Hybrids of acylated homoserine lactone and nitric oxide donors as inhibitors of quorum sensing and virulence factors in Pseudomonas aeruginosa†
Abstract
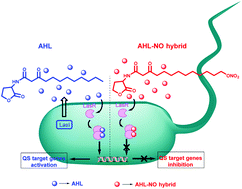
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is an opportunistic pathogen causing a variety of life-threatening diseases such as cystic fibrosis and nosocomial infections in burn victims. The ability of P. aeruginosa to cause infection is attributed to the production of virulence factors such as pyocyanin and elastases. These virulence factors are under the control of quorum sensing (QS) a cell to cell communication process controlled by small diffusible signalling molecules based on N-acyl-homoserine lactones (AHLs) known as autoinducers. The inhibition of QS and thereby virulence factors is seen as a potential new anti-infective strategy. Additionally, the role of nitric oxide (NO) in downstream processes in bacteria such as biofilm dispersal, motility, virulence and antimicrobial defence systems is gaining attention and could be used to control bacterial. Herein we report the design and synthesis of hybrid compounds based on AHL signalling molecules and NO donors as anti-infective agents. A series of AHL-NO hybrids were synthesised and potent inhibitors of QS and virulence factors of P. aeruginosa were identified. This research has led to conversion of agonist AHLs to antagonist AHLs with dual properties of QS inhibition and NO release.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...