New sterically encumbered arylimido hexamolybdates for organic oxidation reactions†
Abstract
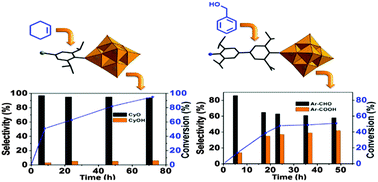
Facile synthesis of mono- and di-functionalised arylimido hexamolybdates, (nBu4N)2[Mo6O18(L1)] (1), (nBu4N)2[Mo6O17(L1)2] (2) and (nBu4N)2[Mo6O18(L2)] (3) (L1 = 4-bromo-2,6-diisopropylaniline, L2 = 2,2′,6,6′-tetraisopropylbenzidine), has been achieved through the reaction of parent (nBu4N)2[Mo6O19] (4) with a series of aniline derivatives. The arylimido derivatives 1–3 have been characterised by both analytical and spectroscopic studies (1H NMR, IR, UV-Vis and mass spectral studies), apart from structural elucidation of all the three compounds by single crystal X-ray diffraction studies. Steric hindrance at the ortho-positions of the arylamine seems to strengthen and effectively protect the newly formed Mo![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) N bonds. The surface modification of the hexamolybdate by aryl amines results in the transformation of otherwise inactive parent compound 4 into useful catalysts 1–3, which effectively catalyse the oxidation of cyclohexene to cyclohexene epoxide and benzyl alcohol to benzaldehyde and benzoic acid.
N bonds. The surface modification of the hexamolybdate by aryl amines results in the transformation of otherwise inactive parent compound 4 into useful catalysts 1–3, which effectively catalyse the oxidation of cyclohexene to cyclohexene epoxide and benzyl alcohol to benzaldehyde and benzoic acid.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Emergent Polyoxometalates and Soft-oxometalates

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...