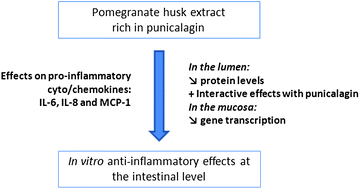
This study aimed at evaluating the anti-inflammatory properties of a pomegranate fruit husk (PomH) polyphenolic extract, rich in punicalagin, using Caco-2 cells, an in vitro model of human intestinal epithelium. Differentiated cells in bicameral inserts were pretreated or not with a PomH extract or punicalagin, as reference, at the apical side, representing the intestinal lumen. Inflammation was then induced with a cocktail of cytokines (Il-1β, TNFα and IFNγ) and LPS. After 24 h incubation, 3 pro-inflammatory markers, i.e., interleukin (IL)-6, IL-8 and monocyte chemoattractant protein (MCP)-1, were assayed both at their gene transcription (qRT-PCR) and secretion (ELISA) levels. As previously described, the pro-inflammatory cocktail significantly stimulated these 3 markers, at the gene transcript and secretion levels. In inflamed cells, a significant down-regulation of the transcription of the genes encoding IL-6 and MCP-1 was observed in the presence of the PomH extract or punicalagin, while IL-8 transcription was unaffected. Both treatments also decreased the amounts of the 3 proteins with dose-response effects, but only in the apical compartment. A lowered ELISA response was also observed when either IL-6, IL-8 or MCP-1 were mixed with punicalagin in a cell-free culture medium, indicating a direct molecular interaction. In conclusion, the punicalagin-rich PomH extract tested showed anti-inflammatory properties in the Caco-2 in vitro intestinal model. It acted both on the pro-inflammatory gene transcription and protein levels, the later phenomenon being possibly due to a direct molecular trapping. These data suggest that pomegranate husk could be an interesting natural source contributing to prevent intestinal chronic inflammation.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...