Effects of fluorine ions on the formation and photocatalytic activities of SnO2 nanoparticles with small sizes
Abstract
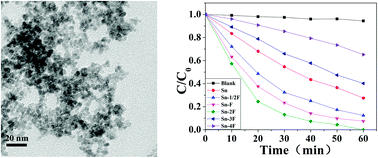
SnO2 nanoparticles with small sizes were synthesized by a simple hydrothermal route with different dosages of fluorine ions. These nanoparticles all showed a typical rutile phase and excessive dosage of fluorine ions would result in other crystallographic phases. The average diameters of the as-prepared products were all smaller than 4 nm. The introduction of fluorine ions had little influence on the morphologies and crystallite sizes, but enhanced the crystallization of the rutile phase and promoted the growth of SnO2 crystallites. XPS patterns showed that some introduced fluorine ions were physically adsorbed on the surface of SnO2 crystals, but not doped in the lattice. The photocatalytic activities were tested by photodecomposition of Rhodamine B (RhB) under a 300 W high-pressure mercury lamp. The results indicated that a suitable amount of fluorine ions on the surface of SnO2 nanoparticles caused significant enhancement of their photocatalytic activities.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...