Halide impact on emission of mononuclear copper(i) complexes with pyrazolylpyrimidine and triphenylphosphine†
Abstract
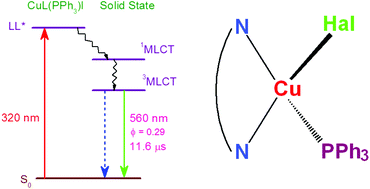
A series of mononuclear heteroleptic copper(I) halide complexes, [CuL(PPh3)X] (X = Cl, Br, I), based on 4-(3,5-diphenyl-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)-6-(piperidin-1-yl)pyrimidine (L) and triphenylphosphine, have been synthesized by reaction between CuX (X = Cl, Br, I), L and PPh3 in a molar ratio of 1/1/1 in MeCN solutions. The copper atom, showing the distorted tetrahedral environment, is bound by the N,N-chelating ligand L, triphenylphosphine and a halide ion. The complexes [CuL(PPh3)Cl] and [CuL(PPh3)Br] are isostructural. In CH2Cl2 solutions, L and the complexes [CuL(PPh3)X] (X = Cl, Br, I) display a luminescence band with λmax = 377 nm and a lifetime of 1.9 ns (ligand-based luminescence (LL*)). However, the complex [CuL(PPh3)I] has an additional weak luminescence band with λmax = 681 nm and a lifetime of 96 ns of 3MLCT origin. In the solid state, L shows the splitting of the luminescence band to λmax = 365 and 384 nm and a slight increase of the lifetime to 2.66 ns. Solid samples of the complexes [CuL(PPh3)X] demonstrate 3MLCT luminescence bands at 620 nm (X = Cl), 605 nm (X = Br) and 559 nm (X = I) with lifetimes in the range 3.6–11.2 μs, whereas the LL* band (377 nm) is absent. Quantum yields and rate constants of radiative and nonradiative processes were determined in CH2Cl2 solutions and in the solid state for all complexes. The luminescence quantum yield and lifetimes for the solid samples increase in the order [CuL(PPh3)Cl] < [CuL(PPh3)Br] < [CuL(PPh3)I]. This is due to the increase of radiative decay and simultaneous suppression of nonradiative decay. The complex [CuL(PPh3)I] shows a high quantum yield of 29.4% and an excited state lifetime of 11.2 μs.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...