Direct amine-functionalisation of γ-Fe2O3 nanoparticles
Abstract
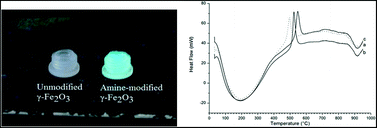
A novel and simple preparation of amine-modified γ-Fe2O3 nanoparticles is described. The presence of amine groups on the surface, instead of hydroxyl groups, will allow conjugation of biologically active molecules to the iron oxide nanoparticles without the need for a size increasing silica shell. Furthermore, the outer amine-layer increases the temperature of the γ-Fe2O3 to α-Fe2O3 structural transition in a similar way to previously reported cationic substitutions. This may suggest the formation of an oxide–nitride outer layer. Re-dispersion of the amine-modified γ-Fe2O3 nanoparticles led to the preparation of stable ferrofluids.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...