Methylated Re(i) tetrazolato complexes: photophysical properties and Light Emitting Devices†
Abstract
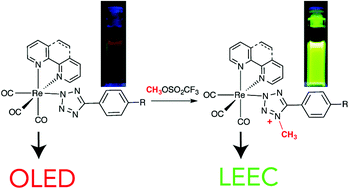
The irreversible reaction of methyl triflate with neutral Re(I) tetrazolato complexes of the type fac-[Re(diim)(CO)3(L)], where diim is either 1,10-phenanthroline or 2,2′-bipyridine and L is a para substituted 5-aryltetrazolate, yielded the corresponding cationic methylated complexes. While methylation occurred regioselectively at the N4 position of the tetrazole ring, the cationic complexes were found to exist in solution as equilibrating mixtures of linkage isomers, where the Re(I) centre was bound to either the N1 or N2 atom of the tetrazole ring. The existence of these isomers was highlighted both by NMR and X-ray crystallography studies. On the other hand, the two isomers appeared indistinguishable by IR, UV-Vis and luminescence spectroscopy. The prepared cationic complexes are all brightly phosphorescent in fluid and rigid solutions, with emission originating from triplet metal-to-ligand charge transfer excited states. Compared to their neutral precursors, which emit from admixtures of triplet metal-to-ligand and ligand-to-ligand charge transfer states, the methylated complexes exhibit blue-shifted emission characterised by elongated excited state lifetimes and increased quantum yields. The nature of the excited states for both the neutral and the methylated complexes was probed by resonance Raman spectroscopy and with the aid of time-dependent density functional theory calculations. Lastly, both the neutral and the methylated species were used as emitting phosphors in the fabrication of Organic Light Emitting Diodes and Light Emitting Electrochemical Cells.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Luminescent Complexes and Materials for Light-Emitting Devices

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...