A novel method to determine the concentration of VOCs at atmospheric pressure
Haiyan
Han
*ab,
Chengyin
Shen
a,
Yannan
Chu
a,
Tao
Chang
b,
Feng
Liu
b and
Hu
Li
c
aLaboratory of Environmental Spectroscopy, Anhui Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics Chinese Academy of Sciences, Hefei 230031, China. E-mail: hanhy0226@163.com
bCollege of Science, Hebei University of Engineering, Handan 056038, China
cCollege of Science, Anhui Universityof Science and Technology, Huainan 232001, China
First published on 11th February 2014
Abstract
A novel method to detect the concentration of electronegative VOCs based on the electron attachment rate at atmospheric pressure, through negative discharge in an ion drift tube, is introduced. When the carrier and drift gas in the drift tube are all high-purity nitrogen, electrons are formed by a negative discharge in the ion source, and are injected into the drift region through the shutter grid. When the electronegative sample molecules are continuously introduced into the drift tube from one end, the neutral molecules are ionized through a collision and capture process with the counterflowing swarm of electrons in the drift region. The electron swarm is exponentially diluted as it travels in the drift region. As a result, negative ions are formed in the drift region and a tail appears in the ion mobility spectrum. These spectra include information such as the intensity of the ions and electrons, the drift time, analyte concentration, the electron capture rate etc. The sample concentration can be calculated using the relative equation including information from the spectrum. As examples, in this work the concentration of electronegative samples of CCl4, CHCl3, and 1,1,1-C2H3Cl3 are studied when the electron energy is about 0.54 eV. The sample concentrations obtained in the experiment using this method are in good agreement with the initial concentrations created using a syringe pump. The comparison shows that the process of utilizing electron capture information to determine concentration is effective. This study provides a novel method to determine the concentrations of VOCs at atmospheric pressure.
1. Introduction
Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) have been one of the major sources of environmental pollution throughout the past century.1 The real time monitoring of the type and concentration of toxic and hazardous VOCs in the environment has become more and more important.2,3 The conventional gas chromatography-mass spectrometry method is valid in the determination of VOCs. However, this technique requires time-consuming gas collection, preconcentration, extraction and separation of the samples prior to gas chromatography and mass spectrometry analysis,4 which makes it difficult for the gas chromatography-mass spectrometry technique to carry out real time monitoring on-site. Besides, mass spectrometry instruments must work in a vacuum, and the whole gas chromatography-mass spectrometry system is bulky and expensive.In recent decades, ion mobility spectrometry (IMS) has been a sensitive analytical technique for the detection of VOCs under atmospheric pressure. IMS was first introduced in the early 1970s.5,6 The principle of IMS is based on determining the drift velocities attained by ionized sample molecules in the weak electric field of a drift tube at atmospheric pressure.7,8 In an IMS drift tube, product ions formed in the reaction region drift towards a detector under the influence of the electric field in the presence of a neutral buffer gas. Different ions migrate through the drift tube at different movement velocities, thus they can be separated. The main advantages of IMS instruments are their high sensitivity, small size, and operation at atmospheric pressure, which make IMS widely applied in many fields, such as drugs and explosives detection,9,10 environment pollution monitoring,11,12 disease diagnosis,13,14 structure analysis of clusters15,16 and biomolecular research.17,18
Most studies of IMS focus on different ionization sources,19,20 reduced mobility,21,22 resolution power,23,24 limit of detection25,26 and analyte categories.9–18 But studies on the measurement of analyte concentration are not as rich as in other areas of research into IMS. Because the concentration of the analyte is difficult to determine with the IMS technique, related research is seldom reported. Most IMS processes for the detection of analyte concentration are achieved through the comparison of ion intensities, between a known concentration and an unknown concentration. In 1995, Thomas et al.27 detected ammonia thermally purged from an aqueous sample stream into the IMS instrument through a silicone membrane. They detected the product ion intensities at 4 different known concentrations, to acquire a calibration curve for the IMS apparatus. By comparing the ion intensities of the product ions with the calibration curve, the analyte concentration could be obtained.
The most frequently used method to obtain calibration curves for IMS is using the exponential dilution flask (EDF) device, which is well known as a sample introduction system. In this method, a known amount of sample is introduced into a vessel and the vessel is then continuously flushed with carrier gas. The outlet analyte concentration is decreased exponentially by dilution using a carrier gas (such as air or nitrogen) with a constant flow rate. The volume of the flask, the flow rate of the carrier gas, and the volume of the syringe can be adjusted to generate a gaseous standard concentration in the appropriate concentration range. The exponential dilution flask device is often used to obtain the detection limits of IMS.28–31
The method to obtain analyte concentration through the comparison of a standard concentration with an unknown concentration is not completely credible. The standard concentration curve can become inappropriate when the experiment conditions or device structure is changed; for example, the temperature, pressure, electric field, the length of drift tube, the shape of the electrode etc. So the standard concentration curve must be recalibrated when the parameters of the conditions or structure are changed.
In this work, we advance a new method to obtain the electronegative analyte concentration using negative corona discharge mode IMS (NCD-IMS). This method is based on the electron attachment reaction between electrons and the neutral analyte. When the sample molecules enter the drift tube carried by drift gas, the ion mobility spectrum is correlated with the ion velocity, the electron velocity, the electron attachment rate, and the sample concentration in the drift tube. If the electron attachment rate constant of the sample is known at a fixed electron energy, the sample concentration can be calculated using a correlative equation. If the electron attachment rate constant of the sample is unknown, it can be detected first using the apparatus described in the following sections.
2. Experiments and methods
2.1 Equipment and conditions
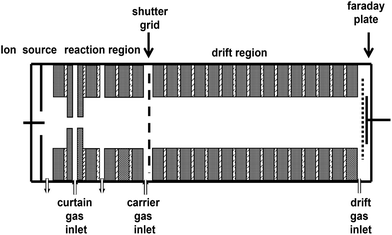
The IMS apparatus with continuous corona discharge as the ionization source that is used in this work is schematically shown in Fig. 1. The experimental apparatus mainly consists of the IMS drift tube and the detection system. The whole drift tube has a length of 20 cm with an internal diameter of 4 cm, and consists of an ion source, reaction region (with length of 5 cm), drift region (with length of 11 cm), ion shutter grid and detection region. The corona discharge ionization source has a point-to-plane geometry, and a typical discharge voltage on the corona needle is around 3 kV. The electrode rings of the drift tube are insulated from each other by 1 mm thick Teflon spacers, and a high voltage is distributed through a series of resistors on these rings so that a uniform electric field along the axis of the drift tube is formed. In order to detect the concentration of samples at different electron energies, the electric field strength in the drift region can be adjusted in the range of 200–500 V cm−1. If a certain concentration of the high electronegativity sample molecules diffuses into the discharge region, the corona discharge may be quenched. There is a special electrode ring called the curtain ring32 located after the discharge plate, with a hole of about 0.8 mm in the center of the electrode ring. Nitrogen gas, called curtain gas, enters the tube between the discharge plate and the curtain electrode ring to provide the diffusion of the sample molecules into the discharge region. If the analyte is injected into the drift tube from the reaction region by the carrier gas, the product ions form through an electron capture process in the reaction region. If the analyte is injected into the drift tube from the end of the drift region by the drift gas, parts of the analyte produce ions through an electron capture process in the drift region. There is an ion shutter grid between the reaction region and the drift region to either allow or prevent the entrance of ions into drift region. This consists of two series of parallel wires biased to a potential voltage. It can create an orthogonal field relative to the drift field and can be switched periodically to inject pulses of ions into the downstream drift tube. The pulse width of the ion shutter grid can be varied from 100 μs to 300 μs. There is a Faraday plate at the end of the drift tube to collect the ion current. The current signal, amplified by the amplifier, is fed to the computer data processing system. The ion current versus the drift time is recorded as the ion mobility spectrum. In this method, the sample concentration can be calculated and confirmed through the information provided by the spectrum at a fixed electron energy.2.2 Introduction system and samples
A linear syringe pump apparatus is used to get different concentrations of the sample. A mixed gas, containing sample-saturated vapor and pure nitrogen, is pulled into the glass micro-injector with a volume from 1 μl to 50 μl and injected into the drift gas by the syringe pump. The final concentration of the sample in the drift region can be calculated by the syringe pump’s linear movement speed, the initialization concentration, and the flow rate of the drift gas. The different sample concentrations can be obtained by adjusting the syringe pump speed, the glass micro-injector volume and the flow rate of the drift gas.The drift and carrier gases used in these experiments are all high pure nitrogen gas with a purity of 99.9995% (Nanjing Special Gas Co., Ltd, Nanjing, China), and all of the chemical reagents are analytical reagents with a purity of above 99.7% (Shanghai Haohua Chemical Co., Ltd, Shanghai, China).
2.3 Theory and method
In the IMS tube, a swarm of electrons is engendered by the corona discharge ion source, and this enters the drift tube and moves to the collecting plate under the influence of a uniform electric field in nitrogen gas. When the electronegative sample molecules are continuously introduced into the drift gas from the end of the drift tube, the neutral molecules M can capture electrons and negative product ions M− are consequently generated in the drift region, according to reaction (1).| e− + M → M− | (1) |
The electron attachment rate of this reaction can be written as eqn (2) according the definition relating to the chemical reaction equation.
 | (2) |
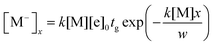 | (3) |
| x = (td − t)vd | (4) |
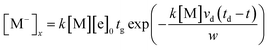 | (5) |
This equation shows that the intensity of the M− ions generated in the drift region varies with time when neutral molecules are continuously introduced into the drift gas. This can form a tail signal before the corresponding ion peak. The logarithm of this tail signal should be a straight line. According this phenomenon, the slope of this line can be obtained through taking the logarithm of eqn (5):
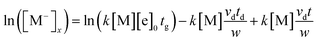 | (6) |
From eqn (6), it can been seen that the ion current intensity versus drift time for the tail before the corresponding ion peak is a straight line, with a slope proportional to the rate constant. The first two terms are the intercept of the straight line and the last term is the slope of the line. So the slope of the line S can be described by eqn (7):
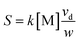 | (7) |
The concentration of neutral molecules [M] can be calculated through a change to eqn (7), forming eqn (8):
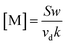 | (8) |
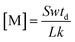 | (9) |
In order to calculate the concentration of the sample, the rate constant k of M with electrons is required. If the drift time td, the electron velocity w and the electron attachment rate constant k are known, the sample concentration can be easily obtained on the basis of eqn (9). But in fact, only a small number of sample rate constants have been determined and reported. When the rate constant of the samples is unknown, it is necessary to first calculate the constant before determining the concentration. In the process of detecting the rate constant, the sample concentration can be obtained using the linear syringe pump apparatus, as described in the introduction. When the above parameters are substituted into eqn (9), the concentration [M] can then be easily obtained.
3. Results and discussion
3.1 Electron peak
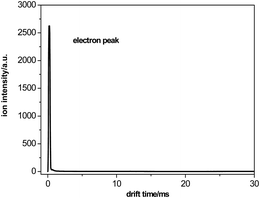
In pure nitrogen, the electrons are effectively produced through a negative corona discharge at the ion source. In the absence of sample molecules, the electrons can pass through the reaction region practically without chemical reactions. Because of their small mass, the electrons exhibit a distinct peak near zero drift time in the spectrum obtained at the end of the collection plate; this spectrum is illustrated in Fig. 2. The intensity of the electron peak varies with the voltage of the ion source, the pulse width of ion shutter grid, the electric field of the drift tube etc.3.2 Ion mobility spectra of the samples
In this section, we use carbon tetrachloride CCl4 as the example to demonstrate the experimental process. It is well known that the low energy electron attachment reaction to CCl4 is a dissociative process, which dissociates to yield a negative halide Cl− ion together with a neutral fragment as reaction (10).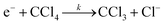 | (10) |
When the sample molecules enter the drift tube from the reaction region, neutral CCl4 molecules are ionized through the capturing electrons, becoming Cl− ions through reaction (10) in the reaction region. The Cl− ions pass through the shutter grid during the opening time as an ion cloud with a width of around 300 μs. These ions are collected by the Faraday plate at the end of the drift region to get the according spectrum. In the mobility spectrum, there is a new ion peak, aside from the electron peak, which appears at around 11 ms. This new peak corresponds to a Cl− ion domain, as trace (a) illustrates in Fig. 3. The background in this spectrum is almost zero and the Cl− ions are the dominant anion in this process.
 | ||
| Fig. 3 The ion mobility spectrum of CCl4. (a) The sample is introduced into the ionization region and (b) the sample is introduced into the drift region. | ||
When a certain concentration of the sample is continuously carried into the drift region from the end of the drift tube by the drift gas, the electrons are captured by the electron-attaching molecules when traveling within the drift gas. Negative ions are consequently generated in the drift region. Eqn (3) shows that the negative ions are exponentially diluted as they travel in the drift region, which causes a tail to arise at the edge of the Cl− peak in the mobility spectrum. This tail corresponds to the Cl− ions produced at different points in the drift region, as the molecules move towards the shutter grid. The shape of this tail reflects the distribution of the Cl− ions in the drift region, as trace (b) presents in Fig. 3.
According to eqn (6), when the sample molecules enter the drift tube from the end side, the variation of the natural logarithm of the ion intensity of this tail plot with the drift time is expected to be a straight line, as illustrated in Fig. 4. The relevancy of the logarithm of intensity and the fit line is about 0.9989.
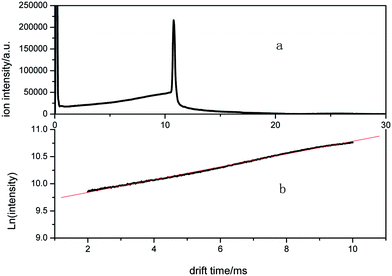 | ||
| Fig. 4 The ion mobility spectrum when the sample is introduced into the drift region and the natural logarithm of the ion intensity of the tail before the Cl− peak. | ||
3.3 Detection of attachment rate constant
In order to obtain the sample concentration, the electron attachment rate constant must be a known value as described in eqn (9). When the rate constant of the sample is unknown, it can be detected first.In order to get electron attachment rate constants at different electron energies, the sample is detected at different drift electric fields from 200 to 500 V cm−1 when entering into the drift tube from the end side, at the same concentration. The spectra are illustrated in Fig. 5. It can be seen that the ion drift times become shorter, and the ion intensity is enhanced, when the electric field is increased. The tails at the edge of the Cl− peaks are obvious. The natural logarithms of the tail plots varying with drift time are illustrated in Fig. 6. The electron attachment rate constant of CCl4 can be calculated using the slope of these lines according to eqn (7). In this equation, the ion velocity td can be obtained through the ratio of the drift length with the drift time of the Cl− ions, and the electron velocity w varying with the electron energy distribution can be obtained from ref. 33. Using this method, the electron attachment rate constants of CCl4 at different electron energies can be obtained. The rate constant curve variation obtained in this work is given in Table 1. It can be seen that the electron attachment rate is a function of the electron energy; the rate exponentially decays from 6.24 × 10−8 to 2.65 × 10−8 cm3 s−1 as the electron energy grows from 0.29 to 0.64 eV in the drift region. The rate constant values of CCl4 obtained in this work are compared with other reported data acquired by a different method in ref. 34, as illustrated in Table 1. From Table 1, it can be seen that data obtained in this work are in good agreement with the reference data. This result proves that finding the value of the electron attachment rate constant is feasible, which ensures that the subsequent section, which focuses on detecting concentration, is credible.
 | ||
| Fig. 5 The ion mobility spectra when the sample is introduced into the drift region at various electric fields. | ||
 | ||
| Fig. 6 Logarithms of the signal intensity for the negative ion tail before Cl− when the sample is introduced into the drift region at various electric fields. | ||
| Electron energy/(eV) | Electron attachment constants k | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CCl4/(10−8 cm3 s−1) | CHCl3/(10−8 cm3 s−1) | 1,1,1-C2H3Cl3/(10−9 cm3 s−1) | ||||
| This work | Ref. 34 | This work | Ref. 35 | This work | Ref. 34 | |
| 0.29 | 6.24 | 6.35 | 1.26 | 1.24 | 8.39 | 8.12 |
| 0.32 | 5.53 | 5.87 | 1.28 | 1.26 | 8.06 | 7.95 |
| 0.36 | 4.96 | 5.27 | 1.27 | 1.27 | 7.65 | 7.54 |
| 0.39 | 4.69 | 4.90 | 1.28 | 1.26 | 6.74 | 6.72 |
| 0.43 | 4.19 | 4.72 | 1.22 | 1.24 | 6.42 | 6.48 |
| 0.47 | 3.93 | 4.31 | 1.20 | 1.20 | 5.94 | 6.04 |
| 0.51 | 3.61 | 4.07 | 1.14 | 1.16 | 5.74 | 5.67 |
| 0.54 | 3.38 | 3.62 | 1.09 | 1.12 | 5.57 | 5.48 |
| 0.57 | 3.13 | 3.23 | 1.06 | 1.07 | 5.38 | 5.29 |
| 0.61 | 2.91 | 2.95 | 1.02 | 1.04 | 4.89 | 4.96 |
| 0.64 | 2.65 | 2.76 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 4.67 | 4.75 |
3.4 Sample concentration detection
Samples at different concentrations can be prepared by the linear syringe pump apparatus. When the syringe pump speed, the micro-injector volume and the flow rate of the carrier gas are fixed, the sample concentration carried in the drift tube can be kept steady. In order to test the capability of sample concentration detection, the samples are prepared at different concentrations from 5 to 300 ppb when the electron energy is at 0.54 eV. The sample CCl4 at different concentrations enters the drift tube from the end side and the relative spectra are obtained. Several logarithm lines of the tails before Cl− ions in these spectra at several different concentrations are illustrated as examples in Fig. 7. According to eqn (9), the slope of the lines should become greater as the sample concentration increases, because the electron attachment rates are nearly constant at around 3.38 × 10−8 cm3 s−1, as displayed in Fig. 7. This result proves that the electron attachment rate constant is not relative to the concentration of the sample but to the energy of the electrons in the drift region. According to eqn (9), the calculated concentrations can vary from 5 to 300 ppb. The final calculated results are illustrated in Fig. 8. | ||
| Fig. 7 The logarithm lines of the tails before Cl− ions at different concentration when the drift field is 410 V cm−1. | ||
In this figure, the horizontal axis (x axis) describes the sample concentrations at different values prepared using the apparatus, and the vertical axis (y axis) describes the sample concentrations at different calculated values according to eqn (9). A line of y = x is added in Fig. 8, which can offer a standard of comparison between the x and y values. From the results, the data obtained through measurement and calculation in this work are in good agreement with the data prepared initially. However, at a low concentration range, the plots are under the y = x line, which indicates that the calculation results are a little less than the prepared concentrations at this range. This may be due to adsorption of the pipeline at low concentrations. At a high concentration range, the plots are above the y = x line, which indicates that the calculation results are a little higher than the prepared concentrations at this range. This may be due to diffusion of the high concentration samples towards the ionization source.
To further investigate the feasibility of this method, the other two samples trichloromethane CHCl3 and trichloroethane 1,1,1-C2H3Cl3 were also determined. The electron attachment rate constants of the two samples were obtained as the electron energy grew from 0.29 to 0.64 eV. The measurement data and the reference data of the two samples are shown in Table 1. By comparing the two, it can be seen that the measurement results are consistent with the reference data. The concentrations of the two samples were also determined, as shown in Fig. 8. The detection ranges of CHCl3 and 1,1,1-C2H3Cl3 are 70–520 ppb and 110–1400 ppb respectively. From Fig. 8, the detection concentrations are in agreement with the preparation concentrations, which further shows that this method is feasible.
4. Conclusions
In this work, a novel method is introduced to measure electronegative VOC concentrations, based on the dissociative electron attachment rate at atmospheric pressure, using NCD-IMS. During the detection process, the electron attachment rate constants are successfully obtained from tails in the negative ion mobility spectra, when the sample is introduced into the drift region. The sample electron attachment rate constant is invariable at a fixed electron energy. Using this characteristic, the sample concentration can be calculated from the corresponding spectrum when the electron energy is fixed. The concentrations of three electronegative samples CCl4, CHCl3, and 1,1,1-C2H3Cl3 are studied as examples in this article, using the acquired rate constants. The sample concentrations obtained in the experiment using this method agree well with the preparation concentrations obtained using a syringe pump at different measurement ranges. This method is proved accurate and feasible, and provides a novel means to determine the concentrations of VOCs in the environment. Since there is no need for a vacuum in this technique, the use of IMS for such studies is simple, rapid, and inexpensive compared to other techniques.Halogenated compounds normally produce halide ions via a dissociative electron capture reaction. From the results of this work, it can be seen that the product ions of three samples CCl4, CHCl3, and 1,1,1-C2H3Cl3 are all Cl− ions. The concentrations of a single sample can be easily obtained using this method, because of the different electron attachment rate constants. However, in the case of halogenated compounds with the same halogen, the samples normally produce the same halide ions via a dissociative electron capture reaction. Therefore, it is difficult to distinguish halogenated compounds with the same halogen with a single IMS apparatus. Therefore a pre-separation technique such as gas chromatography is required for analysis of the mixture in the case of halogenated compounds containing the same halogen. Another method to eliminate the influence of the dissociative reaction is to use ion molecule reaction rates instead of the ambient electron capture reaction rates. This needs further research to make it feasible.
Acknowledgements
The work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 20907054), the Natural Science Foundation of Hebei Province (no. B2012402064, B2012402001, A2012402002), the Science Research and Development Foundation of Handan City (no. 1223109092-6) and the Natural Science Research Project in the Universities of Anhui Province (no. KJ2012Z080).References
- P. R. Veres, P. Faber, F. Drewnick, J. Lelieveld and J. Williams, Atmos. Environ., 2013, 77, 1052 CrossRef PubMed.
- Z. Boltic, N. Ruzic, M. Jovanovic, M. Savic, J. Jovanovic and S. Petrovic, J. Cleaner Prod., 2013, 44, 123 CrossRef PubMed.
- S. P. Chen, W. T. Liu, C. F. Ouyang, J. S. Chang and J. L. Wang, Atmos. Environ., 2014, 84, 1 CrossRef PubMed.
- T. M. Allen, T. M. Falconer and M. E. Cisper, Anal. Chem., 2001, 73, 4830 CrossRef.
- M. J. Cohen and F. W. Karasek, J. Chromatogr. Sci., 1970, 8, 330 CrossRef.
- H. H. Hill, W. F. Siems, R. H. Stlouis and D. G. McMinn, Anal. Chem., 1990, 62, A1201 CrossRef.
- R. H. Stlouis and H. H. Hill, Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem., 1990, 21, 321 CrossRef.
- R. P. Erickson, A. Tripathi, W. M. Maswadeh, A. P. Snyder and P. A. Smith, Anal. Chim. Acta, 2006, 556, 455 CrossRef PubMed.
- J. R. Verkouteren and J. L. Staymates, Forensic Sci. Int., 2011, 206, 190 CrossRef PubMed.
- M. Tabrizchi and V. Ilbeigi, J. Hazard. Mater., 2010, 176, 692 CrossRef PubMed.
- I. M. Sillero, E. A. Herrador, S. Cardenas and M. Valcarcel, TrAC, Trends Anal. Chem., 2011, 30, 677 CrossRef PubMed.
- P. Shahdousti and N. Alizadeh, Anal. Chim. Acta, 2011, 684, 67 CrossRef PubMed.
- V. Ruzsanyi, J. I. Baumbach, S. Sielemann, P. Litterst, M. Westho and L. Freitag, J. Chromatogr. A, 2005, 145, 1084 Search PubMed.
- Z. Karpas, B. Tilman, R. Gdalevsky and A. Lorber, Anal. Chim. Acta, 2002, 155, 463 Search PubMed.
- E. Oger, R. Kelting, P. Weis, A. Lechtken, D. Schooss, N. R. M. Crawford, R. Ahlrichs and M. M. Kappes, J. Chem. Phys., 2009, 130, 124305 CrossRef PubMed.
- P. Weis, Int. J. Mass Spectrom., 2005, 1, 245 Search PubMed.
- B. C. Bohrer, S. I. Mererbloom, S. L. Koeniger, A. E. Hilderbrand and D. E. Clemmer, Rev. Anal. Chem., 2008, 1, 293 CrossRef PubMed.
- C. M. Benton, C. K. Lim, C. Moniz and D. J. L. Jones, Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom., 2012, 26, 480 CrossRef PubMed.
- A. Rahmanian, H. S. Ghaziaskar and T. Khayamian, J. Chromatogr. A, 2013, 1272, 126 CrossRef PubMed.
- K. M. Rosciolia, X. Zhang, S. X. Li, G. H. Goetzb, G. Chengb, Z. L. Zhang, W. F. Siemsa and H. H. Hill, Int. J. Ion Mobility Spectrom., 2013, 336, 27 Search PubMed.
- C. S. Creaser and J. R. Griffiths, Anal. Chim. Acta, 2001, 436, 273 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Borsdorf, E. G. Nazarov and G. A. Eiceman, Int. J. Mass Spectrom., 2004, 232, 117 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- G. F. Verbeck, B. T. Ruotolo, K. J. Gillig and D. H. Russell, J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom., 2004, 15, 1320 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Sysoev, A. Adamov, J. Vildanoja, R. A. Ketoja, R. Kostiainen and T. Kotiaho, Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom., 2004, 18, 3131 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Z. Xie, S. Sielemann, H. Schmidt, F. Li and J. I. Baumbach, Anal. Bioanal. Chem., 2002, 372, 606 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. Pozzi, F. Pinelli, P. Bocchini and G. C. Galletti, Anal. Chim. Acta, 2004, 504, 313 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. R. M. Przybylko, C. L. P. Thomas, P. J. Anstice, P. R. Fielden, J. Brokenshire and F. Irons, Anal. Chim. Acta, 1995, 311, 77 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Sielemanna, J. I. Baumbacha, H. Schmidt and P. Pilzecker, Anal. Chim. Acta, 2001, 431, 293 CrossRef.
- T. Khayamian and M. Tabrizchi, Fresenius. J. Anal. Chem., 2001, 370, 1114 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Y. Han, H. M. Wang, H. H. Jiang, M. Stano, M. Sabo, S. Matejcik and Y. N. Chu, Chin. J. Chem. Phys., 2009, 22, 605 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Li, W. Q. Niu, H. M. Wang, C. Q. Huang, H. H. Jiang and Y. N. Chu, Spectrosc. Spectral Anal., 2012, 32, 29 CAS.
- M. Tabrizchi and A. Abedi, J. Phys. Chem. A, 2004, 108, 6319 CrossRef CAS.
- G. K. Jarvis, R. A. Kennedy and C. A. Mayhew, Int. J. Mass Spectrom., 2001, 205, 253 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Shimamori, Y. Tatsumi, Y. Ogawa and T. Sunagawa, J. Chem. Phys., 1992, 97, 6335 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. Sunagawa and H. Shimamori, Int. J. Mass Spectrom., 2001, 205, 285 CrossRef CAS.
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 |