Structural insights into flavones as protein kinase CK2 inhibitors derived from a combined computational study†
Min Lv,
Shuying Ma,
Yueli Tian,
Xiaoyun Zhang*,
Honglin Zhai and
Wenjuan Lv
College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou, 730000, Gansu Province, People's Republic of China. E-mail: xyzhang@lzu.edu.cn; Fax: +86 931 891 2582; Tel: +86 931 8912578
First published on 13th November 2014
Abstract
Flavones, which belong to the large group of flavonoids, have attracted considerable attention in relation to their therapeutic potential. Recently, this series of compounds has been shown to inhibit CK2 with outstanding efficiency and safety. However, to date, the exact binding modes between CK2 and flavones, as well as the basis of their effects on the biological activities remain unclear. In this study, we report the detailed account of the interactions between CK2 and flavones at the atomic level through computational approaches. Starting from four different molecular docking protocols, we obtained the relatively reliable initial complex structures by comparing docking scores. With subsequent molecular dynamic simulations and binding free energy calculations and decompositions, we found that the predicted binding free energies correlated well with pIC50 (R = 0.86), shedding light on the necessity of MD studies. Moreover, the results clearly confirmed that hydrophobic residues such as Val39, Val47, Ile60, Phe107, Asn112, Met157 and Ile168 were responsible for flavones binding and identified the key structural elements necessary for their bioactivities. Based on the structural and energetic features of receptor–ligand interaction mechanism, we designed a series of novel compounds and their higher inhibitory activities were confirmed by a comprehensive modeling study. We expect that these findings could serve as a paradigm for facilitating the process of developing novel and more promising inhibitors targeting CK2.
1 Introduction
Flavonoids are ubiquitous in nature, extensively distributed as prominent plant secondary metabolites.1,2 As a subgroup of flavonoids, flavones have elicited interesting attention because they are considered relatively non-toxic and play a wide range of various biological effects. Flavones have shown to have beneficial effects on human health, including anxiolytic,3 antioxidant,4 antiinflammatory,5 antiallergic,6 neuroprotective,7 antiviral,8 antibacterial,9 antimutagenic10 and antiproliferative11 activities in lung, prostate, colorectal, pancreas, and ovarian cancer cells. All the properties of flavones can be attributed to their abilities to inhibit numerous groups of protein kinases, such as inducible nitric oxide synthase,5 cyclooxygenase-2,5 reactive C-protein,5 and tankyrase.12Recently, flavones were discovered to act as bioactive inhibitors of protein kinase CK2 (casein kinase II).13 CK2 is a heterotetrameric α2β2 Ser/Thr protein kinase that is involved in cancer, signal transduction, transcriptional control, apoptosis and cell cycle. The catalytic α-subunit of the kinase has been shown to serve as an oncogene product, thus making CK2 abnormally elevated in a large variety of solid tumors. In case of tumorogenesis, CK2 enhances the cancer phenotype by blocking apoptosis and stimulation of cell growth.14 In the light of these observations, CK2 represents an important pharmacological target and the development of specific inhibitors of CK2 may have therapeutical potential. Therefore, the identification and design of more promising CK2 inhibitors is indispensable.
Rapid emergence of new and exciting available strategies promoted the development of novel anti-CK2 anticancer agents. Diverse in vitro and in vivo experiments presented different classes of CK2 inhibitors with a broad biological activity, e.g. bromobenzimidazoles,15 ellagic acid,16 and 3-carboxy-4(1H)-quinolones.17 Moreover, a series of computational research efforts have also concentrated on streamline CK2 inhibitors discovery, design, development and optimization.18–22 To date, due to limited selectivity, potency or potential toxicity only one highly selective and potent CK2 inhibitor CX-4945 has been used in clinical trials.23 The recent experimental results indicated that flavones could offer low-toxic scaffolds to inhibit CK2.13 However, the molecular level understanding of the detailed interaction mechanism between the flavones and CK2 still remains unlimited.
Herein, several computational approaches were carried out to study the structural and energetic features of CK2–flavone interactions. First, four different molecular docking simulations were performed to predict the binding of CK2 with different flavone inhibitors. Then, the accurate but more expensive molecular dynamic (MD) simulation techniques were used to predict more reliable protein–ligand complex structures. Subsequently, binding free energy calculations and energy decomposition analysis were conducted using the molecular mechanics/generalized born surface area (MM/GBSA) method.24 Finally, based on the information derived from the integrated computational approach, a few potential inhibitors were designed and validated by molecular dynamic simulations along with binding free energy analysis.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Biological data set
Generally, the biological activity of a compound against a receptor is largely determined by the binding, which rests upon the geometric and energetic behavior.25 The structures of the ligands and their respective experimental IC50 values against CK2 were retrieved from the literature.13 Here, half maximal inhibitory concentration, represented as IC50, was measured as a function of the ability of compounds to inhibit recombinant human CK2 holoenzyme (New England Biolabs). For further investigation, IC50 values were converted into pIC50 values representing the logarithmic values. The structures of these inhibitors and the corresponding biological activities (pIC50) are summarized in Table S1 in the ESI.†2.2 Protein preparation
The crystal structure of CK2 in complex with inhibitor luteolin was obtained from the Protein Data Bank (PDB ID: 4DGN) and further used as the initial structure for molecular docking.26 Then, the structure was prepared by the protein preparation wizard available in Schrödinger 9.0.27 All crystallographic water molecules were removed from the complex. Missing residues were added and refined. All hydrogen atoms were added, which were subsequently minimized with optimized potentials for liquid simulations (OPLS) 2005 force field28 and the impact molecular mechanics engine. Minimization was performed to relieve steric clashes until the average root mean square deviation (RMSD) of the nonhydrogen atoms reached a maximum cutoff of 0.3 Å.2.3 Ligand preparation
The 3D conformations of the inhibitors were sketched with Maestro and further processed with LigPrep in Schrödinger 9.0,27,29 which could generate a number of structures from each input structure with various ionization states, tautomers, stereochemistry, and ring conformations, and eliminate molecules using various criteria, including molecular weight or specified number and types of functional groups present.2.4 Molecular docking
Schrödinger 9.0 was used as a molecular docking tool in order to carry out the docking simulations.27,30 The binding box was centered at the mass center of the co-crystal ligand to confine the mass center of each docked ligand. All the ligands were docked into the binding site of CK2 using four different docking methods, RRD with XP and SP scoring mode, IFD with XP scoring mode, and QPLD with XP scoring mode.First, the RRD protocol without considering the flexibility of CK2 was used to obtain the initial structures of the complexes, including the XP scoring mode and SP scoring mode. To soften the potential for non-polar parts of the ligand, the scaling factor was set as 0.8 with a partial atomic charge of 0.15. No constraints were applied for all the docking studies.
Second, in order to consider the flexibility of the protein, flexible docking was carried out by the IFD protocol in Schrödinger. The standard module of docking (Glide SP) was used in the initial phase of docking, and the final stage of docking was run using the extra precision mode. All the docking studies were run with the default parameters.
Third, the quantum mechanics/molecular mechanics (QM/MM) docking considering the polarization in the binding process was employed by the QPLD protocol in Schrödinger.27 The docking was started by Glide SP followed by XP refinement. Subsequently, the best binding poses for each ligand were used to calculate the polarizable ligand charges with QSite at the B3LYP/6-31G* level. Then, these poses with new QM-ESP charges were re-docked by Glide with the XP scoring mode.
2.5 Molecular dynamic simulations
All the studied inhibitors were classified in six groups according to the difference in bioactivities. In each group, four or five molecules were randomly chosen. In total, 18 molecules were extracted as representatives to subject to molecular dynamic simulations.Single point calculations of the corresponding inhibitors were carried out at the HF/6-31G* level using the Gaussian 09 program.31 Antechamber module was used to generate atomic partial charges of the inhibitors using restrained electrostatic potential (RESP) procedure.32 The general AMBER force field (GAFF)33 was used as the parameter for the inhibitors, and the ff99Bildn force field was used for the protein.34 The missing hydrogen atoms and counter ions for neutralization were added using the leap module in AMBER11.35 Each complex was immersed in a rectangular box of TIP3P water molecules with a margin of 12 Å.36 Initial minimization was performed for 1000 steps for the steepest descent minimization followed by 3000 steps of conjugate gradient minimization holding protein and inhibitor atoms constrained to their original positions by a force constraint to 10 kcal (mol−1 Å−1). Subsequently, all the systems were heated in the NVT ensemble from 0 to 298.15 K for 50 ps. Then, five MD equilibrations of 50 ps each with a decreased restraint weight from 10.0, to 5.0, to 2.0, to 1.0, to 0.5, to 0.1 were carried out. These were followed by the last MD equilibration step of 150 ps without any restraint on each system. The Unrestrained production MD runs were performed for 10 ns in the NPT ensemble at a temperature of 298.15 K and a pressure of 1 atm using the PMEMD program supporting CUDA in AMBER 11.35 During the simulations, periodic boundary conditions were employed and all electrostatic interactions were calculated using the particle-mesh Ewald (PME) method with a dielectric constant of unity.37,38 A 10.0 Å cutoff was used to calculate the direct space sum of PME. The SHAKE algorithm was used to restrain bond lengths involving hydrogen atoms.39
2.6 Binding free energy calculations (MM/GBSA)
The binding free energies for all the studied systems were calculated by the MM/GBSA approach implemented in AMBER11.35 A total number of 400 snapshots were extracted every 10 ps from the last 4 ns for each MD trajectory. For each snapshot, a free energy was calculated for each molecular species (complex, receptor, and ligand), and the binding free energy was calculated by the following equation:24,40–43| ΔGbind = Gcomplex − Gprotein − Gligand = ΔH + ΔGsolvation − TΔS = ΔEMM + ΔGGB + ΔGSA − TΔS |
2.7 Binding free energy decomposition
Binding free energy decomposition was performed based on MM/GBSA to further analyze the interactions between the inhibitors and the surrounding residues. The residue–inhibitor binding interaction consists of four components, including the van der Waals contribution (ΔEvdw), the electrostatic contribution (ΔEele), the polar part of desolvation (ΔGGB) and the non-polar part of desolvation (ΔGSA).41,44| ΔG = ΔEvdw + ΔEele + ΔGsol = ΔEvdw + ΔEele + ΔGGB + ΔGSA |
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Molecular docking
The most significant methods for evaluating the accuracy of molecular docking are to determine the discrepancy between the real and the best-scored conformance and to calculate the correlation coefficient between the docking scores and the experimental pIC50. Here, all the docking protocols were validated by removing the compound luteolin from the binding site and re-docking it into the binding site of CK2. On the basis of the above two methods, we can conclude that RRD with XP docking method represents the best protocol in the present study (Fig. S2 and S3†).
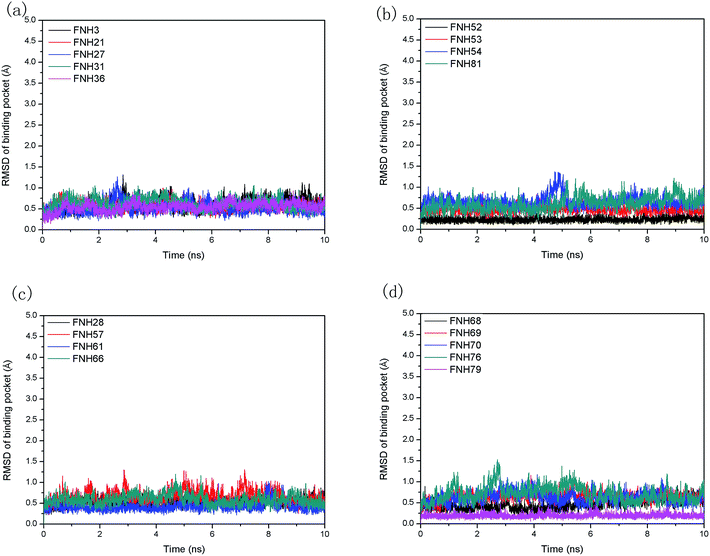
3.2 MD simulations
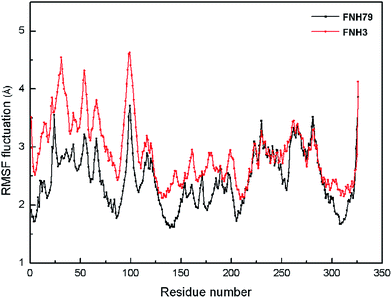
Moreover, the root-mean-square fluctuation (RMSF) was monitored along the molecular simulation process to explore the flexibility of individual residues. The most active inhibitor (FNH79) and the most inactive one (FNH3) were selected as representatives. As shown in Fig. 5, the two complexes share similar RMSF distributions and similar trends of dynamic features. We can observe that the regions around the residues Thr24, Gln98 and Asn326 exhibit considerably larger dynamic fluctuations as they locate in the non-active site regions or around the N- and C-terminals. In addition, the regions of relatively small fluctuations (Val110, Met157 and Ile168) can be assigned to binding pockets. Furthermore, the binding pocket of CK2–FNH79 exhibits less fluctuation than that of CK2–FNH3, which indicates that FNH79 may form stronger interactions with CK2 compared to FNH3. This phenomenon is in accordance with experimental bioactivities.
 | ||
| Fig. 6 The correlation between experimental activities and (a) the docking scores predicted by RRD with XP mode; (b) the binding free energies predicted by MM/GBSA. | ||
| No. | ΔEvdw | ΔEele | ΔGSA | ΔGGB | ΔGpred | pIC50 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a Denotes the predicted activities pIC50. | ||||||
| FNH3 | −35.91 ± 3.40 | −0.04 ± 6.68 | −4.59 ± 0.37 | 9.71 ± 5.72 | −30.84 ± 4.56 | 4.52 |
| FNH21 | −35.35 ± 2.94 | −5.30 ± 4.60 | −4.27 ± 0.25 | 12.18 ± 2.77 | −32.75 ± 2.92 | 4.55 |
| FNH27 | −35.47 ± 2.30 | 6.36 ± 1.62 | −4.20 ± 0.18 | 2.77 ± 1.69 | −30.54 ± 2.66 | 4.68 |
| FNH28 | −40.85 ± 2.65 | −29.22 ± 5.35 | −5.34 ± 0.12 | 34.19 ± 3.66 | −41.22 ± 3.24 | 7.00 |
| FNH31 | −40.39 ± 3.30 | −0.85 ± 8.23 | −5.04 ± 0.27 | 13.46 ± 5.65 | −32.82 ± 3.49 | 4.59 |
| FNH36 | −31.89 ± 2.41 | −9.31 ± 3.48 | −4.33 ± 0.16 | 14.54 ± 2.36 | −30.99 ± 2.47 | 4.72 |
| FNH52 | −37.95 ± 2.33 | 2.28 ± 2.39 | −4.71 ± 0.15 | 5.47 ± 1.83 | −34.91 ± 3.13 | 5.66 |
| FNH53 | −37.10 ± 2.49 | −10.45 ± 3.51 | −4.86 ± 0.11 | 13.94 ± 1.90 | −38.47 ± 2.62 | 5.80 |
| FNH54 | −33.25 ± 2.55 | −8.97 ± 4.13 | −4.52 ± 0.20 | 12.16 ± 2.72 | −34.58 ± 3.35 | 5.10 |
| FNH57 | −39.73 ± 2.24 | −1.85 ± 5.11 | −5.02 ± 0.15 | 10.14 ± 3.58 | −36.46 ± 2.57 | 6.49 |
| FNH61 | −44.89 ± 2.88 | −16.04 ± 5.75 | −5.70 ± 0.19 | 27.17 ± 4.83 | −39.45 ± 3.32 | 6.82 |
| FNH66 | −38.34 ± 2.64 | −25.75 ± 3.48 | −5.18 ± 0.14 | 29.95 ± 2.63 | −39.32 ± 2.63 | 6.10 |
| FNH68 | −42.54 ± 2.91 | −17.33 ± 9.93 | −5.34 ± 0.16 | 22.73 ± 7.06 | −42.48 ± 3.87 | 8.00 |
| FNH69 | −43.55 ± 2.81 | −22.53 ± 3.99 | −5.41 ± 0.13 | 30.37 ± 2.86 | −41.12 ± 2.74 | 7.70 |
| FNH70 | −38.24 ± 3.49 | −19.55 ± 3.60 | −4.85 ± 0.24 | 24.85 ± 3.20 | −37.79 ± 3.41 | 7.92 |
| FNH76 | −42.38 ± 2.36 | 1.57 ± 5.85 | −5.16 ± 0.19 | 9.12 ± 4.36 | −36.86 ± 3.33 | 7.40 |
| FNH79 | −43.93 ± 2.55 | −4.55 ± 4.77 | −5.17 ± 0.15 | 12.03 ± 3.17 | −41.62 ± 2.96 | 8.40 |
| FNH81 | −43.14 ± 2.71 | −3.35 ± 8.86 | −5.14 ± 0.20 | 13.05 ± 5.75 | −38.57 ± 4.73 | 5.70 |
| N1 | −46.48 ± 3.06 | −24.79 ± 7.39 | −5.90 ± 0.15 | 31.30 ± 6.63 | −45.87 ± 3.53 | 9.79a |
| N2 | −43.82 ± 2.64 | −13.67 ± 4.92 | −5.43 ± 0.15 | 19.03 ± 3.10 | −43.90 ± 4.30 | 9.01a |
| N3 | −50.02 ± 2.98 | −10.20 ± 4.78 | −5.99 ± 0.25 | 20.89 ± 3.30 | −45.31 ± 3.21 | 9.57a |
 | ||
| Fig. 7 Ligand–residue interaction spectra for CK2 complexes. (a) CK2–FNH21 complex; (b) CK2–FNH28 complex; (c) CK2–FNH27 complex; (d) CK2–FNH79 complex; (e) CK2–FNH76 complex; (f) CK2–FNH68 complex. | ||
To elucidate the interaction mechanism between the inhibitors and the protein, the percentage of time important hydrogen bonds existed were calculated on the basis of the data from the last 4 ns of the equilibration stage in the MD simulation. Formation of a hydrogen bond was defined by a distance between the donor and acceptor of less than 3.5 Å and a donor-hydrogen⋯acceptor angle larger than 120°.46 Here, the hydrogen bonds between the donor and acceptor for each system are listed in Table 2. Additionally, the time evolution of the population of hydrogen bonds between CK2 and four related ligands is shown in Fig. 11. It is apparent that FNH28 can form two hydrogen bonds with the highest occurrence frequency. This is the reason why the electrostatic interaction between FNH28 and CK2 is the strongest one among all the studied systems. The number of hydrogen bonds in complex CK2–FNH21 is equal to CK2–FNH79, which was in accord with the comparison analysis of electrostatic terms (Fig. 11 and Table 1). Compared with FNH21 and FNH79, FNH68 can form more potential hydrogen bonds with CK2, thus leading to the relatively stronger electrostatic interaction. Furthermore, the distance of the hydrogen bond between the ligands and CK2 was also monitored along the simulations, as shown in Fig. 12. For CK2–FNH28, small fluctuations occurred in the length of the hydrogen bonds after 6 ns. This is another reason why the electrostatic term serves as an essential factor for FNH28 binding. Corresponding with the RMSD fluctuations, the analysis of the hydrogen bonds confirms the stabilities of the four systems. Then, we performed structural binding mode analysis in addition to detailed energetic analysis to compare the two inhibitors in each inhibitor pair.
| Complex | Donor | Acceptor | Distance (Å) | Angle (°) | Occupancy (percent) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK2–FNH21 | FNH21(O19–H31) | Val110(O) | 2.701 | 156.96 | 87.55 |
| Asn112(N–H) | FNH21(O19) | 3.280 | 147.82 | 45.55 | |
| Val110(N–H) | FNH21(O17) | 3.233 | 154.15 | 39.05 | |
| CK2–FNH28 | Lys62(NZ–HZ2) | FNH28(O21) | 3.030 | 158.57 | 32.05 |
| Lys62(NZ–HZ1) | FNH28(O21) | 3.018 | 160.21 | 30.25 | |
| Lys62(NZ–HZ3) | FNH28(O21) | 3.030 | 158.28 | 20.45 | |
| Lys62(NZ–HZ1) | FNH28(O17) | 2.926 | 157.75 | 30.35 | |
| Lys62(NZ–HZ2) | FNH28(O17) | 2.912 | 160.07 | 29.70 | |
| Lys62(NZ–HZ3) | FNH28(O17) | 2.943 | 158.70 | 20.20 | |
| CK2–FNH68 | Lys62(NZ–HZ1) | FNH68(O18) | 3.076 | 158.44 | 11.75 |
| Lys62(NZ–HZ2) | FNH68(O18) | 3.030 | 158.68 | 20.10 | |
| Lys62(NZ–HZ3) | FNH68(O18) | 3.052 | 158.52 | 12.35 | |
| Lys62(NZ–HZ1) | FNH68(O21) | 3.118 | 155.75 | 19.10 | |
| Lys62(NZ–HZ2) | FNH68(O21) | 3.102 | 156.69 | 28.00 | |
| Lys62(NZ–HZ3) | FNH68(O21) | 3.118 | 155.58 | 20.05 | |
| Trp170(N–H) | FNH68(O18) | 3.120 | 143.28 | 70.60 | |
| FNH68(O18–H29) | Glu75(OE2) | 2.592 | 140.99 | 91.85 | |
| FNH68(O18–H29) | Glu75(OE1) | 3.256 | 175.08 | 6.00 | |
| CK2–FNH79 | FNH79(O18–H29) | Asp169(OD2) | 2.764 | 147.32 | 52.60 |
| Val110(N–H) | FNH79(O17) | 3.057 | 151.07 | 82.30 | |
| Asp169(N–H) | FNH79(O18) | 3.356 | 168.59 | 14.95 |
 | ||
| Fig. 11 Numbers of hydrogen bonds vs. simulation time (ns) for (a) CK2–FNH28 (b) CK2–FNH68, CK2–FNH79 and CK2–FNH21. | ||
The first comparison is between inhibitors FNH27 and FNH79. These two inhibitors have four structural differences. Inhibitor FNH79 contains a hydroxyl group at the R4′ position, instead of a methyl group at the R4′ position, as in inhibitor FNH27. The methyl moiety at the R6 position and R8 position in FNH27 are replaced by a bromine group in FNH79, respectively. The additional difference at the R3′ position is that a methoxy group replaces the hydrogen in inhibitor FNH79, whereas for inhibitor FNH27 it does not. These changes cause an increase in bioactivity from 21 μM (inhibitor FNH27) to 0.004 μM (inhibitor FNH79). According to Table 1, the difference in the calculated binding free energies between FNH27 and FNH79 is −11.08 kcal mol−1, which is contributed by both the difference of the non-polar contribution (−9.43 kcal mol−1) and that of the polar contribution (−1.65 kcal mol−1). Notably, the non-polar contribution plays a prominent role in distinguishing the bioactivities of the two inhibitors. As shown in Fig. 8b, Tyr109, Val110 and Asp169 are the key residues responsible for the energy difference between inhibitor FNH27 and FNH79. While inhibitor FNH27 forms no hydrogen bond with the protein, inhibitor FNH79 participates in forming two stable hydrogen bonds with Val110 (82.30 percent occupancy) and Asp169 (52.60 percent occupancy), accompanied by another occasionally formed hydrogen bond with Asp169 (14.95 percent occupancy). This explains why inhibitor FNH79 forms stronger polar interaction with Val110 and Asp169 compared to inhibitor FNH27 (Fig. 8c). Therefore, it is possible that a hydroxyl at the R4′ position can enhance the ligand–protein interactions. In addition, Tyr109 is a hydrophobic residue, which can form more van der Waals contacts with the bromine at the R6 position in inhibitor FNH79. This phenomenon is in agreement with the energy contribution of the residue to the total binding free energy (Fig. 8b and c). The result also suggests that the addition of hydrophobic groups to the R6 position of the phenyl ring can lead to improved binding affinity.
The second comparison is between inhibitors FNH68 and FNH76. The obvious difference is at the R8 position, at which the methyl moiety in inhibitor FNH68 is replaced by a chlorine group in inhibitor FNH76. Compared with inhibitor FNH76, inhibitor FNH68 shows better inhibitory activity. By inspection of Table 1, we can easily find that the difference in the binding free energy between the two inhibitors is 5.62 kcal mol−1. The non-polar contribution between inhibitor FNH68 and CK2 (−47.88 kcal mol−1) is slightly favorable than that between inhibitor FNH76 and CK2 (−47.54 kcal mol−1). Notably, the major difference in the binding free energies between the inhibitors FNH68 and FNH76 is the polar interaction (−5.29 kcal mol−1), primarily through the electrostatic energy term. The calculated electrostatic contributions to the binding free energies for the two systems are markedly different, with the value of −17.33 kcal mol−1 (inhibitor FNH68) and 1.57 kcal mol−1 (inhibitor FNH76). Compared with inhibitor FNH76, as can be seen in Fig. 9b, the contributions of Glu75 and Trp170 are prominently promoted in inhibitor FNH68, which can be attributed to the hydrogen bonds between the hydroxyl at the R4′ position. Table 2 shows that a stable hydrogen bond is formed between the hydroxyl group of inhibitor FNH68 and the oxygen atom of Glu75 with a high occupancy of 91.85 percent. Moreover, there also exists a hydrogen bond between the hydroxyl group of inhibitor FNH68 and the amino group of Trp170 with an occupation time of 70.60 percent. However, the inhibitor FNH68 forms no hydrogen bonds with Glu75 and Trp170. Due to the strong hydrogen bonding of Glu75 and Trp170, inhibitor FNH68 can move to the deeper site, allowing the benzene ring of the inhibitor to be come closer to the benzene ring of Phe107 (Fig. 9a). During this, the conjugation effect between the benzene ring of inhibitor FNH68 and the benzene ring of Phe107 is reinforced, thus leading to a significant increase in the non-polar contribution of the residue to the binding free energy. The above discussion concludes that the chlorine group at the R8 position is more favorable than a methyl group at the same position.
The third comparison is between inhibitor FNH28 and FNH21. These two inhibitors have several structural differences. Inhibitor FNH21 has two hydroxyl groups: one group is at the R3 position and the other group is at the R2′ position. There is only one hydroxyl group at the R4′ position in inhibitor FNH28. The hydrogen atom at the R3′ position in inhibitor FNH21 is replaced by a methoxy group in inhibitor FNH28, and the hydrogen atom at the R5′ position in inhibitor FNH28 is substituted by a bromine moiety in inhibitor FNH21. The last difference is at the R8 position, at which the hydrogen atom in inhibitor FNH21 is substituted by the methyl group in inhibitor FNH28. As shown in Table 1, the predicted binding free energy for inhibitor FNH21 is weaker than that for inhibitor FNH28 by 8.47 kcal mol−1. In Fig. 10a, the ligand FNH28 is anchored at the top of the binding pocket, whereas the ligand FNH21 rotated nearly 180° and is located at the bottom of the binding pocket. The hydrogen bonding between inhibitor FNH28 and CK2 warrants the orientation of the hydroxyl group and the dynamic stability, thus playing a significant role in anchoring the ligand into the binding pocket. The hydroxyl moiety at the R3 position in inhibitor FNH21 is stabilized via two hydrogen bonds with residues Val110 and Asn112, leading to the location of the inhibitor at the bottom of the pocket. Consequently, ligand FNH28 forms stronger van der Waals interactions with residue Val47, Phe107 and Ile168 compared to ligand FNH21, which is consistent with the binding energy decomposition analysis (Fig. 10b and c). The location of inhibitor FNH21 results in the situation that the ligand is closer to the residues including Asn112, Val110 and Val39. It is interesting to find that these residues are hydrophobic and can form stronger van der Waals forces with inhibitor FNH21 rather than with FNH28. In conclusion, the conformation differences and the non-polar interaction with different amino acid residues may be the two crucial factors that produce different bioactivities of the two ligands.
3.3 Insight for the future design of more potent inhibitors
The molecular modeling studies discussed above shed light on some important and favorable patterns between CK2 and flavone inhibitors: (1) the hydrogen bonding interactions between R3′ and some residues (Asp169 and Lys62); (2) the hydrogen bonding interactions between R4′ and some key residues (Glu75 and Lys62); (3) the van der Waals interactions between R6 and Tyr109; (4) the van der Waals interactions between R8 and Phe107. In order to design more promising inhibitors of CK2, it is necessary to consider these favorable protein–ligand interaction patterns. Additionally, some other residues, including Val39, Val47, Ile60, Asn112, Met157 and Ile168, mentioned in the above section also play an important role for inhibitor binding.The hydroxyl group at the R4′ position is crucial for ligand binding as it can form stable hydrogen bonding interactions with CK2. It is interesting to find that replacing the hydroxyl group with other hydrophilic groups, including methoxyl and ethoxyl, leads to a dramatic loss of bioactivity.13 Thus, retaining the hydroxyl group at the R4′ position may be a good choice. Furthermore, the addition of hydrophobic groups to the R6 and R8 positions is favorable to significantly increase the binding and inhibitory efficiency.
On the basis of the above conclusions from the energetic analysis and structural analysis, several potent inhibitors were obtained by optimizing the scaffold of flavone (Table 3). Structural optimization of FNH79 leads to the generation of N1, which exhibits a 25-fold better inhibitory potency. The inhibitory activity of N2 is four times higher than that of FNH79. N3 shows a 15-fold better inhibitory potency when compared with FNH79. The binding affinities of the inhibitors were predicted by an integrated computational study that combined molecular docking, molecular dynamics and binding free energy calculations. Inhibitor FNH79 was selected as a control for its best bioactivity. As shown in Table 1, N1 (ΔGpred = −45.87 kcal mol−1), N2 (ΔGpred = −43.90 kcal mol−1) and N3 (ΔGpred = −45.31 kcal mol−1) have stronger binding affinities compared to FNH79 (ΔGpred = −41.62 kcal mol−1), indicating that they prove to be promising inhibitors of CK2.
In order to gain a better understanding on the structural and energetic origin of their better binding potency, we broke down the binding energies for the new inhibitors into individual protein residue contributions. Fig. 13 shows the binding free energy decomposition for the different residues located within the active site of protein kinase CK2. Moreover, three structures of new inhibitors binding with the key residues of the active site taken from the averaged MD-simulated structures are displayed in Fig. 14. The stronger polar and non-polar interactions that make inhibitor N1 anchored well in the binding pocket of CK2 contribute to the improved binding affinity (Table 1). As shown in Fig. 14a, the formation of a hydrogen bond with residue Glu75 induces phenyl ring B of the inhibitor N1 to get closer to residue Phe107, thus increasing the non-polar contribution to the binding free energy. Comparing N2 with FNH79, we notice that the interaction for most of the residues is the same as those for both inhibitors while the only apparent differences are limited to residue Lys62 (Fig. 13b). This is mainly because of the stable hydrogen bond between N2 and Lys62 that stabilizes the inhibitor to interact with the binding pocket (Fig. 14b). Additionally, the hydrophobic scores of N3 are higher than those of FNH79, which can be attributed to the optimization of the hydrophobic force with the hydrophobic region of the enzyme active site (Table 1). Interestingly, for N3 and FNH79, one can notice a common interaction pattern with all the residues except for residue Asn112 (Fig. 13c). Obviously, Asn112 is a hydrophobic residue, and can form strong van der Waals interactions with the ortho-chlorophenyl moiety at R6 in N3 (Fig. 14c). This is the reason why Asn112 forms strong non-polar interactions with inhibitor N3, whereas inhibitor FNH79 does not. Therefore, the combination of molecular docking and molecular dynamic simulations revealed the interaction modes of the new compounds with the kinase active site and proved their higher inhibitory potency against CK2.
 | ||
| Fig. 13 Inhibitor–residue interaction spectra for (a) the CK2–FNH79 and CK2–N1 complex, (b) the CK2–FNH79 and CK2–N2 complex and (c) the CK2–FNH79 and CK2–N3 complex. | ||
4 Conclusions
In summary, we explored the structural details of the binding modes between flavone inhibitors and CK2 to provide accurate information for drug design targeting CK2. A comprehensive modeling protocol consisting of molecular docking, molecular dynamics simulations, free energy calculations and energy decompositions was carried out to characterize the interactions between CK2 and a series of recently synthesized flavone inhibitors. The results suggest that MM/GBSA has a better capability to rank the bioactivities with a satisfactory correlation coefficient and highlight the need to perform MD simulations. Moreover, the non-polar contribution, especially the van der Waals term, is responsible for the difference in the binding affinities of the investigated inhibitors. Residue decompositions show that hydrophobic residues, such as Val39, Val47, Ile60, Phe107, Asn112, Met157 and Ile168, play a critical role for flavone binding. Moreover, we also achieved structural evidence supporting the action of the inhibitors. The electrostatic interactions with the Lys62, Glu75 and Asp169 residues of CK2 are the important factors in the binding efficiency. The non-polar forces between inhibitors and some key residues, including Phe107 and Tyr109, contribute to the inhibitory activities, which indicates that the addition of hydrophobic groups to the R6 and R8 positions is favorable to significantly increase inhibitory potency. On the basis of the key structural elements necessary for their bioactivities, several potent inhibitors were designed and further evaluated by molecular dynamics in conjunction with binding free energy analysis. The improved inhibitory activities of new compounds against CK2 are confirmed by detailed structural and energetic analysis. Therefore, the current study can provide potential insight to further design more promising CK2 inhibitors.Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no competing financial interest.Acknowledgements
The present work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC, no. 21275067).References
- B. Havsteen, Biochem. Pharmacol., 1983, 32, 1141–1148 CrossRef CAS.
- N. Cotelle, J.-L. Bernier, J.-P. Catteau, J. Pommery, J.-C. Wallet and E. M. Gaydou, Free Radicals Biol. Med., 1996, 20, 35–43 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Marder and A. C. Paladini, Curr. Top. Med. Chem., 2002, 2, 853–867 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Škerget, P. Kotnik, M. Hadolin, A. R. Hraš, M. Simonič and Ž. Knez, Food Chem., 2005, 89, 191–198 CrossRef PubMed.
- V. García-Mediavilla, I. Crespo, P. S. Collado, A. Esteller, S. Sánchez-Campos, M. J. Tuñón and J. González-Gallego, Eur. J. Pharmacol., 2007, 557, 221–229 CrossRef PubMed.
- H. Cheong, S.-Y. Ryu, M.-H. Oak, S.-H. Cheon, G.-S. Yoo and K.-M. Kim, Arch. Pharmacal Res., 1998, 21, 478–480 CrossRef CAS.
- S. S. Kang, J. Y. Lee, Y. K. Choi, G. S. Kim and B. H. Han, Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett., 2004, 14, 2261–2264 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. Vrijsen, L. Everaert and A. Boeyé, J. Gen. Virol., 1988, 69, 1749–1751 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Sato, S. Fujiwara, H. Tsuchiya, T. Fujii, M. Iinuma, H. Tosa and Y. Ohkawa, J. Ethnopharmacol., 1996, 54, 171–176 CrossRef CAS.
- D. Wożniak, E. Lamer-Zarawska and A. Matkowski, Food, 2004, 48, 9–12 Search PubMed.
- M. Cabrera, M. Simoens, G. Falchi, M. L. Lavaggi, O. E. Piro, E. E. Castellano, A. Vidal, A. Azqueta, A. Monge and A. L. de Cerain, Bioorg. Med. Chem., 2007, 15, 3356–3367 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Narwal, T. Haikarainen, A. Fallarero, P. M. Vuorela and L. Lehtiö, J. Med. Chem., 2013, 56, 3507–3517 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. G. Golub, V. G. Bdzhola, O. V. Ostrynska, I. V. Kyshenia, V. M. Sapelkin, A. O. Prykhod'ko, O. P. Kukharenko and S. M. Yarmoluk, Bioorg. Med. Chem., 2013, 21, 6681–6689 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. I. Loizou, S. F. El-Khamisy, A. Zlatanou, D. J. Moore, D. W. Chan, J. Qin, S. Sarno, F. Meggio, L. A. Pinna and K. W. Caldecott, Cell, 2004, 117, 17–28 CrossRef CAS.
- M. A. Pagano, M. Andrzejewska, M. Ruzzene, S. Sarno, L. Cesaro, J. Bain, M. Elliott, F. Meggio, Z. Kazimierczuk and L. A. Pinna, J. Med. Chem., 2004, 47, 6239–6247 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- G. Cozza, P. Bonvini, E. Zorzi, G. Poletto, M. A. Pagano, S. Sarno, A. Donella-Deana, G. Zagotto, A. Rosolen and L. A. Pinna, J. Med. Chem., 2006, 49, 2363–2366 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. G. Golub, O. Y. Yakovenko, V. G. Bdzhola, V. M. Sapelkin, P. Zien and S. M. Yarmoluk, J. Med. Chem., 2006, 49, 6443–6450 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- E. Vangrevelinghe, K. Zimmermann, J. Schoepfer, R. Portmann, D. Fabbro and P. Furet, J. Med. Chem., 2003, 46, 2656–2662 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Bortolato and S. Moro, J. Chem. Inf. Model., 2007, 47, 572–582 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- N. Zhang and R. Zhong, Eur. J. Med. Chem., 2010, 45, 292–297 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Sun, X. Xu, X. Wu, X. Zhang, F. Liu, J. Jia, X. Guo, J. Huang, Z. Jiang and T. Feng, J. Chem. Inf. Model., 2013, 53, 2093–2102 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Wang, P. Pan, Y. Li, D. Li and T. Hou, Mol. BioSyst., 2014, 10, 1196–1210 RSC.
- A. Siddiqui-Jain, D. Drygin, N. Streiner, P. Chua, F. Pierre, S. E. O'Brien, J. Bliesath, M. Omori, N. Huser and C. Ho, Cancer Res., 2010, 70, 10288–10298 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. Hou, J. Wang, Y. Li and W. Wang, J. Chem. Inf. Model., 2010, 51, 69–82 CrossRef PubMed.
- S. K. Tripathi, R. Muttineni and S. K. Singh, J. Theor. Biol., 2013, 334, 87–100 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. M. Berman, J. Westbrook, Z. Feng, G. Gilliland, T. Bhat, H. Weissig, I. N. Shindyalov and P. E. Bourne, Nucleic Acids Res., 2000, 28, 235–242 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Schrödinger, version9.0, Schrödinger, LLC, New York, NY, 2009 Search PubMed.
- G. A. Kaminski, R. A. Friesner, J. Tirado-Rives and W. L. Jorgensen, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2001, 105, 6474–6487 CrossRef CAS.
- LigPrep, version9.0, Schrödinger, LLC, New York, NY, 2009 Search PubMed.
- P. Ambure and K. Roy, RSC Adv., 2014, 4, 6702–6709 RSC.
- M. Frisch, G. Trucks, H. Schlegel, G. Scuseria, M. Robb, J. Cheeseman, J. Montgomery Jr, T. Vreven, K. Kudin and J. Burant, Guassian 03, revision D. 01, Guassian, Inc, Wallingford, CT, 2004 Search PubMed.
- C. I. Bayly, P. Cieplak, W. Cornell and P. A. Kollman, J. Phys. Chem., 1993, 97, 10269–10280 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Wang, R. M. Wolf, J. W. Caldwell, P. A. Kollman and D. A. Case, J. Comput. Chem., 2004, 25, 1157–1174 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- V. Hornak, R. Abel, A. Okur, B. Strockbine, A. Roitberg and C. Simmerling, Proteins: Struct., Funct., Bioinf., 2006, 65, 712–725 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. Case, T. Darden, T. Cheatham III, C. Simmerling, J. Wang, R. Duke, R. Luo, R. Walker, W. Zhang and K. Merz, AMBER 11, University of California, San Francisco, 2010 Search PubMed.
- W. L. Jorgensen, J. Chandrasekhar, J. D. Madura, R. W. Impey and M. L. Klein, J. Chem. Phys., 1983, 79, 926–935 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- N. H. N. Moorthy, N. F. Brás, M. J. Ramos and P. A. Fernandes, RSC Adv., 2014, 4, 19550–19568 RSC.
- T. Darden, D. York and L. Pedersen, J. Chem. Phys., 1993, 98, 10089–10092 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J.-P. Ryckaert, G. Ciccotti and H. J. Berendsen, J. Comput. Phys., 1977, 23, 327–341 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Hou, J. Wang, Y. Li and W. Wang, J. Comput. Chem., 2011, 32, 866–877 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Shen, S. Zhou, Y. Li, P. Pan, L. Zhang and T. Hou, Mol. BioSyst., 2013, 9, 361–374 RSC.
- H. Tzoupis, G. Leonis, T. Mavromoustakos and M. G. Papadopoulos, J. Chem. Theory Comput., 2013, 9, 1754–1764 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Zhou, H. Luo, R. Li and Z. Ding, RSC Adv., 2013, 3, 22532–22543 RSC.
- T. Hou, Z. Xu, W. Zhang, W. A. McLaughlin, D. A. Case, Y. Xu and W. Wang, Mol. Cell. Proteomics, 2009, 8, 639–649 CAS.
- A. C. Wallace, R. A. Laskowski and J. M. Thornton, Protein Eng., 1995, 8, 127–134 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- W. Xue, M. Wang, X. Jin, H. Liu and X. Yao, Mol. BioSyst., 2012, 8, 2753–2765 RSC.
Footnote |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available: Figures show the alignments of 51 docked structures at the binding site of protein kinase CK2, the superposition of the Glide XP re-docked luteolin and its original structure in the crystallographic complex, the correlation between experimental pIC50 and the docking scores predicted by different docking protocols and the RMSD values relative to the initial structure of the new complexes, including CK2–N1, CK2–N2, and CK2–N3, during the MD simulations. Tables list the structures, bioactivities and docking scores of the 51 studied structures. See DOI: 10.1039/c4ra10381e |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 |