Hopeachinols E–K, novel oligostilbenoids from the stem bark of Hopea chinensis†
Yi-Qing Cheng,
Rong Jiang,
Wei Huang,
Wei Wei,
Chao-Jun Chen,
Ren-Xiang Tan* and
Hui-Ming Ge*
Institute of Functional Biomolecules, State Key Laboratory of Pharmaceutical Biotechnology, Nanjing University, Nanjing, People's Republic of China. E-mail: hmge@nju.edu.cn; rxtan@nju.edu.cn
First published on 19th June 2014
Abstract
Five new stilbenolignans, hopeachinols E–I (1–5), and two new stilbenoids, hopeachinols J and K (6 and 7), together with the known resveratrol trimer, vaticanol A (8), were isolated from the stem bark of Hopea chinensis. The structures and relative configurations of these natural products were elucidated by using spectroscopic and spectrometric methods. The (8R) absolute configuration of 1 was assigned by using the modified Mosher ester method. Hopeachinols E–I (1–5) possess unprecedented stilbenolignan skeletons, in which a stilbene trimer is linked with a phenylpropanoid unit through a pyran bridge. Hopeachinols J and K (6 and 7) have new skeletons in which a stilbene trimer is connected by an additional two-carbon unit through a furan moiety. An evaluation of the cytotoxicities against HCT116, MDA-MB-231, SMMC-7721, and HepG2 cell lines of the new hopeachinols showed that 1, 2, 4, and 6 have moderate activities with IC50 values in the 10.39–18.72 μM range.
Introduction
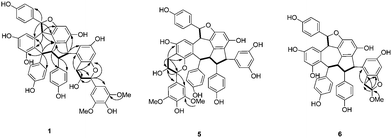
Plants belonging to the Dipterocarpaceae family, mostly distributed in Southeast Asia, are well documented sources of biologically active stilbenoids.1–3 They include stilbene dimers, trimers, tetramers, hexamers, heptamers and octamers with various molecular frameworks resulting from different oxidative condensation of resveratrol monomer. Some of these compounds have broad ranges of bioactivities including antimicrobial,4 antitumor,5,6 anti-inflammatory,7 and anti-HIV.8 Our previous studies on Hopea chinensis, a unique dipterocarpaceae species growing only in South China, have led to the identification of a number of oligostilbenoids that possess immunosuppressive and acetylcholinesterase (AChE) inhibitory activities.9,10 In continuing studies, we have isolated five new stilbenolignans 1–5 and two stilbenoids 6 and 7, along with one known oligostilbene 8 (Fig. 1) from the stem bark of H. chinensis. Compounds 1–5 share an unprecedented stilbenolignan skeleton in which a stilbene trimer is linked with a phenylpropanoid unit through a pyran ring.11 In contrast, 6 and 7 are composed of a stilbene trimer connected by an additional two-carbon unit through a dihydrofuran. Biological evaluation showed that 1, 2, 4, and 6 are cytotoxic towards HCT116, MDA-MB-231, SMMC-7721, and HepG2 cancer cells. Herein we describe their isolation, structure elucidation, and cytotoxicity evaluation.Results and discussion
The stilbenolignans, hopeachinols E–I (1–5), and two stilbenoids, hopeachinols J and K (6 and 7), together with the known resveratrol trimer vaticanol A (8) were isolated from an EtOAc extract of the stem bark of Hopea chinensis by using successive chromatographic procedures (silica gel, Sephadex LH-20, RP-18, and HPLC).Hopeachinol E (1), obtained as a yellow amorphous powder, was determined to have the molecular formula C53H44O13 (m/z 889.2850 [M + H]+, calcd 889.2855) by using positive ion HRESIMS and 13C NMR data (Table 2). The1 H NMR data (Table 1) showed the presence of three 4-hydroxyphenyl groups [δH 7.29 (2H, d, J = 8.4 Hz, H-2a/H-6a), 6.83 (2H, d, J = 8.4 Hz, H-3a/H-5a); 7.07 (2H, d, J = 8.4 Hz, H-2b/H-6b), 6.60 (2H, d, J = 8.4 Hz, H-3b/H-5b); 6.60 (2H, d, J = 8.4 Hz, H-2c/H-6c), and 6.36 (2H, d, J = 8.4 Hz, H-3c/H-5c)]; three 1,2,3,5-tetrasubstituted phenyl rings [δH 6.07 (1H, d, J = 2.4 Hz, H-12a), 6.46 (1H, d, J = 2.4 Hz, H-14a); 6.23 (1H, d, J = 2.4 Hz, H-10c), 6.22 (1H, d, J = 2.4 Hz, H-12c); and 6.76 (2H, s, H-2/H-6)]; a penta-substituted phenyl ring [δH 6.24 (1H, s, H-12b)]; a set of mutually coupled aliphatic protons [δH 6.18 (1H, d, J = 4.2 Hz, H-7a), and 4.51 (1H, d, J = 4.2 Hz, H-8a)]; and a contiguous sequence of four aliphatic methine protons [δH 5.16 (1H, s, H-7b), 4.48 (1H, d, J = 7.2 Hz, H-8b); 3.58 (1H, d, J = 7.2 Hz, H-7c), and 4.40 (1H, s, H-8c)]. Additionally, resonances were observed at δH 4.66 (1H, d, J = 7.8 Hz, H-7), 4.01 (1H, m, H-8), 2.80 (1H, dd, J = 15.6, 9.0 Hz, H-9α), 2.98 (1H, dd, J = 15.6, 4.8 Hz, H-9β), and 3.83 (6H, s, OCH3). Comparison of the 13C NMR data of 1 with those of vaticanol A (8) suggested that it possesses a substructure sharing the same skeleton with 8.12 HMBC correlations (Fig. 2) between H-7/C-2, C-8 and H-9/C-7, C-8, and1H-1H COSY correlations between H-9/H-8 and H-8/H-7 showed that the remaining motif present in 1 is a C6–C3 moiety. The two partial structures of 1 are connected by an ether linkage between C-7/C-13c and a C–C bond between C-9/C-14c based on HMBC correlations between H-9/C-9c, C-13c and H-7/C-13c. Finally, long-range HMBC correlations showed that the methoxy groups are located at C-3 and C-5.
| 1a | 2a | 3b | 4a | 5a | 6a | 7a | 8b | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a Measured at 600 MHz for 1H NMR in acetone-d6.b Measured at 500 MHz for 1H NMR in acetone-d6. | ||||||||
| 2a, 6a | 7.29 (d, 8.4) | 7.28 (d, 8.4) | 7.27 (d, 8.5) | 7.28 (d, 8.4) | 7.26 (d, 8.4) | 7.27 (d, 9.0) | 7.27 (d, 8.4) | 7.28 (d, 8.5) |
| 3a, 5a | 6.83 (d, 8.4) | 6.83 (d, 8.4) | 6.83 (d, 8.5) | 6.83 (d, 8.4) | 6.82 (d, 8.4) | 6.82 (d, 9.0) | 6.82 (d, 8.4) | 6.84 (d, 8.5) |
| 7a | 6.18 (d, 4.2) | 6.18 (d, 4.2) | 6.18 (d, 3.5) | 6.17 (d, 4.2) | 6.14 (d, 3.6) | 6.17 (d, 3.6) | 6.16 (d, 3.6) | 6.18 (d, 3.5) |
| 8a | 4.51 (d, 4.2) | 4.51 (d, 4.2) | 4.50 (d, 3.5) | 4.50 (d, 4.2) | 4.53 (d, 3.6) | 4.49 (d, 3.6) | 4.50 (d, 3.6) | 4.50 (d, 3.5) |
| 12a | 6.07 (d, 2.4) | 6.06 (d, 2.4) | 6.05 (d, 2.0) | 6.05 (d, 2.4) | 6.06 (d, 2.4) | 6.06 (d, 2.4) | 6.08 (d, 2.0) | |
| 14a | 6.46 (d, 2.4) | 6.46 (d, 2.4) | 6.46 (d, 2.0) | 6.45 (d, 2.4) | 6.61 (s) | 6.47 (d, 2.4) | 6.46 (d, 2.4) | 6.49 (d, 2.0) |
| 2b, 6b | 7.07 (d, 8.4) | 7.07 (d, 8.4) | 7.06 (d, 8.5) | 7.06 (d, 8.4) | 7.14 (d, 8.4) | 7.05 (d, 8.4) | 7.04 (d, 8.4) | 7.08 (d, 8.5) |
| 3b, 5b | 6.60 (d, 8.4) | 6.60 (d, 8.4) | 6.60 (d, 8.5) | 6.60 (d, 8.4) | 6.60 (d, 8.4) | 6.59 (d, 8.4) | 6.58 (d, 8.4) | 6.62 (d, 8.5) |
| 7b | 5.16 (s) | 5.16 (s) | 5.13 (s) | 5.13 (s) | 5.17 (s) | 5.14 (s) | 5.12 (s) | 5.16 (s) |
| 8b | 4.48 (d, 7.2) | 4.47 (d, 6.6) | 4.51 (d, 6.5) | 4.51 (d, 7.2) | 4.43 (d, 7.2) | 4.49 (d, 7.2) | 4.43 (d, 7.2) | 4.53 (d, 7.0) |
| 12b | 6.24 (s) | 6.24 (s) | 6.24 (s) | 6.24 (s) | 6.23 (s) | 6.22 (s) | 6.22 (s) | 6.25 (s) |
| 2c, 6c | 6.60 (d, 8.4) | 6.60 (d, 8.4) | 6.56 (d, 8.5) | 6.55 (d, 8.4) | 6.34 (d, 8.4) | 6.54 (d, 8.4) | 6.56 (d, 8.4) | 6.55 (d, 8.5) |
| 3c, 5c | 6.36 (d, 8.4) | 6.36 (d, 8.4) | 6.35 (d, 8.5) | 6.35 (d, 8.4) | 6.39 (d, 8.4) | 6.38 (d, 8.4) | 6.37 (d, 8.4) | 6.39 (d, 8.5) |
| 7c | 3.58 (d, 7.2) | 3.58 (d, 6.6) | 3.46 (d, 6.5) | 3.46 (d, 7.2) | 3.50 (d, 7.2) | 3.58 (d, 7.2) | 3.56 (d, 7.2) | 3.65 (d, 7.0) |
| 8c | 4.40 (s) | 4.40 (s) | 4.38 (s) | 4.37 (s) | 4.11 (s) | 4.19 (s) | 4.22 (s) | 4.21 (s) |
| 10c | 6.23 (d, 2.4) | 6.23 (d, 2.4) | 6.22 (d, 2.5) | 6.22 (d, 2.4) | 6.24 (d, 2.4) | 6.11 (d, 2.4) | 6.11 (d, 2.4) | 6.30 (d, 2.0) |
| 12c | 6.22 (d, 2.4) | 6.21 (d, 2.4) | 6.21 (d, 2.5) | 6.21 (d, 2.4) | 6.16 (t, 2.4) | 6.19 (d, 2.4) | 6.20 (d, 2.4) | 6.23 (t, 2.0) |
| 14c | 6.24 (d, 2.4) | 6.30 (d, 2.0) | ||||||
| 1 | 3.16 (dd, 15.6, 6.6) β | 3.35 (dd, 15.6, 6.6) α | ||||||
| 2.90 (dd, 15.6, 2.4) α | 2.73 (dd, 15.6, 1.8) β | |||||||
| 2 | 6.76 (s) | 6.92 (dd, 8.4, 1.8) | 6.76 (s) | 6.91 (dd, 7.8, 1.8) | 6.67 (s) | 5.67 (dd, 6.6, 2.4) | 5.69 (dd, 6.6, 1.8) | |
| 3 | 6.81 (d, 8.4) | 6.82 (d, 7, 8) | ||||||
| 6 | 6.76 (s) | 7.05 (d, 1.8) | 6.76 (s) | 7.05 (d, 1.8) | 6.67 (s) | |||
| 7 | 4.66 (d, 7.8) | 4.68 (d, 8.4) | 4.57 (d, 8.0) | 4.59 (d, 7.8) | 3.80 (d, 9.0) | |||
| 8 | 4.01 (m) | 4.01 (m) | 4.16 (m) | 4.16 (m) | 3.68 (m) | |||
| 9 | 2.98 (dd, 15.6, 4.8) β | 2.97 (dd, 15.6, 4.8) β | 3.11 (dd, 16.0, 5.5) α | 3.09 (dd, 15.6, 5.4) α | 3.04 (dd, 15.6, 5.4) | |||
| 2.80 (dd, 15.6, 9.0) α | 2.81 (dd, 15.6, 9.0) α | 2.63 (dd, 16.0, 9.0) β | 2.64 (dd, 15.6, 9.0) β | 2.37 (dd, 15.6, 10.8) | ||||
| OCH3 | 3.83 (6H, s) | 3.85 (3H, s) | 3.82 (6H, s) | 3.84 (3H, s) | 3.82 (6H, s) | 3.48 (3H, s) | 3.44 (3H, s) | |
NOESY experiments were conducted to determine the relative configurations at the stereocenters in 1 (Fig. 3). The presence of NOE correlations between H-7a/H-14a and H-8a/H-2a(6a) suggested that the methine protons H-7a, H-8a are trans disposed, and that between H-8a/H-2b(6b) indicated that ring B1 is α-oriented (H-7b: β-oriented). The NOE correlations between H-7b/H-2c(H-6c), H-8b/H-2b(H-6b), H-8b/H-10c and H-8c/H-2c(H-6c) showed that the relative orientations of the methine protons at C-7b, C-8b, C-7c and C-8c are β, α, α, and β oriented, respectively. Importantly, the similar NOE associations showed that the relative configurations of the stereocenters in the stilbene trimer unit in 1 are the same as those in vaticanol A (8).12 In addition, H-7 and H-8 in 1 were trans oriented based on the NOE correlations between H-8/H-2(H-6). Finally, clear cross-peaks between H-7/H-9α and H-9β/H-8c were also observed.
Hopeachinol F (2), also obtained as a yellow amorphous powder, was shown to have the molecular formula C52H42O12 (m/z 859.2745 [M + H]+, calcd to be 859.2749) by analysis of its HRESIMS spectrometric and 13C NMR data. The 1H and 13C NMR spectra of 2 (Table 1 and 2) were closely similar to those of 1 except that the C-3 methoxy proton and carbon resonances at C-3 in the spectra of 1 are replaced by an aromatic proton and carbon in 2. Moreover, the NOESY spectra of 1 and 2 are almost the same, indicating that both substances have the same relative configuration at their corresponding stereocenters.
| 1a | 2a | 3b | 4a | 5a | 6a | 7a | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a Measured at 150 MHz for 13C NMR in acetone-d6.b Measured at 125 MHz for 13C NMR in acetone-d6. | |||||||
| 1a | 134.5 | 134.5 | 134.5 | 134.4 | 134.4 | 134.3 | 134.3 |
| 2a, 6a | 128.2 | 128.2 | 128.1 | 128.1 | 128.1 | 128.1 | 128.1 |
| 3a, 5a | 116.2 | 116.2 | 116.2 | 116.2 | 116.2 | 116.1 | 116.1 |
| 4a | 158.1 | 158.1 | 158.1 | 158.2 | 158.1 | 158.0 | 158.1 |
| 7a | 86.8 | 86.8 | 86.9 | 86.8 | 86.7 | 86.7 | 86.9 |
| 8a | 50.3 | 50.3 | 50.4 | 50.3 | 50.0 | 50.3 | 50.3 |
| 9a | 144.9 | 144.9 | 144.9 | 144.9 | 141.8 | 144.8 | 144.8 |
| 10a | 119.5 | 119.5 | 119.4 | 119.3 | 120.3 | 119.1 | 119.4 |
| 11a | 157.9 | 157.9 | 157.9 | 157.9 | 154.3 | 157.9 | 157.8 |
| 12a | 101.4 | 101.4 | 101.5 | 101.4 | 107.2 | 101.2 | 101.3 |
| 13a | 156.4 | 156.4 | 156.5 | 156.5 | 153.9 | 156.4 | 156.4 |
| 14a | 103.5 | 103.4 | 103.5 | 103.4 | 103.3 | 103.1 | 103.2 |
| 1b | 138.7 | 138.7 | 138.7 | 138.7 | 138.7 | 138.6 | 138.7 |
| 2b, 6b | 129.3 | 129.4 | 129.3 | 129.3 | 129.4 | 129.2 | 129.3 |
| 3b, 5b | 115.5 | 115.5 | 115.5 | 115.5 | 115.5 | 115.4 | 115.4 |
| 4b | 155.9 | 155.9 | 155.9 | 155.9 | 155.9 | 155.8 | 155.8 |
| 7b | 36.0 | 36.0 | 36.1 | 36.0 | 36.1 | 36.1 | 36.1 |
| 8b | 48.5 | 48.5 | 48.6 | 48.5 | 48.3 | 48.8 | 48.6 |
| 9b | 145.4 | 145.4 | 145.4 | 145.4 | 145.0 | 145.1 | 145.2 |
| 10b | 119.0 | 119.0 | 119.1 | 119.0 | 118.8 | 118.8 | 118.8 |
| 11b | 160.2 | 160.2 | 160.2 | 160.2 | 160.0 | 160.1 | 160.1 |
| 12b | 95.5 | 95.5 | 95.6 | 95.5 | 95.5 | 95.3 | 95.3 |
| 13b | 155.4 | 155.4 | 155.3 | 155.3 | 155.8 | 155.4 | 155.6 |
| 14b | 122.5 | 122.4 | 122.6 | 122.6 | 122.4 | 121.5 | 121.4 |
| 1c | 135.4 | 135.4 | 135.5 | 135.5 | 136.0 | 135.6 | 135.5 |
| 2c, 6c | 130.0 | 130.0 | 129.9 | 129.9 | 129.6 | 129.6 | 129.7 |
| 3c, 5c | 115.0 | 115.0 | 115.2 | 115.1 | 115.2 | 115.1 | 115.0 |
| 4c | 156.6 | 156.6 | 156.7 | 156.7 | 156.6 | 156.5 | 156.5 |
| 7c | 62.2 | 62.2 | 62.9 | 62.8 | 64.6 | 63.1 | 62.5 |
| 8c | 54.0 | 54.0 | 53.9 | 53.8 | 57.4 | 55.2 | 55.4 |
| 9c | 145.1 | 145.1 | 145.4 | 145.4 | 147.3 | 142.3 | 142.1 |
| 10c | 107.4 | 107.4 | 107.3 | 107.3 | 106.8 | 106.1 | 106.3 |
| 11c | 157.2 | 157.2 | 157.3 | 157.3 | 159.4 | 158.7 | 158.7 |
| 12c | 101.9 | 101.9 | 102.0 | 102.0 | 101.4 | 96.2 | 96.3 |
| 13c | 156.7 | 156.8 | 156.8 | 156.8 | 159.4 | 160.2 | 160.2 |
| 14c | 111.6 | 111.6 | 111.6 | 111.5 | 106.8 | 115.4 | 115.5 |
| 1 | 130.9 | 132.0 | 131.0 | 132.0 | 131.1 | 36.0 | 36.1 |
| 2 | 106.1 | 121.4 | 106.3 | 121.6 | 105.9 | 108.8 | 108.7 |
| 3 | 148.5 | 115.4 | 148.6 | 115.5 | 148.3 | ||
| 4 | 136.7 | 147.3 | 136.7 | 147.4 | 136.3 | ||
| 5 | 148.5 | 148.1 | 148.6 | 148.2 | 148.3 | ||
| 6 | 106.1 | 111.9 | 106.3 | 111.8 | 105.9 | ||
| 7 | 83.2 | 82.9 | 83.2 | 82.9 | 82.8 | ||
| 8 | 68.9 | 68.9 | 68.7 | 68.6 | 68.5 | ||
| 9 | 32.9 | 33.0 | 32.5 | 32.5 | 30.3 | ||
| OCH3 | 56.6 | 56.3 | 56.7 | 56.3 | 56.6 | 55.6 | 55.6 |
Hopeachinol G (3), having the molecular formula C53H44O13 was isolated as a yellow amorphous powder. The 1H and 13C NMR (Table 1 and 2), HSQC, HMBC, 1H-1H COSY (see ESI S15–S17†), and NOESY data (Fig. 3) showed that 3 has the same planar structure and similar relative configurations as 1. Structural difference between 1 and 3 was deduced using NOE correlations between H-7/H-9β, H-9α/H-7c and H-9β/H-8c, which showed that H-7 and H-8 are β- and α-oriented, respectively, in 3.
Hopeachinol H (4), isolated as a yellow amorphous powder and having a molecular formula C52H42O12, has a 30 mass units lower (-OCH2) molecular weight than 3. The spectroscopic data of 4 showed that it possesses a structure that is similar to 3, except for the absence of a methoxy group. The D ring proton resonances in the 1H NMR spectrum of 3, which appear as an A2 system [δH 6.76 (2H, s, H-2/H-6)], are replaced by an ABC system [δH 6.91 (1H, dd, J = 7.8, 1.8 Hz, H-2), 6.82 (1H, d, J = 7.8 Hz, H-3), 7.05 (1H, d, J = 1.8 Hz, H-6)] in 4 (Table 1). 1H-1H COSY, HMBC, and NOESY data provide support for the proposal that 4 is a demethoxy derivative of 3.
1H and 13C NMR (Table 1 and 2), and HMBC (Fig. 2) data of hopeachinol I (5), obtained as a yellow amorphous powder and having the molecular formula of C53H44O13, showed that this substance contains the same substructure as vaticanol A (8) and the same phenylpropanoid motif as 1. The difference between 1 and 5 is the position of the C6–C3 unit. HMBC cross-peaks for H-9/C-11a, C-13a indicate that the two partial structures in 5 are connected by an ether linkage between C-7/C-11a and a C–C bond between C-9/C-12a. NOESY correlations (Fig. 3) show that the relative configurations at the stereogenic carbons in the stilbene trimer part of 5 are the same as those in vaticanol A (8). Also, the NOE correlations between H-2/H-8 and H-2/H-2b show that the methine protons at C-7 and C-8 are β- and α-oriented, respectively.
The 1H NMR spectrum of hopeachinols J (6) (Table 1), which has the molecular formula C45H36O10 and was isolated as a yellow amorphous powder, contains resonances for three sets of ortho-coupled protons on p-substituted phenyl moieties as an A2B2 system [δH 7.27 (2H, d, J = 9.0 Hz, H-2a/H-6a), 6.82 (2H, d, J = 9.0 Hz, H-3a/H-5a); 7.05 (2H, d, J = 8.4 Hz, H-2b/H-6b), 6.59 (2H, d, J = 8.4 Hz, H-3b/H-5b); 6.54 (2H, d, J = 8.4 Hz, H-2c/H-6c), and 6.38 (2H, d, J = 8.4 Hz, H-3c/H-5c)]; two sets of meta-coupled protons as an AB system corresponding to 1,2,3,5-tetrasubstituted phenyl moieties [δH 6.06 (1H, d, J = 2.4 Hz, H-12a), 6.47 (1H, d, J = 2.4 Hz, H-14a); 6.11 (1H, d, J = 2.4 Hz, H-10c), and 6.19 (1H, d, J = 2.4 Hz, H-12c)]; a proton of a penta-substituted phenyl group [δH 6.22 (1H, s, H-12b)]; a sequence of four aliphatic methane protons [δH 5.14 (1H, s, H-7b), 4.49 (1H, d, J = 7.2 Hz, H-8b); 3.58 (1H, d, J = 7.2 Hz, H-7c), and 4.19 (1H, s, H-8c)]; and a set of mutually coupled aliphatic protons [δH 6.17 (1H, d, J = 3.6 Hz, H-7a), and 4.49 (1H, d, J = 3.6 Hz, H-8a)]. In addition, other resonances occurred at δH 3.16 (1H, dd, J = 15.6, 6.6 Hz, H-1β), 2.90 (1H, dd, J = 15.6, 2.4 Hz, H-1α), 5.67 (1H, dd, J = 6.6, 2.4 Hz, H-2), and 3.48 (3H, s, OCH3). 13C and 2D NMR (1H-1H COSY, HMBC, and NOESY) data showed that 6 is also structurally similar to vaticanol A (8).12 HMBC correlations (Fig. 2) between H-1/C-9c, C-13c and H-2/C-1, C-13c, C-14c revealed the existence of a C-14c/C-1/C-2 sequence, and that a methoxy group is located at C-2. Finally, cross-peaks in NOE correlations (Fig. 3) between H-1β/H-2, H-1β/H-8c, H-1α/H-7c and H-1α/H-8c showed that H-2 is β-oriented.
The final substance isolated as an amorphous yellow powder from the stem bark of H. chinensis is hopeachinol K (7, C45H36O10). 1H and 13C NMR (Table 1 and 2), HSQC, HMBC, and 1H-1H COSY data (see ESI S39–S41†) demonstrated that 7 had the same molecular structure as 6. However, H-2 in 7 is α-oriented based on the NOE correlations of H-2/H-1α and H-1β/H-8c (Fig. 3).
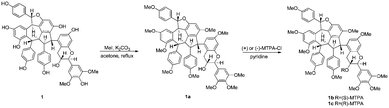
To further assign the absolute configurations of these compounds, the C-8-OH Mosher ester of 1 was prepared after protection of the phenol groups (Scheme 1).13,14 The Δδ (δS–δR) value distribution pattern clearly indicated an 8R configuration (Fig. 4). Thus, the absolute configuration of 1 was 7aR, 8aR, 7bR, 8bS, 7cS, 8cS, 7S, 8R. Moreover, the CD spectrum of 1 was similar to those of 2–8, indicating that these compounds have the same absolute configurations at the stereogenic carbons in their common substructure, vaticanol A (8) (Fig. 5). Therefore, their structures were determined as shown in Fig. 1.
Cytotoxicities of all of the new natural products characterized in this investigation were determined against four human cancer cell lines (HCT116, MDA-MB-231, SMMC-7721, and HepG2) using the MTT method15 with doxorubicin as a positive control (Table 3). Hopeachinols H (4) and J (6) are cytotoxic against HepG2 with respective IC50 values of 15.76 and 12.35 μM. In addition, hopeachinols E (1) and F (2) exhibit moderate cytotoxic activities against HCT116, MDA-MB-231, and SMMC-7721 cell lines with IC50 values in the 10.39–18.72 μM range, whereas their stereoisomeric analogs 3 and 4 are inactive (IC50 > 40 μM) against these same cell lines, indicating that stereochemistry may play an important role in determining cytotoxic activity.
| Compound | HCT116 | MDA-MB-231 | SMMC-7721 | HepG2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| a Positive control; NA not active (IC50 > 40 μM); ± results are expressed as mean ± SEM, n = 3. | ||||
| 1 | 17.89 ± 1.27 | 14.34 ± 0.65 | 12.18 ± 0.36 | NA |
| 2 | 14.74 ± 0.93 | 18.72 ± 0.71 | 10.39 ± 0.87 | NA |
| 3 | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| 4 | NA | NA | NA | 15.76 ± 1.05 |
| 5 | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| 6 | NA | NA | NA | 12.35 ± 0.43 |
| 7 | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| Doxorubicina | 1.79 ± 0.21 | 3.54 ± 0.34 | 2.98 ± 0.53 | 1.27 ± 0.28 |
Conclusions
In summary, we isolated and characterized a number of new stilbenolignan natural products from the stem bark of dipterocarp H. chinensis, including hopeachinols E–I (1–5), and two stilbenoids, hopeachinols J and K (6 and 7). Dipterocarp plants typically use resveratrol as a building block to construct resveratrol oligomers having diverse carbon skeletons.1–10 However, stilbenolignans are rare in nature, especially those in which the stilbenoid and lignan motifs are connected by C–C bonds. Examples of stilbenolignans are aiphanol from Aiphanes aculeate,11 shanciol A and shanciol B from Pleione bulbocodioides,16 and trigonopol B from Dendrobium trigonopus.17 To the best of our knowledge, hopeachinols E–I (1–5) are the first examples of stilbenolignans in which a stilbene trimer and one lignan unit are linked through a pyran ring. It is possible to speculate that 1–7 are biosynthetically derived from the common intermediate vaticanol A (8) via a route involving sequential intramolecular free radical cyclization reactions with phenylpropanoid or two-carbon units.Experimental section
General experimental procedures
Optical rotations were recorded on a Rudolph Autopol III automatic polarimeter. UV spectra were recorded on a Hitachi U-3000 spectrophotometer in MeOH. IR spectra were measured on a Nexus 870 FT-IR spectrometer. CD spectra were acquired on a JASCO J-810 spectrometer. HRESIMS spectra were recorded on an Agilent 6210 TOF LC/MS equipped with an electrospray ionization (ESI) probe operating in positive or negative ion mode with direct infusion. The semi-preparative HPLC was accomplished over a Hypersil ODS column (5 μm, 250 mm × 10 mm, Thermo Fisher Scientific, USA) on a Hitachi HPLC system consisted of a L-7110 pump (Hitachi) and a L-7420 UV-vIS Detector (Hitachi). NMR spectroscopic data were acquired in acetone-d6 or CDCl3 on BRUKER DRX500, BRUKER AVANCE III 600, or BRUKER AVANCE III 400 NMR spectrometer with tetramethylsilane (TMS) and solvent signals as internal references. Acetone-d6 or CDCl3 for NMR measurements were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich Chemicals. Analytical TLC was performed on GF254 (Qingdao Marine Chemical Factory, Qingdao, China) plates with 0.2 mm layer thickness. Column chromatography was performed on silica gel (200–300 mesh; Qingdao Marine Chemical Factory, Qingdao, China), reverse phase (ODS) silica gel (12 nm, S-50 μm, YMC, Japan) or Sephadex LH-20 (GE, USA). All chemicals used in the study were of analytical grade.Plant material
The stems and twigs of H. chinensis were collected in August 2008 from the Botanical Garden at Jianfeng Town, Ledong County, Hainan Island (China). A voucher specimen (no. IFB-20080820) was preserved at the Institute of Functional Biomolecules, Nanjing University. The specimen was identified by Prof. X. J. Tian (Nanjing University, Nanjing, China).Extraction and isolation
All of the fractions left over from previous isolations9,10 were combined and concentrated to a residue (63 g), which gave six fractions A-F upon column chromatography on silica gel (1 kg, 200–300 mesh) using a gradient of CH2Cl2–MeOH (100![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10 to 0
10 to 0![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 100) based on TLC monitoring. All fractions were analyzed by LC-HRMS to search for the unusual molecular formulas, which may indicate the existence of new compounds. Fraction C and D were selected for further separation. Fraction C (9.8 g), given by elution with CH2Cl2–MeOH (100
100) based on TLC monitoring. All fractions were analyzed by LC-HRMS to search for the unusual molecular formulas, which may indicate the existence of new compounds. Fraction C and D were selected for further separation. Fraction C (9.8 g), given by elution with CH2Cl2–MeOH (100![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 20), was subjected to reversed phase ODS column with a step gradient of MeOH–H2O (20
20), was subjected to reversed phase ODS column with a step gradient of MeOH–H2O (20![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 80 to 100
80 to 100![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 0) to give six subfractions C1–C7, respectively. Chromatography of C2 over Sephadex LH-20 (100% MeOH) followed by the semi-preparative HPLC (MeCN–H2O, 31
0) to give six subfractions C1–C7, respectively. Chromatography of C2 over Sephadex LH-20 (100% MeOH) followed by the semi-preparative HPLC (MeCN–H2O, 31![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 69, 2 mL min−1) gave 6 (1.2 mg, tR = 37.1 min) and 7 (1.1 mg, tR = 41.7 min). Compound 4 (1.0 mg, tR = 53.2 min) and 1 (11.5 mg, tR = 87.1 min) were obtained from HPLC (MeOH–H2O, 41
69, 2 mL min−1) gave 6 (1.2 mg, tR = 37.1 min) and 7 (1.1 mg, tR = 41.7 min). Compound 4 (1.0 mg, tR = 53.2 min) and 1 (11.5 mg, tR = 87.1 min) were obtained from HPLC (MeOH–H2O, 41![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 59, 2 mL min−1) over C3. C4 was chromatographed over Sephadex LH-20 (100% MeOH) to give 8 (530 mg). Fraction D (4.2 g), given by elution with CH2Cl2–MeOH (100
59, 2 mL min−1) over C3. C4 was chromatographed over Sephadex LH-20 (100% MeOH) to give 8 (530 mg). Fraction D (4.2 g), given by elution with CH2Cl2–MeOH (100![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 30), was further purified by using Sephadex LH-20 (100% MeOH) and column chromatography (CH2Cl2–MeOH from 100
30), was further purified by using Sephadex LH-20 (100% MeOH) and column chromatography (CH2Cl2–MeOH from 100![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 15 to 100
15 to 100![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 30) followed by HPLC (MeOH/H2O, 40 : 60, 2 mL min−1) gave 3 (8.0 mg, tR = 23.0 min), 5 (5.0 mg, tR = 29.2 min), and 2 (3.0 mg, tR = 40.1 min).
30) followed by HPLC (MeOH/H2O, 40 : 60, 2 mL min−1) gave 3 (8.0 mg, tR = 23.0 min), 5 (5.0 mg, tR = 29.2 min), and 2 (3.0 mg, tR = 40.1 min).
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) ε) = 209 (5.91), 284 (4.91) nm. CD (MeOH): λmax (Δε) = 210 (−11.78), 234 (+0.17), 252 (−1.90), 269 (−0.30), 295 (−1.99) nm; IR (KBr): vmax = 3357, 2965, 2930, 2850, 1614, 1513, 1456, 1330, 1261, 1220, 1174, 1138, 1109, 1039, 827 cm−1. HRESIMS: m/z 889.2850 [M + H]+ (calcd for C53H45O13, 889.2855). For 1D and 2D NMR data, see Table 1 and 2, and ESI.†
ε) = 209 (5.91), 284 (4.91) nm. CD (MeOH): λmax (Δε) = 210 (−11.78), 234 (+0.17), 252 (−1.90), 269 (−0.30), 295 (−1.99) nm; IR (KBr): vmax = 3357, 2965, 2930, 2850, 1614, 1513, 1456, 1330, 1261, 1220, 1174, 1138, 1109, 1039, 827 cm−1. HRESIMS: m/z 889.2850 [M + H]+ (calcd for C53H45O13, 889.2855). For 1D and 2D NMR data, see Table 1 and 2, and ESI.†![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) ε) = 204 (5.23), 284 (4.22) nm. CD (MeOH): λmax (Δε) = 211 (−21.39), 234 (+0.35), 252 (−3.09), 274 (−0.45), 295 (−3.14) nm; IR (KBr): vmax = 3358, 2963, 2925, 2852, 1614, 1513, 1455, 1384, 1262, 1174, 1137, 1097, 1035, 802 cm−1. HRESIMS: m/z 859.2745 [M + H]+ (calcd for C52H43O12, 859.2749). For 1D and 2D NMR data, see Table 1 and 2, and ESI.†
ε) = 204 (5.23), 284 (4.22) nm. CD (MeOH): λmax (Δε) = 211 (−21.39), 234 (+0.35), 252 (−3.09), 274 (−0.45), 295 (−3.14) nm; IR (KBr): vmax = 3358, 2963, 2925, 2852, 1614, 1513, 1455, 1384, 1262, 1174, 1137, 1097, 1035, 802 cm−1. HRESIMS: m/z 859.2745 [M + H]+ (calcd for C52H43O12, 859.2749). For 1D and 2D NMR data, see Table 1 and 2, and ESI.†![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) ε) = 204 (5.98), 283 (4.88) nm. CD (MeOH): λmax (Δε) = 211 (−39.29), 238 (+2.03), 254 (−4.41), 268 (−0.41), 294 (−5.41) nm; IR (KBr): vmax = 3362, 2967, 2933, 2849, 1614, 1513, 1456, 1330, 1220, 1174, 1138, 1112, 1039, 831 cm−1. HRESIMS: m/z 889.2850 [M + H]+ (calcd for C53H45O13, 889.2855). For 1D and 2D NMR data, see Table 1 and 2, and ESI.†
ε) = 204 (5.98), 283 (4.88) nm. CD (MeOH): λmax (Δε) = 211 (−39.29), 238 (+2.03), 254 (−4.41), 268 (−0.41), 294 (−5.41) nm; IR (KBr): vmax = 3362, 2967, 2933, 2849, 1614, 1513, 1456, 1330, 1220, 1174, 1138, 1112, 1039, 831 cm−1. HRESIMS: m/z 889.2850 [M + H]+ (calcd for C53H45O13, 889.2855). For 1D and 2D NMR data, see Table 1 and 2, and ESI.†![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) ε) = 204 (4.82), 284 (3.61) nm. CD (MeOH): λmax (Δε) = 211 (−13.15), 237 (+1.12), 254 (−1.78), 275 (−0.20), 295 (−2.19) nm; IR (KBr): vmax = 3355, 2925, 2853, 2062, 1662, 1614, 1513, 1456, 1384, 1261, 1224, 1174, 1138, 1108, 1036, 821, 803 cm−1. HRESIMS: m/z 859.2745 [M + H]+ (calcd for C52H43O12, 859.2749). For 1D and 2D NMR data, see Table 1 and 2, and ESI.†
ε) = 204 (4.82), 284 (3.61) nm. CD (MeOH): λmax (Δε) = 211 (−13.15), 237 (+1.12), 254 (−1.78), 275 (−0.20), 295 (−2.19) nm; IR (KBr): vmax = 3355, 2925, 2853, 2062, 1662, 1614, 1513, 1456, 1384, 1261, 1224, 1174, 1138, 1108, 1036, 821, 803 cm−1. HRESIMS: m/z 859.2745 [M + H]+ (calcd for C52H43O12, 859.2749). For 1D and 2D NMR data, see Table 1 and 2, and ESI.†![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) ε) = 204 (5.65), 222 (5.70), 287 (5.01) nm. CD (MeOH): λmax (Δε) = 208 (+2.30), 223 (−2.19), 239 (−0.86), 252 (−1.67), 272 (−0.12), 294 (−1.28) nm; IR (KBr): vmax = 3366, 2962, 2926, 2853, 1613, 1513, 1463, 1384, 1336, 1261, 1221, 1174, 1108, 1040, 832, 806 cm−1. HRESIMS: m/z 889.2857 [M + H]+ (calcd for C53H45O13, 889.2855). For 1D and 2D NMR data, see Table 1 and 2, and ESI.†
ε) = 204 (5.65), 222 (5.70), 287 (5.01) nm. CD (MeOH): λmax (Δε) = 208 (+2.30), 223 (−2.19), 239 (−0.86), 252 (−1.67), 272 (−0.12), 294 (−1.28) nm; IR (KBr): vmax = 3366, 2962, 2926, 2853, 1613, 1513, 1463, 1384, 1336, 1261, 1221, 1174, 1108, 1040, 832, 806 cm−1. HRESIMS: m/z 889.2857 [M + H]+ (calcd for C53H45O13, 889.2855). For 1D and 2D NMR data, see Table 1 and 2, and ESI.†![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) ε) = 204 (5.09), 284 (4.16) nm. CD (MeOH): λmax (Δε) = 206 (−21.51), 232 (+0.60), 251 (−3.70), 272 (−0.40), 294 (−3.26) nm; IR (KBr): vmax = 3365, 2962, 2926, 2854, 1613, 1512, 1450, 1384, 1261, 1225, 1174, 1101, 1035, 802 cm−1. HRESIMS: m/z 737.2379 [M + H]+ (calcd for C45H37O10, 737.2381). For 1D and 2D NMR data, see Table 1 and 2, and ESI.†
ε) = 204 (5.09), 284 (4.16) nm. CD (MeOH): λmax (Δε) = 206 (−21.51), 232 (+0.60), 251 (−3.70), 272 (−0.40), 294 (−3.26) nm; IR (KBr): vmax = 3365, 2962, 2926, 2854, 1613, 1512, 1450, 1384, 1261, 1225, 1174, 1101, 1035, 802 cm−1. HRESIMS: m/z 737.2379 [M + H]+ (calcd for C45H37O10, 737.2381). For 1D and 2D NMR data, see Table 1 and 2, and ESI.†![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) ε) = 204 (4.85), 284 (3.90) nm. CD (MeOH): λmax (Δε) = 206 (−15.30), 234 (−0.07), 251 (−2.55), 272 (−0.31), 294 (−2.28) nm; IR (KBr): vmax = 3343, 2957, 2926, 2854, 1705, 1614, 1513, 1455, 1384, 1261, 1228, 1175, 1105, 1036, 1004, 932, 833 cm−1. HRESIMS: m/z 737.2366 [M + H]+ (calcd for C45H37O10, 737.2381). For 1D and 2D NMR data, see Table 1 and 2, and ESI.†
ε) = 204 (4.85), 284 (3.90) nm. CD (MeOH): λmax (Δε) = 206 (−15.30), 234 (−0.07), 251 (−2.55), 272 (−0.31), 294 (−2.28) nm; IR (KBr): vmax = 3343, 2957, 2926, 2854, 1705, 1614, 1513, 1455, 1384, 1261, 1228, 1175, 1105, 1036, 1004, 932, 833 cm−1. HRESIMS: m/z 737.2366 [M + H]+ (calcd for C45H37O10, 737.2381). For 1D and 2D NMR data, see Table 1 and 2, and ESI.†Methylation of compound 1
Hopeachinol E (1, 10 mg) was allowed to react with K2CO3 (300 mg) and MeI (200 mg) in dry acetone under reflux for 12 h. Upon completion of the reaction, the resulting mixture was dried under a N2 stream, dissolved in CH2Cl2 (10 mL), washed with water (15 mL) and brine (15 mL), dehydrated with MgSO4, followed by in vacuo evaporation of the organic solvent, and then purified by Sephadex LH-20 column (CH2Cl2–MeOH 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) to give 1a (11 mg) as a white amorphous powder. 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3): 7.31 (2H, d, J = 8.0 Hz, H-2a/H-6a), 7.09 (2H, d, J = 8.0 Hz, H-2b/H-6b), 6.88 (2H, d, J = 8.0 Hz, H-3a/H-5a), 6.71 (2H, s, H-2/H-6), 6.64 (2H, d, J = 8.0 Hz, H-3b/H-5b), 6.52 (2H, br d, J = 8.0 Hz, H-2c/H-6c), 6.49 (1H, br s, H-14a), 6.43 (2H, br d, J = 8.0 Hz, H-3c/H-5c), 6.42 (1H, d, J = 2.0 Hz, H-12c), 6.36 (1H, d, J = 2.0 Hz, H-10c), 6.35 (1H, s, H-12b), 6.23 (1H, d, J = 3.0 Hz, H-7a), 5.94 (1H, br s, H-12a), 5.14 (1H, s, H-7b), 4.73 (1H, d, J = 9.0 Hz, H-7), 4.54 (1H, d, J = 6.5 Hz, H-8b), 4.52 (1H, d, J = 3.0 Hz, H-8a), 4.38 (1H, s, H-8c), 4.07 (1H, m, H-8), 3.88 (6H, s, OMe), 3.86 (3H, s, OMe), 3.81 (3H, s, OMe), 3.74 (3H, s, OMe), 3.71 (3H, s, OMe), 3.69 (3H, s, OMe), 3.68 (3H, s, OMe), 3.66 (3H, s, OMe), 3.52 (1H, d, J = 6.5 Hz, H-7c), 3.23 (3H, s, OMe), 3.11 (1H, dd, J = 16.0, 5.5 Hz, H-9), 2.77 ppm (1H, dd, J = 16.0, 9.0 Hz, H-9). HRESIMS: m/z: found 1023.3974, calcd. for C61H60O13Na, 1023.3926 [M + Na]+.
1) to give 1a (11 mg) as a white amorphous powder. 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3): 7.31 (2H, d, J = 8.0 Hz, H-2a/H-6a), 7.09 (2H, d, J = 8.0 Hz, H-2b/H-6b), 6.88 (2H, d, J = 8.0 Hz, H-3a/H-5a), 6.71 (2H, s, H-2/H-6), 6.64 (2H, d, J = 8.0 Hz, H-3b/H-5b), 6.52 (2H, br d, J = 8.0 Hz, H-2c/H-6c), 6.49 (1H, br s, H-14a), 6.43 (2H, br d, J = 8.0 Hz, H-3c/H-5c), 6.42 (1H, d, J = 2.0 Hz, H-12c), 6.36 (1H, d, J = 2.0 Hz, H-10c), 6.35 (1H, s, H-12b), 6.23 (1H, d, J = 3.0 Hz, H-7a), 5.94 (1H, br s, H-12a), 5.14 (1H, s, H-7b), 4.73 (1H, d, J = 9.0 Hz, H-7), 4.54 (1H, d, J = 6.5 Hz, H-8b), 4.52 (1H, d, J = 3.0 Hz, H-8a), 4.38 (1H, s, H-8c), 4.07 (1H, m, H-8), 3.88 (6H, s, OMe), 3.86 (3H, s, OMe), 3.81 (3H, s, OMe), 3.74 (3H, s, OMe), 3.71 (3H, s, OMe), 3.69 (3H, s, OMe), 3.68 (3H, s, OMe), 3.66 (3H, s, OMe), 3.52 (1H, d, J = 6.5 Hz, H-7c), 3.23 (3H, s, OMe), 3.11 (1H, dd, J = 16.0, 5.5 Hz, H-9), 2.77 ppm (1H, dd, J = 16.0, 9.0 Hz, H-9). HRESIMS: m/z: found 1023.3974, calcd. for C61H60O13Na, 1023.3926 [M + Na]+.
Preparation of the (S)- and (R)-MTPA esters (1b and 1c) of compound 1a
To two separate solutions of compound 1a (2.0 mg) in pyridine (1 mL) with DMAP (4N,N-dimethylaminopyridine, 1.0 mg), R- and S-MTPA chloride (10 μL) were respectively added. The mixture was allowed to react for 12 h at rt and then quenched by the addition of CH3OH (100 μL). The acylation products (1b and 1c) were purified by reversed-phase HPLC (MeOH–H2O, 92![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 8). S-(1b) and R-MTPA esters (1c) were eluted at the retention times of 15.6 and 16.8 min, respectively. The 1H chemical shifts around the stereocenters of 1b and 1c were assigned unequivocally by 1H NMR and COSY analyses. S-MTPA ester (1b): 1H NMR (selected signals, 400 MHz, CDCl3): 6.58 (2H, s, H-2/H-6), 6.47 (2H, br d, J = 8.8 Hz, H-2c/H-6c), 6.42 (1H, d, J = 2.4 Hz, H-12c), 6.38 (2H, br d, J = 8.8 Hz, H-3c/H-5c), 6.36 (1H, d, J = 2.4 Hz, H-10c), 5.66 (1H, m, H-8), 5.11 (1H, s, H-7b), 4.93 (1H, d, J = 8.4 Hz, H-7), 4.50 (1H, d, J = 6.8 Hz, H-8b), 4.33 (1H, s, H-8c), 3.42 (1H, d, J = 6.8 Hz, H-7c), 3.18 (1H, dd, J = 16.0, 5.6 Hz, H-9), 2.97 ppm (1H, dd, J = 16.0, 9.2 Hz, H-9); ESIMS m/z 1239.4 [M + Na]+. R-MTPA ester (1c): 1H NMR (selected signals, 400 MHz, CDCl3): 6.69 (2H, s, H-2/H-6), 6.43 (1H, d, J = 2.4 Hz, H-12c), 6.38 (2H, br d, J = 8.8 Hz, H-2c/H-6c), 6.36 (2H, br d, J = 8.8 Hz, H-3c/H-5c), 6.35 (1H, d, J = 2.4 Hz, H-10c), 5.53 (1H, m, H-8), 5.11 (1H, s, H-7b), 5.06 (1H, d, J = 8.4 Hz, H-7), 4.49 (1H, d, J = 6.8 Hz, H-8b), 4.30 (1H, s, H-8c), 3.42 (1H, d, J = 6.8 Hz, H-7c), 3.24 (1H, dd, J = 16.0, 5.6 Hz, H-9), 2.86 ppm (1H, dd, J = 16.0, 9.2 Hz, H-9); ESIMS m/z 1239.4 [M + Na]+.
8). S-(1b) and R-MTPA esters (1c) were eluted at the retention times of 15.6 and 16.8 min, respectively. The 1H chemical shifts around the stereocenters of 1b and 1c were assigned unequivocally by 1H NMR and COSY analyses. S-MTPA ester (1b): 1H NMR (selected signals, 400 MHz, CDCl3): 6.58 (2H, s, H-2/H-6), 6.47 (2H, br d, J = 8.8 Hz, H-2c/H-6c), 6.42 (1H, d, J = 2.4 Hz, H-12c), 6.38 (2H, br d, J = 8.8 Hz, H-3c/H-5c), 6.36 (1H, d, J = 2.4 Hz, H-10c), 5.66 (1H, m, H-8), 5.11 (1H, s, H-7b), 4.93 (1H, d, J = 8.4 Hz, H-7), 4.50 (1H, d, J = 6.8 Hz, H-8b), 4.33 (1H, s, H-8c), 3.42 (1H, d, J = 6.8 Hz, H-7c), 3.18 (1H, dd, J = 16.0, 5.6 Hz, H-9), 2.97 ppm (1H, dd, J = 16.0, 9.2 Hz, H-9); ESIMS m/z 1239.4 [M + Na]+. R-MTPA ester (1c): 1H NMR (selected signals, 400 MHz, CDCl3): 6.69 (2H, s, H-2/H-6), 6.43 (1H, d, J = 2.4 Hz, H-12c), 6.38 (2H, br d, J = 8.8 Hz, H-2c/H-6c), 6.36 (2H, br d, J = 8.8 Hz, H-3c/H-5c), 6.35 (1H, d, J = 2.4 Hz, H-10c), 5.53 (1H, m, H-8), 5.11 (1H, s, H-7b), 5.06 (1H, d, J = 8.4 Hz, H-7), 4.49 (1H, d, J = 6.8 Hz, H-8b), 4.30 (1H, s, H-8c), 3.42 (1H, d, J = 6.8 Hz, H-7c), 3.24 (1H, dd, J = 16.0, 5.6 Hz, H-9), 2.86 ppm (1H, dd, J = 16.0, 9.2 Hz, H-9); ESIMS m/z 1239.4 [M + Na]+.
Cytotoxic activity assay
Compound 1–7 were evaluated for cytotoxicity against four cell lines, HCT116 (human colon cancer), MDA-MB-231 (human breast cancer), SMMC-7721 (human hepatic carcinoma), HepG2 (human hepatic carcinoma) (all from the Jiangsu Provincial Center for Disease Prevention and Control), using the MTT [3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide] colorimetric method.15 Doxorubicin HCl (Sigma-Aldrich) was used as a positive control, and the medium without compounds as a negative control in the bioassay.Acknowledgements
This work was cofinanced by the NSFC (81172948, 81121062 and 21132004) and 863 project (2013AA092903).Notes and references
- J. R. Zgoda-Pols, A. J. Freyer, L. B. Killmer and J. R. Porter, J. Nat. Prod., 2002, 65, 1554–1559 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. Ito, T. Tanaka, M. Iinuma, K. Nakaya, Y. Takahashi, R. Sawa, J. Murata and D. Darnaedi, J. Nat. Prod., 2004, 67, 932–937 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- E. K. Seo, H. Chai, H. L. Constant, T. Santisuk, V. Reutrakul, C. W. W. Beecher, N. R. Farnsworth, G. A. Cordell, J. M. Pezzuto and A. D. Kinghorn, J. Org. Chem., 1999, 64, 6976–6983 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. A. G. P. Gunawardana, S. Sotheeswaran, M. U. S. Sultanbawa, S. Surendrakumar and P. Bladon, Phytochemistry, 1986, 25, 1498–1500 CrossRef.
- M. A. Shibata, Y. Akao, E. Shibata, Y. Nozawa, T. Ito, S. Mishima, J. Morimoto and Y. Otsuki, Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol., 2007, 60, 681–691 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. Ito, Y. Akao, T. Tanaka, M. Iinuma and Y. Nozawa, Biol. Pharm. Bull., 2002, 25, 147–148 CAS.
- K. S. Huang, M. Lin and G. F. Cheng, Phytochemistry, 2001, 58, 357–362 CrossRef CAS.
- J. R. Dai, Y. F. Hallock, J. H. Cardellina II and M. R. Boyd, J. Nat. Prod., 1998, 61, 351–353 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. Yan, T. Wang, W. Wei, N. Jiang, Y. H. Qin, R. X. Tan and H. M. Ge, Planta Med., 2012, 78, 1015–1019 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. M. Ge, W. H. Yang, Y. Shen, N. Jiang, Z. K. Guo, Q. Luo, Q. Xu, J. Ma and R. X. Tan, Chem.–Eur. J., 2010, 16, 6338–6345 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. Lee, M. Cuendet, J. S. Vigo, J. G. Graham, F. Cabieses, H. H. S. Fong, J. M. Pezzuto and A. D. Kinghorn, Org. Lett., 2001, 3, 2169–2171 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. Tanaka, T. Ito, K. Nakaya, M. Iinuma and S. Riswan, Phytochemistry, 2000, 54, 63–69 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. H. Qin, J. Zhang, J. T. Cui, Z. K. Guo, N. Jiang, R. X. Tan and H. M. Ge, RSC Adv., 2011, 1, 135–141 RSC.
- T. Kusumi, Y. Fujita, I. Ohtani and H. Kakisawa, Tetrahedron Lett., 1991, 32, 2923–2926 CrossRef CAS.
- R. Menicagli, S. Samaritani, G. Signore, F. Vaglini and L. D. Via, J. Med. Chem., 2004, 47, 4649–4652 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. Bai, M. Yamaki and S. Takagi, Phytochemistry, 1998, 47, 1125–1129 CrossRef CAS.
- J. M. Hu, J. J. Chen, H. Yu, Y. X. Zhao and J. Zhou, J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res., 2008, 10, 647–651 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
Footnote |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available: 1D and 2D NMR spectra of compounds 1–7. See DOI: 10.1039/c4ra03371j |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 |