige colored plates; Mp 200 °C. 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3) δ = 4.01 (s, 3H), 6.70 (s, 1H), 7.33–7.53 (m, 6H), 7.57 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H), 7.61–7.70 (m, 6H), 7.72 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H), 7.93 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H). 13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3) δ = 37.9 (CH3), 103.5 (CH), 126.1 (CH), 127.1 (CH), 127.3 (CH), 127.4 (CH), 127.5 (CH), 127.6 (CH), 127.88 (CH), 128.91 (CH), 129.1 (CH), 129.3 (CH), 129.6 (Cquat), 132.6 (Cquat), 140.4 (Cquat), 140.5 (Cquat), 141.0 (Cquat), 141.6 (Cquat), 145.0 (Cquat), 150.4 (Cquat). IR (ATR):
1, v/v) to give 142 mg (37%) of pyrazole 7 as beige colored plates; Mp 200 °C. 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3) δ = 4.01 (s, 3H), 6.70 (s, 1H), 7.33–7.53 (m, 6H), 7.57 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H), 7.61–7.70 (m, 6H), 7.72 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H), 7.93 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H). 13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3) δ = 37.9 (CH3), 103.5 (CH), 126.1 (CH), 127.1 (CH), 127.3 (CH), 127.4 (CH), 127.5 (CH), 127.6 (CH), 127.88 (CH), 128.91 (CH), 129.1 (CH), 129.3 (CH), 129.6 (Cquat), 132.6 (Cquat), 140.4 (Cquat), 140.5 (Cquat), 141.0 (Cquat), 141.6 (Cquat), 145.0 (Cquat), 150.4 (Cquat). IR (ATR): ![[small nu, Greek, tilde]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/i_char_e0e1.gif) [cm−1] 3028 (w), 2938 (w), 1477 (m), 1437 (m), 1277 (w), 1184 (w), 1119 (w), 1001 (m), 959 (m), 918 (w), 847 (s), 826 (m), 785 (m), 762 (s), 729 (m), 692 (s), 671 (m). GC-MS (m/z (%)): 388 (5), 387 (31), 386 (100), 343 (5), 281 (3), 207 (9), 206 (2), 194 (6), 193 (22), 180 (4), 179 (10), 165 (5), 153 (3), 152 (7), 133 (2), 77 (3), 73 (4). UV/Vis (CH2Cl2): λmax [nm] (ε [L cm−1 mol−1]) = 288.5 (62
[cm−1] 3028 (w), 2938 (w), 1477 (m), 1437 (m), 1277 (w), 1184 (w), 1119 (w), 1001 (m), 959 (m), 918 (w), 847 (s), 826 (m), 785 (m), 762 (s), 729 (m), 692 (s), 671 (m). GC-MS (m/z (%)): 388 (5), 387 (31), 386 (100), 343 (5), 281 (3), 207 (9), 206 (2), 194 (6), 193 (22), 180 (4), 179 (10), 165 (5), 153 (3), 152 (7), 133 (2), 77 (3), 73 (4). UV/Vis (CH2Cl2): λmax [nm] (ε [L cm−1 mol−1]) = 288.5 (62![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 500). Emission (CH2Cl2): λmax [nm] (Φf) = 367.0 (0.07). Stokes shift [cm−1] = 7400. HRMS calcd for C28H22N2+H+: 387.1856; found 387.1856.
500). Emission (CH2Cl2): λmax [nm] (Φf) = 367.0 (0.07). Stokes shift [cm−1] = 7400. HRMS calcd for C28H22N2+H+: 387.1856; found 387.1856.
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 (v/v)) to give the desired pyrazoles 8.
1 (v/v)) to give the desired pyrazoles 8.
| Entry | Acid chloride 1 mg (mmol) | Alkyne 2 mg (mmol) | Hydrazine 3c mg (mmol) | Boronic acid 4 mg (mmol) | 1-Biarylsubstituted pyrazoles 8 mg (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a PdCl2(PPh3)2 (14.0 mg, 0.02 mmol), CuI (7.62 mg, 0.04 mmol), Et3N (106 mg, 1.05 mmol), Cs2CO3 (978 mg, 3.00 mmol), PPh3 (52.3 mg, 0.2 mmol). b PdCl2(PPh3)2 (29.0 mg, 0.04 mmol), CuI (16.7 mg, 0.09 mmol), Et3N (223 mg, 2.20 mmol), Cs2CO3 (2.05 g, 6.30 mmol), PPh3 (110 mg, 0.42 mmol). | |||||
| 1a | 143 (1.00) of 1a | 109 (1.10) of 2b | 246 (1.10) of 3c | 183 (1.50) of 4b | 212 (57) of 8a |
| 2 | 281 (2.00) of 1a | 204 (2.00) of 2b | 492 (2.20) of 3c | 411 (3.00) of 4a | 456 (59) of 8b |
| 3 | 285 (2.00) of 1a | 208 (2.00) of 2b | 492 (2.20) of 3c | 439 (3.00) of 4e | 494 (62) of 8c |
| 4 | 283 (2.00) of 1a | 209 (2.00) of 2b | 493 (2.20) of 3c | 385 (3.00) of 4f | 431 (55) of 8d |
| 5b | 361 (2.10) of 1e | 211 (2.10) of 2b | 493 (2.20) of 3c | 417 (3.10) of 4a | 365 (44) of 8e |
| 6 | 345 (2.00) of 1f | 212 (2.10) of 2b | 493 (2.20) of 3c | 411 (3.00) of 4a | 159 (19) of 8f |
| 7 | 306 (2.00) of 1c | 209 (2.10) of 2b | 493 (2.20) of 3c | 409 (3.00) of 4a | 430 (55) of 8g |
| 8 | 286 (2.00) of 1a | 164 (2.00) of 2d | 493 (2.20) of 3c | 409 (3.00) of 4a | 440 (60) of 8h |
![[small nu, Greek, tilde]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/i_char_e0e1.gif) [cm−1] 3061 (w), 3032 (w), 1960 (w), 1896 (w), 1819 (w), 1605 (m), 1524 (m), 1487 (m), 1462 (m), 1435 (w), 1361 (m), 1217 (w), 1186 (w), 972 (m), 955 (m), 916 (m), 839 (m), 760 (s), 729 (m), 690 (s), 656 (m). GC-MS (m/z (%)): 373 (29), 372 (100), 344 (3), 295 (7), 268 (16), 267 (10), 254 (3), 241 (8), 166 (8), 152 (40), 151 (12), 139 (8), 115 (7), 103 (6), 102 (7), 90 (4), 89 (12), 77 (49), 51 (16). UV/Vis (CH2Cl2): λmax [nm] (ε [L cm−1 mol−1]) = 257.0 (36
[cm−1] 3061 (w), 3032 (w), 1960 (w), 1896 (w), 1819 (w), 1605 (m), 1524 (m), 1487 (m), 1462 (m), 1435 (w), 1361 (m), 1217 (w), 1186 (w), 972 (m), 955 (m), 916 (m), 839 (m), 760 (s), 729 (m), 690 (s), 656 (m). GC-MS (m/z (%)): 373 (29), 372 (100), 344 (3), 295 (7), 268 (16), 267 (10), 254 (3), 241 (8), 166 (8), 152 (40), 151 (12), 139 (8), 115 (7), 103 (6), 102 (7), 90 (4), 89 (12), 77 (49), 51 (16). UV/Vis (CH2Cl2): λmax [nm] (ε [L cm−1 mol−1]) = 257.0 (36![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 300), 293.0 sh (25
300), 293.0 sh (25![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000). Emission (CH2Cl2): λmax [nm] (Φf) = 385.0 (0.41). Stokes shift [cm−1] = 8200. Anal. calcd for C27H20N2 (372.5): C 87.07, H 5.41, N 7.52; found: C 86.85, H 5.17, N 7.54%.
000). Emission (CH2Cl2): λmax [nm] (Φf) = 385.0 (0.41). Stokes shift [cm−1] = 8200. Anal. calcd for C27H20N2 (372.5): C 87.07, H 5.41, N 7.52; found: C 86.85, H 5.17, N 7.54%.
![[small nu, Greek, tilde]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/i_char_e0e1.gif) [cm−1] 3026 (w), 2961 (w), 2916 (w), 1485 (m), 1460 (m), 1362 (m), 1267 (w), 1171 (w), 1005 (w), 972 (m), 955 (w), 916 (w), 849 (w), 808 (s), 760 (s), 733 (w), 692 (s). GC-MS (m/z (%)): 386 ([M+], 100), 282 (15), 165 ([C13H9+], 25), 91 ([C7H7+], 5), 77 ([C6H5+], 24), 65 ([C5H5+], 6), 51 ([C4H3+], 8). UV/Vis (CH2Cl2): λmax [nm] (ε [L cm−1 mol−1]) = 257.0 (32
[cm−1] 3026 (w), 2961 (w), 2916 (w), 1485 (m), 1460 (m), 1362 (m), 1267 (w), 1171 (w), 1005 (w), 972 (m), 955 (w), 916 (w), 849 (w), 808 (s), 760 (s), 733 (w), 692 (s). GC-MS (m/z (%)): 386 ([M+], 100), 282 (15), 165 ([C13H9+], 25), 91 ([C7H7+], 5), 77 ([C6H5+], 24), 65 ([C5H5+], 6), 51 ([C4H3+], 8). UV/Vis (CH2Cl2): λmax [nm] (ε [L cm−1 mol−1]) = 257.0 (32![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000), 296.0 sh (23
000), 296.0 sh (23![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000). Emission (CH2Cl2): λmax [nm] (Φf) = 388.0 (0.33). Stokes shift [cm−1] = 8000. Anal. calcd for C28H22N2 (386.5): C 87.01, H 5.74, N 7.25; found: C 86.83, H 5.91, N 7.51%.
000). Emission (CH2Cl2): λmax [nm] (Φf) = 388.0 (0.33). Stokes shift [cm−1] = 8000. Anal. calcd for C28H22N2 (386.5): C 87.01, H 5.74, N 7.25; found: C 86.83, H 5.91, N 7.51%.
![[small nu, Greek, tilde]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/i_char_e0e1.gif) [cm−1] 3044 (w), 2220 (w), 1605 (m), 1495 (s), 1481 (w), 1460 (m), 1435 (w), 1362 (m), 1287 (w), 1082 (w), 1065 (w), 1026 (w), 1005 (w), 970 (m), 955 (w), 918 (w), 820 (s), 766 (w), 735 (w), 692 (s), 667 (w). ESI (m/z (%)): 398 ([M+ + H], 1), 397 ([M+], 4), 309 (49), 308 (100), 232 (13), 105 (12), 77 ([C6H5+], 12), 51 ([C4H3+], 3). UV/Vis (CH2Cl2): λmax [nm] (ε [L cm−1 mol−1]) = 257.0 (27
[cm−1] 3044 (w), 2220 (w), 1605 (m), 1495 (s), 1481 (w), 1460 (m), 1435 (w), 1362 (m), 1287 (w), 1082 (w), 1065 (w), 1026 (w), 1005 (w), 970 (m), 955 (w), 918 (w), 820 (s), 766 (w), 735 (w), 692 (s), 667 (w). ESI (m/z (%)): 398 ([M+ + H], 1), 397 ([M+], 4), 309 (49), 308 (100), 232 (13), 105 (12), 77 ([C6H5+], 12), 51 ([C4H3+], 3). UV/Vis (CH2Cl2): λmax [nm] (ε [L cm−1 mol−1]) = 257.0 (27![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 400), 307.5 sh (18
400), 307.5 sh (18![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 900). Emission (CH2Cl2): λmax [nm] (Φf) = 387.0 (0.12). Stokes shift [cm−1] = 6700. Anal. calcd for C29H19N3 (397.5): C 84.61, H 4.82, N 10.57; found: C 84.53, H 4.61, N 10.28%.
900). Emission (CH2Cl2): λmax [nm] (Φf) = 387.0 (0.12). Stokes shift [cm−1] = 6700. Anal. calcd for C29H19N3 (397.5): C 84.61, H 4.82, N 10.57; found: C 84.53, H 4.61, N 10.28%.
![[small nu, Greek, tilde]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/i_char_e0e1.gif) [cm−1 ] 3065 (w), 2980 (w), 2914 (w), 1545 (w), 1512 (m), 1485 (m), 1460 (m), 1433 (w), 1362 (w), 1261 (w), 1215 (w), 1180 (w), 1163 (w), 1107 (w), 972 (m), 914 (w), 837 (s), 802 (s), 758 (s), 702 (m), 687 (s), 667 (w). GC-MS (m/z (%)): 392 ([M+], 1), 330 (20), 297 (22), 296 (100), 295 ([C21H15N2+], 53), 192 ([C14H14N2+], 8), 165 ([C13H9+], 11), 77 ([C6H5+], 10), 51 ([C4H3+], 4). UV/Vis (CH2Cl2): λmax [nm] (ε [L cm−1 mol−1]) = 268.5 (29
[cm−1 ] 3065 (w), 2980 (w), 2914 (w), 1545 (w), 1512 (m), 1485 (m), 1460 (m), 1433 (w), 1362 (w), 1261 (w), 1215 (w), 1180 (w), 1163 (w), 1107 (w), 972 (m), 914 (w), 837 (s), 802 (s), 758 (s), 702 (m), 687 (s), 667 (w). GC-MS (m/z (%)): 392 ([M+], 1), 330 (20), 297 (22), 296 (100), 295 ([C21H15N2+], 53), 192 ([C14H14N2+], 8), 165 ([C13H9+], 11), 77 ([C6H5+], 10), 51 ([C4H3+], 4). UV/Vis (CH2Cl2): λmax [nm] (ε [L cm−1 mol−1]) = 268.5 (29![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 500). Emission (CH2Cl2): λmax [nm] (Φf) = 385.0 (0.29). Stokes shift [cm−1] = 11
500). Emission (CH2Cl2): λmax [nm] (Φf) = 385.0 (0.29). Stokes shift [cm−1] = 11![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 300. Anal. calcd for C26H20N2S (392.5): C 79.56, H 5.14, N 7.14; found: C 79.39, H 4.89, N 7.18%.
300. Anal. calcd for C26H20N2S (392.5): C 79.56, H 5.14, N 7.14; found: C 79.39, H 4.89, N 7.18%.
![[small nu, Greek, tilde]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/i_char_e0e1.gif) [cm−1] 2997 (w), 2917 (w), 1609 (w), 1501 (m), 1485 (m), 1456 (w), 1433 (m), 1358 (w), 1246 (m), 1169 (w), 1111 (w), 1030 (m), 955 (w), 924 (w), 841 (m), 806 (s), 764 (s), 733 (w), 698 (m), 675 (m). ESI (m/z (%)): 416 ([M+], 5), 327 (5), 326 ([C22H18N2O+], 19), 239 (14), 238 (86), 237 (100), 223 (11), 195 (12), 165 ([C13H9+], 11), 135 (55), 107 ([C7H7O+], 11), 103 (13), 92 ([C7H8+], 12), 77 ([C6H5+], 27), 65 ([C5H5+], 3), 51 ([C4H3+], 6), 43 (48). UV/Vis (CH2Cl2): λmax [nm] (ε [L cm−1 mol−1]) = 261.5 (39
[cm−1] 2997 (w), 2917 (w), 1609 (w), 1501 (m), 1485 (m), 1456 (w), 1433 (m), 1358 (w), 1246 (m), 1169 (w), 1111 (w), 1030 (m), 955 (w), 924 (w), 841 (m), 806 (s), 764 (s), 733 (w), 698 (m), 675 (m). ESI (m/z (%)): 416 ([M+], 5), 327 (5), 326 ([C22H18N2O+], 19), 239 (14), 238 (86), 237 (100), 223 (11), 195 (12), 165 ([C13H9+], 11), 135 (55), 107 ([C7H7O+], 11), 103 (13), 92 ([C7H8+], 12), 77 ([C6H5+], 27), 65 ([C5H5+], 3), 51 ([C4H3+], 6), 43 (48). UV/Vis (CH2Cl2): λmax [nm] (ε [L cm−1 mol−1]) = 261.5 (39![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 900), 288.0 sh (29
900), 288.0 sh (29![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 600), 311.0 sh (20
600), 311.0 sh (20![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 500). Emission (CH2Cl2): λmax [nm] (Φf) = 386.5 (0.37). Stokes shift [cm−1] = 6300. Anal. calcd for C29H24N2O (416.5): C 83.63, H 5.82, N 6.73; found: C 83.43, H 5.89, N 6.66%.
500). Emission (CH2Cl2): λmax [nm] (Φf) = 386.5 (0.37). Stokes shift [cm−1] = 6300. Anal. calcd for C29H24N2O (416.5): C 83.63, H 5.82, N 6.73; found: C 83.43, H 5.89, N 6.66%.
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1. 13C NMR (151 MHz, CDCl3) δ = 21.2 (CH3), 107.0 (CH), 124.3 (CH), 126.0 (CH), 127.0 (CH), 127.3 (CH), 128.2 (CH), 128.8 (CH), 129.7 (CH), 130.2 (CH), 130.4 (CH), 130.55 (Cquat), 132.3 (CH), 133.1 (Cquat), 134.2 (Cquat), 137.3 (Cquat), 137.5 (Cquat), 139.2 (Cquat), 139.9 (Cquat), 141.1 (Cquat), 151.9 (Cquat); additional signal for the minor regioisomer: δ = 109.3 (CH). IR (ATR):
1. 13C NMR (151 MHz, CDCl3) δ = 21.2 (CH3), 107.0 (CH), 124.3 (CH), 126.0 (CH), 127.0 (CH), 127.3 (CH), 128.2 (CH), 128.8 (CH), 129.7 (CH), 130.2 (CH), 130.4 (CH), 130.55 (Cquat), 132.3 (CH), 133.1 (Cquat), 134.2 (Cquat), 137.3 (Cquat), 137.5 (Cquat), 139.2 (Cquat), 139.9 (Cquat), 141.1 (Cquat), 151.9 (Cquat); additional signal for the minor regioisomer: δ = 109.3 (CH). IR (ATR): ![[small nu, Greek, tilde]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/i_char_e0e1.gif) [cm−1] 3022 (w), 2918 (w), 1601 (w), 1503 (s), 1456 (m), 1362 (w), 1124 (w), 1113 (w), 955 (m), 918 (w), 849 (m), 812 (s), 800 (m), 764 (s), 725 (m), 683 (s). ESI (m/z (%)): 421 ([M+], 5), 420 (14), 333 (7), 332 (34), 331 (31), 330 (100), 329 (30), 296 (13), 295 (54), 267 (10), 192 ([C14H14N2+], 17), 165 ([C13H9+], 16), 147 ([C11H16+], 14), 146 (14), 91 ([C7H7+], 5), 77 ([C6H5+], 16), 51 ([C4H3+], 6). UV/Vis (CH2Cl2): λmax [nm] (ε [L cm−1 mol−1]) = 256.5 (27
[cm−1] 3022 (w), 2918 (w), 1601 (w), 1503 (s), 1456 (m), 1362 (w), 1124 (w), 1113 (w), 955 (m), 918 (w), 849 (m), 812 (s), 800 (m), 764 (s), 725 (m), 683 (s). ESI (m/z (%)): 421 ([M+], 5), 420 (14), 333 (7), 332 (34), 331 (31), 330 (100), 329 (30), 296 (13), 295 (54), 267 (10), 192 ([C14H14N2+], 17), 165 ([C13H9+], 16), 147 ([C11H16+], 14), 146 (14), 91 ([C7H7+], 5), 77 ([C6H5+], 16), 51 ([C4H3+], 6). UV/Vis (CH2Cl2): λmax [nm] (ε [L cm−1 mol−1]) = 256.5 (27![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 300), 296.0 (28
300), 296.0 (28![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 400). Emission (CH2Cl2): λmax [nm] (Φf) = 388.5 (0.35). Stokes shift [cm−1] = 8000. HRMS calcd for C28H21N2Cl + H+: 421.1472; found: 421.14564.
400). Emission (CH2Cl2): λmax [nm] (Φf) = 388.5 (0.35). Stokes shift [cm−1] = 8000. HRMS calcd for C28H21N2Cl + H+: 421.1472; found: 421.14564.
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1. 13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3) δ = 21.3 (CH), 105.2 (CH), 125.9 (CH), 126.4 (CH), 126.7 (CH), 127.07 (CH), 127.50 (CH), 127.54 (CH), 127.57 (CH), 128.2 (CH), 128.8 (CH), 129.7 (CH), 131.5 (Cquat), 132.9 (Cquat), 137.3 (Cquat), 137.7 (Cquat), 138.3 (Cquat), 138.9 (Cquat), 141.2 (Cquat), 152.1 (Cquat). IR (ATR):
1. 13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3) δ = 21.3 (CH), 105.2 (CH), 125.9 (CH), 126.4 (CH), 126.7 (CH), 127.07 (CH), 127.50 (CH), 127.54 (CH), 127.57 (CH), 128.2 (CH), 128.8 (CH), 129.7 (CH), 131.5 (Cquat), 132.9 (Cquat), 137.3 (Cquat), 137.7 (Cquat), 138.3 (Cquat), 138.9 (Cquat), 141.2 (Cquat), 152.1 (Cquat). IR (ATR): ![[small nu, Greek, tilde]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/i_char_e0e1.gif) [cm−1] 3080 (w), 2945 (w), 1915 (w), 1603 (w), 1499 (s); 1449 (m), 1362 (w), 1283 (w), 1229 (w), 1159 (m), 1115 (w), 1006 (m), 959 (m), 918 (w); 831 (m), 812 (s), 795 (m), 766 (s), 741 (w), 692 (s). GC-MS (m/z (%)): 392 ([M+], 11), 302 ([C19H14N2S+], 12), 215 (14), 214 (65), 213 ([C13H11NS+], 100), 185 (24), 111 ([C6H7S+], 30), 103 ([C8H7+], 13), 77 ([C6H5+], 14), 51 ([C4H3+], 6). UV/Vis (CH2Cl2): λmax [nm] (ε [L cm−1 mol−1]) = 272.5 (39
[cm−1] 3080 (w), 2945 (w), 1915 (w), 1603 (w), 1499 (s); 1449 (m), 1362 (w), 1283 (w), 1229 (w), 1159 (m), 1115 (w), 1006 (m), 959 (m), 918 (w); 831 (m), 812 (s), 795 (m), 766 (s), 741 (w), 692 (s). GC-MS (m/z (%)): 392 ([M+], 11), 302 ([C19H14N2S+], 12), 215 (14), 214 (65), 213 ([C13H11NS+], 100), 185 (24), 111 ([C6H7S+], 30), 103 ([C8H7+], 13), 77 ([C6H5+], 14), 51 ([C4H3+], 6). UV/Vis (CH2Cl2): λmax [nm] (ε [L cm−1 mol−1]) = 272.5 (39![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 600). Emission (CH2Cl2): λmax [nm] (Φf) = 394.0 (0.30). Stokes shift [cm−1] = 11
600). Emission (CH2Cl2): λmax [nm] (Φf) = 394.0 (0.30). Stokes shift [cm−1] = 11![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 300. Anal. calcd for C26H20N2S (392.5): C 79.56, H 5.14, N 7.14; found: C 79.41, H 5.35, N 6.91%.
300. Anal. calcd for C26H20N2S (392.5): C 79.56, H 5.14, N 7.14; found: C 79.41, H 5.35, N 6.91%.
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1. 13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3) δ = 14.1 (CH3), 21.2 (CH3), 22.8 (CH2), 28.2 (CH2), 32.0 (CH2), 107.0 (CH), 125.4 (CH), 127.0 (CH), 127.3 (CH), 128.2 (CH), 128.6 (CH), 128.8 (CH), 129.65 (CH), 131.1 (Cquat), 137.4 (Cquat), 139.3 (Cquat), 139.8 (Cquat), 143.5 (Cquat), 154.5 (Cquat); additional signals for the minor regioisomer: δ = 103.0 (CH), 127.1 (CH), 127.7 (CH), 128.7 (CH), 129.74 (CH). IR (ATR):
1. 13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3) δ = 14.1 (CH3), 21.2 (CH3), 22.8 (CH2), 28.2 (CH2), 32.0 (CH2), 107.0 (CH), 125.4 (CH), 127.0 (CH), 127.3 (CH), 128.2 (CH), 128.6 (CH), 128.8 (CH), 129.65 (CH), 131.1 (Cquat), 137.4 (Cquat), 139.3 (Cquat), 139.8 (Cquat), 143.5 (Cquat), 154.5 (Cquat); additional signals for the minor regioisomer: δ = 103.0 (CH), 127.1 (CH), 127.7 (CH), 128.7 (CH), 129.74 (CH). IR (ATR): ![[small nu, Greek, tilde]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/i_char_e0e1.gif) [cm−1] 3032 (w), 2955 (w), 2928 (w), 1605 (w), 1503 (s), 1456 (w), 1423 (w), 1369 (m), 1261 (w), 1192 (w), 1105 (w), 999 (w), 966 (m), 920 (w), 851 (m), 812 (s), 768 (s), 698 (s), 673 (w). GC-MS (m/z (%)): 366 ([M+], 19), 355 (24), 337 (12), 325 (26), 324 (100), 281 (19), 221 (24), 147 (21), 77 (3). UV/Vis (CH2Cl2): λmax [nm] (ε [L cm−1 mol−1]) = 286.0 (22
[cm−1] 3032 (w), 2955 (w), 2928 (w), 1605 (w), 1503 (s), 1456 (w), 1423 (w), 1369 (m), 1261 (w), 1192 (w), 1105 (w), 999 (w), 966 (m), 920 (w), 851 (m), 812 (s), 768 (s), 698 (s), 673 (w). GC-MS (m/z (%)): 366 ([M+], 19), 355 (24), 337 (12), 325 (26), 324 (100), 281 (19), 221 (24), 147 (21), 77 (3). UV/Vis (CH2Cl2): λmax [nm] (ε [L cm−1 mol−1]) = 286.0 (22![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 900). Emission (CH2Cl2): λmax [nm] (Φf) = 382.5 (0.33). Stokes shift [cm−1] = 8800. HRMS calcd for C26H26N2 + H+: 367.2174; found: 367.2175.
900). Emission (CH2Cl2): λmax [nm] (Φf) = 382.5 (0.33). Stokes shift [cm−1] = 8800. HRMS calcd for C26H26N2 + H+: 367.2174; found: 367.2175.
Acknowledgements
Dedicated to Prof. Dr Karl Kleinermanns on the occasion of his 65th birthday. The authors cordially thank the Fonds der Chemischen Industrie for financial support.Notes and references
- P. S. Parameswaran, C. G. Naik and V. R. Hegde, J. Nat. Prod., 1997, 60, 802 CrossRef CAS.
- K. Motoba, H. Nishizawa, T. Suzuki, H. Hamaguchi, M. Uchida and S. Funayama, Pestic. Biochem. Physiol., 2000, 67, 73 CrossRef CAS; M. Beckmann and K.-J. Haack, Chem. Unserer Zeit, 2003, 37, 88 CrossRef.
- R. E. Orth, J. Pharm. Sci., 1968, 57, 537 CrossRef CAS PubMed; A. Chauhan, P. K. Sharma and N. Kaushik, Int. J. ChemTech Res., 2011, 3, 11 Search PubMed; M. A. H. Ismail, J. Lehmann, D. A. Abou El Ella, A. Albohy and K. A. M. Abouzid, Med. Chem. Res., 2009, 18, 725 CrossRef; S. R. Stauffer, C. J. Coletta, R. Tedesco, G. Nishiguchi, K. Carlson, J. Sun, B. S. Katzenellenbogen and J. A. Katzenellenbogen, J. Med. Chem., 2000, 43, 4934 CrossRef PubMed.
- R. A. Singer, S. Caron, R. E. McDermott, R. Arpin and N. M. Do, Synthesis, 2003, 1727 CrossRef CAS; A. Mukherjee and A. Sarka, Tetrahedron Lett., 2004, 45, 9525 CrossRef.
- A. Dorlars, C.-W. Schellhammer and J. Schroeder, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 1975, 14, 665 CrossRef.
- J. Catalan, F. Fabero, R. M. Claramunt, M. D. Santa Maria, M. de la Concepcion Foces-Foces, F. Hernandez Cano, M. Martinez-Ripoll, J. Elguero and R. Sastre, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1992, 114, 5039 CrossRef CAS.
- Z. Yang, K. Zhang, F. Gong, S. Li, J. Chen, J. Shi Ma, L. N. Sobenina, A. I. Mikhaleva, B. A. Trofimov and G. Yang, J. Photochem. Photobiol., A, 2011, 217, 29 CrossRef CAS.
- For a recent monograph, see Organic Light-Emitting Diodes – Synthesis, Properties, and Applications, ed. K. Müllen and U. Scherf, Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim, 2006 Search PubMed.
- For diversity oriented syntheses of functional π-systems, see (a) T. J. J. Müller and D. M. D'Souza, Pure Appl. Chem., 2008, 80, 609 CrossRef; (b) T. J. J. Müller, in Functional Organic Materials. Syntheses, Strategies, and Applications, ed. T. J. J. Müller and U. H. F. Bunz, Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim, 2007, p. 179 Search PubMed; (c) For the concept of diversity oriented synthesis, see e. g. M. D. Burke and S. L. Schreiber, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2004, 43, 46 CrossRef PubMed.
- (a) B. Willy and T. J. J. Müller, Eur. J. Org. Chem., 2008, 4157 CrossRef CAS; (b) B. Willy and T. J. J. Müller, Org. Lett., 2011, 13, 2082 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) C. F. Gers, J. Rosellen, E. Merkul and T. J. J. Müller, Beilstein J. Org. Chem., 2011, 7, 1173 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (d) L. Levi, C. Boersch, C. F. Gers, E. Merkul and T. J. J. Müller, Molecules, 2011, 16, 9340 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- I. B. Berlham, J. Phys. Chem., 1970, 74, 3085 CrossRef.
- H. S. Im and E. R. Bernstein, J. Chem. Phys., 1988, 88, 7337 CrossRef CAS.
- S. A. McFarland and N. S. Finney, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2001, 123, 1260 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. M. D'Souza and T. J. J. Müller, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2007, 36, 1095 RSC; N. T. Patil, V. S. Shinde and B. Gajula, Org. Biomol. Chem., 2012, 10, 211 Search PubMed.
- T. J. J. Müller, Top. Organomet. Chem., 2006, 19, 149 CrossRef.
- E. Merkul, C. Boersch, W. Frank and T. J. J. Müller, Org. Lett., 2009, 11, 2269 CrossRef CAS PubMed; A. Zanardi, J. A. Mata and E. Peris, Organometallics, 2009, 28, 4335 CrossRef.
- J. A. Burkhard, B. Wagner, H. Fischer, F. Schuler, K. Müller and E. M. Carreira, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2010, 49, 3524 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- ESI.†.
- F. Vollmer, W. Rettig and E. Birckner, J. Fluoresc., 1994, 4, 65–69 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- E. Lippert, Z. Elektrochem. Ber. Bunsenges. Phys. Chem., 1957, 61, 692 Search PubMed; A. Dienes, C. V. Shank and A. M. Trozzolo, Dye Lasers, in Creation and Detection of the Excited State, ed. W. R. Ware, Dekker, New York, 1974, vol. 2, p. 149 Search PubMed.
- N. Boens, W. Qin, N. Basarić, J. Hofkens, M. Ameloot, J. Pouget, J.-P. Lefèvre, B. Valeur, E. Gratton, M. van de Ven, N. D. Silva Jr, Y. Engelborghs, K. Willaert, A. Sillen, G. Rumbles, D. Phillips, A. J. W. G. Visser, A. van Hoek, J. R. Lakowicz, H. Malak, I. Gryczynski, A. G. Szabo, D. T. Krajcarski, N. Tamai and A. Miura, Anal. Chem., 2007, 79, 2137 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- For determination of fluorescence quantum yields, see e. g. S. Fery-Forgues and D. Lavabre, J. Chem. Educ., 1999, 76, 1260 CrossRef CAS.
- F. Hirayama, W. Rothman and S. Lipsky, Chem. Phys. Lett., 1970, 5, 296 CrossRef CAS.
- M. J. Frisch, G. W. Trucks, H. B. Schlegel, G. E. Scuseria, M. A. Robb, J. R. Cheeseman, G. Scalmani, V. Barone, B. Mennucci, G. A. Petersson, H. Nakatsuji, M. Caricato, X. Li, H. P. Hratchian, A. F. Izmaylov, J. Bloino, G. Zheng, J. L. Sonnenberg, M. Hada, M. Ehara, K. Toyota, R. Fukuda, J. Hasegawa, M. Ishida, T. Nakajima, Y. Honda, O. Kitao, H. Nakai, T. Vreven, J. A. Montgomery Jr, J. E. Peralta, F. Ogliaro, M. Bearpark, J. J. Heyd, E. Brothers, K. N. Kudin, V. N. Staroverov, R. Kobayashi, J. Normand, K. Raghavachari, A. Rendell, J. C. Burant, S. S. Iyengar, J. Tomasi, M. Cossi, N. Rega, J. M. Millam, M. Klene, J. E. Knox, J. B. Cross, V. Bakken, C. Adamo, J. Jaramillo, R. Gomperts, R. E. Stratmann, O. Yazyev, A. J. Austin, R. Cammi, C. Pomelli, J. W. Ochterski, R. L. Martin, K. Morokuma, V. G. Zakrzewski, G. A. Voth, P. Salvador, J. J. Dannenberg, S. Dapprich, A. D. Daniels, O. Farkas, J. B. Foresman, J. V. Ortiz, J. Cioslowski and D. J. Fox, GAUSSIAN 09 (Revision A.02), Gaussian, Inc., Wallingford CT, 2009 Search PubMed.
- C. Lee, W. Yang and R. G. Parr, Phys. Rev. B: Condens. Matter Mater. Phys., 1988, 37, 785 CrossRef CAS; A. D. Becke, J. Chem. Phys., 1993, 98, 1372 CrossRef; A. D. Becke, J. Chem. Phys., 1993, 98, 5648 CrossRef; K. Kim and K. D. Jordan, J. Phys. Chem., 1994, 98, 10089 CrossRef; P. J. Stephens, F. J. Devlin, C. F. Chabalowski and M. J. Frisch, J. Phys. Chem., 1994, 98, 11623 CrossRef.
- R. Krishnan, J. S. Binkley, R. Seeger and J. A. Pople, J. Chem. Phys., 1980, 72, 650 CrossRef CAS.
- G. Scalmani and M. J. Frisch, J. Chem. Phys., 2010, 132, 114110 CrossRef PubMed.
- H.-S. Im and E. R. Bernstein, J. Chem. Phys., 1988, 88, 7337 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Yanai, D. Tew and N. Handy, Chem. Phys. Lett., 2004, 393, 51 CrossRef CAS.
- A. M. Berezhkovskii, Chem. Phys., 1992, 164, 331 CrossRef CAS; R. Cammi and J. Thomasi, Int. J. Quantum Chem., Quantum Chem. Symp., 1995, 29, 465 CrossRef; B. Mennucci, R. Cammi and J. Tomasi, J. Chem. Phys., 1998, 109, 2798 CrossRef; X.-Y. Li and K.-X. Fu, J. Comput. Chem., 2004, 25, 500 CrossRef PubMed; R. Cammi, S. Corni, B. Mennucci and J. Tomasi, J. Chem. Phys., 2005, 122, 104513 CrossRef PubMed.
- Density functional theory for excited states: equilibrium structure and electronic spectra. F. Furche and D. Rappoport, ch. III of “Computational Photochemistry”, M. Olivucci, ed., vol. 16 of “Computational and Theoretical Chemistry”, Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2005.
- TURBOMOLE V6.3 2013, a development of University of Karlsruhe and Forschungszentrum Karlsruhe GmbH, 1989–2007, TURBOMOLE GmbH, since 2007, available from http://www.turbomole.com.
- Electronic Structure Calculations on Workstation Computers: The Program System TURBOMOLE. R. Ahlrichs, M. Bär, M. Häser, H. Horn and C. Kölmel, Chem. Phys. Lett., 1989, 162, 165 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Schäfer, C. Huber and R. Ahlrichs, J. Chem. Phys., 1994, 100, 5829 CrossRef.
- A. Klamt and G. Schüürmann, J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. 2, 1993, 799 RSC.
- F. Furche and R. Ahlrichs, J. Chem. Phys., 2002, 117, 7433 CrossRef CAS.
Footnote |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available: Synthesis of reference compound 9, 1H and 13C NMR spectra, UV/Vis and fluorescence spectra of compounds 5, 6, 7, 8, and 9; computed xyz-coordinates of the S0 state of the pyrazoles 5c, 6d, and 8b, computed UV/Vis spectra of TD-DFT calculated structures of 5c, 6d, and 8b, computed xyz-coordinates of the S1 state of pyrazole 6d. CCDC 1049137. For ESI and crystallographic data in CIF or other electronic format see DOI: 10.1039/c5ra03104d |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 |