Metallacycle-mediated cross-coupling with substituted and electronically unactivated alkenes
Holly A.
Reichard
and
Glenn C.
Micalizio
*
The Department of Chemistry, The Scripps Research Institute, Scripps–Florida, 130 Scripps Way #3A2, Jupiter, FL 33458, USA. E-mail: micalizio@scripps.edu; Fax: +561 228 3092; Tel: +561 228 2463
First published on 15th November 2010
Abstract
This perspective surveys the history of – and recent advances in – metallacycle-mediated coupling chemistry of substituted alkenes. While the reaction of preformed metal–π complexes with ethylene was reported nearly 30 years ago, the generalization of this mode of bimolecular C–C bond formation to the regio- and stereoselective union of complex substrates has only recently begun to emerge. This perspective discusses early observations in this area, the challenges associated with controlling such processes, the evolution of a general strategy to overcome these challenges, and a summary of highly regio- and stereoselective convergent coupling reactions that are currently available via metallacycle-mediated cross-coupling of substituted alkenes.
 Holly A. Reichard | Holly A. Reichard received a BS in Chemistry from Penn State University in 2004. Shortly thereafter, she began graduate studies in the Department of Chemistry at Yale University, where she joined the laboratory of Professor Glenn C. Micalizio. After relocating with Professor Micalizio to the Department of Chemistry at The Scripps Research Institute, Scripps Florida, she completed her dissertation focused on titanium-mediated cross-coupling of unactivated π-systems and application to the leptomycin family of natural products. Recently, she joined Envoy Therapeutics as a medicinal chemist. |
 Glenn C. Micalizio | Glenn C. Micalizio obtained a PhD at the University of Michigan in 2001 under the supervision of Professor William R. Roush. After postdoctoral study as a Fellow of the Helen Hay Whitney Foundation at Harvard University in the laboratory of Professor Stuart L. Schreiber, he moved to Yale University where he began his independent academic career as an Assistant Professor in the Department of Chemistry (2003). In 2008, he was recruited to join the Department of Chemistry at The Scripps Research Institute as an Associate Professor. His research is focused on the development of new synthetic methods and application of these methods to chemical synthesis. |
1. Introduction
The chemical sciences are advancing at an impressive pace, with frequent reports describing novel patterns of reactivity and selectivity in organic chemistry. While contributions that impact synthesis at the tactical level are abundant, those that offer advances at the strategic level (via the establishment of novel bond constructions) are rare, yet have a unique and perhaps more significant impact on the evolution of chemical synthesis.1 Modern advances in this vein include asymmetric olefin oxidation,2 metal-catalyzed cross-coupling (Pd-, Ni- and Cu- catalysis),3 and olefin metathesis chemistry.4 While much recent attention has been given to the manner in which these processes proceed (i.e. reagent stoichiometry), their broad impact in chemical synthesis is arguably derived from the novel synthetic transformations that they define. It is from this perspective that the current review is written, presenting a brief history of – and recent advances in – metallacycle mediated cross-coupling of substituted alkenes.Bimolecular, or convergent, C–C bond formation defines the backbone of organic synthesis, and advances that provide new avenues for such bond construction can broadly impact strategic planning in chemical synthesis. It is widely accepted that points of convergency (enabled by such processes) in synthesis pathways greatly enhance efficiency and throughput, in part by decreasing the longest linear sequence of steps required to prepare a target. Despite their rather central role in chemistry, one can argue that only a few general modes of reactivity are typically exploited for such bond construction:
1. Nucleophilic substitution,
2. Nucleophilic addition to a polarized π-bond,
3. Cycloaddition,
4. Metal-catalyzed cross-coupling, and more recently,
5. Crossed olefin metathesis.
While carbometalation chemistry of alkenes and alkynes (Fig. 1A) could be considered as another mode of reactivity suitable to be included in this list, such processes are often significantly limited in substrate scope.5 This rather general statement is supported by the accepted difficulty associated with carbometalation of highly substituted and electronically unactivated π-systems (i.e. those that are not highly polarized), and the challenges associated with the control of site- and stereoselectivity in the C–C bond-forming event. Despite these barriers to utility, significant advances have been made in harnessing this mode of reactivity for the functionalization of alkynes.6 Unfortunately, similar success has not been realized in the related transformations of substituted and electronically unactivated alkenes. The focus of this Perspective is to present the potential utility of metallacycle-mediated bond construction for such transformations (Fig. 1B), outline a selected historical account of advances in the field, and conclude by highlighting a collection of synthetic methods that have emerged from our studies in this area (Fig. 2).
 | ||
| Fig. 1 Functionalization of electronically unactivated π-systems by carbometalation. | ||
 | ||
| Fig. 2 Examples of metallacycle-mediated coupling by way of olefin functionalization. | ||
2. Background and challenges
2.1. Initial observations in metal-centered [2 + 2 + 1] for alkene functionalization
An early example of metallacycle-mediated coupling of alkenes is the Pauson–Khand reaction, where treatment of a preformed Co–alkyne complex and a reactive alkene result in the formation of a cyclopentenone (Fig. 3).7 While this process was initially reported in the context of intermolecular annulation, the utility of the intramolecular reaction has far exceeded the bimolecular process in part due to challenges associated with controlling regioselection.8 That said, strategies are emerging to control a subset of intermolecular variations of this cyclopentenone annulation.9![Cyclopentene annulation via Co-centered [2 + 2 + 1].](/image/article/2011/SC/c0sc00394h/c0sc00394h-f3.gif) | ||
| Fig. 3 Cyclopentene annulation via Co-centered [2 + 2 + 1]. | ||
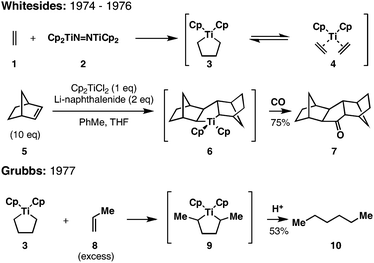
The development of related group IV metal-centered [2 + 2 + 1] chemistry for alkene functionalization soon followed. In 1974, Whitesides hypothesized that the reaction of ethylene with Cp2TiN![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) NTiCp2 (2) leads to an equilibrium mixture of a saturated titanacyclopentane (3) and the corresponding bis-ethylene complex (4) (Fig. 4).10 Two years later, he demonstrated the ability to dimerize alkenes (5) en route to cyclopentanones (7) through the in situreduction of Cp2TiCl2 with Li-naphthalenide, dimerizationvia formation of an intermediate metallacyclopentane (6), and carbonylation.11 Soon thereafter, Grubbs described a dimerization process that proceeds by exposure of a preformed metallacyclopentane (3) to an excess of a terminal olefin of interest (8).12 Overall, hydrocarbon products of homodimerization (10) result viaolefin exchange with the preformed titanacyclopentane 3.
NTiCp2 (2) leads to an equilibrium mixture of a saturated titanacyclopentane (3) and the corresponding bis-ethylene complex (4) (Fig. 4).10 Two years later, he demonstrated the ability to dimerize alkenes (5) en route to cyclopentanones (7) through the in situreduction of Cp2TiCl2 with Li-naphthalenide, dimerizationvia formation of an intermediate metallacyclopentane (6), and carbonylation.11 Soon thereafter, Grubbs described a dimerization process that proceeds by exposure of a preformed metallacyclopentane (3) to an excess of a terminal olefin of interest (8).12 Overall, hydrocarbon products of homodimerization (10) result viaolefin exchange with the preformed titanacyclopentane 3.
 | ||
| Fig. 4 Homodimerization via saturated metallacyclopentanes. | ||
While these initial reports documented the interesting behavior of metallacyclopentanes based on Cp2Ti, their apparent limitation to homodimerization of terminal or strained alkenes greatly constrained the potential impact of these transformations in synthetic organic chemistry.
A significant advance was described by Erker in 1979 that documented the ability to control this mode of reactivity for cross-coupling reactions of benzyne with terminal alkenes.13 As depicted in Fig. 5, mild heating of Cp2ZrPh2 (11) results in the formation of a benzyne-Zr complex (12) that, when exposed to a terminal alkene, undergoes cross-coupling to deliver a substituted metallaindane (13). Interestingly, exposure of this complex to strained or unhindered terminal alkenes results in an olefin exchange reaction, presumably viaregeneration of a reactive Zr-benzyne complex (12) and subsequent carbometalation (→ 14).
 | ||
| Fig. 5 Cross-coupling with alkenesvia metallacyclopentenes. | ||
The conclusion of this discussion, regarding the early development of metal-centered [2 + 2 + 1] chemistry as a means for cross-coupling of alkenes, is suitably focused on contributions from the Bercaw laboratory. After confirming the structure of a (Cp*)2Ti-ethylene complex by X-ray diffraction, Bercaw and co-workers demonstrated that this organometallic species is a viable intermediate for the generation of saturated metallacyclopentanes (17).14 Unfortunately, while insertion of ethylene is effective, related reactions of higher olefins were not possible. That said, carbometalation of a range of other π-systems, including internal alkynes (i.e. → 18), nitriles, carbon dioxide and acetaldehyde were successful.
By 1985, a series of early observations regarding the basic reactivity of Cp2Ti- and Cp2Zr- in metallacycle-mediated bimolecular C–C bond formation had been reported. However, the difficulties associated with controlling the general mode of reactivity associated with these species relegated their chemistry to playing a minor role in organic synthesis.
2.2. The emergence of more general cross-coupling procedures: Cp2Zr- and Cp2Ti-mediated alkyne–alkene and imine–alkene coupling
Over the next fifteen years, progress from Erker's Zr–benzyne and metallaindane chemistry (illustrated in Fig. 5) fueled the development of some general classes of cross-coupling based on the chemistry of zirconacyclopropenes and aza-zirconacyclopropanes – prepared from the decomposition of Cp2Zr(Me)–R complexes (Fig. 6A–D).15 Here, Buchwald demonstrated that intermediate zirconacyclopropanes undergo bimolecular coupling with ethylene and a small subset of unhindered terminal alkenes. As previously established by Erker, the regiochemistry of insertion with terminal alkenes is such that C–C bond formation occured at the internal carbon of the terminal alkene (i.e.27 and 30). | ||
| Fig. 6 Early Cp2Zr-based methods for metallacycle-mediated coupling of ethylene and some unhindered terminal alkenes. | ||
Overall, the contributions depicted in Fig. 6 defined a significant step forward from the initial findings of Whitesides, Grubbs, Erker and Bercaw. These advances provided a means to overcome the problems associated with homodimerization of alkenes or alkynes in group IV metal-mediated coupling, yet substantial barriers associated with substrate scope and selectivity remained unanswered for years to come:
1. Can the control of regiochemistry in metallacycle-mediated cross-coupling between two unsymmetrical systems be general, where regioselection is observed in the functionalization of each unsymmetrical π-system? Very few examples of such complex coupling chemistry had been described (for one example, see Fig. 6D).
2. Can metal-centered [2 + 2 + 1] chemistry be utilized in coupling reactions that engage complex (substituted and branched) alkenes? To date, nearly all reported olefin functionalization reactions based on metallacycle-mediated cross-coupling employ ethylene as a substrate, with only a handful exploring the reactivity of terminal unbranched olefins.
3. If internal alkenes can be rendered reactive to such metallacyclopropanes, how can regioselection be controlled?
4. Related to the question above, if internal alkenes could be employed, how could relative and/or absolute stereochemistry be controlled in the insertion process?
5. From a practical perspective, is there a means to avoid the use of sensitive solid reagents required to generate the metallacyclopropane intermediates (i.e. without the requirement of glovebox techniques)?
6. Could one get away from the requirement of using metallated substrates (vinyl- and aryl-Grignard and organolithiums) as starting materials? Substrate scope could be markedly enhanced if coupling reactions did not require that one of the substrates be a highly reactive organometallic.
2.3. Metallacycle-mediated functionalization of allylic- and homoallylic alcohols and ethers
In the 1990s, a number of reports surfaced describing metallacycle-mediated functionalization of allylic- and homoallylic alcohols/ethers. Among the first of these, described by Hoveyda and co-workers, was Zr-catalyzed and Zr-promoted addition reactions of EtMgCl to stereodefined allylic and homoallylic systems.16 As illustrated in Fig. 7, Zr-catalyzed addition of EtMgCl to 31a produces the syn-product 32 with up to 95![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 5 levels of diastereoselection, while the same addition reaction to the allylic ether 31b delivers the anti-product 33 with selectivities up to ≥99
5 levels of diastereoselection, while the same addition reaction to the allylic ether 31b delivers the anti-product 33 with selectivities up to ≥99![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1. Interestingly, these authors found that a related stoichiometric process proceeds with an opposite sense of regioselection (36 → 37 + 38). Here, the major products derive from formal SN2′ alkylation. While no comment was made concerning the stereochemistry of the product mixture from this reaction, the related Cp2Zr-promoted coupling of an allylic benzyl ether (40) with a TMS-alkyne (41) delivers a nearly 1
1. Interestingly, these authors found that a related stoichiometric process proceeds with an opposite sense of regioselection (36 → 37 + 38). Here, the major products derive from formal SN2′ alkylation. While no comment was made concerning the stereochemistry of the product mixture from this reaction, the related Cp2Zr-promoted coupling of an allylic benzyl ether (40) with a TMS-alkyne (41) delivers a nearly 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 mixture of stereoisomeric 1,4-dienes (42 + 43).17 The lack of stereoselection associated with these Zr-promoted processes has been uniformly observed with related metal-promoted transformations: (1) Ta-promoted coupling of alkynes with allylic alcohols,18 and (2) Ti-promoted coupling of Grignard reagents with allylic alcohols.19
1 mixture of stereoisomeric 1,4-dienes (42 + 43).17 The lack of stereoselection associated with these Zr-promoted processes has been uniformly observed with related metal-promoted transformations: (1) Ta-promoted coupling of alkynes with allylic alcohols,18 and (2) Ti-promoted coupling of Grignard reagents with allylic alcohols.19
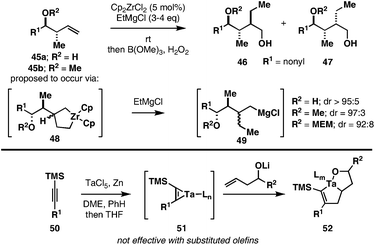
As illustrated in Fig. 8, similar addition reactions of EtMgCl have been realized with homoallylic alcohols and ethers.16cZr-catalyzed ethylmagnesiation of homoallylic alcohol 45a or 45b provides the anti product 46, albeit with varying levels of stereoselection (from 92![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 8 to ≥95
8 to ≥95![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 5).
5).
In studies focused on exploring the use of TaCl5 in metallacycle-mediated bond construction, Utimoto has reported the union of internal alkynes with homoallylic alcohols (Fig. 8).20 Formation of a Ta–alkyne complex (51), followed by addition of a homoallylic alkoxide leads to the generation of an intermediate fused bicyclic metallacycle 52. Interestingly, the regiochemical course of this coupling reaction (with respect to the alkene) is opposite to that seen in related Cp2Zr- and Cp2Ti-mediated chemistry (see Fig. 6C and D). Unfortunately, this alkoxide-directed coupling reaction proved to be significantly limited in substrate scope, proving to be limited to the functionalization of terminal alkenes.
2.4. Metal-catalyzed Alder-ene chemistry for alkyne–alkene cross-coupling
The Alder-ene reaction represents an alternative metallacycle-mediated process for the functionalization of alkenes, where bimolecular C–C bond formation is followed by the formation of a 1,4-diene.21 Ru-catalysis has rendered a collection of Alder-ene chemistry between monosubstituted alkenes and terminal alkynes possible under relatively mild conditions (Fig. 9; 53 + 54 → 55). Unfortunately, the application of this type of bimolecular coupling reaction in complex settings is often challenging, in some cases requiring an extensive screen of substrates, solvent and additive to produce high yields and levels of regioselection (56 + 57 → 58).22 Recent advances in this area include the development of reaction conditions suitable for the regioselective coupling of internal alkynes with terminal alkenes (i.e.60 and 63),23 and the discovery of novel catalysts based on Co (65 + 66 → 67).242.5. Ni-catalyzed cross-coupling reactions
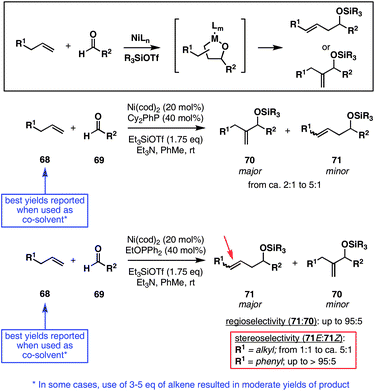
Recently, progress in the chemistry of Ni has led to the elucidation of reaction pathways for the coupling of terminal (monosubstituted) alkenes 68 with aldehydes (Fig. 10). In coupling reactions promoted by 20 mol% of Ni(cod)2 along with 40 mol% of dicyclohexylphenylphosphine, a mixture of regio and stereoisomeric products 70 and 71 (rs = 2![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 to 5
1 to 5![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) is formed in yields in the range 45–95%.25 While advances have been described in an effort to address regioselection, a few notable characteristics of this method warrant consideration: (1) yields are optimal when the alkene is used as co-solvent, (2) Ni(cod)2 is a sensitive starting material (glovebox techniques were reported for experiment set up), and (3) while the reactions are substoichiometric in Ni(cod)2, turnover numbers typically range from only 2 to 5, thereby requiring a significant quantity of a toxic and sensitive metal reagent.25f
1) is formed in yields in the range 45–95%.25 While advances have been described in an effort to address regioselection, a few notable characteristics of this method warrant consideration: (1) yields are optimal when the alkene is used as co-solvent, (2) Ni(cod)2 is a sensitive starting material (glovebox techniques were reported for experiment set up), and (3) while the reactions are substoichiometric in Ni(cod)2, turnover numbers typically range from only 2 to 5, thereby requiring a significant quantity of a toxic and sensitive metal reagent.25f
In related studies, it was discovered that replacing Cy2PhP with EtOPPh2 in the coupling of terminal alkenes with aldehydes alters the regiochemical course of C–C bond formation.25b,c This variation delivers homoallylic silyl ethers with regioselectivities up to 95![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 5; unfortunately, the alkene is typically generated with low levels of stereoselection (E
5; unfortunately, the alkene is typically generated with low levels of stereoselection (E![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) Z from 2
Z from 2![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 to ca. 5
1 to ca. 5![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 when R1 = alkyl).26
1 when R1 = alkyl).26
Most recently, a modified Ni(cod)2-catalyzed coupling reaction was reported for allylic substitution of simple alkenes.27 While most examples to date describe addition reactions of ethylene to allylic ethers and carbonates, a few coupling processes have been reported with terminal (monosubstituted) alkenes (Fig. 11). As seen in related Ni-catalyzed cross-coupling reactions, a large excess of the terminal alkene is required.
 | ||
| Fig. 11 Terminal alkene–allylic carbonate coupling by Ni-catalysis. | ||
2.6. Ta-catalyzed cross-coupling reactions
Tantalum-catalyzed cross-coupling of secondary amines with alkenes represents a unique collection of metallacycle-mediated bimolecular C–C bond-forming processes.28a,b Early accomplishments in this area by Maspero and Nugent led to bond formation, but reactions were plagued with generally low yields, extended reaction times, and low catalyst turnover. Recently, Herzon and Hartwig described significant advances in this area. First, 4–8 mol% Ta[N(CH3)2]5 was found to promote coupling of N-methylaniline with a range of alkenes at 160–165 °C.28c While requiring only 1.25 equiv of alkene, coupled products were formed in 66–96% yield in 27–67 h (eqn (1)). Subsequently, these authors reported that this type of coupling reaction was possible with a range of secondary amines using 2 mol% of [TaCl3(NEt2)2]2 (eqn (2)).28d | (1) |
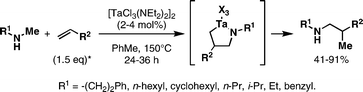 | (2) |
2.7. Summary of background
While effort has been taken to highlight a collection of metallacycle-mediated alkene functionalization reactions, we recognize that this discussion is not comprehensive. Rather, the selected examples serve to document some of what we believe is the most relevant history, and shed light on the relatively small subset of metallacycle-mediated coupling reactions that are suitable for complex stereoselective fragment coupling with alkenes. What should be immediately evident is that this entire class of intermolecular C–C bond forming processes is significantly limited in scope – a limitation that is independent of the nature of the metal employed, or whether that metal is used in a substoichiometric fashion.2.8. Summary of challenges
Metallacycle-mediated bond construction for the functionalization of alkenes has great potential to define powerful fragment union reactions for convergent synthesis. To realize this potential, a variety of problems must be overcome that currently limit this class of chemical reactivity to a boutique collection of coupling processes. While much attention has been given to rendering metallacycle-mediated coupling chemistry substoichiometric with respect to the central metal component, major limitations in this broad area of chemical reactivity are independent of such considerations. To date, the development of metallacycle-mediated coupling chemistry of alkenes is truly in its infancy, with most reactions defining effective solutions to the functionalization of ethylene. In fact, only a handful of reactions are currently available for complex fragment union, and these reside firmly in the coupling chemistry of terminal alkenes with alkynesviaAlder-Ene chemistry.The major barriers that complicate all reaction development in this area are:
1. Low levels of reactivity of substituted olefins in metallacycle-mediated chemistry. Not only are substituted olefins poor substrates for the formation of metal–π complexes, they are also poor substrates for reactions with preformed metal–π complexes.
2. Control of regioselection. While reactivity issues stand first and foremost as a barrier to achieving novel bond construction processes with alkenes, if one could access sufficient reactivity to employ substituted alkenes in metallacycle-mediated coupling, regioselectivity arises as a major un-addressed challenge.
3. Control of diastereoselection. Similarly, if one could use substituted alkenes in metallacycle-mediated bond construction, the issue of diastereoselection emerges as an additional unsolved problem.
3. Design of alkoxide-directed reductive cross-coupling reactions of alkenes
3.1. Our goal
In designing a general process to overcome the limitations of pre-existing methods in reductive cross-coupling technology, we targeted a metal-based system that could be used for the stoichiometric pre-activation of one of the coupling partners – a strategy that would provide a general solution to the control of cross-coupling over homo-dimerization. Given this initial design criteria, the metal-based system needed to be: (1) inexpensive, (2) non-toxic, and (3) result in byproducts that are both non-toxic and easy to remove from the products of interest. In addition, we favored the selection of a metallic system compatible with a range of Lewis-basic functionality, as we aimed to develop coupling reactions of utility in complex molecule synthesis (i.e.natural product synthesis). Furthermore, we desired a system that would be capable of forging C–C bonds in the presence of unprotected heteroatom-based functionality. Finally, we set out to devise a collection of heteroatom-directed reductive cross-coupling reactions where control of reactivity and selectivity would be possible based on the strategic placement of a suitable directing group.293.2. The selection of a titanium alkoxide-based system
Given our goal of providing chemical methods useful for the convergent synthesis of complex natural products, we desired a system capable of being directed by functionalities commonly found embedded in the backbone of such systems. Based on the prevalence of oxygen and nitrogen functionalities in natural products of biomedical relevance, we focused our efforts on defining a collection of directed reductive cross-coupling methods where such functionalities could serve to direct C–C bond formation – excluding organometallic processes that would favor direction by phosphorus, sulfur, aromatic heterocycles or simple π-unsaturation (i.e. a remote alkene).30To identify a suitable system based on these requirements, one needs to consider only a handful of relevant precedents. First, the ability of Ti alkoxides to undergo rapid and reversible ligand exchange has been well-showcased in the Sharpless epoxidation.2a,b Second, Cp2Ti–π complexes are known to participate in reductive coupling chemistry.10–12,14 In fact, this type of system was first demonstrated in the reductive dimerization of diphenylacetylene, later studied by Bercaw,14 and subsequently employed in a variety of intramolecular reductive coupling reactions.31 Finally, the pioneering studies of Kulinkovich and Rothwell demonstrated that titanium alkoxides and aryloxides could be employed to access similar reactivity to Cp2Ti–π complexes.32 Subsequent investigation of the chemistry of Ti-alkoxides in metallacycle-mediated C–C bond-forming processes, primarily in the laboratories of Professors Sato and Cha, has led to the discovery and development of a wide range of novel intra- and intermolecular reactions.33 In the context of bimolecular C–C bond formation (Fig. 12), contributions include: (1) the use of terminal alkenes in the Kulinkovich reaction (78 → 80),33f (2) formation of Ti–alkyne complexes and their use in bimolecular reactions with carbonyls and terminal alkynes (81 → 82 → 83–86),33g–j (3) formation of Ti–silylethylene complexes (87) and their use in related bimolecular coupling reactions,33k (4) formation of Ti–imine complexes (92) and their use in bimolecular coupling reactions with terminal alkynes and carbonyls,33l–m and (5) reductive cross-coupling of simple homoallylic alcohols with pyrrole amides (95 + 96 → 97).33n
 | ||
| Fig. 12 Previous application of Ti(IV) alkoxides in bimolecular C–C bond formation – selected examples. | ||
While the contributions of these authors have established a solid foundation of Ti-mediated metallacycle-based bond constructions in organic chemistry, the previously described barriers related to the control of reactivity and selectivity in metallacycle-mediated functionalization of alkenes have remained firmly in place.
As we further considered the use of Ti(Oi-Pr)4 as a stoichiometric component of our reaction design, issues of cost and toxicity were at the forefront of our thoughts. First, the byproducts from aqueous work-up of stoichiometric Ti(Oi-Pr)4-mediated coupling reactions (i.e. the Kulinkovich reaction) are i-PrOH and TiO2. Fortunately, i-PrOH is a relatively benign solvent and TiO2 is a species encountered daily in most of our lives, as it is a component of products such as toothpaste, chewing gum, sunscreen and paint. The accompanying reducing metal typically employed alongside the titanium(IV) alkoxide is a Grignard reagent, the byproducts of which are simple magnesium salts and hydrocarbons.
Although we will describe Ti(Oi-Pr)4-based reductive cross-coupling methods that provide a means to couple π-systems not currently possible with catalytic methods, a cost analysis between projected use of stoichiometric Ti(Oi-Pr)4versus known catalysts for metallacycle-mediated functionalization of alkenes is informative.34 If one were to conduct a hypothetical metallacycle-mediated coupling reaction on a 1 mole scale, stoichiometric use of Ti(Oi-Pr)4 would cost $18 (Strem 2008) while the catalytic use of 20 mol% Ni(cod)2 would cost over $1,000 (Strem 2008).35
The challenges associated with the development of metal-catalyzed C–C bond-forming reactions is a significant and popular concern in current organic chemistry. While much scientific inquiry has embraced this pursuit, our interests in reaction development were not focused on the stoichiometry of the metal reagent. Rather, our central concern targeted the development of new reactions, enabling novel stereoselective bond-constructions, and offering strategic advances in chemical synthesis. Given these- and previously discussed considerations, that are based on reaction design, cost, toxicity, and the ease with which Ti(Oi-Pr)4 can be handled, we embraced a program aimed at defining alkoxide-directed reductive cross-coupling reactions mediated by stoichiometric Ti(Oi-Pr)4 as a strategy to overcome the barriers that have broadly limited all intermolecular metallacycle-mediated coupling chemistry.
3.3. The design of alkoxide-directed coupling reactions of alkenes
Two strategies were conceived for alkoxide-directed metallacycle-mediated coupling of alkenes. First, we imagined preformation of a Ti–olefin complex followed by alkoxide-directed coupling with a second π-system (Fig. 13A). This reaction design was thought to define a very limited subset of synthetically useful fragment coupling reactions for the following reasons: (1) internal alkenes are typically not effective for the generation of metallacyclopropanes,36 (2) even if producing titanacyclopropanes from disubstituted alkenes could be rendered efficient, the control of stereochemistry at each Ti–C bond would likely need to be addressed, and (3) while directed carbometalation with unsaturated alkoxides (100) was anticipated to deliver metallacyclopentane products, regiochemical control with respect to the alkene (98) would likely be limited to a function of the differential steric environment around the preformed metallacyclopropane 99. | ||
| Fig. 13 Basic considerations in the design of alkoxide-directed metallacycle-mediated coupling of alkenes. | ||
Alternatively, we imagined that introduction of the alkene as the second π-system in a metallacycle-mediated cross-coupling could have significant advantages (Fig. 13B). First, the formation of the initial Ti–π complex could be achieved with established protocols (i.e. internal alkyne, terminal alkene, imine). Second, the intramolecular nature of the carbometalation process, achieved by transient formation of a mixed titanate ester between 104 and 105, should provide a means to achieve bond constructions typically not accessible in bimolecular processes.37 Third, the regiochemical control of alkene functionalization would be based on the position of a pendant hydroxyl, not on the differential steric environment about the alkene. Finally, stereochemical control in the carbometalation of the alkene was thought feasible by translation of stereochemical information from the allylic and/or homoallylic positions of 105.
4. New regio- and stereoselective metallacycle-mediated coupling reactions of alkenes
4.1. Ti-mediated coupling of homoallylic alcohols with internal alkynes
We initiated our investigations with the cross-coupling of homoallylic alcohols with internal alkynes. As depicted in Fig. 14, in situ formation of a Ti–alkyne complex 108 (alkyne, Ti(Oi-Pr)4, c-C5H9MgCl) would be followed by addition of a suitably functionalized alkene (107). Metal-centered [2 + 2 + 1] would then furnish functionalized metallacyclopentenes (109 or 110), protonation of which would deliver cross-coupled product 111 or 112.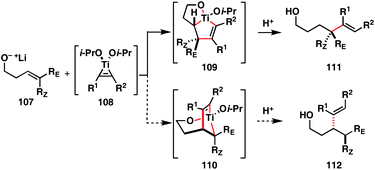 | ||
| Fig. 14 Basic reaction pathways for the coupling of alkenyl alcohols with internal alkynes. | ||
As illustrated in Fig. 15, our initial studies confirmed that the order of bond-forming processes targeted was both sufficient to overcome the poor levels of reactivity associated with substituted alkenes and suitable to attain high levels of regiochemical control.38 Here, the structures of all products isolated (i.e.113–118) were consistent with the formation of a fused bicyclic titanacyclopentene (i.e.109; Fig. 14), delivering products where C–C bond formation had occurred distal to the pendant hydroxyl. The coupling of a hydroxymethyl-substituted cyclohexene and a symmetrical alkyne provided additional evidence that this C–C bond-forming reaction was directed by the neighboring hydroxyl group. Here, 116 was formed with very high levels of regio- and stereoselection (C–C bond formation occurred syn to the neighboring hydroxymethyl substituent).
As evidenced by the highly selective formation of 117 and 118, this alkene–alkyne coupling reaction can be used for highly complex fragment coupling reactions. In both of these cases, coupling of chiral homoallylic alcohols with chiral and unsymmetrically substituted internal alkynes proved effective, despite the pairing of absolute stereochemistries of each coupling partner. In each case, no evidence for the production of minor stereoisomeric products was observed, indicating that the cross-coupling process proceeded with very high levels of regioselection with respect to both unsymmetrically substituted π-systems, while also occuring with very high levels of diastereoselection (presumably derived from the minimization of A-1,3 strain in the (Z)-homoallylic alcohol starting materials – not shown), and without significant perturbation by double asymmetric relationships.
Recently, this regioselective alkene–alkyne cross-coupling reaction was described as a central feature of a novel convergent pathway to substituted spiroketals (Fig. 16).39 Here, TMS-substituted alkynes, derived from formal hydroalkynylation of a homoallylic ether, were coupled to stereodefined homoallylic alcohols to deliver intermediate vinylsilanes. Subsequent oxidative cleavage and acid-promoted spiroacetylization then delivered complex stereodefined spiroketals that contained a substitution pattern that would be quite challenging to prepare with available aldol- or dithiane-based methods (i.e.121, 124, 126 and 129). In all cases, the convergent Ti-mediated alkene–alkyne coupling reaction proceeded with high levels of regio- and stereocontrol (no evidence was found for the production of isomeric products).
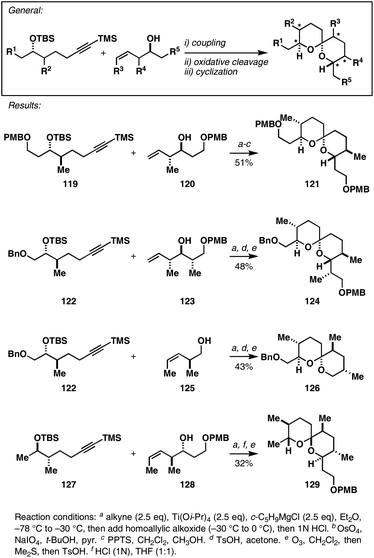 | ||
| Fig. 16 A convergent synthesis of spiroketals viaalkene–alkyne coupling. | ||
4.2. Ti-mediated coupling of homoallylic alcohols with imines
While azatitanacyclopropanes have been prepared from imines,40 and shown to participate in metallacycle-mediated coupling chemistry with terminal alkynes, their potential utility in alkene functionalization had not been demonstrated. This absence was thought to be related to the particularly low levels of reactivity associated with these complexes, as bimolecular carbometalation reactions with internal alkynes are known to be challenging.40Building on our success with homoallylic alcohol–alkyne coupling chemistry, we speculated that a similar reaction strategy may be effective for the union of imines with substituted alkenes (Fig. 17). Here, selective formation of a fused bicyclic azametallacyclopentane would, however, be coupled to a new and complex stereochemical issue – one that ultimately results in the formation of stereodefined 1,5-aminoalcohols 133.
Our initial study of this alkoxide-directed cross-coupling reaction began with evaluation of reactivity and simple diastereoselection for the coupling of a series of achiral homoallylic alcohols with aromatic imines.41 As illustrated in Table 1, this coupling reaction proved effective for the union of terminal-, (Z)-, (E)- and 1,1-disubstituted alkenes. Coupling of (Z)- and (E)-disubstituted alkenes proceeds with exquisite levels of stereoselection and delivers anti- products with ≥20![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 selectivity (in neither instance was any evidence found for the production of regio- or diastereomeric products), while coupling of 1,1-disubstituted alkenes, proceeds with somewhat diminished levels of control. Here, similarly high levels of regioselection were observed, yet 144 was produced as a 4
1 selectivity (in neither instance was any evidence found for the production of regio- or diastereomeric products), while coupling of 1,1-disubstituted alkenes, proceeds with somewhat diminished levels of control. Here, similarly high levels of regioselection were observed, yet 144 was produced as a 4![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 mixture of diastereomers. Despite this observation, as depicted in Table 1, these cross-coupling reactions define a general and convergent stereoselective path to substituted piperidines (136, 139, 142 and 145) by a simple two-step sequence: (1) reductive cross-coupling, and (2) cyclization (PPh3, imidazole, CCl4).
1 mixture of diastereomers. Despite this observation, as depicted in Table 1, these cross-coupling reactions define a general and convergent stereoselective path to substituted piperidines (136, 139, 142 and 145) by a simple two-step sequence: (1) reductive cross-coupling, and (2) cyclization (PPh3, imidazole, CCl4).
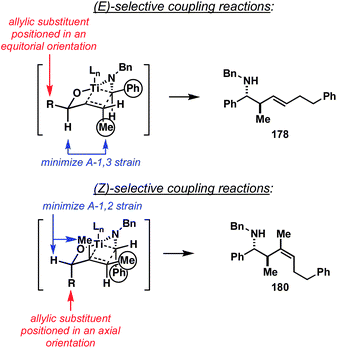
The origin of stereoselection in this coupling reaction remains under investigation, yet the observed selectivity is consistent with a proposal based on kinetically controlled C–C bond formation. As illustrated in Fig. 18, anti-selectivity [in the coupling of (E)- or (Z)- alkenes] is consistent with an empirical model whereby non-bonded steric-interactions about the developing C–C bond are minimized. Here, avoiding eclipsing interactions between the alkene- and imine-substituent is reasoned to result in the observed stereo-convergence (favoring reaction by way of B and C). In the coupling reaction of 1,1-disubstituted alkenes, stereoselection is thought to derive from the preferred orientation of the imine substituent in the cis-fused bicyclo[3.3.0] transition state geometry F.
 | ||
| Fig. 18 Empirical model for simple diastereoselection in reductive cross-coupling between homoallylic alcohols and imines. | ||
While it is well-established that saturated metallacyclopentanes can be in a rapid equilibrium with their corresponding metallacyclopropane and alkene,42 recent investigations have provided support for the proposition that the coupling reactions illustrated in Table 1 proceed under reaction conditions that do not promote such fragmentation.43 These observations are consistent with the assumed underlying principles that govern the empirical model depicted in Fig. 18 and are based on kinetic control in the C–C bond forming event.
The imine–allylic alcohol coupling reaction can also be conducted in an asymmetric fashion. As highlighted in Table 2 entries 1–3, single asymmetric coupling reactions proceed with very high levels of stereoselection, and define a unique stereoselective convergent coupling process for the synthesis of optically active 1,5-aminoalcohols and substituted piperidines. Interestingly, this coupling process is also highly effective in a double asymmetric mode. Coupling of the chiral homoallylic alcohols 152 and 155 with a chiral imine, delivers either the 1,5-syn-1,4-anti-1,5-aminoalcohol product 153 with ≥50![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 selectivity, or the 1,5-anti-1,4-syn-1,5-aminoalcohol product 156 with high, but somewhat lower selectivity (dr = 34
1 selectivity, or the 1,5-anti-1,4-syn-1,5-aminoalcohol product 156 with high, but somewhat lower selectivity (dr = 34![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 4
4![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1). In both cases, this coupling reaction serves as the foundation of a convenient stereoselective synthesis of tetrasubstituted piperidines (i.e.154 and 157).
1). In both cases, this coupling reaction serves as the foundation of a convenient stereoselective synthesis of tetrasubstituted piperidines (i.e.154 and 157).
a
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) Reaction conditions for cross coupling: imine (1 eq), Ti(Oi-Pr)4 (1.5 eq), c-C5H9MgCl (3.0 eq), Et2O (−60 to −30 °C), then add alkoxide (1.5 eq) (–40 to 0 °C or rt). a Reaction conditions for cross coupling: imine (1 eq), Ti(Oi-Pr)4 (1.5 eq), c-C5H9MgCl (3.0 eq), Et2O (−60 to −30 °C), then add alkoxide (1.5 eq) (–40 to 0 °C or rt). a![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) Reaction conditions for cyclization: for 148: 2-NsCl, Et3N, DMAP, CH2Cl2, rt. For 151: MsCl, Et3N, CH2Cl2, rt. R = CH(Ph)CH2OMe. For 154 and 157: (1) H2 (1 atm), Pd(OH)2, AcOH–MeOH (1 Reaction conditions for cyclization: for 148: 2-NsCl, Et3N, DMAP, CH2Cl2, rt. For 151: MsCl, Et3N, CH2Cl2, rt. R = CH(Ph)CH2OMe. For 154 and 157: (1) H2 (1 atm), Pd(OH)2, AcOH–MeOH (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10 v/v), rt, (2) 2-NsCl, Et3N, DMAP, CH2Cl2, 0 °C to rt, (3) PPh3, DIAD, THF, rt. 10 v/v), rt, (2) 2-NsCl, Et3N, DMAP, CH2Cl2, 0 °C to rt, (3) PPh3, DIAD, THF, rt. |
|---|

|
4.3. Ti-mediated coupling of allylic alcohols with alkynes
While allylic alcohols and ethers have been defined as substrates for metallacycle-mediated coupling, transformations that proceed with allylic transposition have been uniformly unselective, delivering products as mixtures of olefin isomers.17–19 In an effort to define a series of synthetically useful stereoselective cross-coupling reactions based on this mode of reactivity, we aimed to control the regio- and stereochemical course of related Ti-mediated coupling reactions of allylic alcohols. As illustrated in Fig. 19, we speculated that alkoxide-directed carbometalation may provide a means to access a rigid boat-like transition state geometry en route to a fused bicyclo-[3.2.0] system (158). Here, the boat-like geometry would be enforced by the mechanistic requirements for bond formation that include: (1) ligand exchange at Ti, and (2) alignment between σTi–C with πC![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C. Once achieved, the resulting fused metallacycle was anticipated to undergo a stereospecific syn-elimination akin to that proposed in the Tebbe olefination.44 In this manner, the relative stereochemistry of the oxatitanacyclobutane intermediate should translate to the alkene geometry in the product.
C. Once achieved, the resulting fused metallacycle was anticipated to undergo a stereospecific syn-elimination akin to that proposed in the Tebbe olefination.44 In this manner, the relative stereochemistry of the oxatitanacyclobutane intermediate should translate to the alkene geometry in the product.
 | ||
| Fig. 19 Strategy for stereoselective reactions of allylic alcohols. | ||
Our initial studies in this area resulted in the elucidation of highly stereoselective coupling reactions for the synthesis of 1,4-dienes.45 As depicted in Fig. 20, (Z)-allylic alcohol starting materials (160) can be selectively coupled with internal alkynes (161) to deliver 1,4-dienes possessing one (E)-disubstituted alkene, one (E)-trisubstituted alkene, and a central C3-substituent (R2; 162).
Alternatively, the stereochemical course of this cross-coupling reaction can be controlled by minimization of A-1,2 strain. Here, allylic alcohols bearing 1,1-disubstituted alkenes (163), can be coupled to internal alkynes (161) en route to 1,4-dienes that contain one (Z)-trisubstituted alkene (164; Fig. 21).
While these initial studies defined the first highly stereoselective coupling reactions of their kind, recent studies have shed light on chemoselectivity associated with this process.46 As depicted in Table 3, 1,5-dienes that possess an allylic and homoallylic alcohol motif can be employed in highly selective coupling reactions. Specifically, when the diene substrates have related levels of substitution, highly chemo- and stereoselective cross-coupling is observed at the allylic alcohol, resulting in the formation of stereodefined skipped polyenes (167, 170, 172, 174 and 176).
a
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) Reaction conditions: alkyne (2–3 equiv.), Ti(Oi-Pr)4 or ClTi(Oi-Pr), c-C5H9MgCl, PhMe (−78 to −35 °C), then cool to −78 °C and add Li alkoxide of the allylic alcohol as a solution in THF (warm to 0 °C). b Reaction conditions: alkyne (2–3 equiv.), Ti(Oi-Pr)4 or ClTi(Oi-Pr), c-C5H9MgCl, PhMe (−78 to −35 °C), then cool to −78 °C and add Li alkoxide of the allylic alcohol as a solution in THF (warm to 0 °C). b![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) Yield reported is over two steps: chemoselective reductive cross-coupling and silyl deprotection with TBAF in THF. Yield reported is over two steps: chemoselective reductive cross-coupling and silyl deprotection with TBAF in THF. |
|---|

|
The alkyne–allylic alcohol coupling process has been demonstrated to be of great utility in natural product synthesis. As depicted in Fig. 22, the first total synthesis and structure elucidation of a phorbasin was accomplished by a chemical pathway that employed an allylic alcohol–alkyne coupling reaction to establish the oxygenated cyclohexene core.47 Here, a highly stereoselective addition reaction, controlled by the stereochemistry of the allylic alcohol 177, was coupled to a bond construction where high levels of site-selectivity for C–C bond formation with respect to each reaction component was observed. In an unrelated campaign in total synthesis, a late stage allylic alcohol–alkyne coupling reaction was used to establish the stereodefined skipped polyene backbone of lehualide B.48 Interestingly, these studies demonstrated that a potentially sensitive γ-pyrone is compatible with this metallacycle-mediated coupling reaction (180 + 178 → 181).
4.4. Ti-mediated coupling of allylic alcohols with vinylsilanes: a stereochemically orthogonal reaction to the Claisen rearrangement
The unique stereochemical course of the alkyne–allylic alcohol coupling reaction, where 1,1-disubstituted olefins deliver (Z)-trisubstituted alkene-containing 1,4-diene products, prompted us to consider the potential of a related coupling reaction for the stereoselective synthesis of isolated alkenes. While Claisen rearrangement chemistry of functionalized allylic alcohols has been established as a strategy for the synthesis of stereodefined trisubstituted olefins, this process typically favors the formation of (E)-trisubstituted alkenes. We wondered whether a Ti-promoted reductive coupling process between the parent allylic alcohol starting material and a vinylsilane could define a stereochemically orthogonal pathway to related products.As depicted in Fig. 23, use of chlorodimethylvinylsilane in titanium alkoxide-mediated reductive cross-coupling with allylic alcohols bearing 1,1-disubstituted alkenes was anticipated to deliver products containing a (Z)-trisubstituted alkene (183). This expectation was in accord with the empirical model for the allylic alcohol–alkyne coupling reaction previously discussed.
 | ||
| Fig. 23 Allylic alcohol–vinylsilane coupling as a stereochemically orthogonal reaction to the Claisen rearrangement. | ||
As illustrated in Fig. 24, this expectation proved correct, providing a highly stereoselective means of preparing products of similar substitution to – but distinct stereochemistry of – those accessible with modern Claisen-rearrangement chemistry (184–189).49
 | ||
| Fig. 24 (Z)-selective allylic alcohol–vinylsilane coupling. | ||
4.5. Ti-mediated coupling of allylic alcohols with imines, a unique pathway to stereodefined homoallylic amines
Based on the high degree of stereochemical control observed in the reductive cross-coupling reactions of substituted allylic alcohols with alkynes and vinylsilanes, we wondered whether the additional aspects of stereochemical control observed in homoallylic alcohol–imine coupling chemistry would translate to a new coupling process between imines and allylic alcohols. In short, we anticipated that preformation of a Ti–imine complex, followed by addition of an allylic alkoxide would result in a highly controlled allyl transfer process proceeding by way of directed carbometalation and syn-elimination. We recognized that this subset of cross-coupling would be significantly more complex than previously discussed allylic alcohol-based transformations, as stereochemical control would have to be addressed in the functionalization of each reaction component.The following discussion breaks down our observations in this interesting coupling reaction, following basic considerations associated with product structure and control of the bimolecular process:
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1).
1).
 | ||
| Fig. 25 Prenylation by imine–allylic alcohol coupling. | ||
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) E ≥ 20
E ≥ 20![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1). Interestingly, when the allylic alcohol contains a 1,2-di- or trisubstituted alkene (201 or 203), the reductive cross-coupling reaction proceeds with both high stereoselectivity for the formation of a substituted alkene product (E-disubstituted or Z-trisubstituted), and high anti-stereochemistry between the allylic and homoallylic stereocenters (dr ≥ 20
1). Interestingly, when the allylic alcohol contains a 1,2-di- or trisubstituted alkene (201 or 203), the reductive cross-coupling reaction proceeds with both high stereoselectivity for the formation of a substituted alkene product (E-disubstituted or Z-trisubstituted), and high anti-stereochemistry between the allylic and homoallylic stereocenters (dr ≥ 20![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1). This sense of stereoselection is consistent with the empirical models depicted in Fig. 27 that merge the factors previously proposed for the control of allylic alcohol–alkyne, and homoallylic alcohol–imine coupling.
1). This sense of stereoselection is consistent with the empirical models depicted in Fig. 27 that merge the factors previously proposed for the control of allylic alcohol–alkyne, and homoallylic alcohol–imine coupling.
 | ||
| Fig. 26 Diastereoselective allylic alcohol–imine coupling reaction. | ||
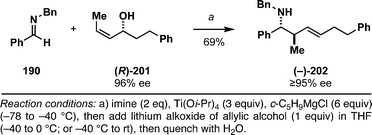 | ||
| Fig. 28 Asymmetric reductive cross-coupling. | ||
While a more thorough discussion of asymmetric reductive cross-coupling reactions of imines with allylic alcohols is not within the scope of this Perspective, recent studies in our laboratory have found that a range of double asymmetric coupling processes are useful for perturbing the stereochemical course of these allyl-transfer processes.52
 | ||
| Fig. 29 Routes to stereodefined heterocycles enabled by a stereoselective reductive cross-coupling between allylic alcohols and imines. | ||
In an unrelated study, chemoselective coupling of allylic alcohols containing a pendent vinyl halide serves as the first step of a one-pot process for the synthesis of substituted lactams (Fig. 29B).54 Here, formation of the intermediate azametallacyclopentane, from the union of 190 with 209, is followed by addition of water, then 2 mol% of a PdCl2, 6 mol% of t-Bu3P, Et3N and CO. Overall, a one-pot annulation results, delivering the fused γ-lactam 210 in 73% yield (dr ≥ 20![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1).
1).
4.6. Ti-mediated coupling of vinylcyclopropanes with alkynes as a route to stereodefined skipped trienes
In a recent study aimed at defining novel stereoselective pathways for the convergent synthesis of skipped trienes, we elucidated a stereospecific reductive cross-coupling reaction of vinylcyclopropanes with alkynes.55 As depicted in Fig. 30A, preformation of a Ti–alkyne complex, followed by alkoxide-directed carbometalation of a vinylcyclopropane was expected to deliver an unstable tricyclic metallacyclopentane. Decomposition of this intermediate (213) by a six-electron process would then deliver, after protonation of the terminal organometallic product, a stereodefined skipped triene (214).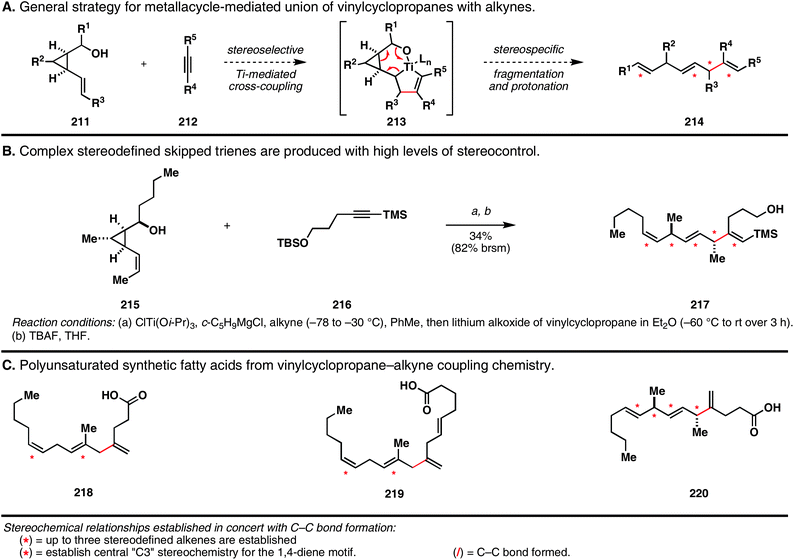 | ||
| Fig. 30 Skipped trienes from the stereoselective reductive cross-coupling of vinylcyclopropanes with alkynes. | ||
One representation of the power of this bond construction is shown in Fig. 30B. Here, union of the stereodefined vinylcyclopropane 215 (itself derived from a four step-functionalization of a simple allylic alcohol) with a TMS-alkyne delivers the complex stereodefined skipped triene 217 in 82% yield based on recovered starting material. While the conversion for this transformation remained relatively low (36% isolated yield), the triene product was formed as a single isomer. Note that this bimolecular C–C bond-forming reaction delivers a skipped triene product that contains three stereodefined alkenes (one (Z)-disubstituted, one (E)-disubstituted, and one (E)-trisubstituted), while also harboring stereodefined substitution at each central sp3carbon of the isolated 1,4-dienes.
In a brief study to explore the utility of this new reductive cross-coupling process, we pursued the synthesis of a collection of complex and diverse polyunsaturated fatty acids (218–220; Fig. 30C). Interestingly, the stereochemical course of this coupling reaction is unique compared to the chemoselective reactions of 1,5-diene-3-ols described in Table 3, as all examples explored provide a central (E)-alkene (di- or trisubstituted). While these polyunsaturated acyclic molecules may appear as relatively simple architectures, one should not overlook the complexity associated with these structures, or the difficulties that would be anticipated during their attempted synthesis using available chemical methods.
Conclusions
Chemo-, regio- and stereoselective intermolecular C–C bond formation represents the backbone of organic synthesis. Despite the central role of these processes in organic chemistry, relatively few general areas of chemical reactivity have proven broadly useful for such bond construction. Carbometalation chemistry is one area of chemical reactivity with great potential to impact the manner in which complex molecules are forged. Unfortunately, major hurdles have stood in the way of advancing broadly useful methods in this area, including the often low reactivity of electronically unactivated alkenes and internal alkynes, as well as the often harsh reaction conditions required to enable addition of preformed organometallic reagents to these systems.While reactions of metallacyclopropanes with ethylene and simple unfunctionalized terminal alkenes have been known for over 20 years, and define a mechanistically unique pathway for carbometallation, the basic pattern of reactivity defined by these reactions has not proven to significantly impact complex organic synthesis – perhaps due to challenges associated with: 1) overcoming limitations in reactivity, and 2) controlling elements of selectivity in the functionalization of complex systems.
Recently, a program aimed at defining complex fragment union reactions based on the chemistry of metallacyclopropanes has resulted in the discovery of a collection of novel synthetic methods that, for the first time, harness the potential of reactive metallacyclopropanes for highly controlled bimolecular C–C bond forming reactions. These accomplishments, enabled by a reaction design that embraces heteroatom-directed metallacycle-mediated fragment coupling, are defining novel stereoselective convergent processes that offer unique synthesis strategies for the assembly of complex molecules. While early demonstrations provide a foundation to support this claim, we look forward to the growth of this, and related areas of reaction development, to deliver tools that revolutionize the manner in which organic synthesis is performed.
Notes and references
-
(a)
E. J. Corey, X. Cheng, The Logic of Chemical Synthesis, John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York, 1989, p. 436 Search PubMed
; (b) K. C. Nicoloau and E. J. Sorensen, Classics in Total Synthesis, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 1996, p. 798 Search PubMed
.
-
(a) T. Katsuki and K. B. Sharpless, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1980, 102, 5974 CrossRef CAS
; (b) T. Katsuki and V. S. Martin, Org. React., 1996, 48, 1 CAS
; (c) H. C. Kolb, M. S. VanNieuwenhze and K. B. Sharpless, Chem. Rev., 1994, 94, 2483 CrossRef CAS
; (d) O. A. Wong and Y. Shi, Chem. Rev., 2008, 108, 3958 CrossRef CAS
.
- For recent reviews, see:
(a)
Metal-catalyzed Cross-Coupling Reactions, ed. A. de Meijere and F. Diederich, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2004, p. 938 Search PubMed
; (b) K. C. Nicolaou, P. G. Bulger and D. Sarlah, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2005, 44, 4442 CrossRef CAS
; (c) E. Negishi, Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn., 2007, 80, 233 CrossRef CAS
; (d) G. Evano, N. Blanchard and M. Toumi, Chem. Rev., 2008, 108, 3054 CrossRef CAS
; (e) I. P. Beletskaya and A. V. Cheprakov, Coord. Chem. Rev., 2004, 248, 2337 CrossRef CAS
.
- For recent reviews, see:
(a) A. H. Hoveyda and A. R. Zhugralin, Nature, 2007, 450, 243 CrossRef CAS
; (b) R. H. Grubbs, Tetrahedron, 2004, 60, 7117 CrossRef CAS
. For a review of metathesis reactions in total synthesis, see: (c) K. C. Nicolaou, P. G. Bulger and D. Sarlah, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2005, 44, 4490 CrossRef CAS
. For a review of enyne metathesis, see: (d) S. T. Diver and A. J. Giessert, Chem. Rev., 2004, 104, 1317 CrossRef CAS
. For a review of olefin cross-metathesis, see: (e) S. J. Connon and S. Blechert, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2003, 42, 1900 CrossRef
.
- For reviews, see:
(a) F. Dénés, A. Pérez-Luna and F. Chemla, Chem. Rev., 2010, 110, 2366 CrossRef CAS
; (b) A. G. Fallis and P. Forgione, Tetrahedron, 2001, 57, 5899 CrossRef CAS
; (c) I. Marek, J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. 1, 1999, 535 RSC
; (d) E. Nakamura, Pure Appl. Chem., 1996, 68, 123 CAS
; (e) E. Negishi, Acc. Chem. Res., 1987, 20, 65 CrossRef CAS
; (f) I. P. Beletskaya and A. V. Cheprakov, Chem. Rev., 2000, 100, 3009 CrossRef CAS
.
- For reviews, see:
(a) J. F. Normant and A. Alexakis, Synthesis, 1981, 841 CrossRef CAS
; (b) B. H. Lipshutz and S. Sengupta, Org. React., 1992, 41, 135 CAS
; (c) I. Marek, J. F. Normant, in Metal-catalyzed Cross-coupling Reactions, ed. F. Diederich and P. J. Stang, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 1998, pp. 271–337 Search PubMed
; (d) H. A. Reichard, M. McLaughlin, M. Z. Chen and G. C. Micalizio, Eur. J. Org. Chem., 2010, 391 CrossRef CAS
.
-
(a) I. U. Khand, G. R. Knox, P. L. Pauson and W. E. Watts, J. Chem. Soc., Chem. Commun., 1971, 36 Search PubMed
; (b) I. U. Khand, G. R. Knox, P. L. Pauson, W. E. Watts and M. I. Foreman, J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. 1, 1973, 977 RSC
.
- For recent reviews on metal-mediated [2 + 2 + 1] annulations, see:
(a) M. P. Croatt and P. A. Wender, Eur. J. Org. Chem., 2010, 19 CAS
; (b) S. E. Gibson and A. Stevenazzi, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2003, 42, 1800 CrossRef
; (c) P. L. Pauson, Tetrahedron, 1985, 41, 5855 CrossRef CAS
.
- For a recent review of the intermolecular Pauson–Khand annulation, see:
(a) S. E. Gibson and N. Mainolfi, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2005, 44, 3022 CrossRef CAS
. For recent examples, see: (b) P. A. Wender, N. M. Deschamps and T. J. Williams, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2004, 43, 3076 CrossRef CAS
. For an intermolecular example of [2 + 2 + 1] between a 2,3-disubstituted diene and norbornene, see: (c) P. A. Wender, M. P. Croatt and N. M. Deschamps, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2004, 126, 5948 CrossRef CAS
.
- J. X. McDermott and G. M. Whitesides, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1974, 96, 947 CrossRef CAS
.
- J. X. McDermott, M. E. Wilson and G. M. Whitesides, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1976, 98, 6529 CrossRef CAS
.
- R. H. Grubbs and A. Miyashita, J. Chem. Soc., Chem. Commun., 1977, 864 RSC
.
- G. Erker and K. Kropp, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1979, 101, 3659 CrossRef CAS
.
-
(a) S. A. Cohen, P. R. Auburn and J. E. Bercaw, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1983, 105, 1136 CrossRef CAS
; (b) S. A. Cohen and J. E. Bercaw, Organometallics, 1985, 4, 1006 CrossRef CAS
.
-
(a) S. L. Buchwald, R. T. Lum and J. C. Dewan, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1986, 108, 7441 CrossRef CAS
; (b) S. L. Buchwald, B. T. Watson and J. C. Huffman, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1987, 109, 2544 CrossRef CAS
; (c) S. L. Buchwald, B. T. Watson, M. W. Wannamaker and J. C. Dewan, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1989, 111, 4486 CrossRef
; (d) J. Cámpora and S. L. Buchwald, Organometallics, 1993, 12, 4182 CrossRef CAS
; (e) K. Aoki, A. J. Peat and S. L. Buchwald, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1998, 120, 3068 CrossRef CAS
.
-
(a) A. H. Hoveyda and Z. Xu, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1991, 113, 5079 CrossRef CAS
; (b) A. H. Hoveyda, Z. Xu, J. P. Morken and A. F. Houri, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1991, 113, 8950 CrossRef CAS
; (c) A. F. Houri, M. T. Didiuk, Z. Xu, N. R. Horan and A. H. Hoveyda, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1993, 115, 6614 CrossRef CAS
.
- N. Suzuki, D. Y. Kondakov, M. Kageyama, M. Kotora, R. Hara and T. Takahashi, Tetrahedron, 1995, 51, 4519 CrossRef CAS
; stereoselection was enhanced if an allylic chloride was used in place of an allylic ether.
- K. Takai, M. Yamada, H. Odaka, K. Utimoto, T. Fujii and I. Furukawa, Chem. Lett., 1995, 315
.
- O. G. Kulinkovich, O. L. Epstein, V. E. Isakov and E. A. Khmel'nitskaya, Synlett, 2001, 49 CAS
.
- K. Takai, M. Yamada, H. Odaka and K. Utimoto, J. Org. Chem., 1994, 59, 5852 CrossRef CAS
.
- B. M. Trost, A. F. Indolese, T. J. J. Müller and B. Treptow, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1995, 117, 615 CrossRef CAS
.
- B. M. Trost, G. D. Probst and A. Schoop, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1998, 120, 9228 CrossRef CAS
. After a thorough investigation of this Alder–ene reaction, optimal levels of regioselectivity were obtained with the diol of 56 (removal of acetonide), 11 mol% of the catalyst, 22 mol% of NH4PF6 and 1.1 eq of the alkyne (rs = 12.5
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1).
1). -
(a) B. M. Trost and J. L. Gunzner, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2001, 123, 9449 CrossRef CAS
; (b) B. M. Trost, M. R. Machacek and Z. T. Ball, Org. Lett., 2003, 5, 1895 CrossRef CAS
. For an interesting example with alkynylborates, see: (c) E. C. Hansen and D. Lee, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2005, 127, 3252 CrossRef CAS
.
- G. Hilt and J. Treutwein, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2007, 46, 8500 CrossRef CAS
.
-
(a) S.-S. Ng and T. F. Jamison, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2005, 127, 14194 CrossRef CAS
; (b) C.-Y. Ho, S.-S. Ng and T. F. Jamison, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2006, 128, 5362 CrossRef CAS
; (c) S.-S. Ng and T. F. Jamison, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2006, 128, 11513 CrossRef CAS
; (d) C.-Y. Ho and T. F. Jamison, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2007, 46, 782 CrossRef CAS
. For a recent review of Ni-catalyzed coupling reactions of alkenes, see: (e) S.-S. Ng, C.-Y. Ho, K. D. Schleicher and T. F. Jamison, Pure Appl. Chem., 2008, 80, 929 CrossRef CAS
; (f) for a discussion of sensitivity and toxicity of Ni(COD)2, see current MSDS.
- High levels of stereoselection were observed when R1 = aromatic or t-Bu.
- R. Matsubara and T. F. Jamison, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2010, 132, 6880 CrossRef CAS
. Allylic alcohols, ethers, carbonates and chlorides were also examined in this coupling reaction.
-
(a) M. G. Clerici and F. Maspero, Synthesis, 1980, 305 CrossRef CAS
; (b) W. A. Nugent, D. W. Ovenall and S. J. Holmes, Organometallics, 1983, 2, 161 CrossRef CAS
; (c) S. B. Herzon and J. F. Hartwig, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2007, 129, 6690 CrossRef CAS
; (d) S. B. Herzon and J. F. Hartwig, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2008, 130, 14940 CrossRef CAS
.
- For reviews, see:
(a) A. H. Hoveyda, D. A. Evans and G. C. Fu, Chem. Rev., 1993, 93, 1307 CrossRef CAS
; (b) M. Catellani, G. P. Chiusoli and M. Costa, J. Organomet. Chem., 1995, 500, 69 CrossRef CAS
; (c) B. Breit, Chem.–Eur. J., 2000, 6, 1519 CrossRef CAS
; (d) M. Oestreich, Eur. J. Org. Chem., 2005, 783 CrossRef CAS
.
- For an example of a P-directed hydroformylation for the synthesis of stereodefined polyketides, see:
(a) I. J. Krauss, C. C.-Y. Wang and J. L. Leighton, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2001, 123, 11514 CrossRef CAS
. For an example of a pyridyl-directed Pauson Khand annulation, see: (b) K. Itami, K. Mitsudo, K. Fujita, Y. Ohashi and J. Yoshida, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2004, 126, 11058 CrossRef CAS
. For an example of an alkene-directed reductive coupling, see: (c) K. M. Miller and T. F. Jamison, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2004, 126, 15342 CrossRef CAS
.
- For examples of Cp2Ti-promoted cyclization reactions, see:
(a) W. A. Nugent and J. C. Calabrese, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1984, 106, 6422 CrossRef CAS
; (b) W. A. Nugent, D. L. Thorn and R. L. Harlow, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1987, 109, 2788 CrossRef CAS
; (c) T. V. RajanBabu, W. A. Nugent, D. F. Taber and P. J. Fagan, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1988, 110, 7128 CrossRef CAS
; (d) S. C. Berk, R. B. Grossman and S. L. Buchwald, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1993, 115, 4912 CrossRef CAS
; (e) S. C. Berk, R. B. Grossman and S. L. Buchwald, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1994, 116, 8593 CrossRef CAS
; (f) F. A. Hicks, N. M. Kablaoui and S. L. Buchwald, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1996, 118, 9450 CrossRef CAS
; (g) S. J. Sturla, N. M. Kablaoui and S. L. Buchwald, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1999, 121, 1976 CrossRef CAS
; (h) F. A. Hicks, N. M. Kablaoui and S. L. Buchwald, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1999, 121, 5881 CrossRef CAS
; see also, ref. 11 and 12.
- For chemistry of Ti-aryloxides, see:
(a) L. R. Chamberlain, L. D. Durfee, P. E. Fanwick, L. Kobriger, S. L. Latersky, A. K. McMullen, I. P. Rothwell, K. Folting, J. C. Huffman, W. E. Streib and R. Wang, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1987, 109, 390 CrossRef CAS
; (b) L. R. Chamberlain, L. D. Durfee, P. E. Fanwick, L. M. Kobriger, S. L. Latesky, A. K. McMullen, B. D. Steffey, I. P. Rothwell, K. Folting and J. C. Huffman, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1987, 109, 6068 CrossRef CAS
; (c) M. G. Thorn, J. E. Hill, S. A. Waratuke, E. S. Johnson, P. E. Fanwick and I. P. Rothwell, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1997, 119, 8630 CrossRef CAS
. For early examples documenting the reactivity of Ti-alkoxides, see: (d) O. G. Kulinkovich, S. V. Sviridov, D. A. Vasilevski and T. S. Pritytskaya, J. Org. Chem. USSR (Engl. Transl.), 1989, 25, 2027
.
- For recent reviews, see:
(a) A. Wolan and Y. Six, Tetrahedron, 2010, 66, 15 CrossRef CAS
; (b) A. Wolan and Y. Six, Tetrahedron, 2010, 66, 3097 CrossRef CAS
; (c) O. Kulinkovich, Eur. J. Org. Chem., 2004, 4517 CrossRef CAS
; (d) F. Sato, H. Urabe and S. Okamoto, Chem. Rev., 2000, 100, 2835 CrossRef
; (e) O. G. Kulinkovich and A. de Meijere, Chem. Rev., 2000, 100, 2789 CrossRef CAS
; (f) J. Lee, H. Kim and J. K. Cha, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1996, 118, 4198 CrossRef CAS
; (g) K. Harada, H. Urabe and F. Sato, Tetrahedron Lett., 1995, 36, 3203 CrossRef CAS
; (h) Y. Gao, K. Harada and F. Sato, Tetrahedron Lett., 1995, 36, 5913 CAS
; (i) Y. Takayanagi, K. Yamashita, Y. Yoshida and F. Sato, Chem. Commun., 1996, 1725 RSC
; (j) T. Hamada, D. Suzuki, H. Urabe and F. Sato, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1999, 121, 7342 CrossRef CAS
; (k) R. Mizojiri, H. Urabe and F. Sato, J. Org. Chem., 2000, 65, 6217 CrossRef CAS
; (l) Y. Gao, Y. Yoshida and F. Sato, Synlett, 1997, 1353 CAS
; (m) K. Fukuhara, S. Okamoto and F. Sato, Org. Lett., 2003, 5, 2145 CrossRef CAS
; (n) O. L. Epstein, J. M. Seo, N. Masalov and J. K. Cha, Org. Lett., 2005, 7, 2105 CrossRef CAS
; (o) Y. Takayama, Y. Gao and F. Sato, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. Engl., 1997, 36, 851 CrossRef CAS
; (p) H. Urabe, K. Mitsui, S. Ohta and F. Sato, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2003, 125, 6074 CrossRef CAS
; (q) S. Okamoto, K. Subburaj and F. Sato, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2001, 123, 4857 CrossRef CAS
.
- For a related discussion in the context of regioselective reductive cross-coupling reactions of internal alkynes, see ref. 6d.
- In the case of Zr-catalyzed transformations, use of 5 mol% Cp2ZrCl2 is approximately as expensive as stoichiometric use of Ti(Oi-Pr)4 ($27 – Strem 2008). Alternatively, if a CpRu(cod)Cl-promoted reaction was performed at the typically published 5 mol%, this catalyst would have to cost ca. $1/g in order to compete (from a costs perspective) with the stoichiometric use of Ti(Oi-Pr)4. While we were unable to locate a commercial vendor for CpRu(cod)Cl, the cost of [Cl2Ru(cod)]n (a potential precursor to CpRu(cod)Cl) is nearly $70/g.
- For a discussion regarding the limitations associated with the Kulinkovich and related reactions, see ref. 33d and 33e.
- The ease with which intramolecular metallacycle-mediated bond formation occurs is supported by the large collection of cyclization reactions reported. For examples based on Ti, see ref. 30.
- H. A. Reichard and G. C. Micalizio, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2007, 46, 1440 CrossRef CAS
. This coupling reaction was demonstrated to be compatible with a range of alkene substitution; however, with alkenes bearing terminal substituents that were α-branched (i.e. i-Pr), the reaction was not effective.
- D. P. Canterbury and G. C. Micalizio, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2010, 132, 7602 CrossRef CAS
.
- Y. Gao, Y. Yoshida and F. Sato, Synlett, 1997, 1353 CAS
.
- M. Takahashi and G. C. Micalizio, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2007, 129, 7514 CrossRef CAS
.
- J. E. Hill, P. E. Fanwick and I. P. Rothwell, Organometallics, 1992, 11, 1775 CrossRef CAS
.
- M. Takahashi and G. C. Micalizio, Chem. Commun., 2010, 46, 3336 RSC
.
-
(a) F. N. Tebbe, G. W. Parshall and G. S. Reddy, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1978, 100, 3611 CrossRef CAS
; (b) N. A. Petasis and E. I. Bzowej, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1990, 112, 6392 CrossRef CAS
.
- F. Kolundzic and G. C. Micalizio, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2007, 129, 15112 CrossRef CAS
.
- P. S. Diez and G. C. Micalizio, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2010, 132, 9576 CrossRef CAS
.
- T. K. Macklin and G. C. Micalizio, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2009, 131, 1392 CrossRef CAS
.
- V. Jeso and G. C. Micalizio, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2010, 132, 11422 CrossRef CAS
.
- J. K. Belardi and G. C. Micalizio, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2008, 130, 16870 CrossRef CAS
.
- M. Takahashi, M. McLaughlin and G. C. Micalizio, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2009, 48, 3648 CrossRef CAS
.
-
Prenylation of imines has represented a significant challenge in organic chemistry. For a route to products such as 170, 172 and 174, based on the reactivity of allylic barium reagents, see: A. Yanagisawa, K. Ogasawara, K. Yasue and H. Yamamoto, Chem. Commun., 1996, 367 Search PubMed
.
- M. Z. Chen, M. McLaughlin, M. Takahashi, M. A. Tarselli, D. Yang, S. Umemura and G. C. Micalizio, J. Org. Chem. Search PubMed
, in press.
- D. Yang and G. C. Micalizio, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2009, 131, 17548 CrossRef CAS
.
- S. Umemura, M. McLaughlin and G. C. Micalizio, Org. Lett., 2009, 11, 5402 CrossRef CAS
.
- T. K. Macklin and G. C. Micalizio, Nat. Chem., 2010, 2, 638 CrossRef CAS
.
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2011 |